Alnico Magnets
An Alnico magnet is a permanent magnet made by combiming aluminum, nickel, iron, cobalt, and other elements. They come in isotropic, non-directional, or anisotropic, mono-directional, form...
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
This article will take an in-depth look at flexible magnets.
The article will bring more detail on topics such as:

In this chapter, we’ll explore the fundamental concepts of flexible magnets, delving into their production process and how they function.
Flexible magnets are composite materials where magnetic particles are set within an elastomer matrix. They are manufactured by blending rubber polymer resin with ferrite powder, which is then shaped using either extrusion or rolling techniques. The final steps involve magnetizing the material and applying a vinyl or adhesive laminate.

These magnets benefit from combining the flexibility of rubber with the magnetism of elastomers, making them suitable for a wide range of technical applications.
As their name suggests, flexible magnets are designed to be pliable and adjustable, catering to specific application needs. They can be easily cut into various shapes, making them ideal for custom and specialized applications.
Flexible magnets find applications across different industries, from manufacturing to households, schools, and businesses. Their flexibility allows them to adapt to diverse uses and can be shaped during or after production. Typically, flexible magnets are manufactured through calendering or extrusion.
While flexible magnets provide unique benefits over traditional solid magnets—like adaptability and customizability—they may not be as durable in specific contexts. Collaborating with a trusted and experienced manufacturer is essential to ensure that you receive solutions tailored to your application’s specific requirements.
Flexible magnets are often divided into two primary types based on their production methods: magnetic sheets and extruded magnetic profiles.

Extruded flexible magnets can be made into profiles that are rolled into coils, commonly in lengths of 33 or 98 feet (10 or 30 m), and used in products like shower doors or refrigerator seals. The cross-section of an extruded profile may have intricate shapes allowing it to fit securely into a corresponding aluminum extrusion with only the front side magnetized and visible.
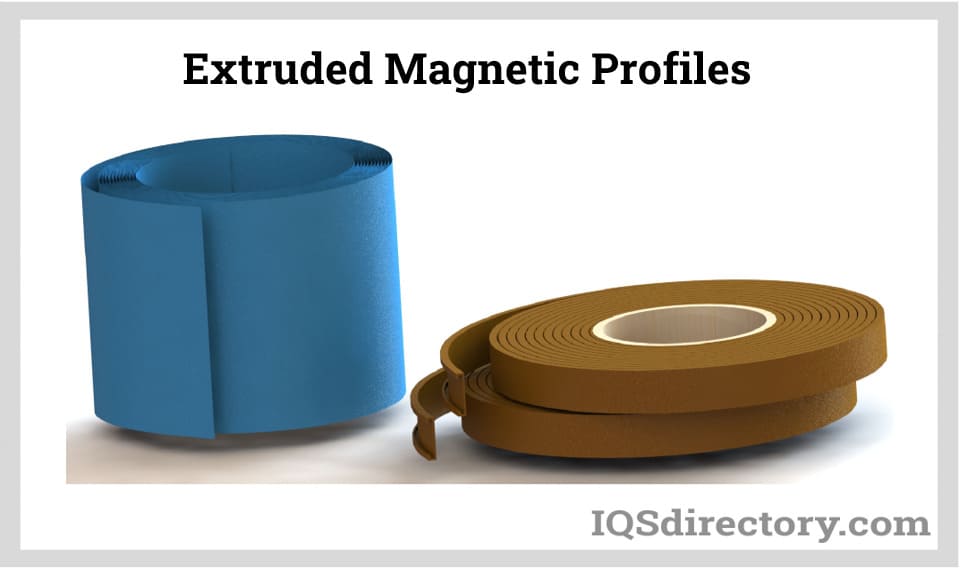
During production, the granular material is heated until melting and then pressurized with a screw feed through a hardened die, electrically discharge machined (EDM) to the desired profile shape. As the material exits, it cools and passes over a magnetizing fixture imparting a two-pole or multi-pole magnetic pattern.
Most flexible magnets are magnetized with pole strips on one side, leaving the other side non-magnetic. Extruded profiles may be rectangular, creating magnetic strips often termed magnetic tape, which can be laminated on the non-magnetic side with high-quality double-sided adhesive tape. Identical strips can be magnetized with matching polarities, allowing them to align perfectly, such as one with NSNSN and the other SNSNS.

Magnetic sheets are produced via calendering, generally available in widths up to 24 inches (610 mm) and lengths of 98 feet (30 m), with a typical thickness ranging from 0.02 to 0.03 inches (0.5 to 0.76 mm). These sheets are frequently used in point-of-sale displays and advertising, such as vehicle graphics for taxis and driving school cars, which can be easily attached and removed based on the vehicle’s use.

This concept applies to company vehicles displaying logos, which might be removed during non-business hours. For such uses, it’s critical to maintain cleanliness and store the sheets flat to avoid ferrous particles clinging to the magnetic surface and damaging the vehicle's finish.
A magnetic graphics system enables the easy updating of variable information or graphics without replacing the whole sign or display.
Powerful flexible magnetic sheeting is strongly magnetized with a multi-pole magnetization pattern, providing consistently distributed magnetic strength across its surface. Generally, thicker materials deliver stronger magnetic abilities.

The magnetism is permanent, so long as the magnet is not exposed to demagnetizing forces or larger magnets.
To summarize, flexible magnets are:
This chapter comprehensively explores magnetizers, magnetic labels, and magnetic paper, detailing their uses, applications, and differences. Learn more about how magnetization technologies and flexible magnetic products are shaping the labeling, signage, and printing industries.
Magnetizers are industrial devices and tools used to impart a magnetic field to substrates that are initially non-magnetic, whether they are packaged, printed, or raw materials. These instruments play a critical role in manufacturing processes, magnetic assembly operations, and quality control for magnetic products. For example, high-strength industrial magnetizers are designed for commercial printing environments, enabling the mass production of flexible magnets, magnetic strips, and custom printed magnetic signage. Additionally, compact handheld magnetizers are available for smaller applications, efficiently magnetizing items up to 30 mils thick. Advanced models can also serve as demagnetizers, allowing for rapid switching between magnetic and non-magnetic states as needed in maintenance, repair, and magnetic tool calibration settings. The correct selection of magnetizer ensures optimal magnet strength, alignment, and magnetization pattern for each application, which is critical for reliable performance in engineering and industrial uses.

Magnetic labels offer a highly versatile and reusable solution for labeling and signage needs in offices, warehouses, stores, classrooms, and industrial settings. Their magnetic backing enables quick attachment and repositioning on a variety of ferrous (iron-containing) metal surfaces such as shelving, racks, bins, whiteboards, and machinery. Available in many formats—such as pre-cut magnetic signs, C-channel cardholders, write-on/wipe-off surfaces, flexible adhesive-backed labels, inkjet-printable magnet sheets, and document pouches—magnetic labels eliminate adhesive residue and reduce material waste, aligning with green business practices.
Applications for magnetic labels include:
Magnetic labeling systems are ideal for environments that require adaptable, changeable, and clear signage. Industries such as logistics, manufacturing, and retail benefit from the time-saving efficiency magnetic labels provide, especially in lean manufacturing and inventory management processes.
Magnetic paper is an innovative composite material that merges the flexibility of printable paper with the holding power of a magnetic layer. Typically, it is manufactured by bonding paper with rubber or plastic containing magnetized strontium ferrite powder or similar ferrite-based compounds. This process produces a printable, cuttable magnetic sheet—usually letter-size (A4)—optimized for use with desktop inkjet printers. Magnetic paper unlocks creative possibilities in home, school, and business environments, enabling the production of custom fridge magnets, instant promotional products, educational manipulatives, magnetic business cards, and interactive visual aids.
The thickness and strength of magnetic paper determine its holding power, making it suitable for temporary magnetic displays, signage, or promotional items. Thicker sheets offer a stronger magnetic pull, although compatibility with standard printers may be affected. Most magnetic paper ranges from glossy to matte finishes, supporting vibrant, high-resolution prints and effortless customization. Standard sizes are widely available, but large-format rolls serve those creating oversized graphics or magnetic displays for trade shows, billboards, or magnetic wall systems. Always print at the highest quality setting, and feed one sheet at a time for optimal results and printer longevity.
Custom shapes and designs can be easily achieved using standard scissors or die-cutters, eliminating the need for bulk orders from specialized magnet manufacturers. Applications span from personalized name tags and magnetic event invitations to classroom learning aids and office signage. For best performance, apply printed magnetic paper to smooth, clean metal surfaces such as refrigerators, lockers, filing cabinets, or signage boards.
Although magnetic paper is a versatile material for creating promotional magnets and custom-printed magnetic products, there are a few limitations. The magnetic layer’s composite construction makes it incompatible with laser printers, as the heat generated during the laser printing process can melt the magnetic material, potentially damaging both the media and the printer. While inkjet printers are generally suitable, older or non-recommended models with elevated operating temperatures may also deform the sheets or distort print quality. Furthermore, direct exposure to excessive ultraviolet (UV) light can degrade the substrate, making it brittle or compromising the magnetization over time. While magnetic paper is rust-resistant and environmentally friendly due to its reusable nature, careful storage and handling away from sunlight will significantly extend its useful lifespan and magnetic strength.
Flexible magnets represent a category of engineered magnetic materials designed for adaptability and a wide range of industrial, commercial, and creative uses. Manufactured from strontium ferrite or rare earth additives embedded within a flexible polymer matrix, these products provide a cost-effective, customizable alternative to rigid magnets. Flexible magnetic products are used extensively for magnetic signage, POP (point-of-purchase) displays, vehicle graphics, doors and window seals, arts and crafts, packaging, and warehouse organization. Below are common types of flexible magnetic materials available to meet diverse project requirements:

Standard energy magnet strips come in continuous rolls or pre-cut sections and are engineered for a balance between flexibility, magnetic strength, and weather resistance. These versatile strips can be die-cut or laminated, and are offered in a variety of pole alignments. Thicker strips yield a higher holding force, ideal for securing lightweight displays, packaging closures, crafts, science kits, toys, and automotive seals. Magnet strips are also commonly used for labeling, display fixture assembly, and as reusable mounting solutions in commercial and educational environments.
High-energy flexible magnet strips incorporate enhanced ferrite or rare earth compositions, offering significantly greater magnetic pull compared to standard strips. These powerful magnets are indispensable in demanding settings where maximum holding strength, reliability, and longevity are key—such as in industrial door latches, magnetic sensors, and robust magnetic assemblies. They are resistant to chipping, demagnetization, and cracking, providing superior safety and performance in high-traffic or harsh environments. Customizable patterns and dimensions allow for integration with both ferrous and non-ferrous mating surfaces, supporting advanced engineering applications.

Magnetization options include across-the-width or through-the-thickness pole arrangements, enhancing design flexibility for manufacturers and product developers.
Standard flexible magnetic sheets are manufactured using a multi-pole magnetization process, delivering high holding strength—up to approximately 144 pounds (65 kg) per square foot. Typically, one side of the sheet features a stronger magnetic pull, with the reverse side optimized for vinyl lamination or adhesive application. Dual-magnetized sheet options are available for specialized mounting or signage needs. Flexible magnetic sheets are produced in an array of thicknesses, colors, and adhesive backings, suitable for large-scale signage, vehicle magnets, point-of-sale promotions, craft projects, and school or office display boards. These sheets can be die-cut or customized to fit complex shapes, making them invaluable for both professional and creative uses.

Printable wide-format magnetic sheets are engineered for desktop, commercial, and industrial wide-format printing, typically ranging in width from 40 to 60 inches (101.6 to 152.4 cm). These large sheets support vibrant graphics with finishes such as matte white PVC, white dry-erase, or custom laminates upon request. The compatibility with tempera or all-purpose adhesives allows for versatile installation on walls, vehicles, and building wraps. Key applications include billboard graphics, magnetic wall systems, trade show displays, control panels, and temporary or interchangeable large-scale promotional signage. These printable magnets are trusted by marketing agencies and design professionals for producing eye-catching, reusable advertising installations.
Recyclable magnetic print sheets offer a sustainable solution for temporary and permanent magnetic signage. Produced with an environmentally friendly printable coating, these magnet sheets eliminate the need for separate laminates and adhesives, streamlining the manufacturing process and reducing cost and waste. Recyclable magnets are available in a variety of thicknesses, custom roll lengths, and standard sheet sizes. Common applications include indoor and outdoor displays, eco-friendly menu boards, magnetic wall graphics, point-of-sale swaps, and vehicle magnets. The ease of clean-cutting and complete recyclability align with green business requirements and sustainable printing initiatives.

When choosing any flexible magnet product—be it strips, sheets, or specialized labels—consider key specifications including magnetization strength, adhesive compatibility, environmental durability, and printer compatibility. Working with reputable suppliers ensures access to technical support and customization for unique magnetic printing, labeling, or signage projects.
Flexible magnets are a key component in modern industries and everyday applications, offering adaptability and convenience for a broad range of solutions. Understanding the different types of flexible magnets—including their structure, functionality, and optimal uses—can help users select the best magnetic material for signage, retail displays, crafting, organizational tools, and industrial product manufacturing.
Flexible magnetic sheets are versatile, printable magnetic materials widely used in commercial, retail, and artistic environments. Common applications include magnetic banners, POP displays, vehicle graphics, refrigerator magnets, and custom promotional items. These magnetic sheets are manufactured using calendared strontium ferrite powder blended with a thermoplastic binder, creating a thin, flexible, and durable magnet strip or roll with the magnetic poles aligned on one side for reliable adhesion.
Flexible magnetic sheets typically feature one magnetic surface designed to attract to ferromagnetic (iron-based) substrates such as mild steel panels or metal fixtures. Because the thermoplastic binder limits heat tolerance, operating temperatures above 176°F (80°C) may result in loss of magnetism as the material softens and demagnetizes. For industrial environments where high heat is a factor, specialized high-temperature flexible magnets may be required.
There is a wide variety of flexible magnetic sheet types and finishes to meet diverse industry requirements. Basic options do not include vinyl or adhesive layers and are favored by printers and manufacturers that want to laminate or print custom graphics for tailored solutions. Other flexible magnetic sheets come pre-applied with a standard acrylic pressure-sensitive adhesive, allowing the magnetic surface to be mounted on non-magnetic materials or substrates quickly and easily for magnetic displays or product labels.
For even greater versatility, vinyl-backed flexible magnetic sheets incorporate a printable, customizable vinyl layer on their non-magnetic side. These are especially popular in the signage, advertising, and graphics sectors—supporting high-resolution prints for branding, wayfinding, vehicle signage, and advertisement boards. Their flexible construction, combined with easy cutting and printing, streamlines production for retail signage, magnetic business cards, warehouse labeling, and point-of-sale displays, among other magnetic graphic applications.
Magnetic sheets or rolls made from synthetic, rubber-based compounds provide permanent magnetic strength and are prized in the visual communications, marketing, and educational industries for their consistent performance and adaptability.
Printable magnetic paper and sheets are engineered to adhere strongly to ferrous metal surfaces, including steel cabinets, shelving, or magnetic whiteboards. These thin magnetic sheets can be cut using scissors or guillotines and are compatible with both inkjet and laser printers, making them ideal for producing custom labels, magnetic business cards, and organizational signage right from your desktop printer.
To utilize printable magnetic sheets, simply load them into an office printer and produce magnetic signs, labels, photo magnets, or barcoded inventory markers in moments. This makes them invaluable for creating personalized home refrigerator planners, custom magnetic invitations, durable magnetic name tags, and rerunnable business signage for offices, warehouses, and stores. Their key advantages include ease of use, strong adhesion to steel, and ongoing reusability for dynamic message boards, safety signage, and commercial labeling systems.
Endless possibilities await with magnetic strips, which offer reliable performance for a variety of display, organizational, and manufacturing needs. These flexible magnet strips can be laminated with protective coatings, such as high-bond acrylic adhesive, to ensure strong magnetic hold and weather resistance even in demanding outdoor installations.

Flexible magnet strips consist of magnetized lines running the length of the material, delivering reliable holding power across the surface. The strongest magnetic strength is usually concentrated on the inside of the roll. Strips can be manufactured in both standard and high-energy formats and may be magnetized through the thickness or along the length (“isotropic” or “anisotropic magnetization”), depending on end use. Available in an array of widths and thicknesses, magnetic strips accommodate diverse project requirements, from lightweight crafts to robust industrial magnetic closures.
Flexible magnetic strips are commonly utilized in sales promotions, shelf labeling, die-cut letters and numbers, visual management boards, craft projects, educational toys, advertising displays, nameplates, games, point-of-purchase displays, secondary glazing systems, magnetic drawer or cabinet closures, shower door seals, and more. They are also popular for retail merchandising, pop-up displays, warehouse identification, and quick-change signage. Their adaptability makes them a vital resource in retail operations, office organization, and equipment manufacturing.
Self-adhesive flexible magnetic tape features a permanent magnetic surface on one side and a strong, easy-peel self-adhesive coating on the other. This product, commonly referred to as magnetic tape or magnetic mounting tape, is extensively used in commercial displays, retail merchandising, exhibition graphics, and DIY projects.
This versatile tape provides a convenient solution for mounting photos, signs, posters, bills, or lightweight promotional materials on non-metallic surfaces. It is often leveraged for magnetic closures, document holders, and as a mounting solution for point-of-sale advertising. Two primary magnetic tape polarities—Type A and Type B—must be paired in applications where mutual attraction is necessary.

In addition to traditional magnetic tape, self-adhesive ferrous and steel tapes are used to convert non-magnetic surfaces to magnet-friendly backgrounds for flexible magnetic products. It is important to test large-scale applications, as surface conditions significantly affect tape or adhesive performance.
For best results during installation, the mounting surface should be meticulously clean, dry, and free of dust or oil. Use a suitable cleaning agent and let the area dry before application. Smooth, flat substrates—such as glass, high-density cardboard, or unvarnished wood—optimize adhesive contact, while rough or porous surfaces may reduce bond strength. To maximize adhesive lifespan, avoid touching the adhesive after removing the protective film and apply immediately.
Examples of compatible surfaces for self-adhesive neodymium or flexible magnets include:
To achieve sustainable magnetic bonding, apply uniform pressure along the entire length of the tape or magnet strip after positioning. Allow adhesives to cure for at least 72 hours for full-strength bonding before subjecting the material to heavy use, load, or stress.
The recommended environmental temperature range for optimal adhesive curing is between 69.8°F and 100.4°F (21°C to 38°C). Exposing adhesives to temperatures higher than 176°F (80°C) or prolonged UV exposure can degrade performance and reduce holding strength over time. Similarly, humidity can impact long-term bond integrity, so consider both indoor and outdoor conditions when choosing magnetic tape or magnets for permanent installations.
Self-adhesive magnetic products have an inherent service life based on adhesive type and application environment:
Keep in mind that these estimates are guidelines. Actual adhesive lifespans may vary depending on surface type, exposure to sunlight, humidity, and tension. With ideal application and minimal exposure to environmental stressors, some adhesives can retain holding power significantly longer.

Premium adhesive backing ensures superior initial tack, long-term adhesion, and enhanced magnetic holding force for both light-duty and industrial applications. Features like quick-release tabs speed up liner removal during installation while robust neodymium or flexible ferrite materials deliver maximum magnetic strength and reliability for magnetic closures, attachment, or display systems.
Neodymium disc magnets with adhesive backings are a popular choice for applications requiring strong magnetic attachment to ferromagnetic surfaces, including steel, iron, and specialty magnetic whiteboards. These high-performance adhesive magnets are commonly arranged in alternating north-south pole sequences, which can significantly enhance attraction force and improve the function of display and closure systems.
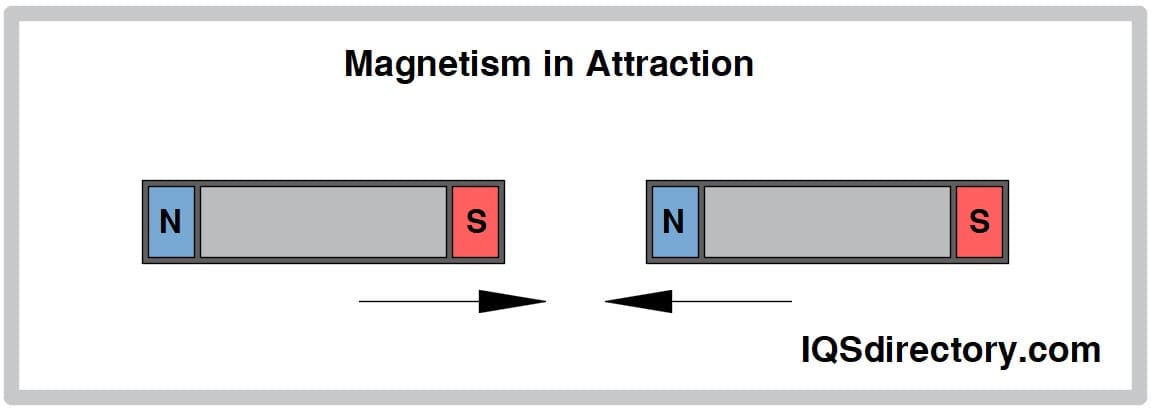
These magnets exhibit classic dipole magnetic behavior: opposite poles (north and south) attract, while like poles repel. Proper arrangement in displays, packaging closures, magnetic fasteners, or mechanical assemblies ensures effective operation and prevents unwanted demagnetization. Commonly seen in custom packaging, arts and crafts, print finishing, stationery folder closures, and even DIY household repairs, these discs are prized for their miniaturized strength and ease of application.
Industries such as print production, promotional products manufacturing, educational resources, and retail merchandising benefit from the versatility of self-adhesive magnets—not only for dynamic displays but for safe, residue-free removability and high adaptability across a wide array of magnetic solutions.
Flexible magnets are composite materials made by mixing rubber polymer resin with ferrite powder. They’re shaped by extrusion or rolling, then magnetized and laminated. This process produces lightweight, adjustable magnetic products for a variety of applications.
The main types include magnetic sheets or rolls, magnetic strips, extruded magnetic profiles, printable magnetic paper, and self-adhesive magnetic tapes. Each type caters to different applications such as signage, labeling, closures, and displays.
Magnetic labels are perfect for reusable signs, shelf labels, whiteboard organization, and workflow markers. Magnetic paper enables easy creation of custom fridge magnets, invitations, business cards, and educational tools using standard inkjet printers.
Flexible magnets generally tolerate temperatures from -15°F to 160°F (-26°C to 71°C) and up to 176°F (80°C) for some sheets. Avoid demagnetizing forces, keep surfaces clean, and store sheets flat to maintain strength and surface integrity.
Adhesive magnetic tapes offer a quick, residue-free method to mount signs, photos, and displays on non-metallic surfaces. Their reliable adhesion and easy removability make them a preferred choice for retail, exhibitions, and office use.
Flexible magnets are usually magnetized in pole strips—across the width or through the thickness. Alternating north-south sequences enhance holding power and precise alignment, crucial for closures, displays, and matched assemblies.
This section will explore the various applications and uses of flexible magnets.
The applications of flexible magnets are:
Magnetic tools are widely utilized to save time and reduce stress in tasks related to vehicular maintenance, garage work, and similar service operations, as outlined below:
Magnetic materials and flexible magnets are employed in various display applications to simplify installation and minimize damage upon removal.


Flexible magnets can be a cost-effective and quick solution for the following applications:
Using adhesive magnets enables innovative designs and manufacturing techniques that are not feasible with brittle or rigid materials. Flexible magnetic products can be twisted, cut, bent, coiled, punched, and shaped without losing their magnetic properties. For instance, bending can create ring magnets, commonly used in small direct current motors. These magnets are also easy to machine with conventional tools.
Flexible magnets are composite materials with magnetic elements arranged in an elastomer matrix. They're made from a combination of rubber polymer resin and ferrite powder by forming them through extrusion or rollers and finally magnetizing and laminating them with vinyl or glue. The compound materials bring together rubber elastic properties and elastomer magnetic properties to bring out flexible materials that are useful in multiple specialized applications. Flexible magnets have been of great help to humanity over the generations, and their application continues to be of great value in multiple fields and sectors.

An Alnico magnet is a permanent magnet made by combiming aluminum, nickel, iron, cobalt, and other elements. They come in isotropic, non-directional, or anisotropic, mono-directional, form...

A ceramic magnet, also known as a ferrite magnet, is a permanent magnet made by combining iron oxide and strontium carbonate. They are a man made magnet produced by heating the two elements to...
Magnets are materials that exert a noticeable force on other materials without physically contacting them. This force is called a magnetic force. The magnetic force can either attract or repel. Most known materials...

A Neodymium (Nd-Fe-B) magnet is a common rare earth magnet composed of neodymium (Nd), iron (Fe), boron (B), and transition metals. They have superior performance in applications because of their strong...
ermanent magnets are materials that generate a magnet field based on the internal structure of the material that forms them. With most materials, magnet fields point in random directions that cancel out the fields. The electrons of such materials spin…
SmCo magnets are strong rare earth permanent magnets that are used for a variety of industrial applications. They have two primary phases, which are SmCo₅ and Sm₂Co₁₇. The difference between the phases is in regard to their magnetic energy…

Power supplies are electrical circuits and devices that are designed to convert mains power or electricity from any electric source to specific values of voltage and current for the target device...
An AC power supply is a type of power supply used to supply alternating current (AC) power to a load. The power input may be in an AC or DC form. The power supplied from wall outlets (mains supply) and...
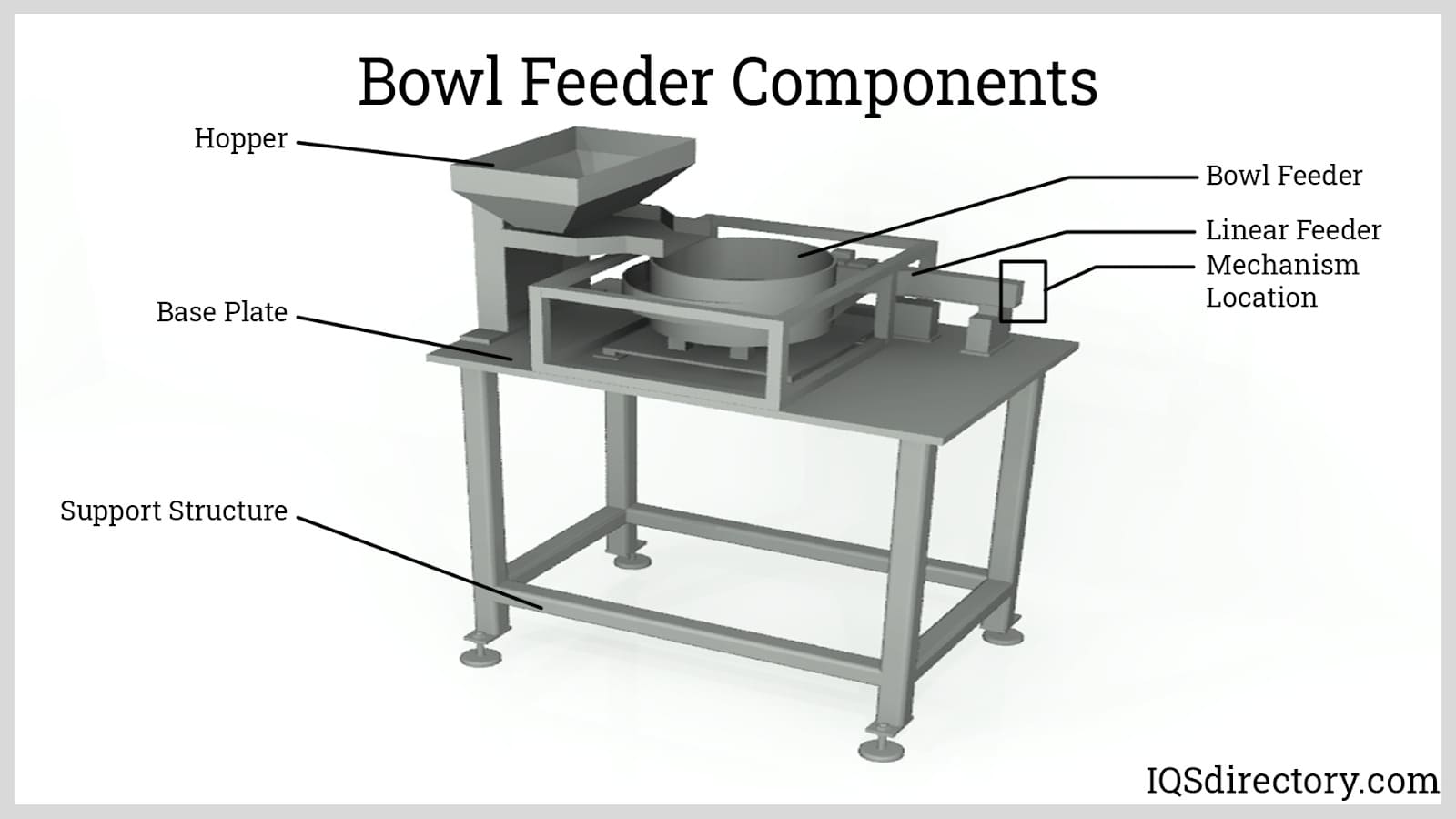

A bowl feeder is a mechanism for supplying small parts and components to a production line or for sorting bulk items for rapid use. A self contained bowl feeder system has a bowl that sets on a spring loaded base that moves vertically...
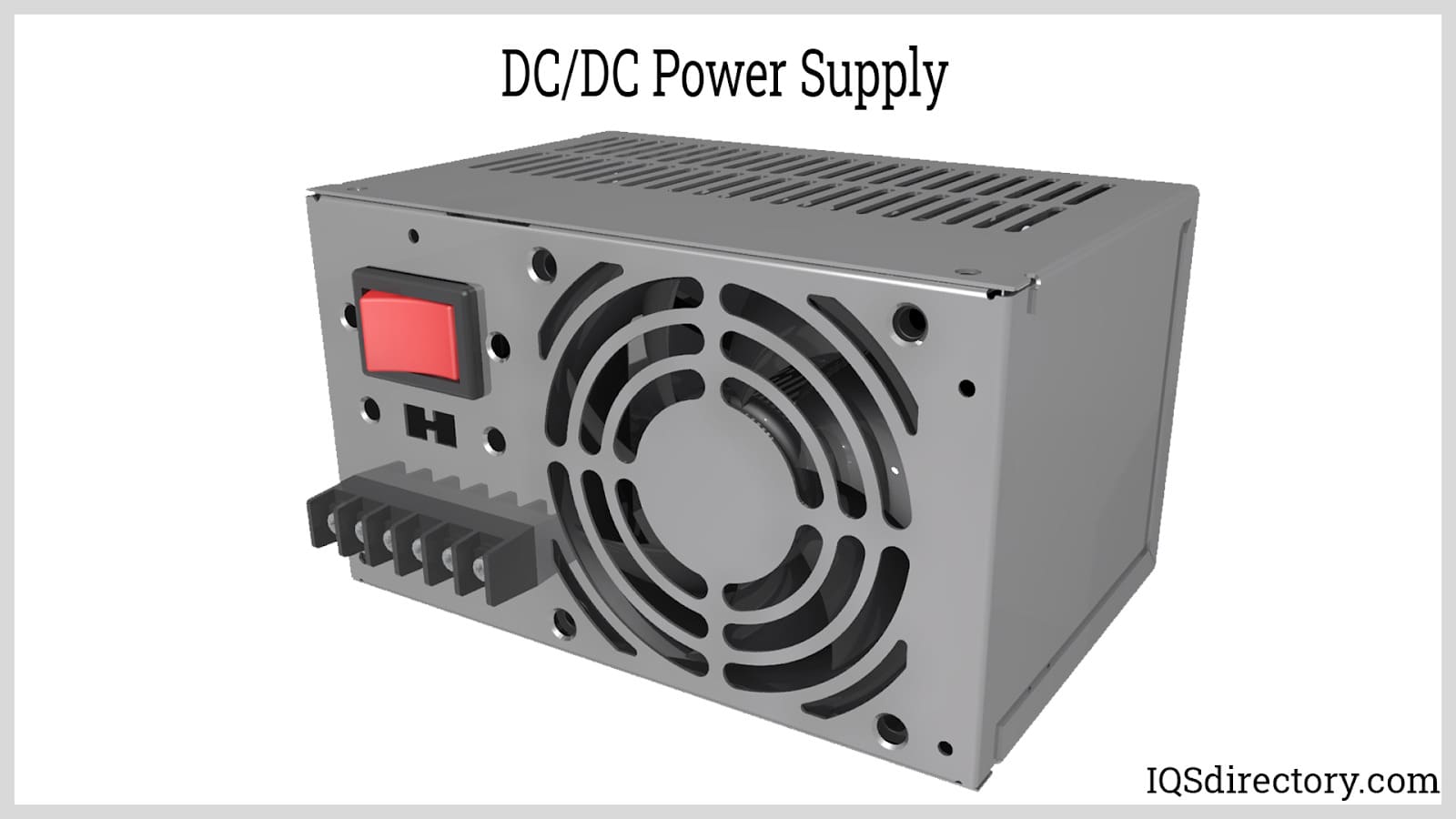

A DC DC power supply (also known as DC DC Converter) is a kind of DC power supply that uses DC voltage as input instead of AC/DC power supplies that rely on AC mains supply voltage as an input...

A DC power supply is a type of power supply that gives direct current (DC) voltage to power a device. Because DC power supply is commonly used on an engineer‘s or technician‘s bench for a ton of power tests...
Electric transformers are static electrical machines that transform electric power from one circuit to the other without changing the frequency. An electrical transformer can increase or decrease the voltage with...
An electromagnetic interference or EMI Filter is an electrical device or circuit that filters specific unwanted frequencies in power lines or offending frequencies that are detrimental to a system. They receive AC or main power...

By definition a power supply is a device that is designed to supply electric power to an electrical load. An electrical load refers to an electrical device that uses up electric power. Such a device can be anything from...

An isolation transformer, just like typical transformers, is a non-moving device that transmits electrical energy from one circuit to another without requiring any physical contact. It works on the idea of magnetic...

Power transformers are electrical instruments used in transmitting electrical power from one circuit to another without changing the frequency. They operate by the principle of electromagnetic induction. They are used in transmitting electrical power between...

A programmable power supply is a method for controlling output voltage using an analog or digitally controlled signal using a keypad or rotary switch from the front panel of the power supply...
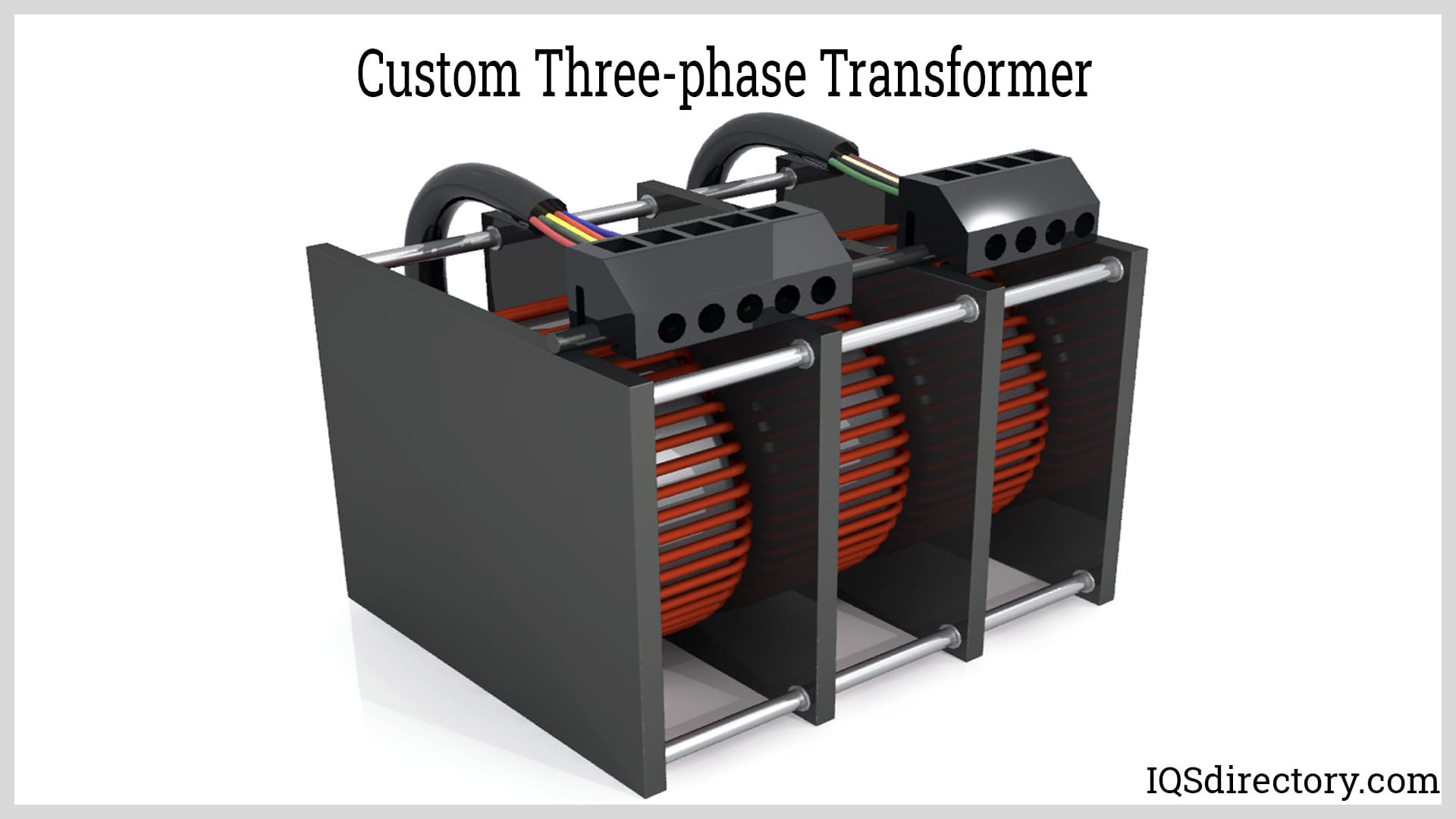

An electrical transformer is a passive machine that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another using a magnetic flux to induce an electromotive force. Transformers are used to increase (step-up) or decrease (step-down) voltages without changing the frequency of the electric current...
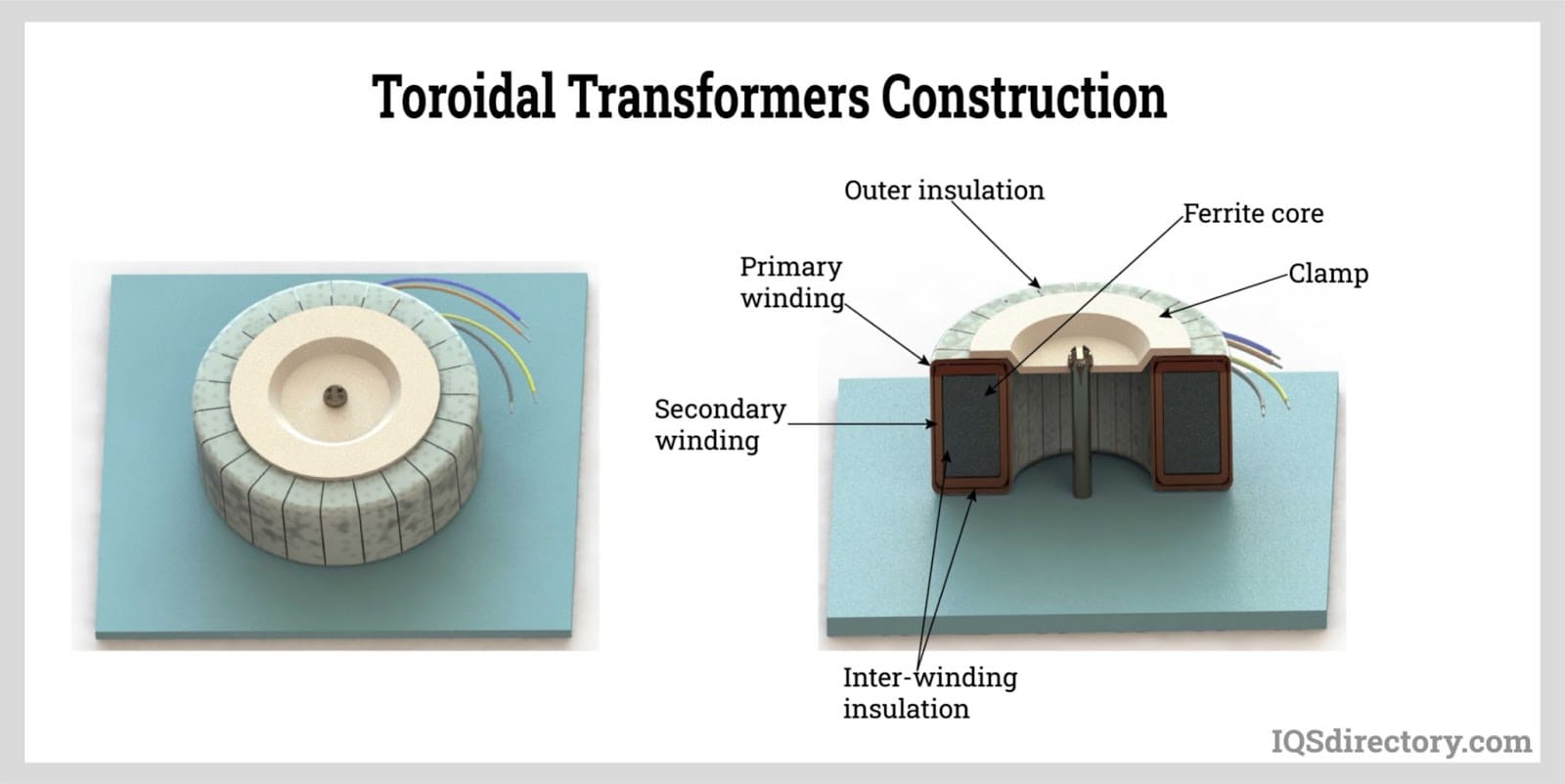
A toroidal transformer is a type of electrical transformer constructed with a torus or donut-shaped core. Its primary and secondary windings are wound across the entire surface of the torus core separated by an insulating material...
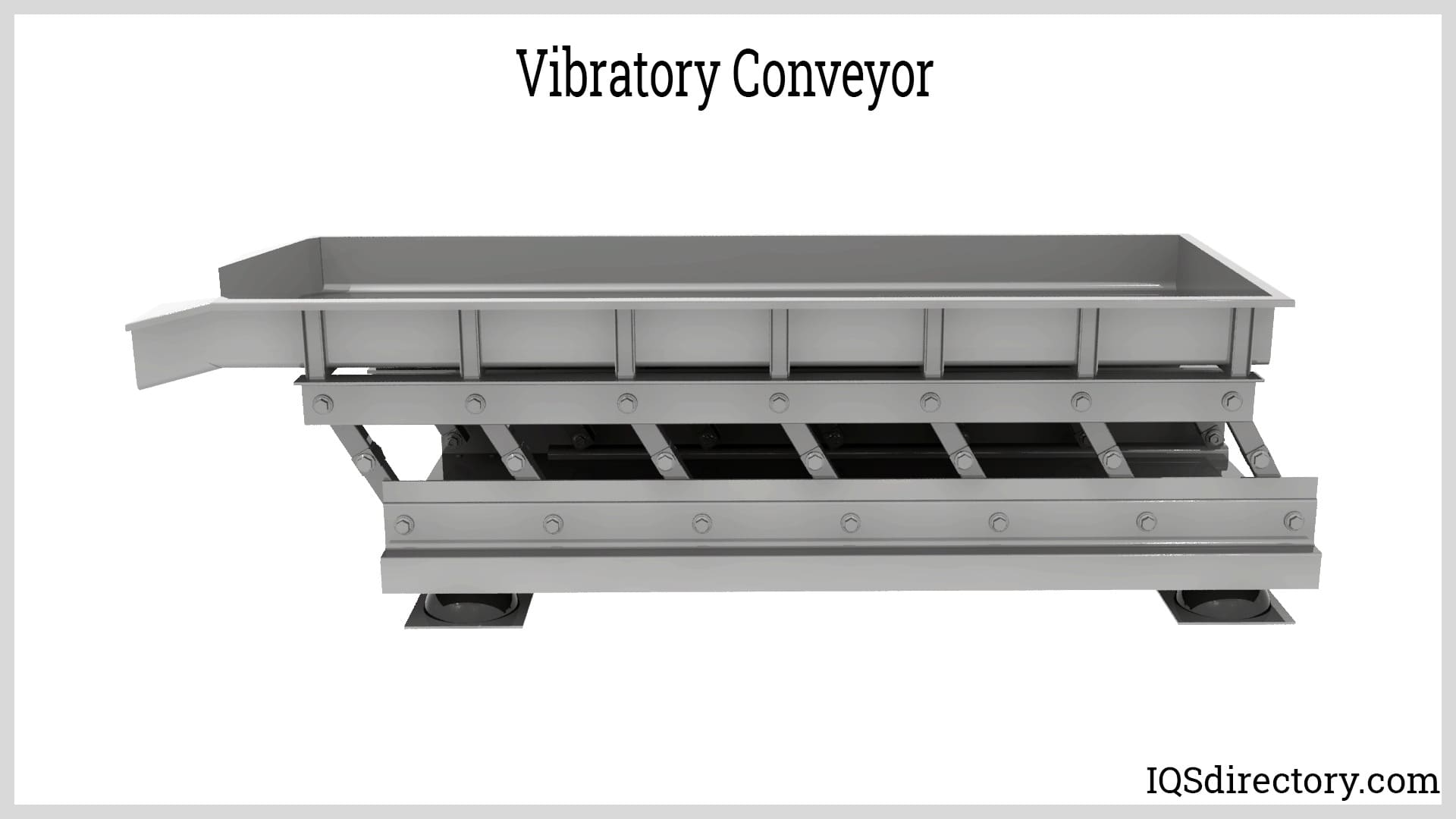

Vibratory conveyors are material-handling equipment used to transport fine to coarse-grained bulk materials. These vibratory conveyors are strong conveying equipment utilized for bulk commodities with fine to coarse graininess...
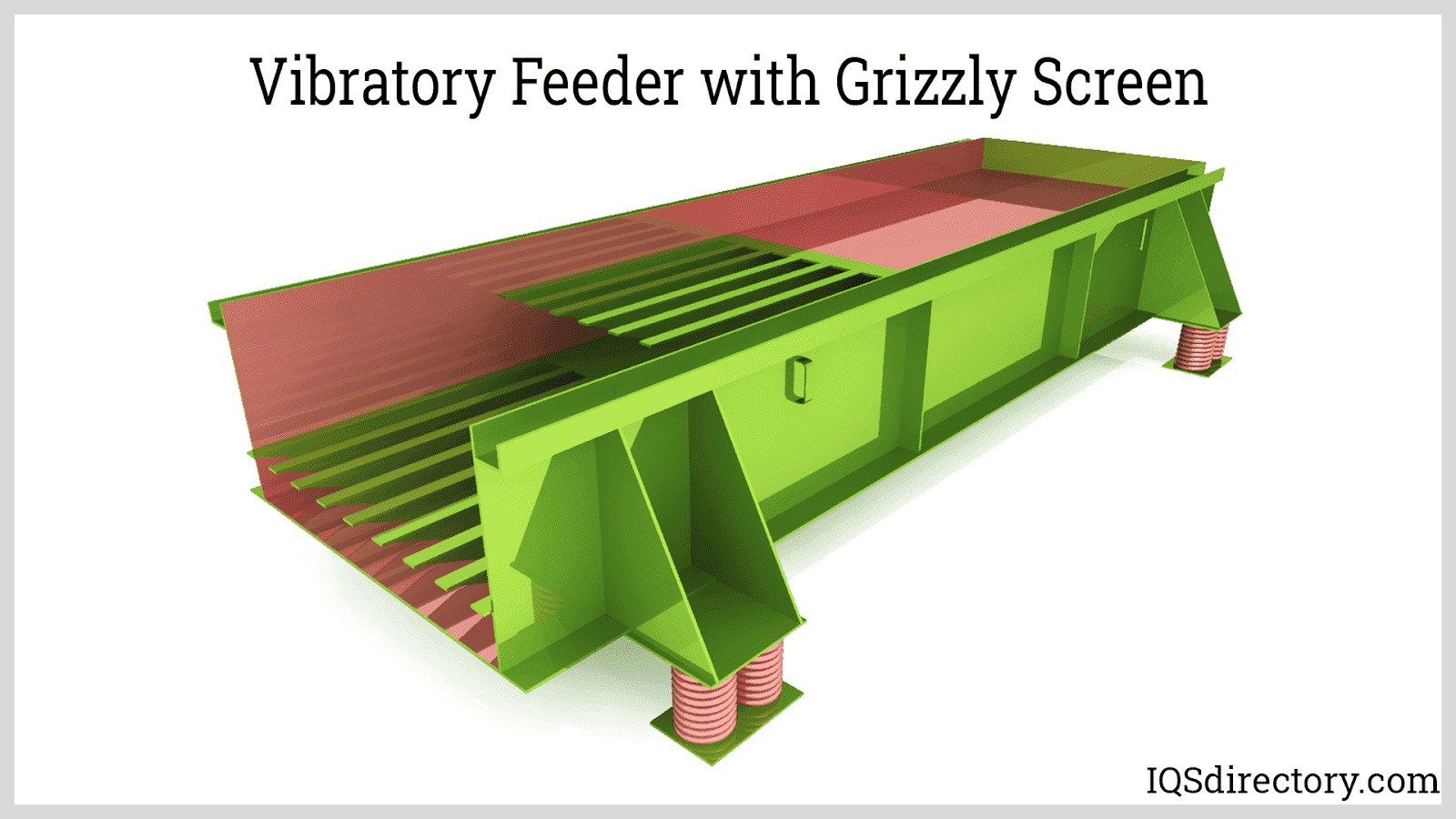
Vibratory feeders are short conveyors used to transport bulk materials utilizing a controlled vibratory force system and gravity. The vibrations impart a combination of horizontal and vertical acceleration through tossing, hopping, or sliding-type of action to the materials being handled...
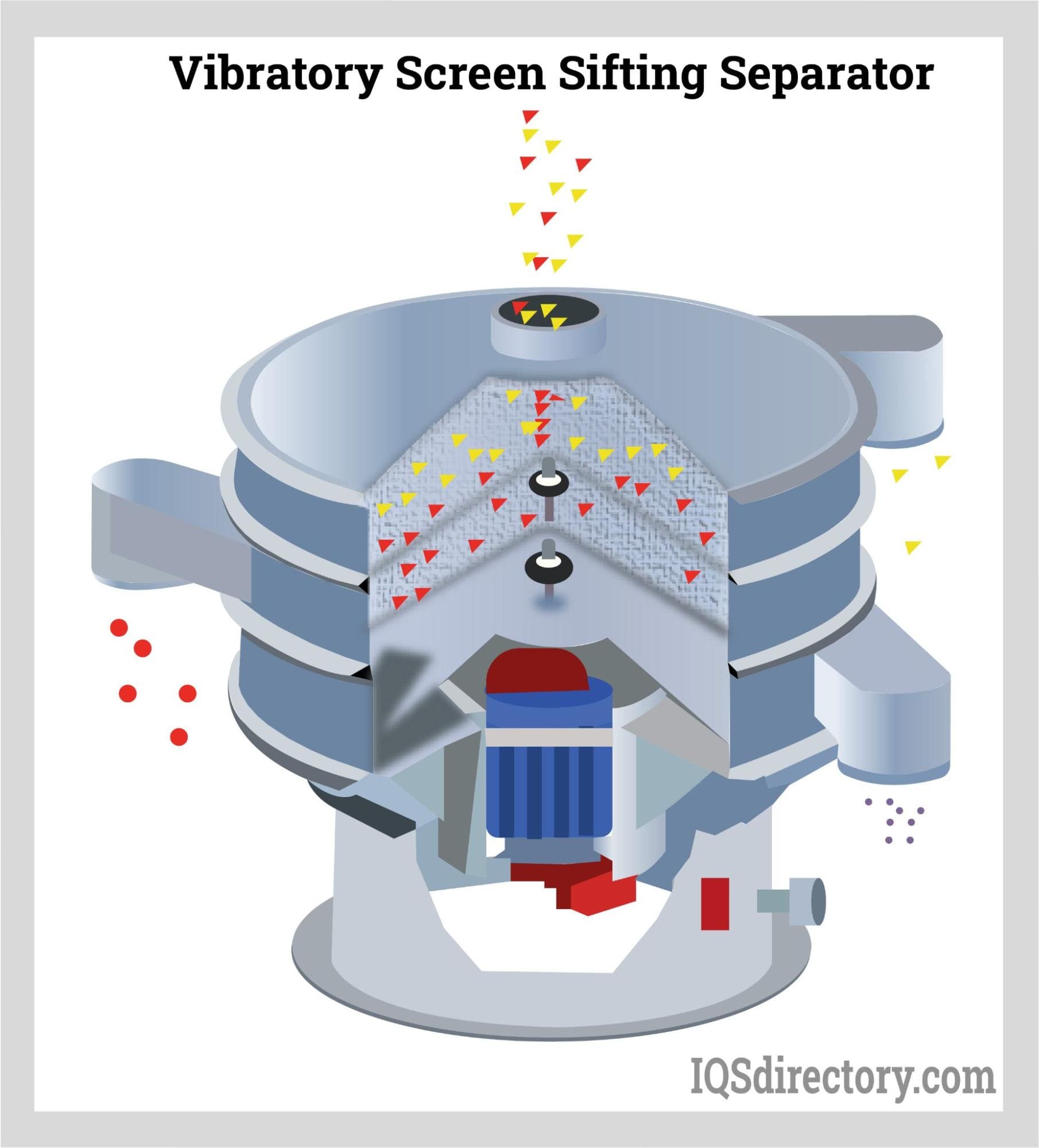
A vibratory screening is a process that separates bulk solid materials from solids and slurries using inertial vibration that causes various sizes of particles to pass through openings in a screen or...
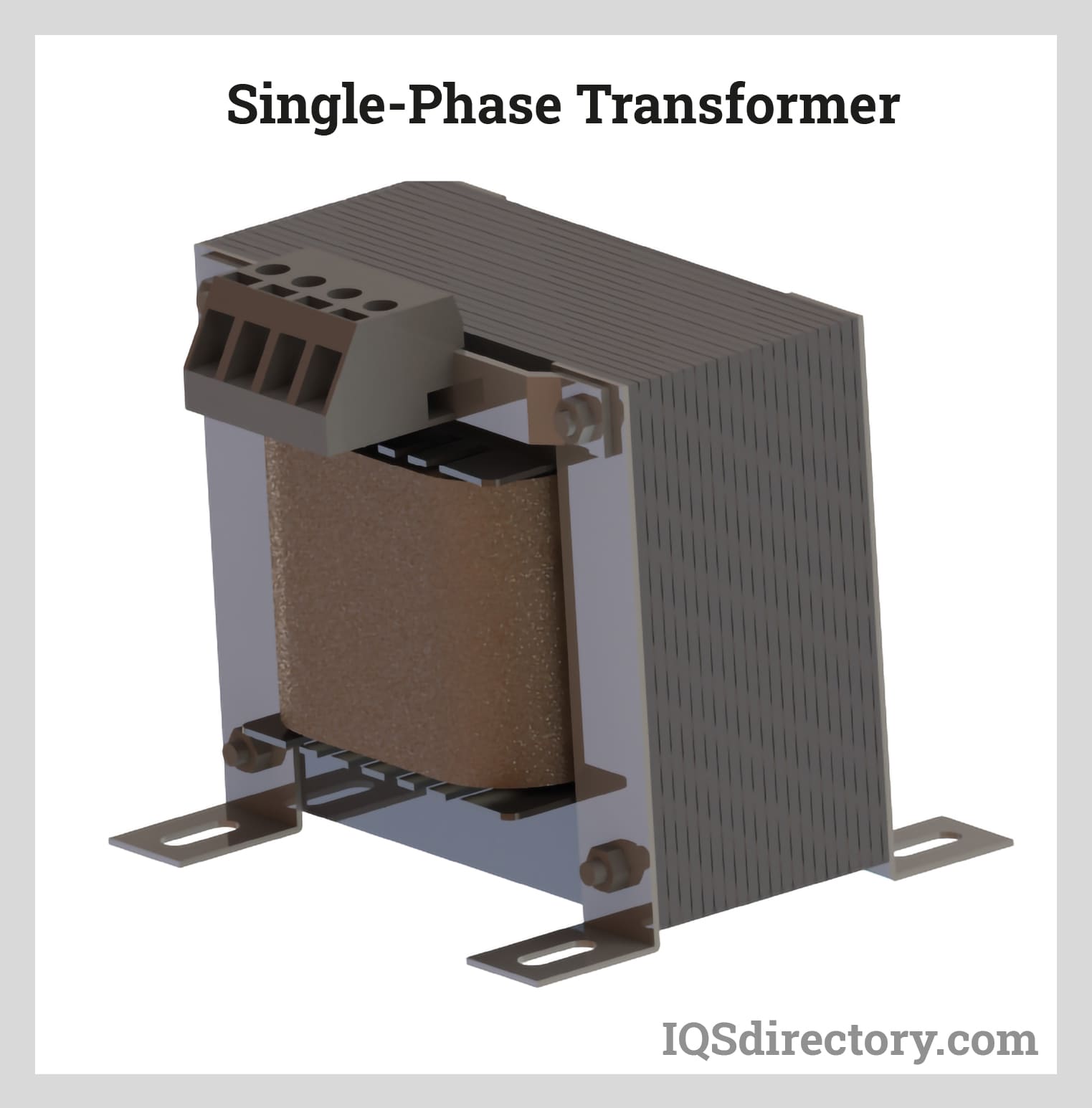
Electronically operated equipment depends on power transformers to convert electrical currents into voltage. Current transformers store and transport energy through power lines and grids...