AC Power Cord

An AC power cord is a detachable way of providing an alternating current of electric energy from a mains power supply to an electrical appliance or equipment. Serving industries like...
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
This article takes an in-depth look at power cords. Read further to learn more about topics such as:
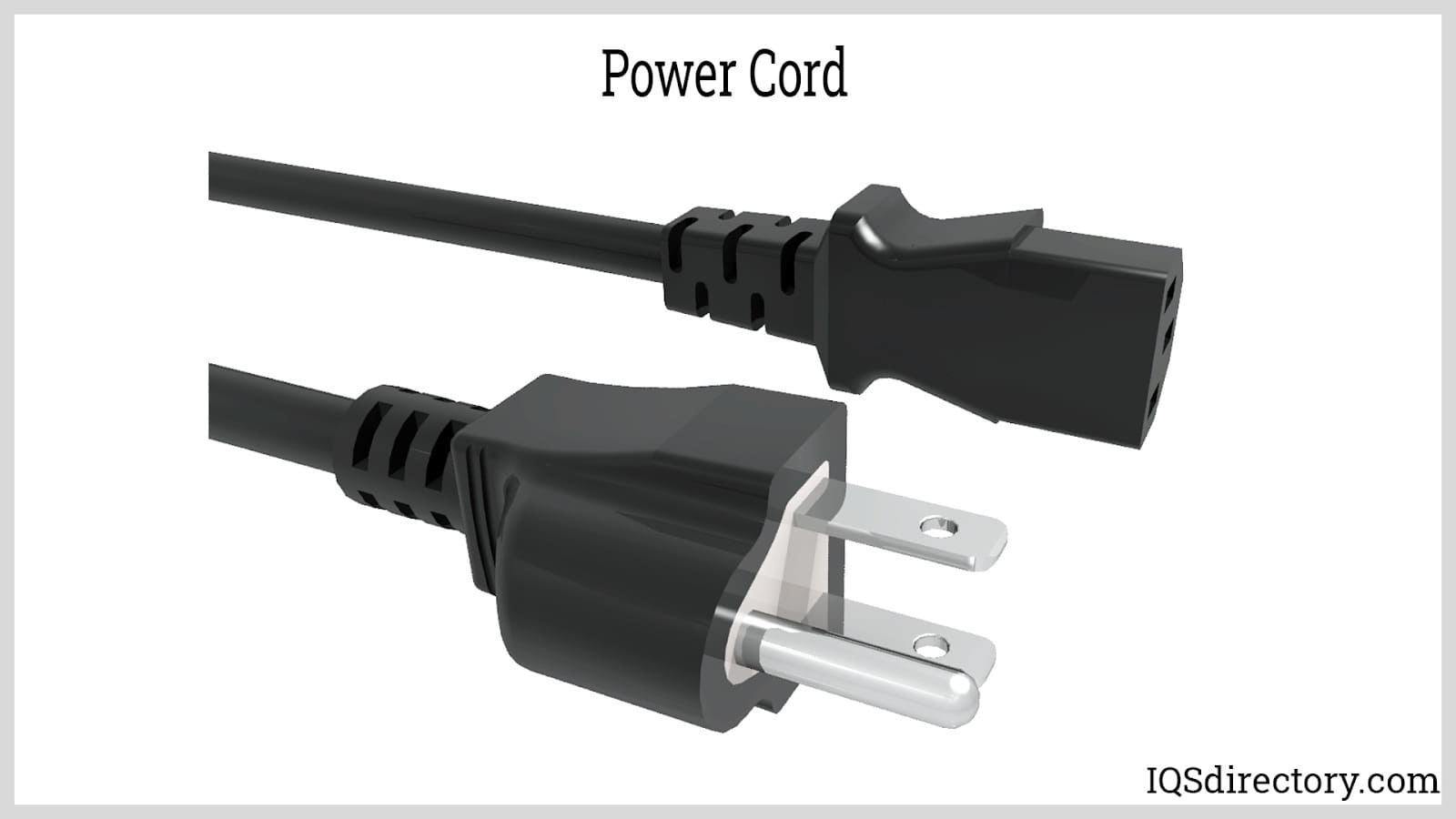
A power cord is a crucial electrical component designed to link appliances to a power source or an electrical utility. It typically consists of an insulated electric cable with connectors molded onto one or both ends. One end generally features a male plug that connects to an electrical outlet, wall socket, or extension cord. The other end commonly has a female connector designed to attach to the appliance or another male plug. In certain scenarios, the female connector might be absent and substituted by a fixed cable that is directly attached to the appliance.

Power cords find widespread application in both residential and commercial environments, linking a variety of electrical devices such as televisions, computing devices, refrigerators, and air conditioning units. However, their use is less prevalent in industrial and manufacturing settings, where machinery typically demands higher current levels and voltages. Power cords are commonly rated to handle currents from 16 A to 20 A and voltages ranging from 125 V to 250 V, which generally fall short for heavy-duty industrial machinery requirements.
Several terminologies are used to specify power cords, and while some terms may be used interchangeably by laypeople, understanding their precise meanings is crucial for selecting the appropriate power cord. Accurate terminology ensures that the power cord meets the necessary specifications for safety, performance, and compatibility. A solid grasp of power cord and electrical cable terminology streamlines the selection process for power distribution, reducing risks of electrical hazards, equipment failure, or incompatibility. This is especially important for those sourcing replacement power cords, extension cords, or custom power cable assemblies.
Although "power cords" and "power cables" are often used interchangeably, there are subtle distinctions between them depending on the context and specific characteristics. Power cords generally refer to flexible cables used to connect appliances to electrical outlets, typically featuring molded connectors on one or both ends. In contrast, power cables may refer to a broader category that includes both flexible and rigid cables designed for various applications, including high-voltage or industrial uses. Understanding these nuances helps in choosing the right product for specific needs and ensures electrical safety and compliance with regulatory standards.
A power cord typically refers to the flexible cable used in consumer electronics and household appliances, such as the cord on a laptop charger, a power supply for desktop computers, or a kitchen blender. In contrast, a power cable is a more general term that includes a wide range of cables used for power transmission, including extension cords, generator cables, and industrial-grade cords. These cables can encompass thicker, less flexible cables designed to handle higher current or voltage levels in commercial settings, data centers, or manufacturing facilities. Understanding these distinctions helps ensure you select the appropriate cable for your specific application, whether that's a standard 15 amp power cord, an industrial extension lead, or a custom-built assembly for high-powered equipment.
Below are the terms used to identify various parts and features of power cords and related electrical cord assemblies. These definitions help users compare and evaluate products based on technical standards and application-specific requirements.
This is the most fundamental designation for devices that transmit electrical current from an outlet to an appliance. Electric cords, also known as electrical cords, can either supply or transfer power and are capable of carrying both AC and DC electricity. They include flexible conductors surrounded by insulation for protection, making them suitable for use in diverse environments—from residential power cords to heavy-duty industrial power cords.
This type of electric cord is primarily used for connecting an appliance to an electrical utility outlet. Power supply cords can be removable or permanently attached and often conform to global safety standards such as UL, CSA, or IEC, depending on their target applications (e.g., IT equipment, kitchen appliances, or medical devices).
A cord set consists of a plug, a power cable, and a connector. It is used to connect an electrical appliance to an electrical utility or power supply. Cord sets are often identified by their connector types (e.g., IEC C13, NEMA 5-15P), length, voltage rating, and wire gauge. Choosing the right cord set is essential for ensuring proper electrical connection and compliance with industry safety regulations.
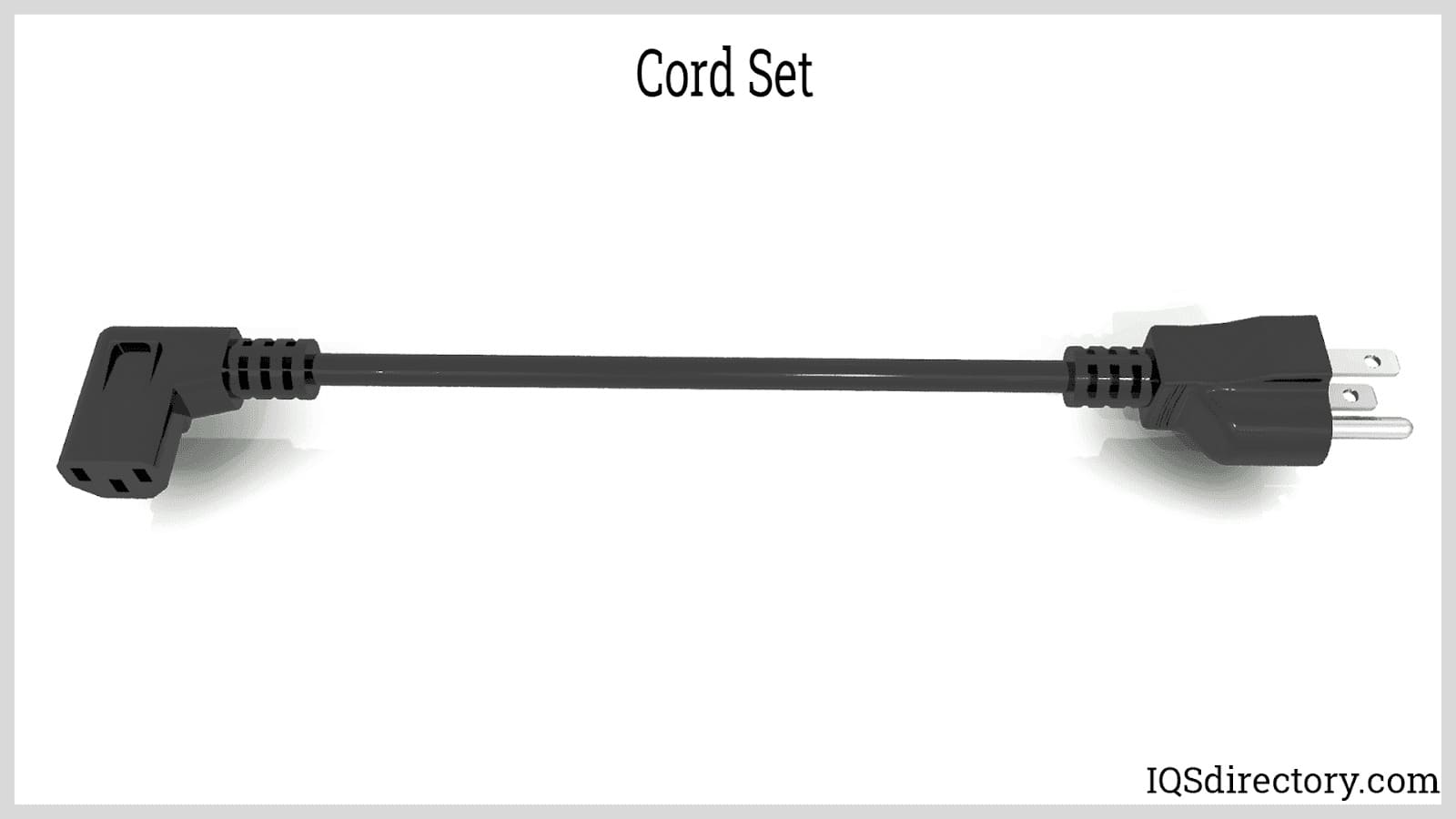
This assembly consists of a male and female connector and is used for connecting two electrical appliances. An example would be a power cord linking a UPS (uninterruptible power supply) to a desktop CPU or monitor. Interconnection cord sets are common in data centers, server rooms, and AV equipment setups where modular connectivity is required.

As the name implies, this power cord is designed to conduct electricity in the form of alternating current (AC), which features a sinusoidal waveform. AC is the standard type of electrical power provided by most electrical outlets in homes, businesses, and industrial facilities around the world. Common applications for AC power cords include personal computers, printers, household appliances, and lighting systems. When searching for AC power cords, considerations include plug type (such as NEMA or international standards), voltage/amperage rating, cable jacket material, and certification (such as UL or RoHS compliance).
These are power cords ordered with specific, customized specifications. Due to the vast range of possible combinations for plugs, connectors, cord characteristics (such as length, gauge, or cable shielding), and color coding, not all configurations are readily available in the market. Leading power cord suppliers offer customization options to meet unique application needs, including medical-grade cords, right-angle plugs, hospital-grade connectors, or weatherproof and outdoor-rated cords. Custom power cable assemblies can be engineered for temperature extremes, hazardous locations, or international export compliance.
These are electrical cords designed to extend the connection between the power source and the appliance. They feature a socket connection on one end and a plug on the other end. Extension cords may be rated for indoor or outdoor use, and come in various lengths and wire gauges to safely handle different power loads. Heavy-duty extension cords are essential for high-wattage tools and machinery, while light-duty extension cords work best for smaller electronics. Always check the ampacity and voltage rating when selecting an extension cord for your electrical devices.
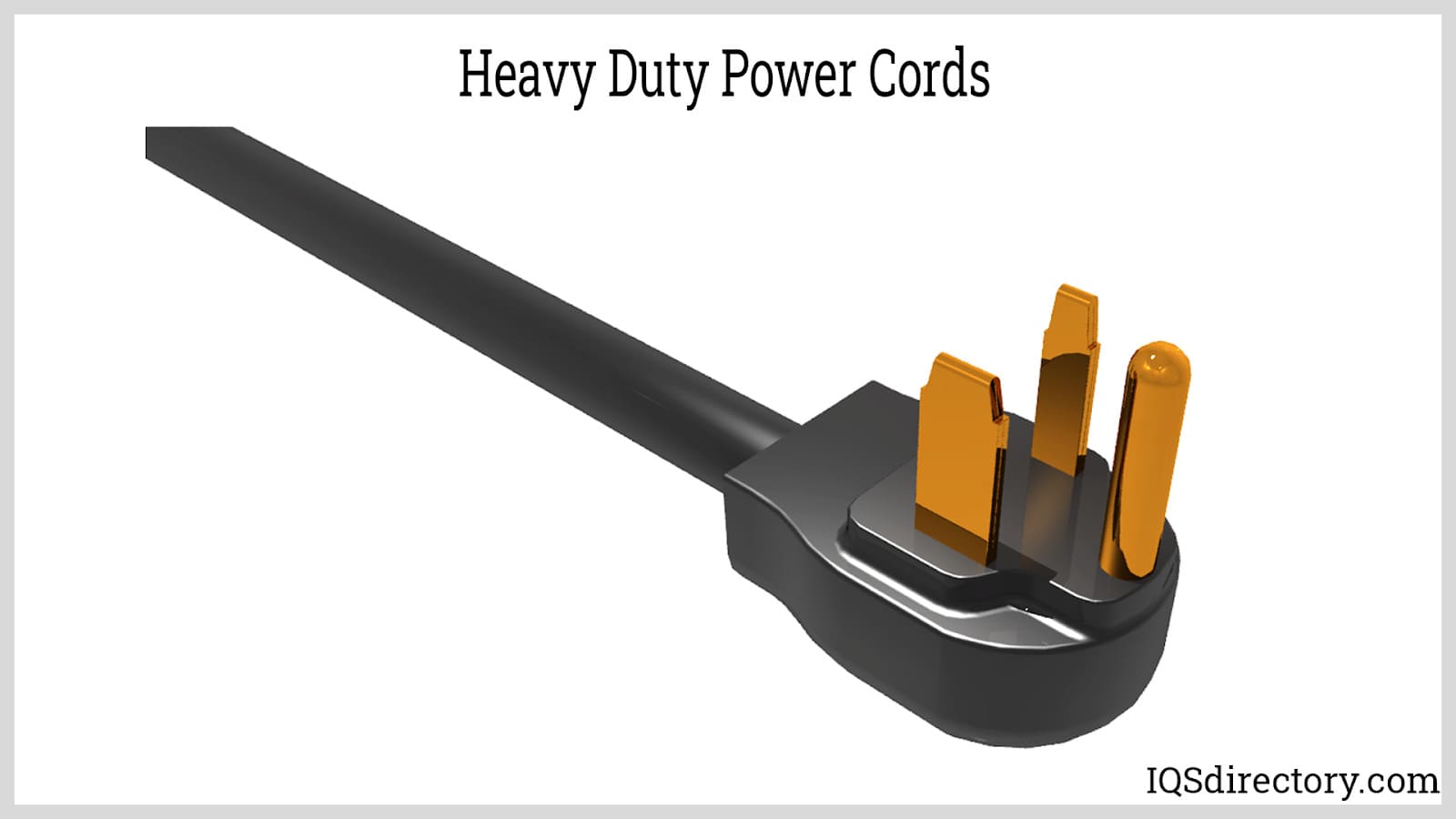
These are typically high-ampere-rated cords designed to handle significant electrical loads. Their current ratings can reach up to 50 A, ensuring that power is effectively distributed from the generator to the utility system. Generator power cords often use weather-resistant and oil-resistant materials to withstand outdoor conditions. It is crucial for generator power cords to match the highest rating and connector type of the generator outlet to prevent insulation breakdown and ensure safe operation. Applications include backup power for homes, RVs, construction sites, and critical infrastructure.
NEMA power cords are electrical cables that adhere to the standards established by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA). These standards specify the design of each component of the power cord. NEMA standards are widely used in North America, Central America, and some regions of South America, ensuring compatibility and interchangeability among a wide variety of electrical outlets and devices. NEMA plug types such as NEMA 5-15P (standard 3-prong plug) and NEMA 6-15P (240V plug) are common in commercial and residential settings.
These power cords are fitted with a Type B electrical plug on one end. NEMA 5-15P denotes a NEMA standard plug rated at 15 A and 125 V. The plugs have three pins: two flat, current-carrying pins (live and neutral) and one round earth pin. NEMA 5-15P power cords are ubiquitous in North American electrical systems for consumer electronics, appliances, office equipment, and small machinery. Make sure to match the plug and outlet types for safety and compliance.
An electrical plug is a movable male connector that pairs with a female connector or socket. It has protruding pins that match the openings on the socket. Plugs can have various features, such as earthing pins or clips, insulated sleeves, a fuse, and rewireable assembly. They come in different shapes, sizes, and standards to meet local regulations and safety codes worldwide. When purchasing replacement plugs, verify compatibility with your appliance, country, and intended application.
Sockets are electrical fixtures designed to accept or receive electrical plugs. The contacts inside the socket are connected to the main electrical supply or power distribution system. Sockets and plugs are standardized to match each other and reduce the risk of misconnection and electrical faults. Specialized sockets, such as GFCI (ground fault circuit interrupter) or weatherproof outlets, offer added protection for specific environments like bathrooms or outdoor settings.
Plug adapters are devices used to connect electrical plugs and sockets of different types. Often referred to as “universal adapters,” they have a socket on one side that can receive any electrical plug. The other side typically features a Type A plug that fits into Type A sockets commonly found in households. Using plug adapters can pose risks, as they can bypass the safety features designed into the original plug or device. For travel, consider adapters that also support voltage conversion and surge protection for international use.
A connector is a part of the power cord designed to provide a temporary attachment to an appliance inlet or another appliance coupler. Different connector types (such as IEC, NEMA, and custom designs) ensure the compatibility and safety of connections. Connectors are a critical component in modular cord sets, enabling quick installation and equipment replacements.
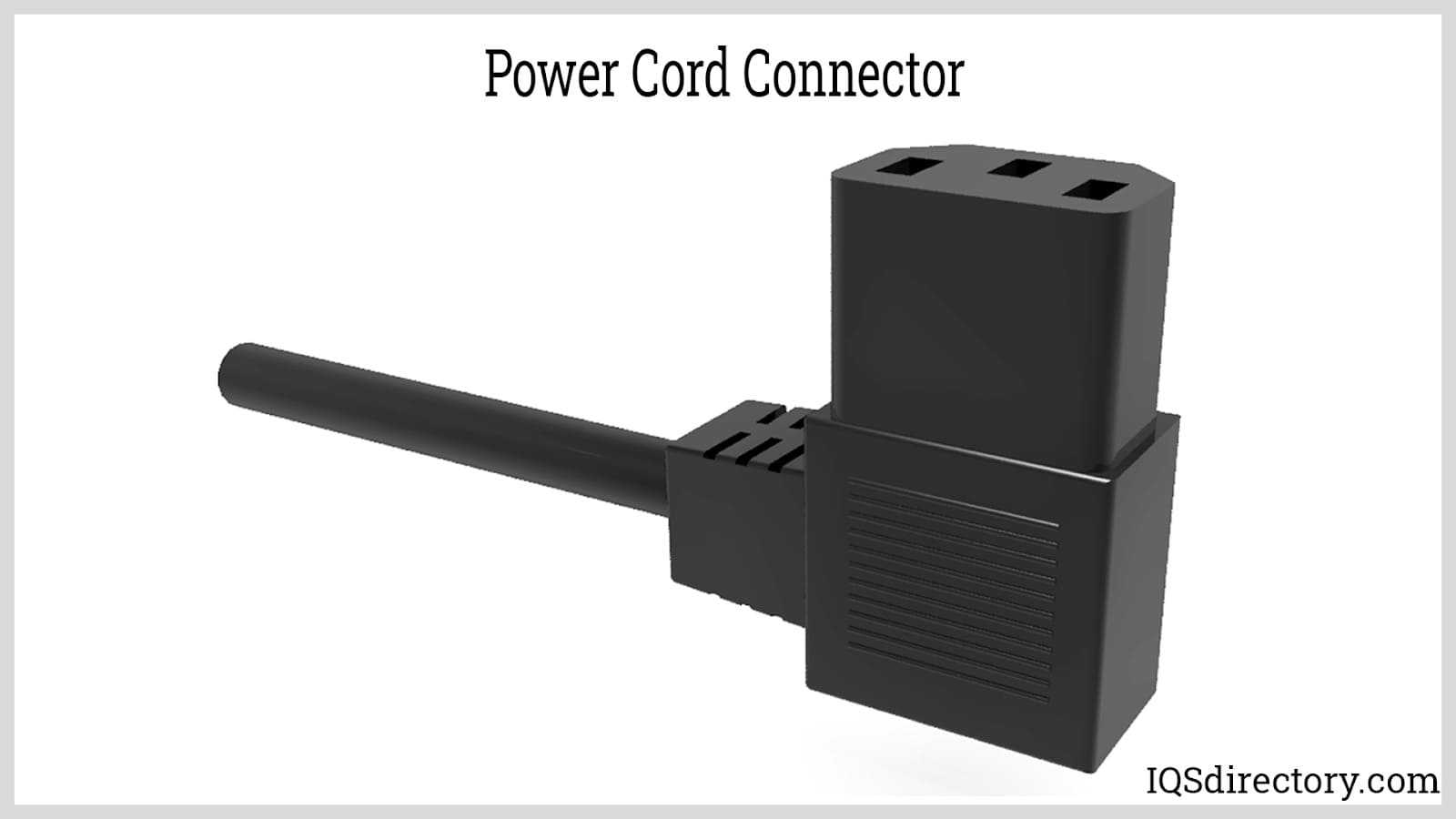
This is the part of the appliance that accepts the power cord connector. Connectors and inlets are standardized by IEC 60320 (or IEC 320 for short), which specifies a range of coupler types (such as C13, C14, C19) used in computers, medical equipment, and networking devices. Matching the inlet and connector ensures dependable and safe operation.
The flexible cord or cable is a component of a cord or interconnection cord set. Made from insulated, stranded wire conductors, it links the plug and connectors. Its length can range from 6.6 to 32.8 feet (2 to 10 meters) depending on the standards used in manufacturing the power cord. Flexible cords are engineered for durability and flexibility, and are often rated for specific temperature ranges and abrasion resistance.
Power cords are 2-core or 3-core, depending on the number of phases of the electrical system. For example, the domestic distribution system is usually single-phase, requiring a 2-core cable. One core or wire is the live wire, colored black in North America or brown internationally, while the other is the neutral wire, colored white in North America or blue internationally. Multi-core cables (such as 4 or 5-core) are used for three-phase power distribution in industrial power cords.
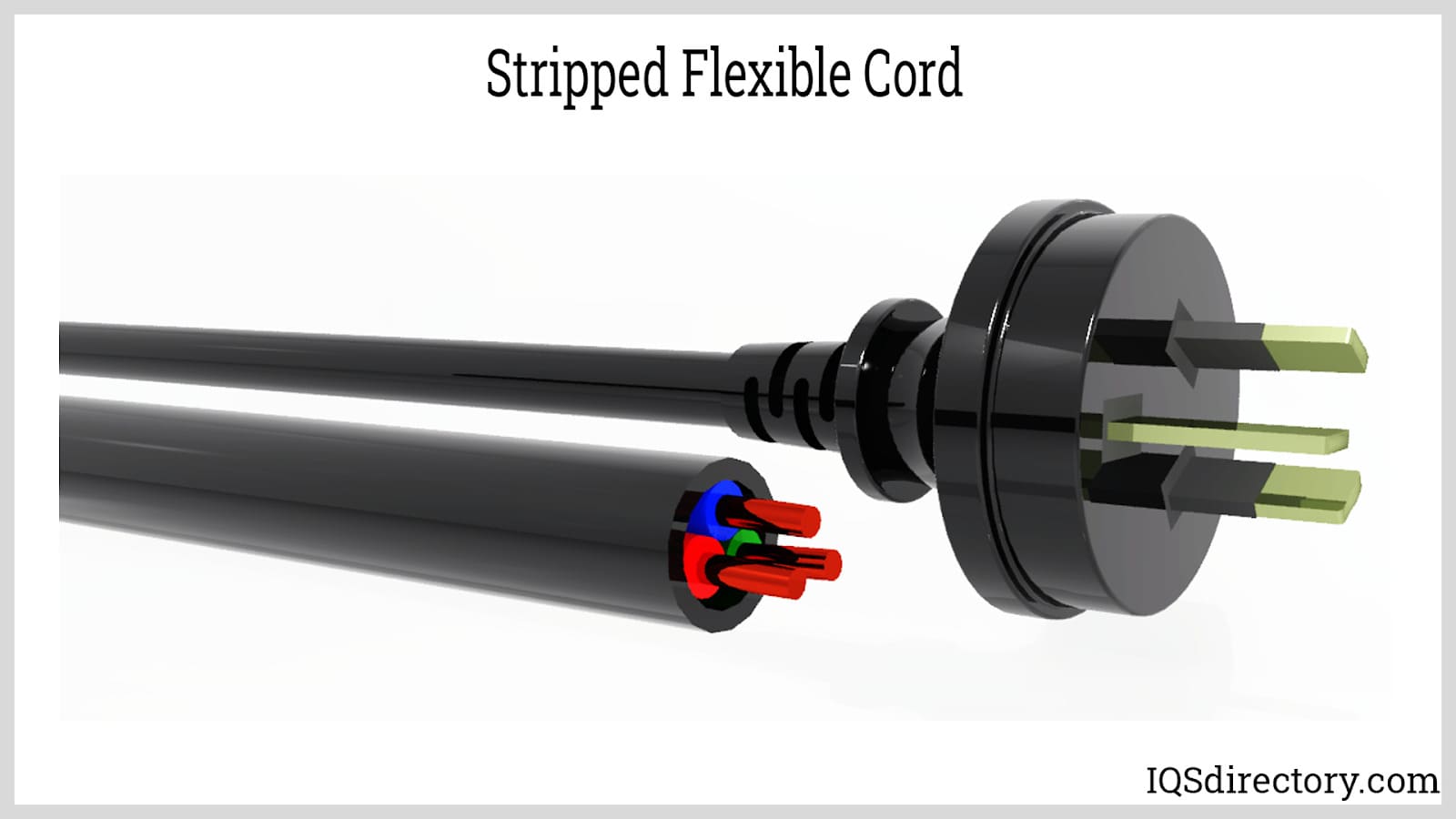
Other flexible cord features include an additional wire smaller than the others. This is the grounding or earth wire, colored green in North America or green with yellow stripes internationally. Cable jacket materials, such as PVC, rubber, or thermoplastic elastomer, affect resistance to chemicals, heat, and moisture.
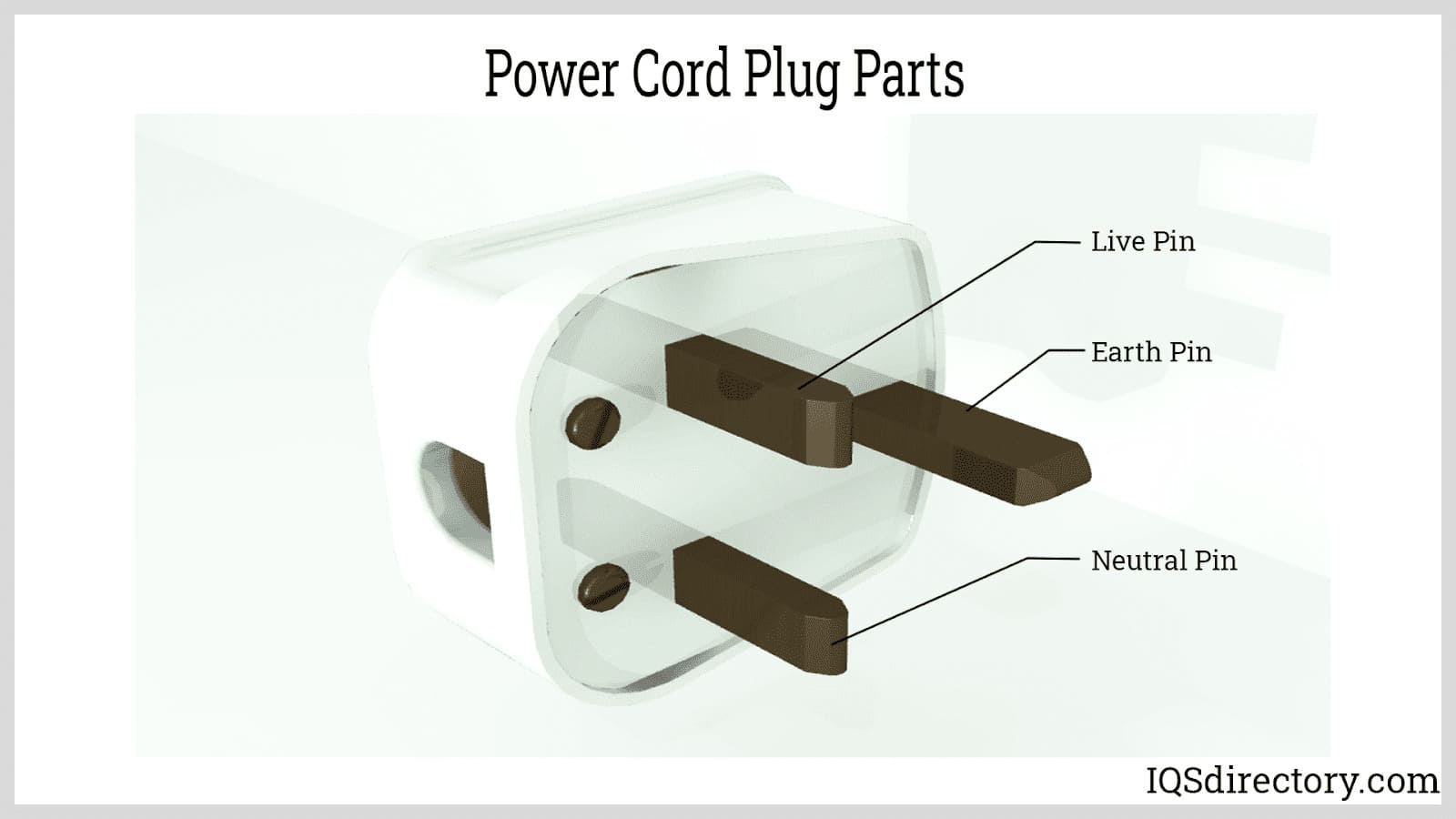
A pin, also known as a prong or lead, is a conductor protruding from the ends of a male connector or plug. It completes the path of the electrical current when connected to the contacts of the socket or connector. Pin count and arrangement vary by country and standard, influencing compatibility and safety.
The live pin, or hot pin, is the conductor connected to the power supply. It is responsible for supplying current from the outlet to the connected device. Identifying the live pin is critical during installation and wiring to prevent electrical accidents.
The neutral pin provides a return path for the electrical current supplied by the live connection. Correct wiring and identification of the neutral pin ensure proper function and reduced risk of electric shock.
The earth pin, or grounding pin, provides a connection between the conductive parts of the appliance and the ground. It enhances the safety of the appliance by directing any stray current directly to the ground. Most plugs and connectors use earth pins that are longer than the live and neutral pins, ensuring that the appliance is grounded before power is supplied. Grounding is a universal electrical safety measure required in most commercial and residential wiring codes.
Insulated sleeves are safety features found in some types of plugs. They are plastic coverings that extend from the base of the pin to a certain length, preventing accidental contact with the pins when the plug is partially connected. Insulated sleeves reduce risks of electric shock, meeting the requirements of many regional and international electrical safety standards.
Polarized connections are designed to be connected in a specific direction, preventing the interchange of live and neutral pins. This helps protect the equipment from reverse flow of electric current. Polarization is achieved through notches, ridges, asymmetric shapes, and offsets in the earth pin. Products with polarized connectors are commonly required in North American residential applications and are critical for user safety in appliances such as lamps, microwaves, and televisions.
Shutters are safety covers designed to prevent foreign objects from entering the openings of sockets. They help protect children from accidentally inserting materials into the socket that could cause electrocution. Typically, the insertion of the earth pin triggers the shutters to open, allowing access for the live and neutral pins. Sockets with integrated shutters are mandatory in many countries and can be a key selling point in family-friendly environments.
Plug covers are non-conductive devices inserted into wall outlets to prevent children from inserting objects into the socket holes. They are used when the socket lacks shutters. For sockets with shutters, plug covers are not recommended, as they can undermine the safety features of the device. Child-proofing electrical outlets with plug covers or tamper-resistant sockets is highly recommended for homes, schools, and childcare centers.
Retainers are mechanical devices that keep the connector properly aligned with a matching inlet and prevent unintended withdrawal. Retainers are particularly useful for medical, industrial, or mission-critical applications where accidental disconnection of power could cause data loss, equipment damage, or safety risks.
This rating indicates the maximum electrical load and voltage that a cord can safely handle. Choosing a power cord with the correct current rating (in amperes) and voltage (in volts) is essential to avoid overheating, fires, or equipment damage. Always consult the device's technical specifications and adhere to local electrical codes when selecting cords for professional or personal use.
Being rewireable is a feature of most plugs and connectors, particularly those used in industrial power cords. This refers to power cords with replaceable flexible cords, allowing for maintenance or replacement of the cord without replacing the entire plug or connector. Rewireable connectors are designed for ease of installation and repair, extending the lifespan of power cable assemblies in demanding environments.
Power cord splitters, also known as dividers or Y-cords, are used to split an electrical signal and supply it to two appliances or electrical circuits from a single outlet. While the signal's waveform is retained, the resulting amplitude or signal strength is reduced; always ensure not to exceed the combined load rating. Splitters provide convenience for users with multiple devices, but correct sizing and overload protection is essential for safety and compliance.
A fuse is a safety device designed to open the circuit when the current passing through the cord or appliance exceeds its rated limit. This helps protect the circuit and equipment from damage due to overcurrent or short circuits. Fuses are commonly found in power strips, surge protectors, and some power cord assemblies—particularly for sensitive or mission-critical equipment. When a fuse blows, it must be replaced with one of the same type and rating to maintain circuit integrity and user safety.
Power cords are essential components for transmitting electrical energy from a power source to electrical devices and appliances. As fundamental parts of electrical distribution systems, power cords facilitate the safe and efficient delivery of electricity to a wide range of electronics, from computers and household appliances to industrial equipment. They consist of several key elements that work together to ensure a reliable connection and minimize electrical hazards. At the core of a power cord are one or more conductors, typically made of high-conductivity copper or sometimes aluminum, which serve as pathways for electric current to travel from the power source—such as a wall outlet, portable generator, or power supply unit—to the device being powered.
Surrounding the conductors is a protective insulating material, most often fabricated from durable rubber or thermoplastic, which safeguards users by preventing direct contact with live wires and reducing the risk of electric shock. In addition to insulation, many power cords include an outer sheath or jacket that provides extra abrasion resistance, environmental protection, and extended product life. This robust construction is especially important for heavy-duty power cords used in industrial environments or outdoor applications.
At each end of the power cord are precision-engineered connectors, such as plugs and sockets, which enable seamless and secure electrical connections to both the power source and end devices. These connectors come in a variety of configurations—including NEMA, IEC, and international plug types—to match specific voltage and current requirements as well as regional standards. Connector design plays a critical role in safety and practicality, ensuring a firm connection and preventing accidental disconnection or arcing that could damage sensitive electronics.
The functionality of power cords relies on the principles of electrical conductivity, insulation, and mechanical durability. When connected to a qualified power source, the internal copper conductors enable free movement of electrons, supplying steady AC (alternating current) or DC (direct current) power as required by the equipment. The insulating materials and sheathing prevent electrical leakage, overheating, and short circuits, ensuring the current reliably follows the designated pathway. Power cords are manufactured to handle a diverse range of voltages, amperages, and environmental conditions, which is why various power cord types, such as extension cords, detachable cords, and specialty medical-grade cords, are available to suit specific industry needs and safety regulations.
When selecting a power cord, key factors include voltage rating, current capacity (amperage), wire gauge (AWG), cord length, plug configuration, and compliance with regulatory standards such as UL, CSA, VDE, or RoHS. Choosing the correct power cord for the application is crucial to avoid electrical hazards, maximize energy efficiency, and extend the service life of both the cord and connected devices. Whether used in consumer electronics, industrial automation, data centers, or medical devices, power cords remain a fundamental component of modern electrical and electronic systems, empowering us to use our equipment safely, reliably, and conveniently every day.
A power cord is an insulated electric cable with connectors, used to link appliances to a power source. It is most commonly used in household and commercial electronics like televisions, computers, and appliances.
A power cord typically refers to a flexible cable with molded connectors for electronic devices, while a power cable is a broader term that includes flexible and rigid cables for various applications, including industrial settings.
Key safety features include insulated sleeves, shutters, grounding (earth pin), polarized connections, and the use of proper current and voltage ratings. These reduce the risk of shocks, electrical faults, and appliance damage.
NEMA power cords comply with National Electrical Manufacturers Association standards, ensuring compatibility and safety. They are primarily used in North America, Central America, and some regions of South America.
Consider voltage rating, current capacity, wire gauge, cord length, plug configuration, insulation material, and compliance with standards such as UL, CSA, or VDE to ensure safety and compatibility.
Plug adapters connect electrical plugs and sockets of different types, making devices usable in countries with varying outlet standards. Some also offer voltage conversion and surge protection for international travel.
Power cord couplers play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of various electrical and electronic devices. These connectors, often overlooked, serve as the interface between power sources and the equipment they power, enabling seamless transmission of electrical energy. Their importance lies in providing a secure and standardized connection, which reduces the risk of electrical accidents, ensures reliable power delivery, and facilitates ease of use. Power cord couplers come in various types and standards to accommodate different devices and voltage requirements, making them a vital component in maintaining electrical safety, compatibility, and overall functionality in both domestic and industrial settings.
IEC 320, or IEC 60320, is the standard used to specify the dimensions and features of appliance couplers. While IEC also developed a standard to unify global appliance coupler regulations, plugs follow a separate system of standardization. The standards for plugs will be discussed in the following chapter.
The table below summarizes IEC 320 appliance couplers.
| Connector (Female) | Appliance Inlet (Male) | Description | Current Rating | Max Cable Length | Temp. Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 |
|
0.2 A | 6.6 ft (2 m) | 158°f (70°C) |
| C3 | C4 |
|
2.5 A | 6.6 ft (2 m) | 158°f (70°C) |
| C5 | C6 |
|
2.5 A | 6.6 ft (2 m) | 158°f (70°C) |
| C7 | C8 |
|
2.5 A | 13.1 ft (4 m) | 158°f (70°C) |
| C9 | C10 |
|
6 A | - | 158°f (70°C) |
| C11 | C12 |
|
10 A | - | 158°f (70°C) |
| C13 | C14 |
|
10 A | 6.6 ft (2 m), 32.8 ft (10 m) | 158°f (70°C) |
| C15 | C16 |
|
10 A | - | 248°F (120°C), 311°F (155°C) |
| C17 | C18 |
|
10 A | - | 158°f (70°C) |
| C19 | C20 |
|
16 A | - | 158°f (70°C) |
| C21 | C22 |
|
16 A | - | 311°F (155°C) |
| C23 | C24 |
|
16 A | - | 158°f (70°C) |
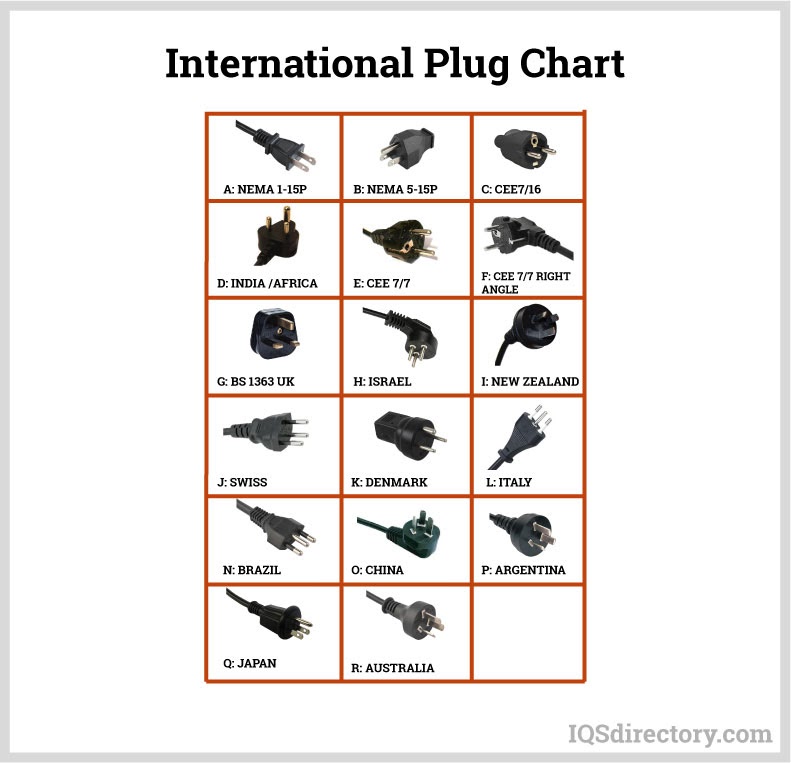
Plugs and sockets can have different configurations based on local regulations, as electrical standards may vary by region, particularly for specific electrical components. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has established a designation system for specifying global plug types. The different plug types and their attributes are summarized in the table below.
| Plug/Socket Type | Description | Region | Standard | Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A |
|
|
|
|
| B |
|
|
|
|
| C |
|
Europe, except UK, Ireland, Cyprus, and Malta | CEE 7/16 | 2.5 A, 250 V |
| D |
|
|
|
|
| E |
|
France, Belgium, Denmark, Poland, Slovakia, and Tunisia among others |
|
16 A, 250 V |
| F |
|
Germany, Austria, Chile, Croatia, Denmark, Finland, Greece, Italy, Netherlands, Spain, and Russia among others |
|
|
| G |
|
UK, Ireland, Cyprus, Malta, Malaysia, Singapore, and Hong Kong among others | BS 1363 | 13 A, 250 V |
| H |
|
Israel | SI 32 | 16 A, 250 V |
| I |
|
|
|
|
| J |
|
|
|
10 A, 250 V |
| K |
|
Denmark, Greenland | 107-2-D1 | 13 A, 250 V |
| L |
|
Italy | CEI 23-50 |
|
| M |
|
South Africa, Swaziland, Lesotho | SANS 164-1 | 16 A, 250 V |
| N |
|
Brazil | NBR 14136 |
|
| O |
|
Thailand | TIS 166-2549 | 16 A, 250 V |

An AC power cord is a detachable way of providing an alternating current of electric energy from a mains power supply to an electrical appliance or equipment. Serving industries like...
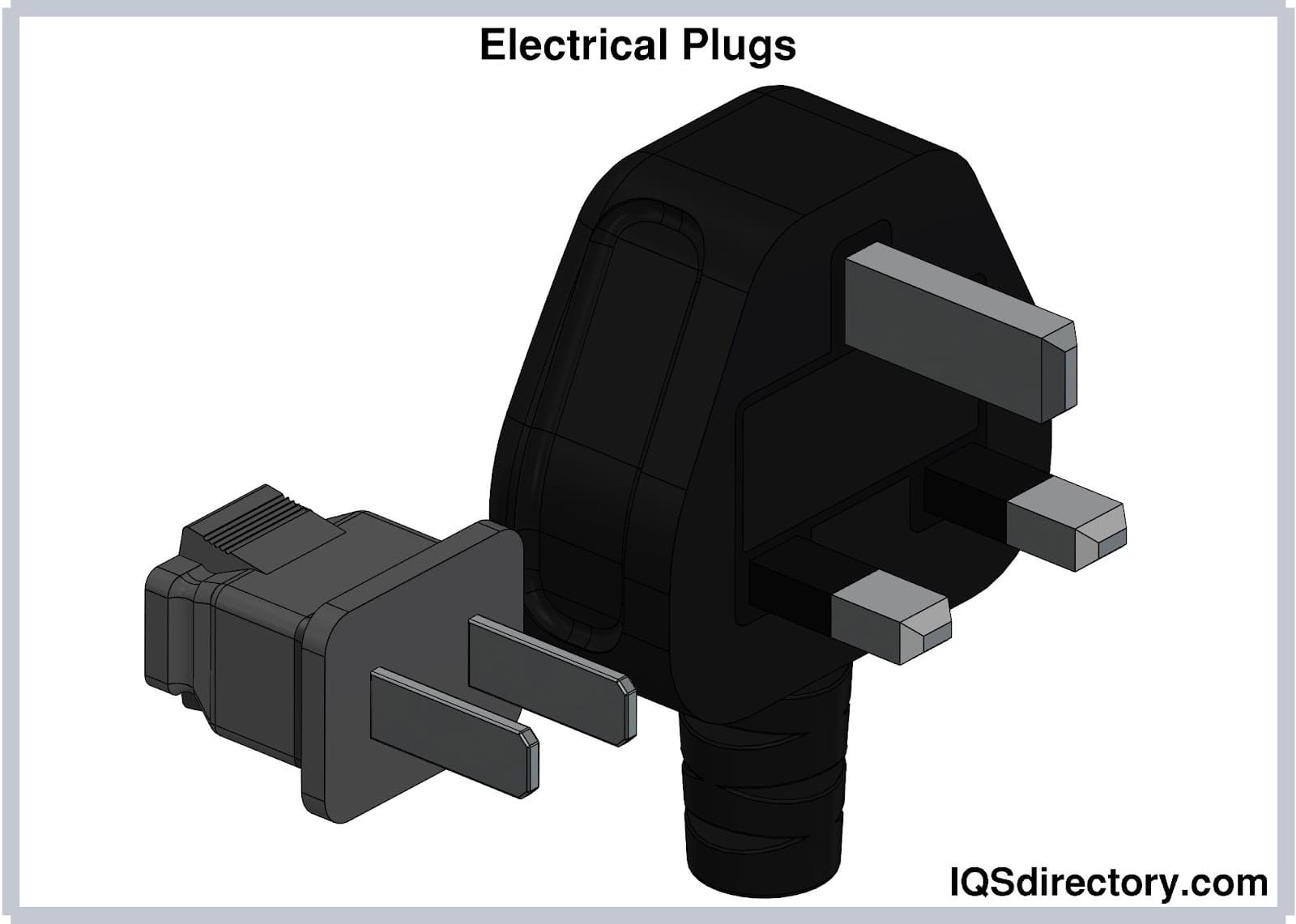
Electrical plugs, commonly known as power plugs, are devices responsible for supplying and drawing current from a receptacle to the circuitry of an electrical appliance...
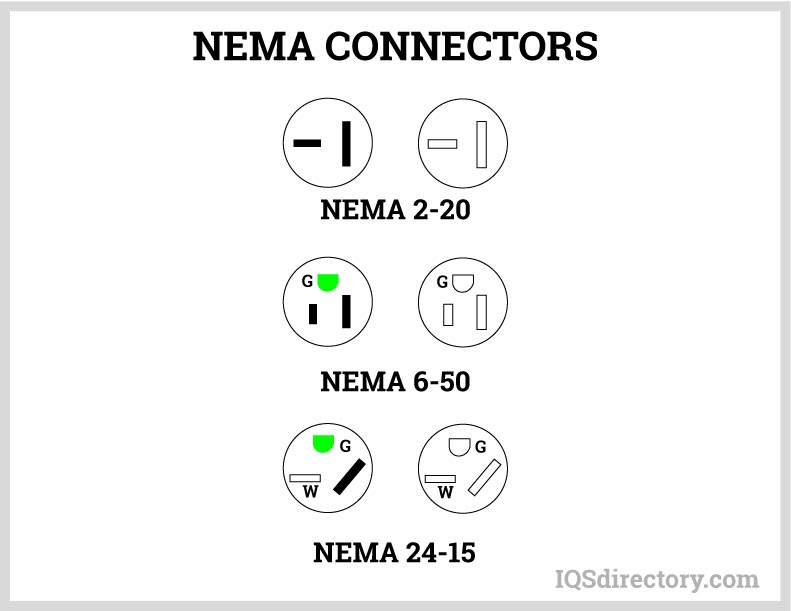
A NEMA connector is a method for connecting electronic devices to power outlets. They can carry alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). AC current is the typical current found in homes, offices, stores, or businesses...
Thomas Edison developed the power distribution system in 1882. He wrapped a copper rod in jute, a soft shiny fiber from plants, as an insulator. The jute wrapped copper rod was placed in a pipe with a bituminous compound...

Power supplies are electrical circuits and devices that are designed to convert mains power or electricity from any electric source to specific values of voltage and current for the target device...
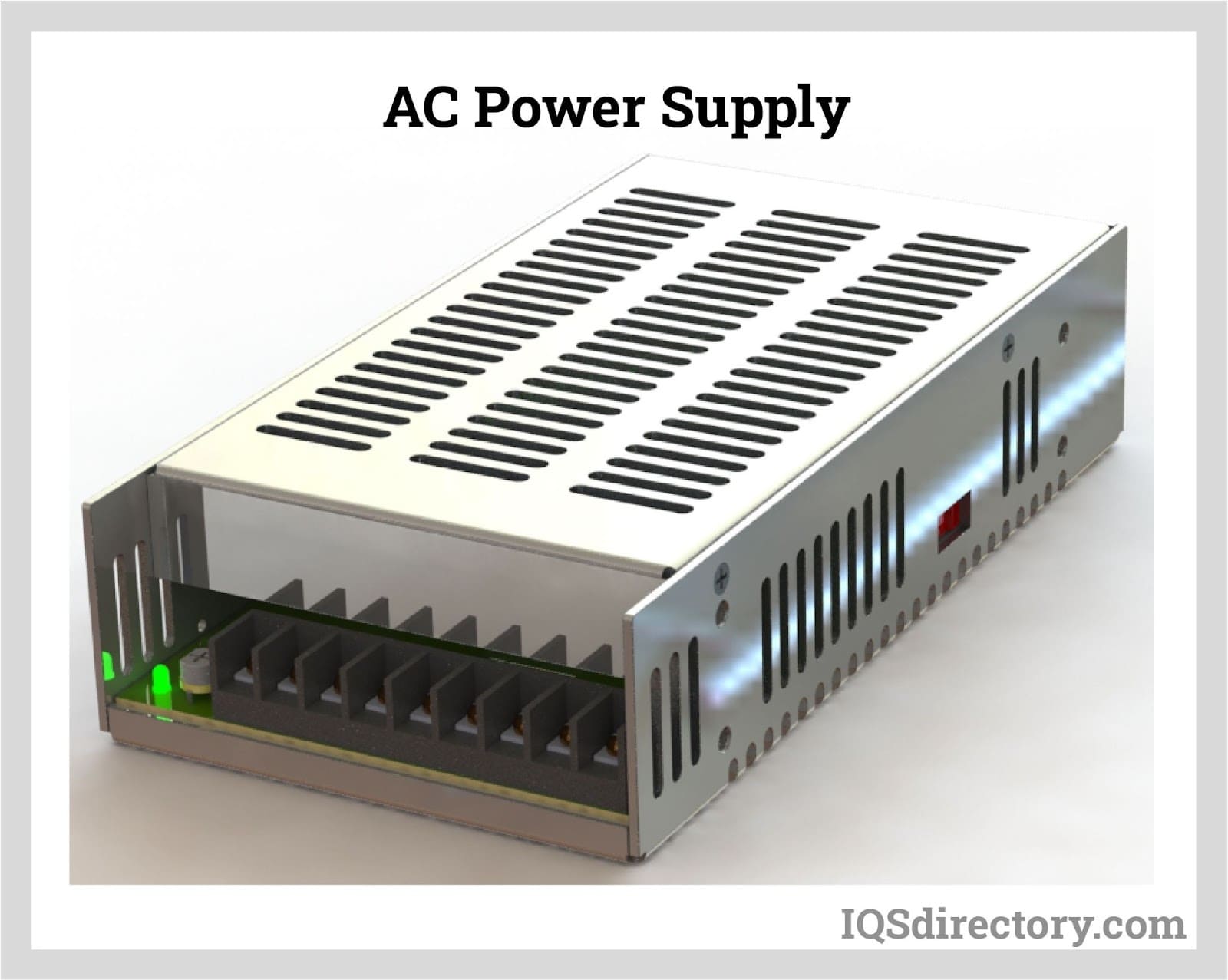
An AC power supply is a type of power supply used to supply alternating current (AC) power to a load. The power input may be in an AC or DC form. The power supplied from wall outlets (mains supply) and...

A DC DC power supply (also known as DC DC Converter) is a kind of DC power supply that uses DC voltage as input instead of AC/DC power supplies that rely on AC mains supply voltage as an input...

A DC power supply is a type of power supply that gives direct current (DC) voltage to power a device. Because DC power supply is commonly used on an engineer‘s or technician‘s bench for a ton of power tests...
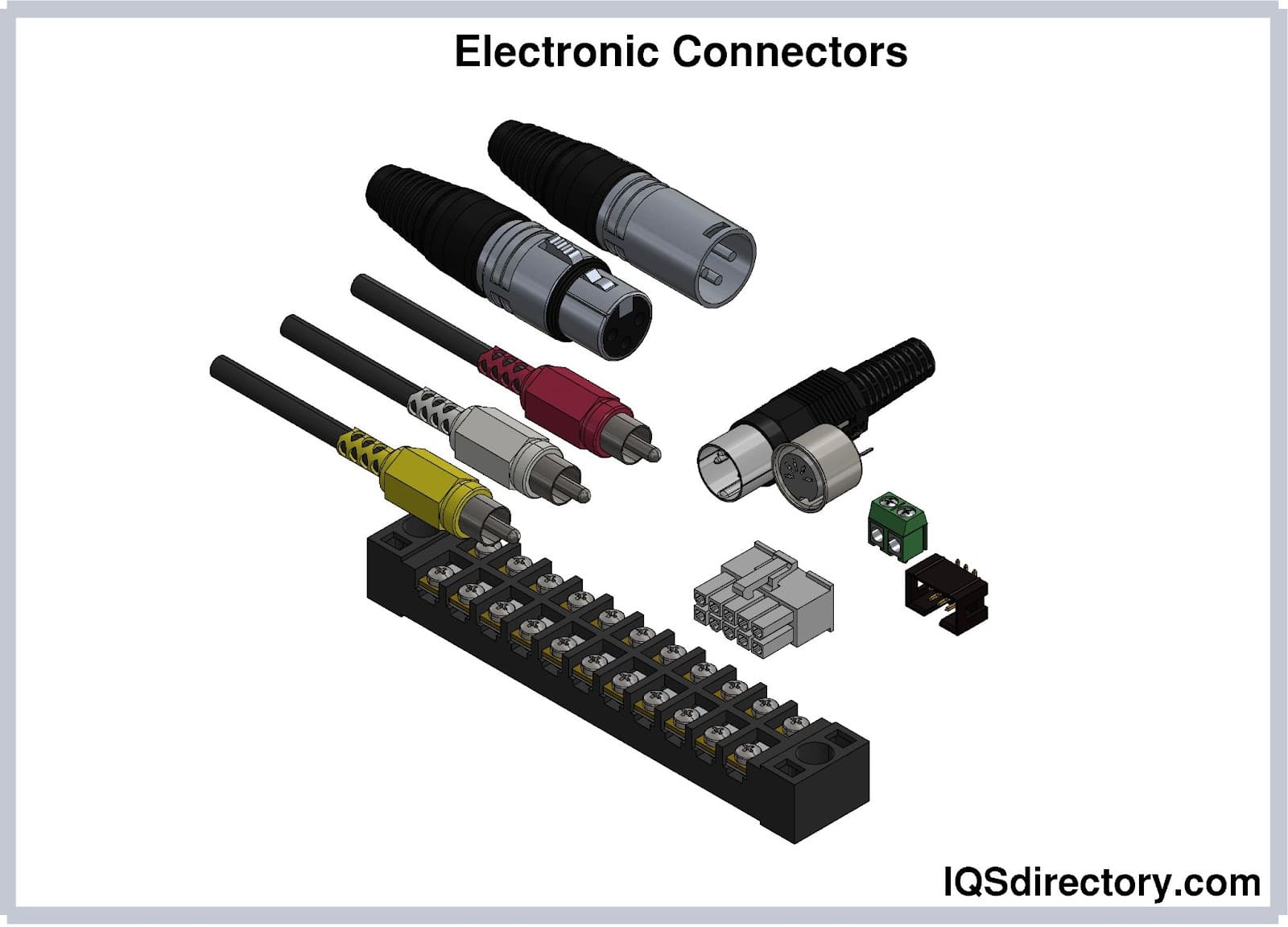
Electronic connectors are devices that join electronic circuits. They are used in assembling, installing, and supplying power to electrical devices. Connectors are an important component of every electronic equipment used in...
An electric switch is a device – usually electromechanical – that is used to open and close an electric circuit. This disables and enables the flow of electric current, respectively...

By definition a power supply is a device that is designed to supply electric power to an electrical load. An electrical load refers to an electrical device that uses up electric power. Such a device can be anything from...

A programmable power supply is a method for controlling output voltage using an analog or digitally controlled signal using a keypad or rotary switch from the front panel of the power supply...
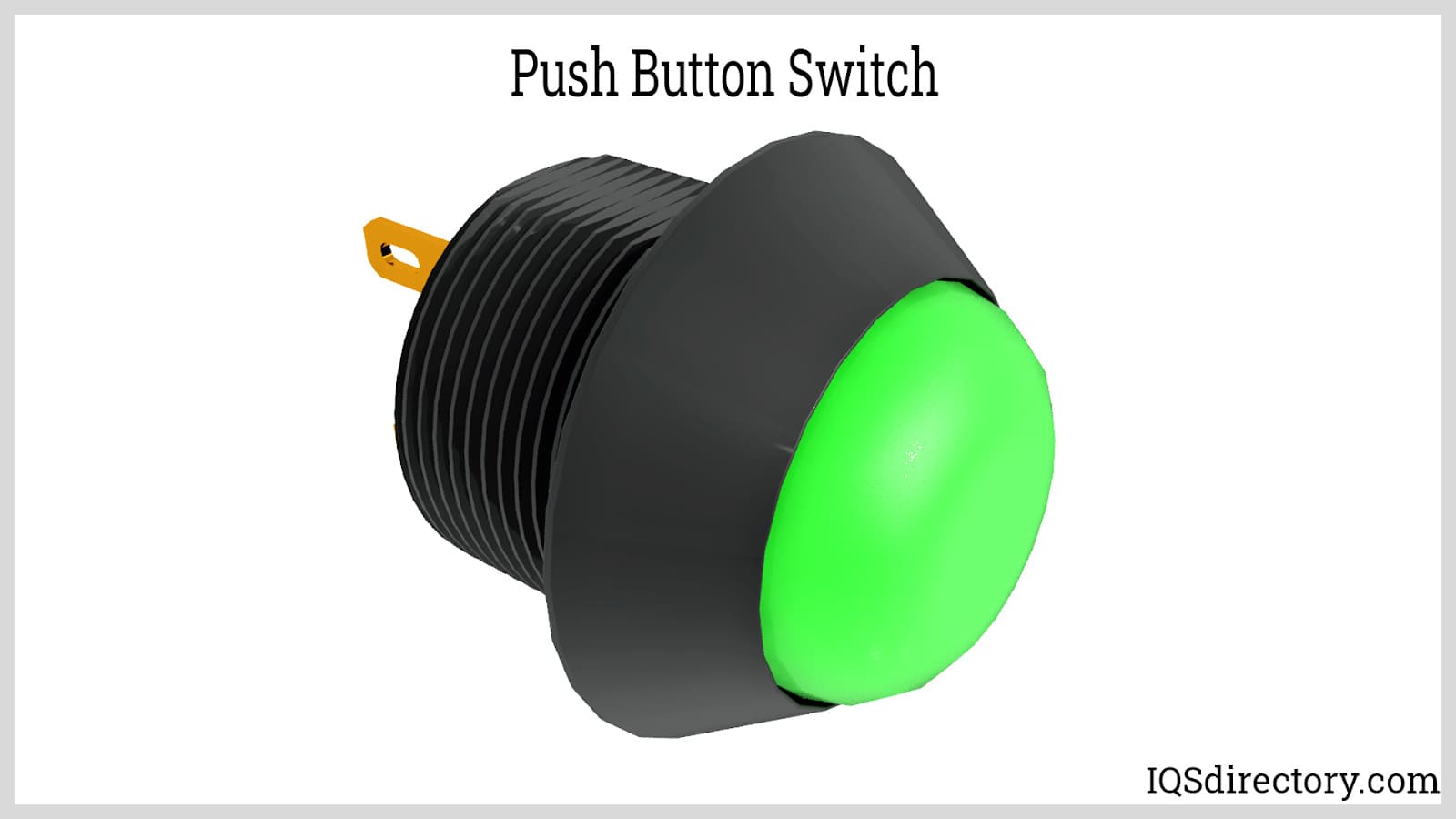
Push button switches are electrical actuators that, when pressed, either close or open the electrical circuits to which they are attached. They are capable of controlling a wide range of electronic gadgets...