AC DC Power Supply

Power supplies are electrical circuits and devices that are designed to convert mains power or electricity from any electric source to specific values of voltage and current for the target device...
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
This article takes an in-depth look at AC power supplies.
Read further and learn more about topics such as:
An AC power supply is a specific type of power supply designed to provide alternating current (AC) electricity to an electrical load. It can accept input power in either AC or DC form. The electricity supplied by mains outlets and some power storage systems is often unsuitable for the requirements of specific loads. To resolve this, an AC power supply converts and adjusts AC electricity from the source to match the voltage, current, and frequency specifications necessary for the particular device. This is achieved through voltage transformation, followed by a filtering process, ensuring the device receives electrical power in a precise and regulated fashion.
Additionally, AC power supplies have the capability to modify the voltage level delivered to the load, while also ensuring that the current drawn remains within safe operational limits.
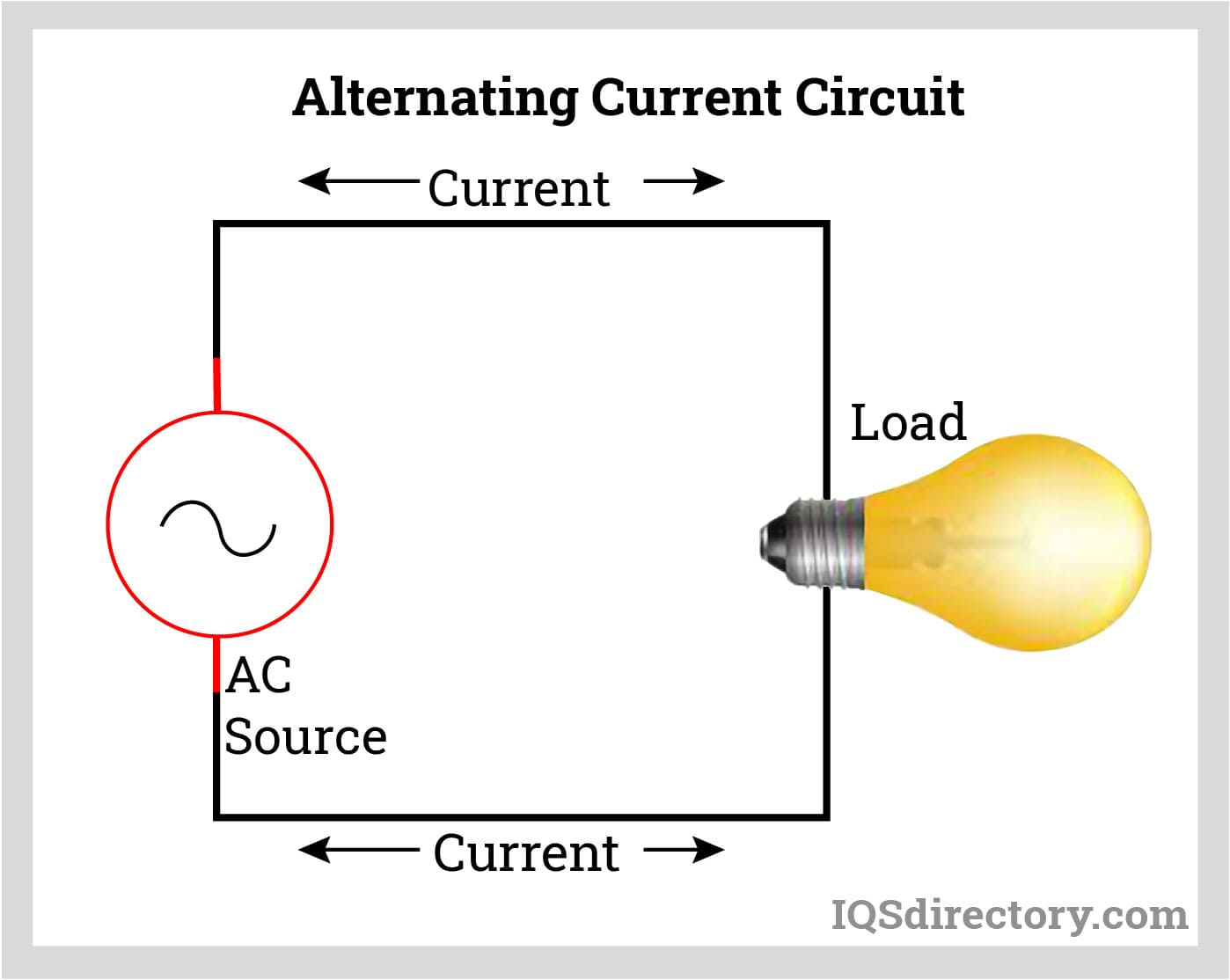
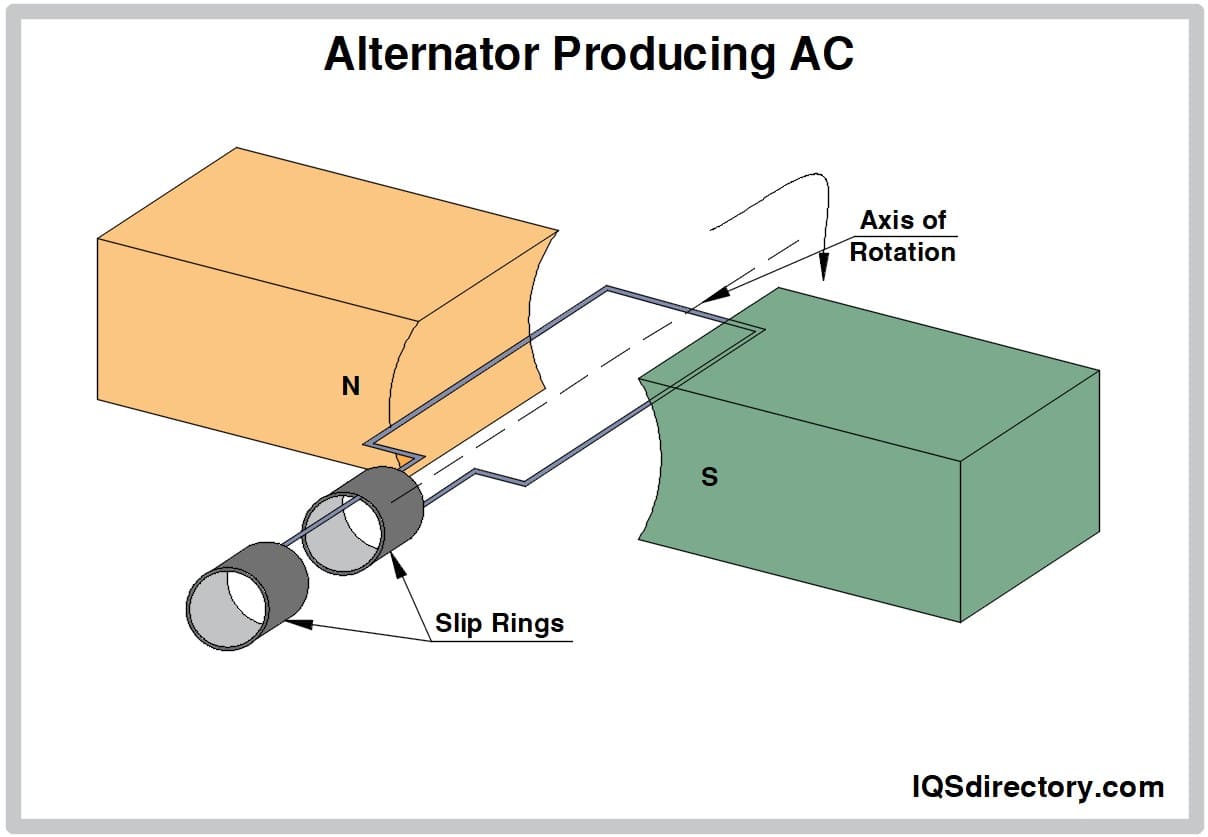
Alternating current (AC) is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering and power transmission. AC refers to a type of electrical power in which the flow of electric current reverses direction periodically, as opposed to flowing steadily in one direction. Consequently, the voltage alternates its polarity over time. This unique behavior is achieved through an AC generator, which leverages the principle of electromagnetic induction. In typical AC generation, a rotating conductor (rotor) moves through stationary magnetic fields (stator) within the generator, inducing an alternating voltage and producing alternating current.
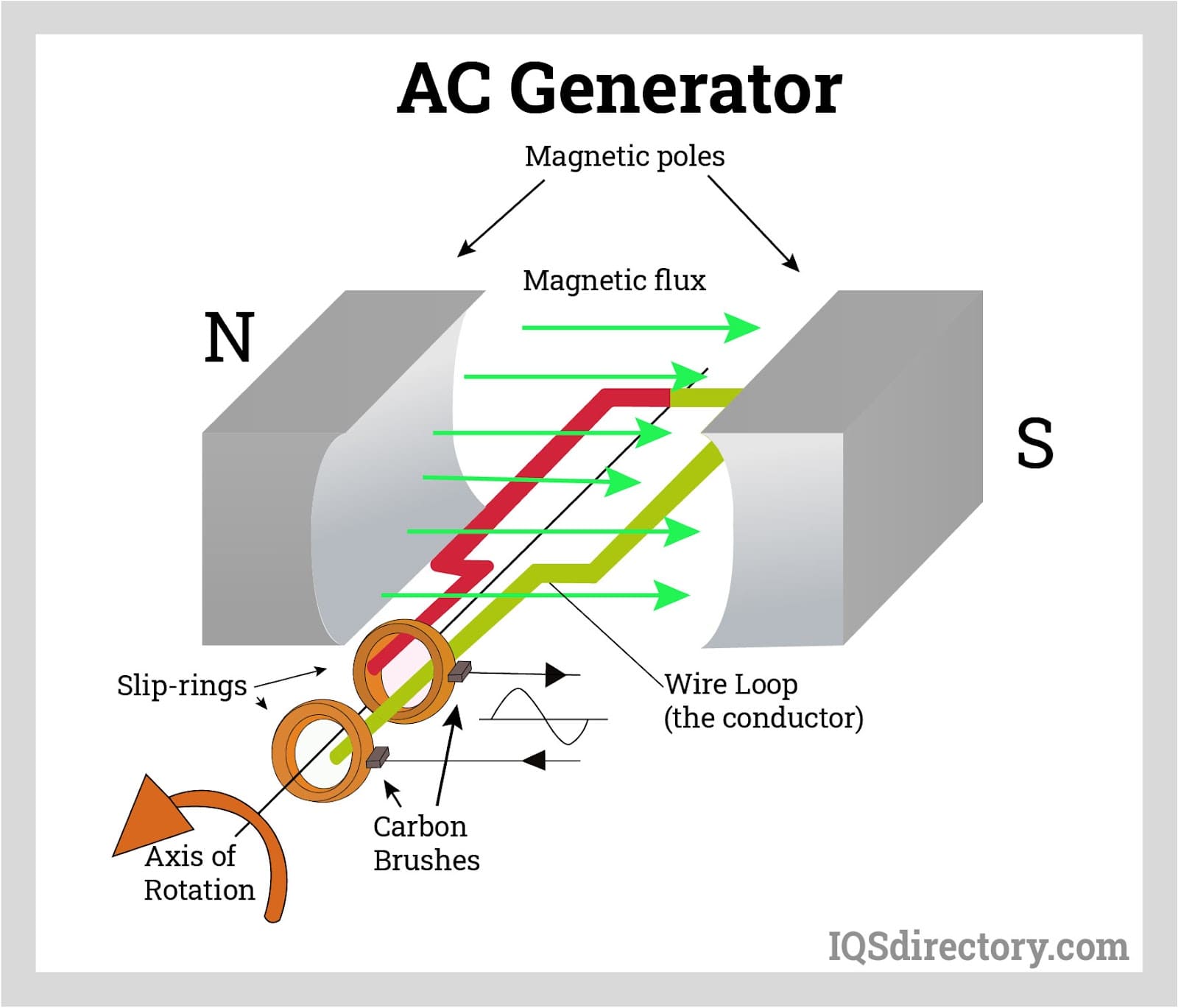
AC stands in sharp contrast to direct current (DC), where both the polarity and direction of the current stay consistent over time. While DC is common in battery-powered electronics, AC is the dominant form for power distribution in electrical grids due to its transmission efficiency and compatibility with electrical transformers.
A waveform visually represents the magnitude and direction of electrical current or voltage over time. AC waveforms are plotted by showing instantaneous values of current or voltage versus time. The most common and significant AC waveform is the sinusoidal waveform, or sine wave, renowned for its smooth, repetitive oscillation and efficiency in energy transfer. Other forms of AC waveforms include triangular, square, and sawtooth waveforms, each of which finds application in various industrial and electronic circuits such as signal processing and switching power supplies.
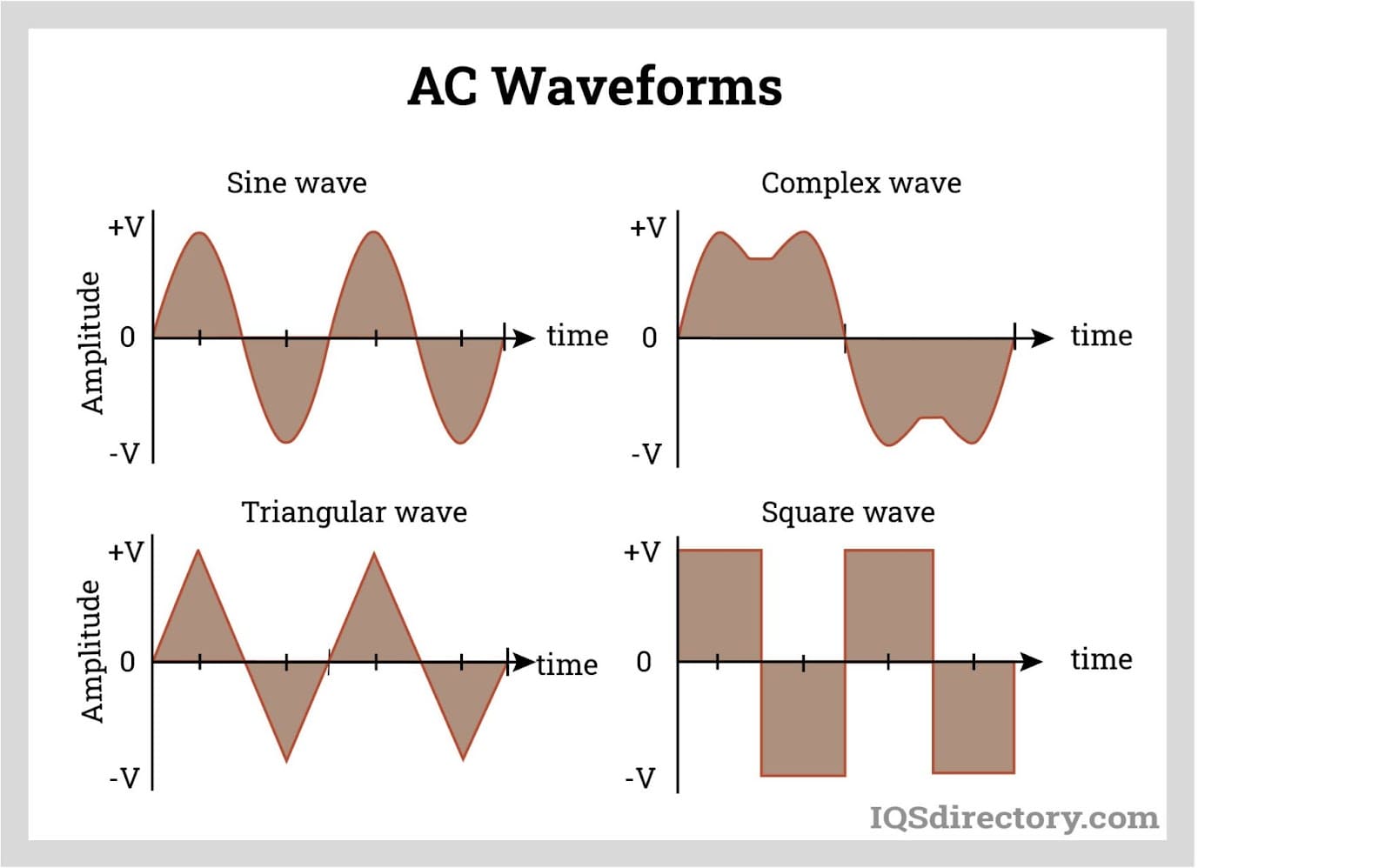
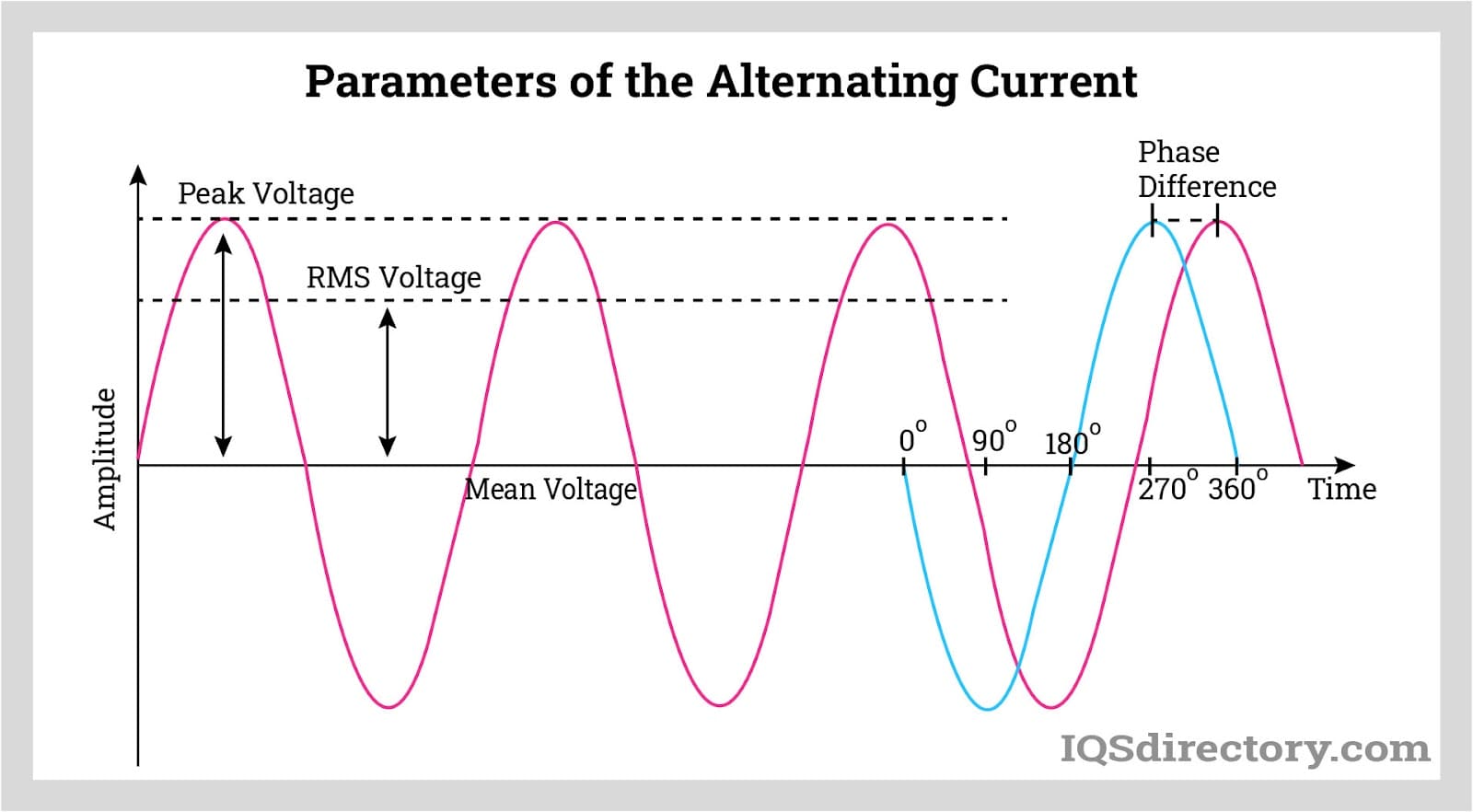
Sine waves exhibit a continuous, smooth, and periodic oscillation, easily identified by their S-shaped curve that fluctuates above and below a zero baseline. In a plot of a sine wave, the x-axis represents time, typically measured in degrees or seconds, while the y-axis denotes voltage or current. A single full cycle is completed when the wave traces its motion from 0° to 360° (or from 0 to 2π radians).
AC sine waves can be described using the mathematical equation: A(t) = Amax sin (2πft), where Amax is the amplitude, f is frequency, and t is time.
Several vital AC parameters are derived from the sinusoidal waveform, shaping how electricity is measured and applied in electrical engineering, power electronics, and utility grids:
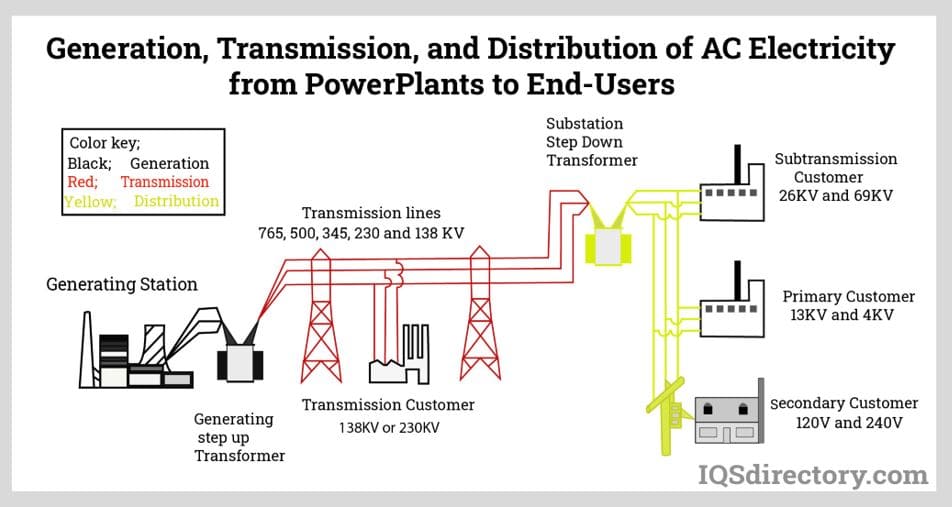
Alternating current electricity is at the core of modern infrastructure. Nearly all electrical power produced by power plants—including those using fossil fuels, nuclear, hydroelectric, wind, or solar sources—is generated and distributed as AC by national and regional electrical grids. AC allows for cost-effective and efficient long-distance power transmission because its voltage can be easily transformed to higher or lower levels using electric transformers. This voltage regulation is key in minimizing transmission losses and ensuring safe delivery to homes and industrial facilities. Transformers only function with AC, relying on its periodically reversing current for electromagnetic induction.
AC power is directly used by an extensive range of electrical appliances and equipment, including lighting (LEDs, lamps), HVAC systems, motors, televisions, refrigerators, and most industrial machinery. While AC is the standard for the electrical grid and building wiring, direct current (DC) is still essential in consumer electronics (like smartphones, laptops, and battery-powered devices), where AC must be converted to DC using rectifiers or AC-DC adapters.
The frequency and voltage of AC power supplied by electrical utilities differs by nation or region. For instance, in the United States, the standard frequency is 60 Hz and common household voltage is 120 volts AC (VAC). In many other countries, such as those in Europe and Asia, the standard is 50 Hz with 220–240 VAC. This variation is vital to recognize when importing or traveling with electronic devices internationally, as using the incorrect voltage or frequency can cause electrical failures or device damage.
Specialized AC power supplies—such as power inverters, voltage converters, and step-down/step-up transformers—enable compatibility between devices and local power standards. Reliable power quality and the correct input voltage are crucial for the safe, efficient operation of electrical tools, industrial machines, and sensitive electronics. Before plugging in, always verify the rated power requirements of your power supply and devices to avoid costly damage and ensure optimal performance in your regional electrical system.
As renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines become more prevalent, modern power systems increasingly rely on flexible AC power conditioning and conversion equipment (such as inverters, uninterruptible power supplies, and smart grid components). These advanced technologies help deliver consistent, safe, and efficient AC power for both residential and industrial applications, highlighting the enduring value and adaptability of alternating current in the evolving global energy landscape.
AC power supplies are classified into two major types based on their phase configuration: single-phase and three-phase power supplies. These foundational systems are critical components within the field of electrical engineering, with each power supply type playing a distinct role in powering various electrical devices and industrial equipment. Understanding the key differences between single-phase and three-phase AC power supply systems is essential for selecting the optimal solution for your specific voltage and current requirements.
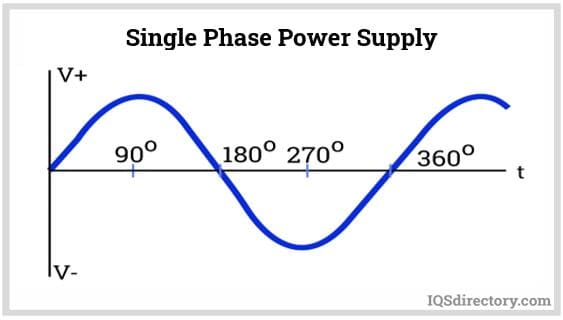
A single-phase power supply comprises two conductors: the phase wire and the neutral wire. AC electricity flows from the phase wire to the electrical load, and after passing through the load, it returns to the source via the neutral wire. This type of alternating current (AC) supply is known for its simpler design and straightforward installation compared to three-phase electrical systems, as it requires fewer conductors and reduced wiring complexity.
Single-phase AC power is illustrated by a sine wave that completes one full cycle at 360°. The wave reaches its positive peak at 90° and its negative peak at 270°. Due to the fluctuating voltage, the power delivery is not constant; instead, it pulses as the voltage alternates. As a result, single-phase current can cause voltage dips under heavy load, making it less efficient for high-power applications.
Single-phase power supplies are ideal for lower power applications and devices with modest electricity requirements. They are commonly found in residential environments and light commercial settings, where they power everyday household appliances such as fans, coolers, lighting fixtures, refrigerators, small air conditioners, and lamps. Typical single-phase voltage ratings include 120V or 240V, depending on region. However, single-phase AC is not suitable for running large industrial motors or heavy-duty equipment with high power demands due to its limited capacity and efficiency.
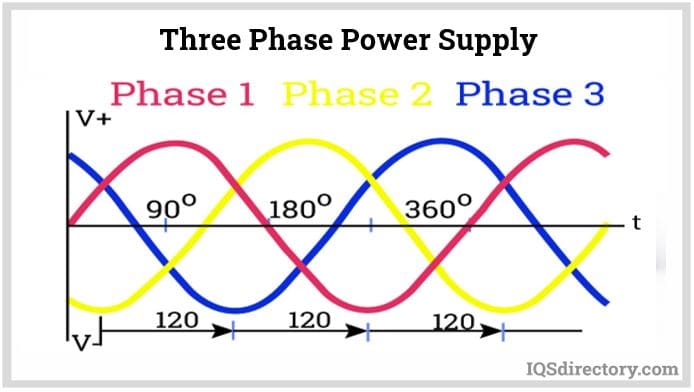
Three-phase power supplies typically use three conductors—known as live or phase wires—that carry current in alternating cycles. Systems may be configured in either a wye (star) or delta (triangle) arrangement, with a neutral wire present in wye configurations to provide additional stability and safety. The use of three separate wires ensures that power delivery remains virtually continuous, minimizing electrical interruptions and providing more balanced load distribution.
In a three-phase AC power system, three sine waves represent the three conductors, each phase shifted by 120° relative to the others. All three phases share the same frequency and amplitude. This configuration allows the waves to reach their respective peak voltages twice per cycle, meaning the resulting voltage supplied to the load never falls to zero. The consistent, uninterrupted flow of electrical energy translates to higher reliability and greater overall efficiency for demanding industrial applications. Three-phase AC power supplies can deliver more power than single-phase systems while using less conductor material, which reduces costs for large-scale operations.
Three-phase electrical systems are the standard power supply for industrial and commercial facilities requiring large amounts of electricity to operate heavy equipment. Typical uses include high-power electric motors, industrial pumps, electric heaters, air compressors, conveyors, and large-capacity HVAC systems. Three-phase circuits are also found in data centers, manufacturing plants, and other environments where a reliable and stable power source is critical.
To summarize, the primary difference between single-phase and three-phase AC power supplies lies in their phase configurations and power delivery. Single-phase AC power supplies best serve residential and light commercial applications by offering simple, cost-effective solutions for low power demand. Conversely, three-phase AC power systems are the industry standard for industrial operations and facilities with high voltage and large current needs, due to their enhanced efficiency, load handling, and voltage stability. Carefully evaluating the specific requirements of your devices or machinery is vital when choosing between these electrical supply systems to ensure safe operation, energy efficiency, and long-term reliability.
An AC power supply provides alternating current electricity to a load. It converts input AC or DC power and adjusts voltage, current, and frequency using voltage transformation and filtering, ensuring regulated and safe output for specific devices.
AC is preferred for power grids because its voltage can be easily transformed for efficient long-distance transmission, minimizing energy loss. Transformers, which require AC, enable safe voltage adjustment for distribution to homes and industries.
Single-phase AC uses two wires and delivers pulsating power, suitable for homes and small devices. Three-phase AC uses three wires for nearly uninterrupted power, ideal for industrial equipment and heavy loads due to higher efficiency and stability.
AC frequency and voltage differ regionally. In the United States, the standard is 60 Hz at 120 volts. Many other countries, including those in Europe and Asia, use 50 Hz and 220–240 volts. Always check device compatibility before use.
Three-phase AC power is commonly used in industrial and commercial environments to operate high-power machinery, motors, pumps, compressors, HVAC systems, data centers, and manufacturing plants requiring stable and large-scale electricity.
AC to AC converters adjust the input AC power to match the specific frequency, voltage, and phase requirements of a device. The main types of AC to AC converters include:
DC-linked AC to AC converters use a rectifier and a DC-link to first rectify and smoothen the supplied AC power into DC. The DC-link capacitor bridges the power source and the inverter and acts as a load-balancing energy storage device that regulates the voltage and prevents voltage spikes and EMI in the inverter. Once the current is transformed into DC, the inverter will convert it back to AC with the required output frequency and voltage. These converters have two types:
Cycloconverters change AC power from one frequency to an output with a lower frequency directly. Unlike other types of converters, cycloconverters do not convert the AC to DC as an intermediate step, which helps reduce costs and minimize losses.
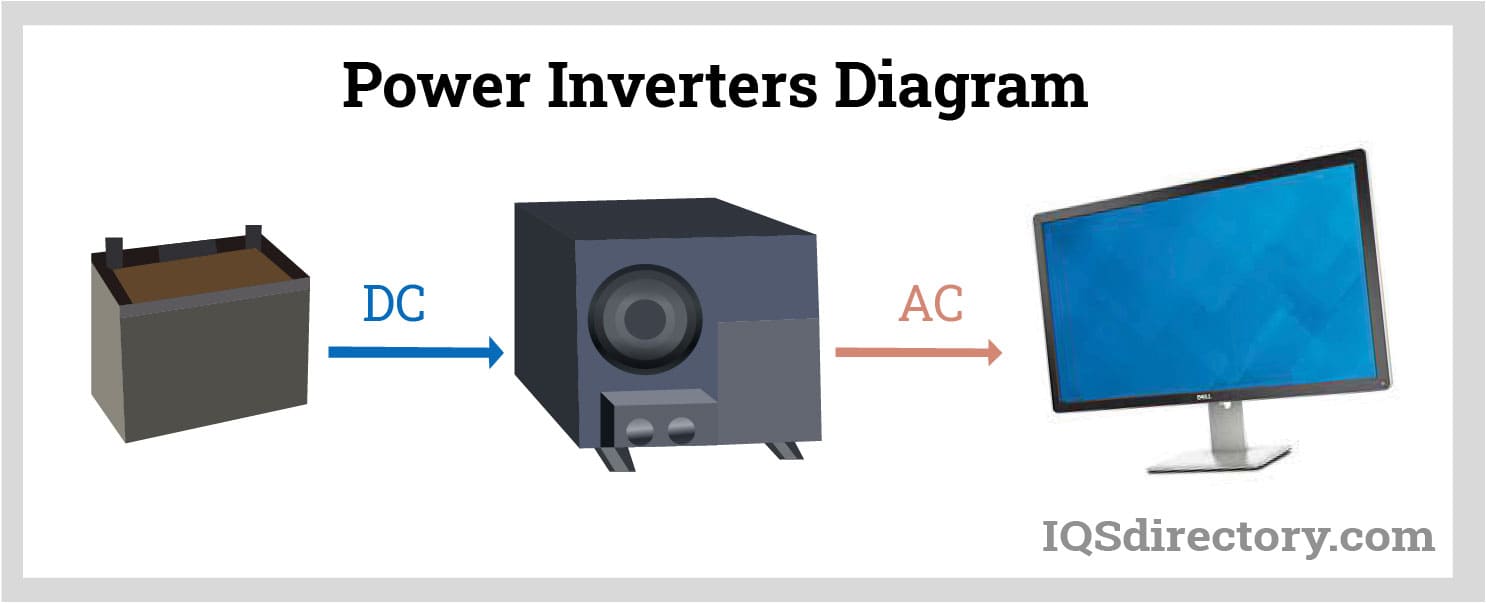
Power inverters or DC to AC inverters are types of AC power supply that convert an input low-voltage direct current into a useful alternating current that can run AC electronic devices. It is used in portable and emergency power sources. Power inverters allow you to utilize the DC power from batteries, fuel cells, and renewable energy sources to operate vehicles, appliances, and other electronics requiring AC power. Power inverters are the opposite of rectifiers which convert AC to DC current and are commonly used in DC power supplies.
In DC power systems, current flows from the negative terminal of the power source (such as a battery) to the load and then returns to the battery through the positive terminal. Power inverters function by taking DC power and converting it into an oscillating AC signal, reversing its direction and frequency. In older models of power inverters, this conversion process involved several steps to alternate the direction of the incoming DC power:
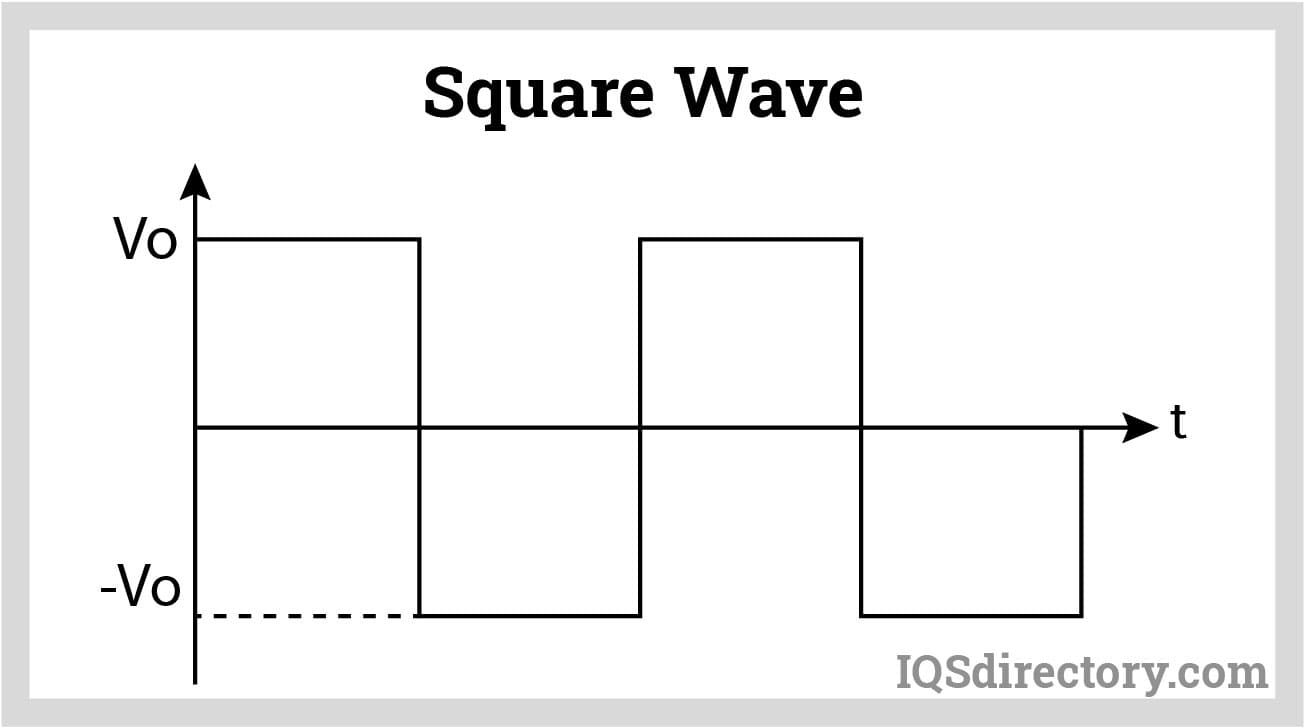
This method generates a square wave due to the sudden switching of DC power. However, square waves can be problematic for sensitive electronic devices, as they may not offer a consistent power supply. Modern power inverters, such as pure sine wave and modified or quasi sine wave inverters, create a smoother and more gradual alternation of the current.
Pure Sine Wave (PSW) inverters generate an AC waveform that closely resembles the standard sinusoidal shape of household electricity. They achieve this using specialized electronic components like capacitors, resistors, and transistors (such as MOSFETs), or through a Wien bridge oscillator. PSW inverters are highly compatible with a wide range of electronic devices, including sensitive smart devices that require AC power, ensuring smooth operation. However, they are typically more expensive, often costing twice as much as Modified Sine Wave (MSW) inverters.
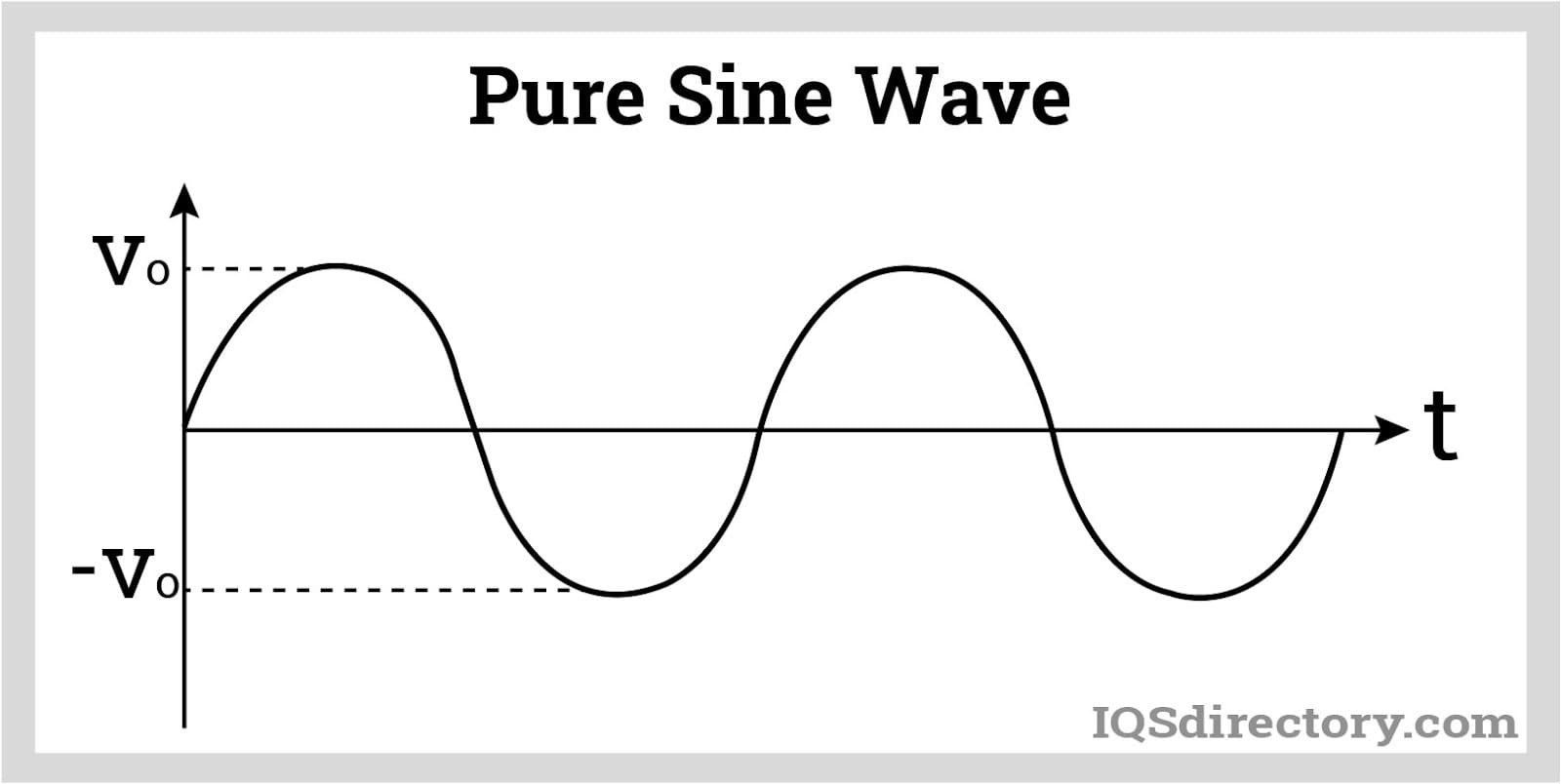
Modified Sine Wave (MSW) inverters generate a square-like AC waveform with rounded corners, resembling a pixelated sine wave. These inverters utilize less expensive components, such as diodes and thyristors, making them more affordable than Pure Sine Wave (PSW) inverters. While MSW inverters are suitable for many basic electronic devices, they may not perform well with devices such as clocks, refrigerators, microprocessor-controlled equipment, and medical devices.
Batteries store power in low voltage DC, typically around 12-24 VDC. To provide power to a load that requires a higher AC voltage, usually between 110-240 VAC, the DC power first passes through a transformer within the inverter that steps up the voltage.
An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) provides backup or emergency electrical power to a load for a short period of time in case the primary power source drops its voltage or fails. It also protects sensitive equipment from power fluctuation, instantaneous voltage spikes and falls, noise, and harmonic distortion. It is often used in computers, data storage systems, telecommunication systems, industrial equipment, and healthcare facilities; it has a critical role in the healthcare system as it provides backup power for life-supporting equipment found in hospitals, particularly in intensive care units.

An AC to AC UPS delivers output AC power to a load by first converting incoming AC power into DC using a rectifier. This DC power is used to charge a battery, which stores energy for use during a power interruption. When needed, the stored DC power is fed into an inverter, which then converts it back into AC power for the output.
There are three main types of UPS systems:
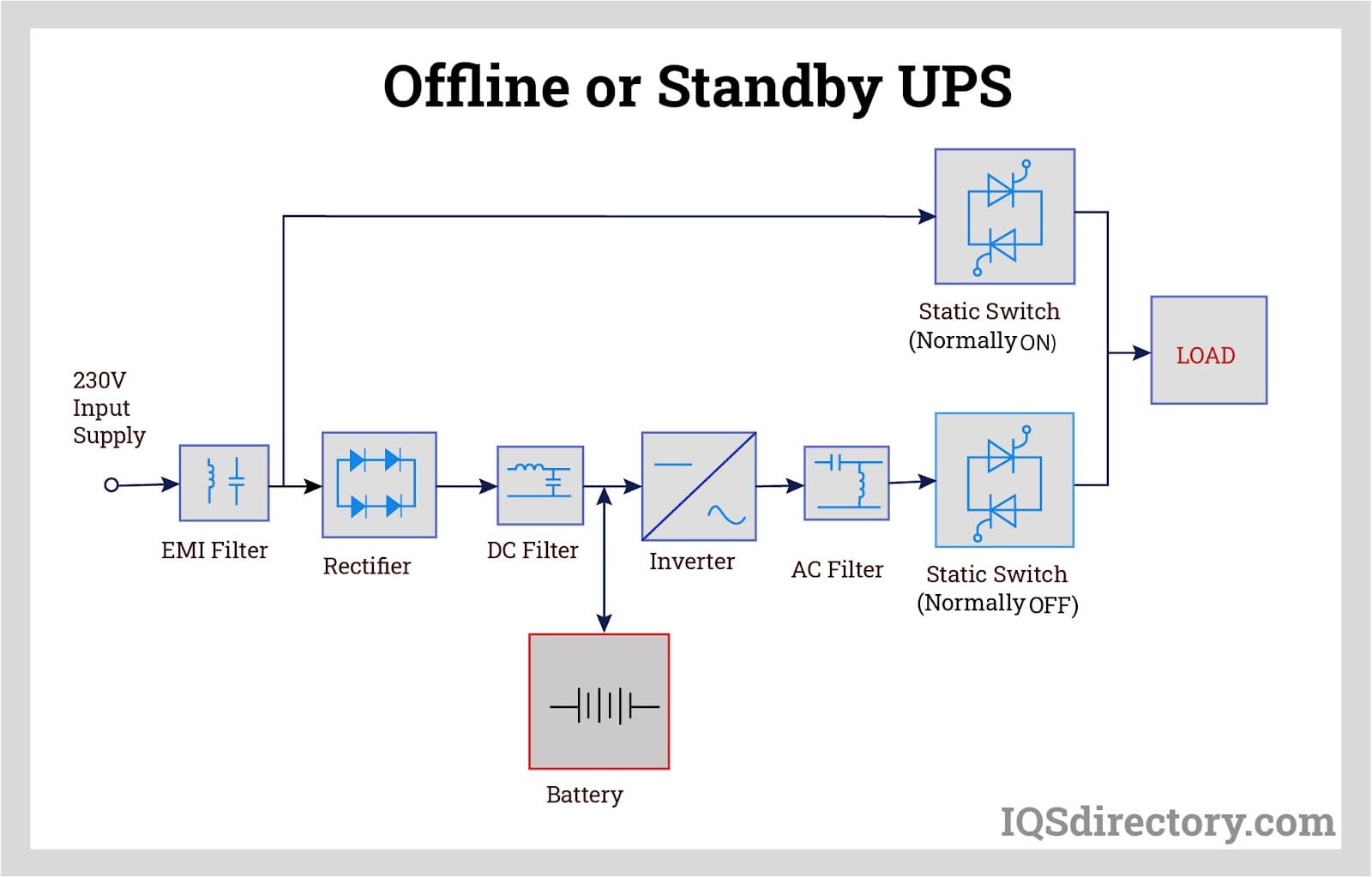
In a typical online UPS operation, all incoming AC power is first converted into DC power. Some of this DC power is used to charge the battery via a charge controller circuit. The battery is connected directly to the inverter, while the remaining DC power is supplied to the inverter to provide AC power to the load. Both the rectifier and inverter are continuously active. During a power outage, the battery ensures a constant supply of current without any switching delay, resulting in zero transfer time.
Online UPS systems are ideal for sensitive electronic equipment where even a brief power interruption can cause significant issues. However, because of the multiple power conversion stages, these systems tend to have higher power losses. Additionally, the constant charging requires a large battery, which may have a shorter lifespan due to the continuous charging cycle.
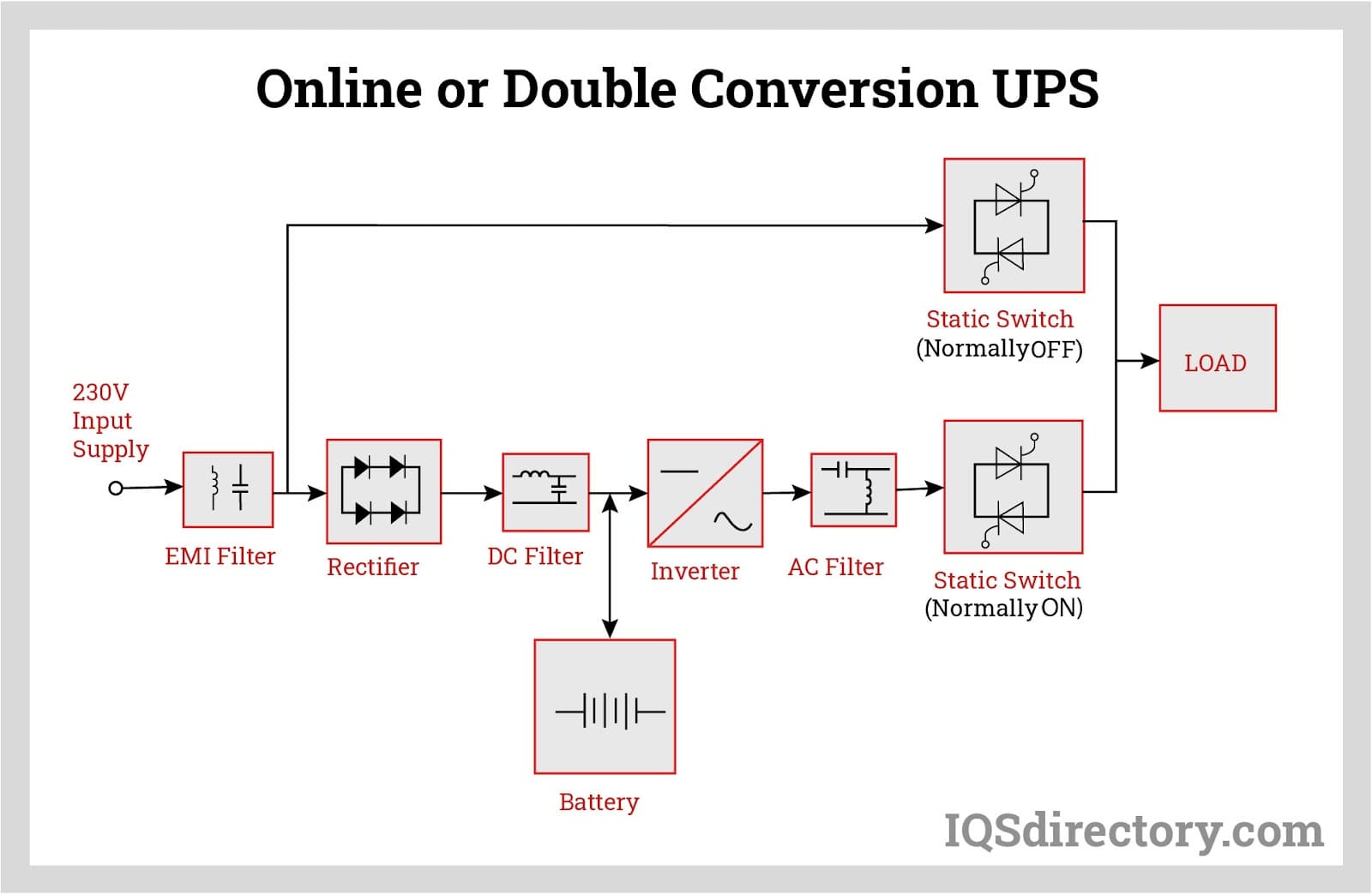
In a typical offline UPS operation, most of the incoming AC power is directly supplied to the load, while a portion is converted to DC power to charge the battery. During a power outage, the static transfer switch shifts the power supply to the inverter. The inverter activates only when needed, causing a delay in the flow of AC power to the load. This switching delay can range from 5 to 25 milliseconds.
As a result, offline UPS systems are suited for non-critical devices, such as personal computers, that can handle brief power fluctuations. With fewer power conversions involved, these systems generally experience lower power losses.
A line-interactive UPS delivers a regulated voltage output using a variable voltage autotransformer and a filter. It can handle minor over-voltage or under-voltage situations without drawing from the battery's DC power. The battery's stored DC power is utilized only if the power outage extends beyond a brief period.
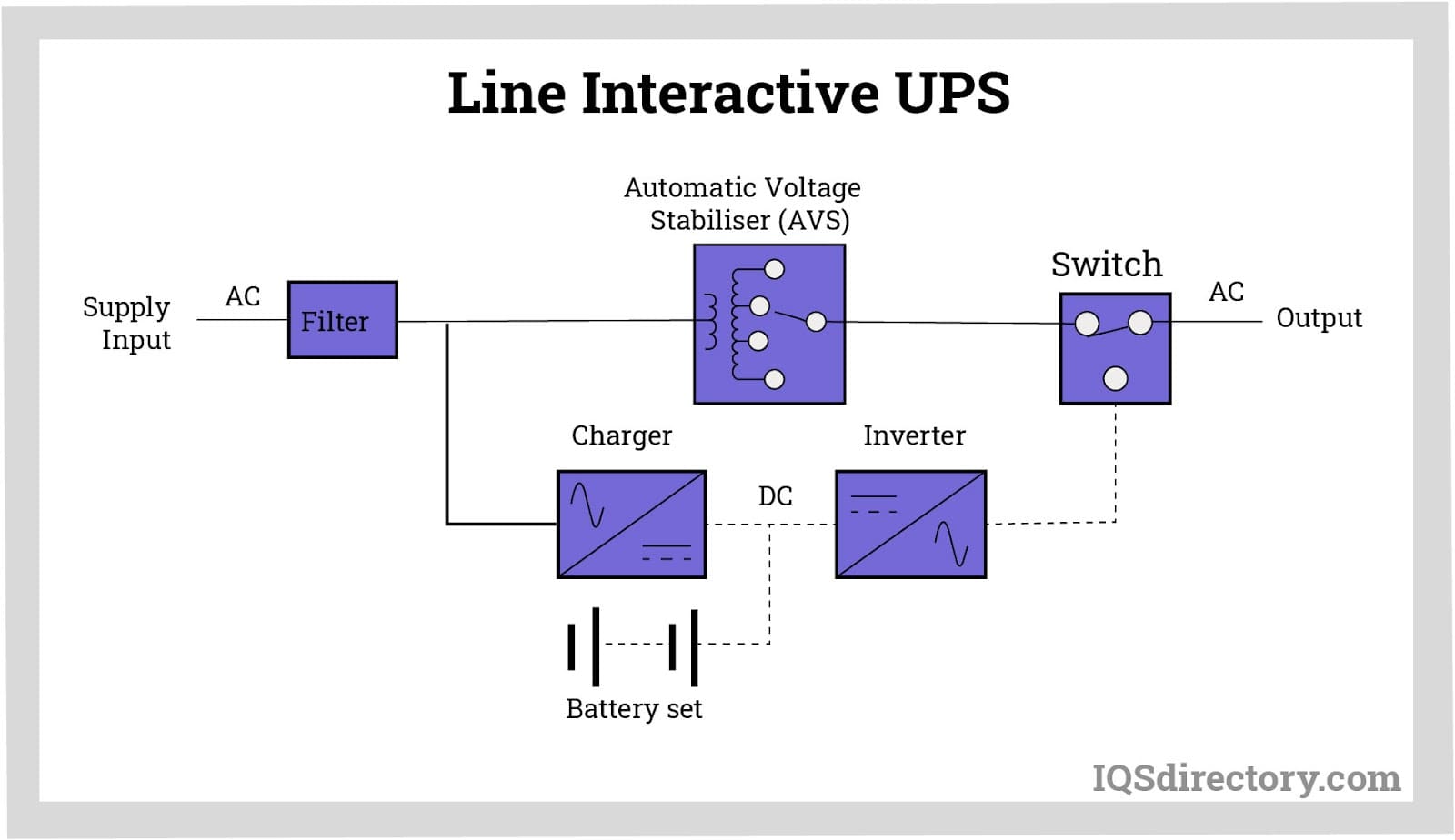
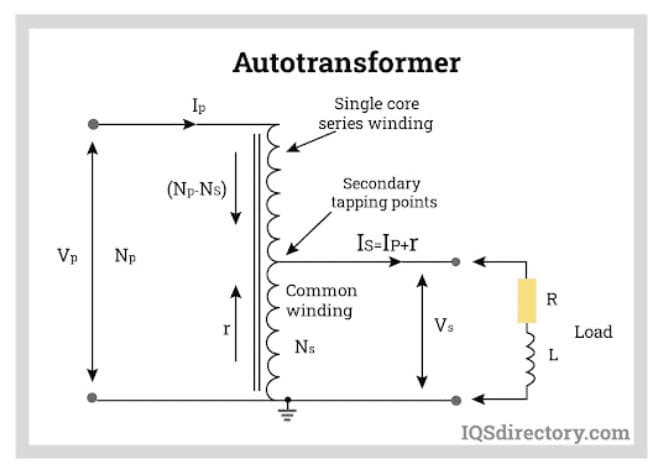
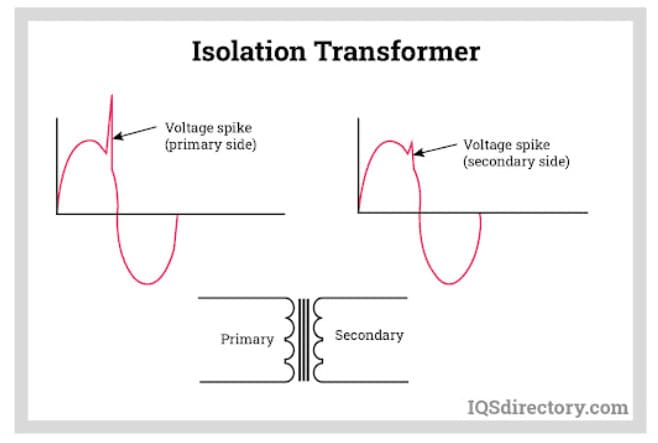
Transformers are used to either increase or decrease AC voltage to the level required by a device. They are often integrated into various AC power supplies for voltage adjustment. An autotransformer, used in line-interactive UPS systems, features a single winding on a common core, making it both cost-effective and compact. In contrast, an isolation transformer provides AC power to equipment without altering the voltage. Its main function is to shield the equipment from electrical noise and voltage spikes, with both the primary and secondary windings having an equal number of turns.
An AC to AC adapter is a power supply device that reduces the voltage of alternating current from a mains supply to meet the needs of a load requiring a lower voltage. It effectively transforms the AC power to provide the necessary reduced voltage output.
Commonly referred to as wall plug-in transformers, wall bumps, power cubes, wall adapters, or wall warts, these adapters are housed in a compact plastic casing. To function, they must be plugged into wall outlets, connecting to the mains power supply to draw electrical current.

Programmable power supplies are benchtop power supplies that deliver power to a load and can remotely control the output voltage, frequency, and current. They are capable of supplying both AC and DC power. The remote operation of these power supplies is made possible by an analog or digital interface and integral microcomputers to control and monitor the power supply to the device. Programmable power supplies are commonly used in semiconductor fabrication, crystal growth processes, and X-ray generators.


Power supplies are electrical circuits and devices that are designed to convert mains power or electricity from any electric source to specific values of voltage and current for the target device...

A DC DC power supply (also known as DC DC Converter) is a kind of DC power supply that uses DC voltage as input instead of AC/DC power supplies that rely on AC mains supply voltage as an input...

A DC power supply is a type of power supply that gives direct current (DC) voltage to power a device. Because DC power supply is commonly used on an engineer‘s or technician‘s bench for a ton of power tests...

By definition a power supply is a device that is designed to supply electric power to an electrical load. An electrical load refers to an electrical device that uses up electric power. Such a device can be anything from...

A programmable power supply is a method for controlling output voltage using an analog or digitally controlled signal using a keypad or rotary switch from the front panel of the power supply...

An AC power cord is a detachable way of providing an alternating current of electric energy from a mains power supply to an electrical appliance or equipment. Serving industries like...
Electrical plugs, commonly known as power plugs, are devices responsible for supplying and drawing current from a receptacle to the circuitry of an electrical appliance...
Electronic connectors are devices that join electronic circuits. They are used in assembling, installing, and supplying power to electrical devices. Connectors are an important component of every electronic equipment used in...
An electric switch is a device – usually electromechanical – that is used to open and close an electric circuit. This disables and enables the flow of electric current, respectively...
A NEMA connector is a method for connecting electronic devices to power outlets. They can carry alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). AC current is the typical current found in homes, offices, stores, or businesses...
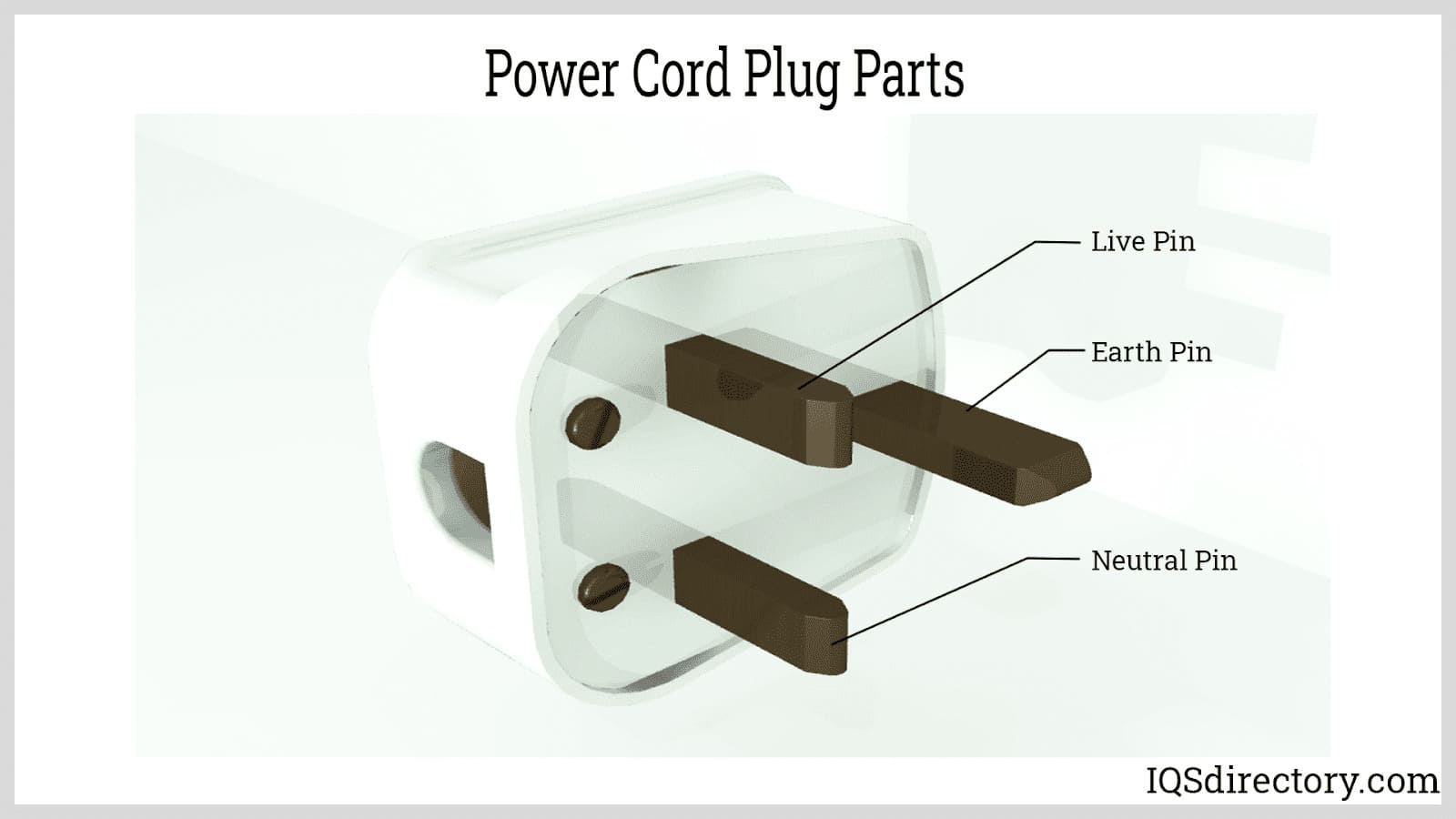
A power cord is an electrical component used for connecting appliances to an electrical utility or power supply. It is made from an insulated electrical cable with one or both ends molded with connectors...
Push button switches are electrical actuators that, when pressed, either close or open the electrical circuits to which they are attached. They are capable of controlling a wide range of electronic gadgets...
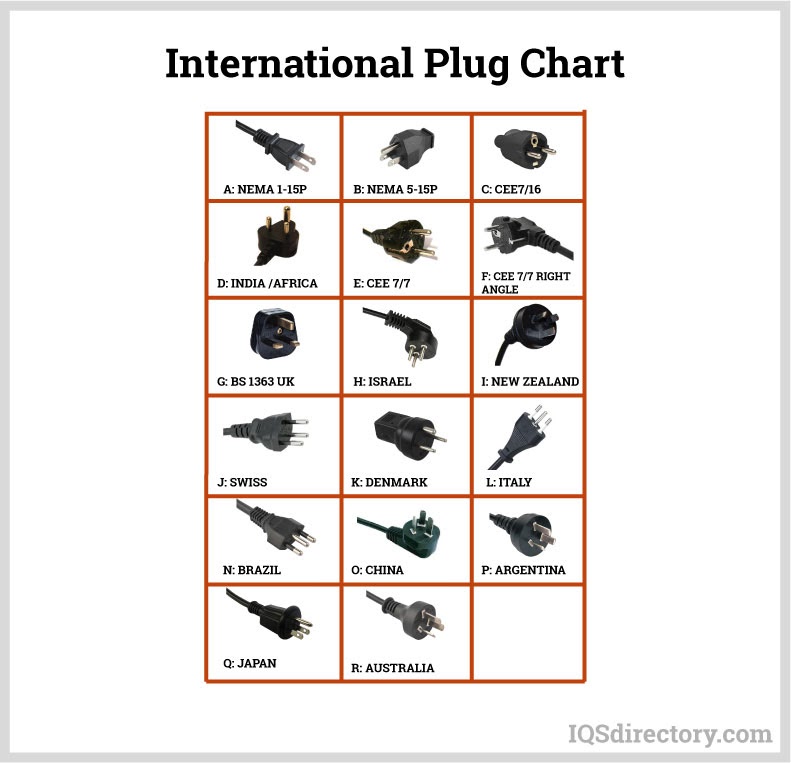
Thomas Edison developed the power distribution system in 1882. He wrapped a copper rod in jute, a soft shiny fiber from plants, as an insulator. The jute wrapped copper rod was placed in a pipe with a bituminous compound...