Aluminized Steel

Aluminized steels are steels that have been hot-dip coated with pure aluminum or aluminum-silicon alloys. This hot-dip coating process is termed hot-dip aluminizing (HAD)...
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
This article will take an in-depth look at Tungsten metal.
The article will look at topics such as:

This section delves into the various aspects of Tungsten metal, examining its natural occurrences, manufacturing processes, and notable properties.
Tungsten is a commonly available, silvery-gray metal known for its impressive hardness. It exhibits outstanding tensile strength and can withstand extremely high temperatures, with a melting point of 6191°F (3421.7°C) and a boiling point of 10220°F (5660°C). Tungsten, identified by the atomic number 74, is part of the transition metals group in the periodic table.

Tungsten is naturally found in minerals like wolframite and scheelite. Wolframite, recognized as an iron-manganese tungstate with the formula (FeMn)WO4, is a solid solution of ferberite (FeWO4) and hubnerite (MnWO4). Scheelite, which is calcium tungstate with the formula CaWO4, is another important source. Various tungsten minerals differ in rarity and economic importance, with some being moderately common and others extremely rare with little economic value.

Below are some critical terms affiliated with tungsten metal, covering its applications and descriptions of tungsten alloys.
An alloy is produced by combining two or more elements to harness the properties of each metal, resulting in optimal performance. Noteworthy tungsten alloys include tungsten carbide (a mixture of tungsten and carbon), Hastelloy (which combines nickel, chrome, molybdenum, and tungsten), and various tungsten nickel alloys, to name a few.
The brittleness of a material indicates its propensity to fracture under stress. Pure tungsten tends to be vulnerable to cracking, leading to its alloying with other metals to boost durability. For instance, combining tungsten with carbon can significantly enhance its strength, making it suitable for applications that would otherwise be impractical for pure tungsten.
A filament is a thin metal wire used in bulbs, adept at converting electricity to light and enduring high temperatures without melting or snapping.
The melting point defines the temperature at which tungsten transitions to a liquid state. It has an exceptionally high melting point of 3,422°C (6,192°F).
Superalloys are metals noted for their high tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and elevated melting points.
In engineering contexts, tensile strength refers to the extreme stress level beyond which a metal deforms or breaks.
The alternative name, "wolfram," comes from tungsten's chief ore, wolframite, which is the primary resource for this metal.
Tungsten displays the following properties:
Positioned among the transition metals in the periodic table, tungsten exhibits multiple oxidation states: +2, +3, +4, +5, and +6. Its atomic number is 74, and with a relative atomic mass of 183.84, it stays solid at room temperature because of its stable isometric crystal framework, which X-ray analysis can discern.
Tungsten resists corrosion from most acids except nitric and hydrofluoric acids. It can also react with alkaline oxidizers like potassium nitrate or sodium hydroxide but tends to remain generally resistant. However, at high temperatures, tungsten can quickly react with oxygen to form trioxides.
Tungsten exists as a mixture of five stable isotopes: tungsten-180, tungsten-182, tungsten-183, tungsten-184, and tungsten-186. Their respective proportions are approximately 0.12%, 26.5%, 14.3%, 30.6%, and 28.4%.
Tungsten, in its pure form, is a shiny white metal quite easy to handle. However, the presence of minute quantities of oxygen and carbon can make it fragile under severe stress and pressure.

This metal is the densest engineering material, with a density of 19.25 g/cm³ due to its compact crystal arrangement. It boasts a melting point of 3,140°C and a boiling point of 5,700°C. It has the lowest vapor pressure among metals and achieves the highest modulus of elasticity at 400 GPa.
Tungsten has a minimal thermal expansion coefficient of 4.4×10⁻⁶ mm/°C, parallel to that of borosilicate glass, making it ideal for glass-metal seals. Moreover, tungsten is environmentally robust and does not easily break down.
As a metal, tungsten embodies numerous conventional metallic properties. It efficiently conducts electricity owing to its free electrons and remains an excellent conductor of heat. Tungsten alloys maintain these essential conductive properties, making them invaluable for electrical industries.
Tungsten is known for its corrosion resistance, distinguishing it as a unique metal. Despite its advantageous properties, tungsten can be brittle in its pure form. Therefore, it is generally alloyed with other metals to produce more robust and manageable compounds.
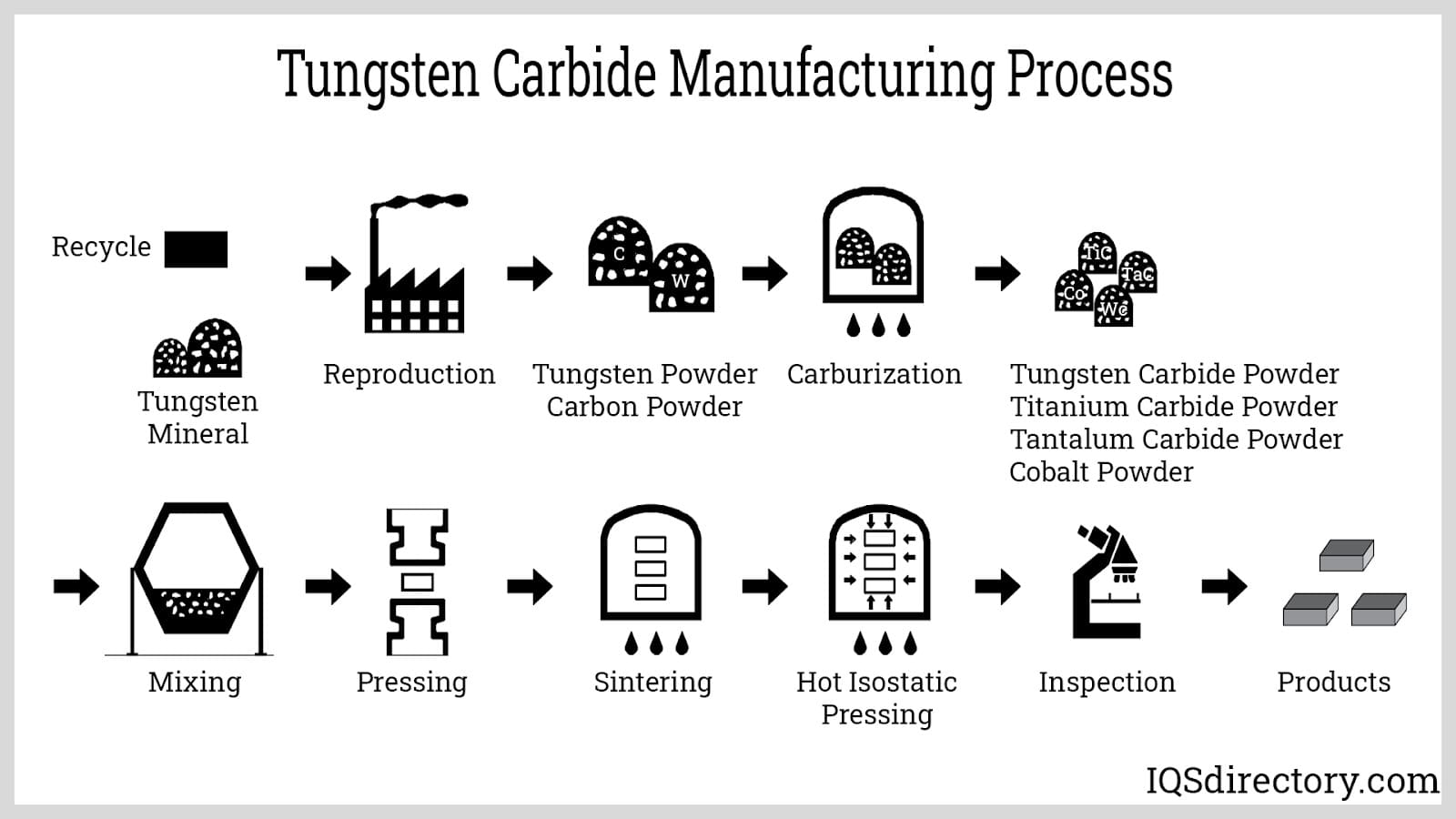
Tungsten goes through a multi-step extraction and refining process. Initially, tungsten ore is transformed into tungsten (VI) oxide (WO3). This oxide is then subjected to heating with hydrogen or carbon to create tungsten powder. Due to its high melting point, forming tungsten ingots is technically challenging and commercially unfeasible.
Tungsten powder is combined with small amounts of nickel or other metals before undergoing sintering, allowing nickel to diffuse and form tungsten alloys.
The powder can also be obtained by reducing tungsten hexafluoride (WF6) using hydrogen.
WF6 + 3H2 → W + 6HF
For manufacturing tungsten products, sintered tungsten alloys are molded into billets, later processed into foils, bars, plates, or sheets by grounding, drawing, die cutting, or molding. Some articles may need additional processing steps.
Tungsten products come in three primary forms: black (with a lubricant layer), oxide, and cleaned (surface stripped with chemicals). The ground form is further refined using diamond or silicon carbide tools for precision and smoothness.
Items made from tungsten are adaptable and find usage in manufacturing tungsten electrodes, drilling equipment, light bulbs, industrial machines, tools, military armament, material coatings (such as for boats), X-ray screens, and construction tools.

Tungsten alloys are instrumental in weapon production and developing effective heat sinks for thermal management. They are also essential in turbine blade fabrication and heavy-duty equipment manufacturing, such as weights and ballasts used in fitness applications.
The corrosion resistance of tungsten extends tool lifespan and quality. Tungsten is used for producing electrodes suitable for high-temperature applications, capable of withstanding water without rust or degradation.
Tungsten is integral to welding equipment for transmitting high voltage and currents across metal sheets. Its applications also include electrical discharge machines and tungsten gas arc welding setups.
Tungsten possesses five primary alloy forms: alloyed tungsten, cemented carbide, tungsten carbide, tungsten-based chemicals, and pure tungsten. These tungsten alloy types are classified based on their nominal tungsten content and the ultimate tensile strength of each alloy. Understanding the different varieties of tungsten alloys is essential when evaluating materials for industrial applications due to their unique mechanical, chemical, and physical properties.
Tungsten carbide is a specialized alloy produced by combining tungsten and carbon in nearly equal proportions. It initially appears as a fine, gray powder that is further processed into an extensive range of industrial materials and components. Renowned for its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and extreme durability, tungsten carbide boasts the ability to withstand exposure to harsh chemicals, including acids and alkalis, oxidation, and water. With hardness nearly twice that of high-grade steel and a density surpassing both titanium and steel, tungsten carbide sets an industry benchmark for strength and resilience. More than 20 unique grades of tungsten carbide powder exist, each differing in grain size, tensile strength, hardness, and melting points, making it highly adaptable to diverse application environments.
The manufacturing process of tungsten carbide involves advanced sintering and pressing techniques, shaping the powder into robust, long-lasting products, precision tools, and wear-resistant components. Tungsten carbide’s remarkable strength and abrasion resistance account for its widespread use in mining, oil and gas drilling, construction, metalworking, manufacturing, and machining. In fact, approximately 60% of all tungsten carbide alloys are manufactured specifically for critical applications in these industries, underscoring its dominance in high-performance tooling markets.
Tungsten carbide is a cornerstone material in tool manufacturing. Often referred to simply as “carbide,” this alloy forms the cutting edges of industrial tools such as saw blades, drill bits, end mills, lathe tools, and reamers—enabling these cutting tools to deliver superior durability and longer service life under extreme working conditions. In CNC machining and precision manufacturing, tungsten carbide remains indispensable, being used to produce complete tooling solutions that withstand the high loads and repetitive stresses of automated machine processes. Unlike conventional hand tools, CNC machining implements often utilize solid tungsten carbide for their entire structure, maximizing wear resistance, temperature stability, and edge retention. The use of tungsten carbide in metal cutting, high-speed machining, and tool grinding offers substantially increased productivity, minimized downtime, and lower replacement costs for manufacturers and machinists.
This advanced alloy stands out for its outstanding strength and impressive resistance to corrosion caused by chemicals such as acids and alkalis, as well as from oxidation and water exposure over time. With more than 20 available powder grades covering a wide spectrum of grain sizes, hardness ratings, tensile strengths, and melting points, tungsten carbide’s versatility ensures that professionals can select the optimal material for each demanding engineering or manufacturing application.
Tungsten carbide is processed through specialized sintering techniques to produce an array of durable products, machine parts, wear plates, and tooling inserts, making the alloy exceptionally prized in mining, construction, oil and gas, aerospace, wood processing, and advanced manufacturing. Its properties, such as high compressive and tensile strength, extreme surface hardness, low coefficient of expansion, and high melting point, guarantee outstanding wear resistance and stability—even in challenging environments with abrasive or corrosive exposures.
Tungsten carbide alloy is produced by reacting tungsten metal with carbon at extremely high temperatures, typically in the range of 1,400 to 2,000°C. Alternative methods include a low-temperature fluid bed process, where tungsten metal or blue tungsten oxide (WO3) is combined with carbon dioxide or carbon monoxide and hydrogen gases at temperatures between 900 and 1,200°C. These optimized production protocols yield high-purity, fine-grain carbide particles essential for advanced industrial and tooling applications.
Further chemical vapor deposition (CVD) techniques have been developed for high-purity carbide formation, including the following reactions:
Tungsten hexachloride is reacted with hydrogen (serving as a reducing agent) and methane (as the carbon source) at a precisely controlled temperature of 670°C.
WCl6 + H2 + CH4 → WC + 6HCl
Tungsten hexafluoride is also reacted with hydrogen as a reducing agent and methanol as a carbon source at a temperature of 350°C.
WF6 + 2H2 + CH3OH → WC + 6HF + H2O
Tungsten carbide features a macrocrystalline structure that imparts unparalleled strength, toughness, and longevity compared to most other metal alloys. The addition of carbon in the structure lowers its melting point to approximately 2,870°C while providing a notable boost in hardness, allowing it to achieve a score of 9 on the Mohs mineral hardness scale—rivaling corundum and surpassed only by diamond and some advanced ceramics. While this alloy demonstrates superior acid resistance, high compressive strength (exceeding 540,000 psi in some grades), and robust corrosion resistance, it can react with oxygen and strong oxidizers when subjected to very high temperatures.
Tungsten carbide is both hard and durable, with excellent performance in tensile and compressive strength and moderate electrical conductivity. Its density (typically around 15 g/cm3) further enhances its performance in applications demanding stability, vibration damping, and dimensional accuracy over long operational lifespans.
Tungsten carbide is the industry standard for manufacturing high-performance cutting tools, drill bits, milling inserts, saw blades, mining picks, wear-resistant machine parts, and gauge blocks. Its high abrasion resistance and ability to maintain sharp cutting edges at elevated temperatures make it the preferred material for production lines, metal fabrication, CNC machining, casting, and aerospace part manufacturing. Carbide tooling remains sharper and usable much longer than steel-based rivals, offering tremendous value by decreasing tool changeover frequency, reducing production downtime, and improving manufacturing throughput.

Furthermore, tungsten carbide is essential in defense and ammunition manufacturing, where its extreme hardness and density enable it to produce armor-piercing ammunition, kinetic energy penetrators, and other specialized rounds capable of breaching reinforced targets such as tank armor and concrete fortifications. The alloy is foundational in mining and drilling, being commonly used to construct rock drill bits, rotary cutters, plow chisels, tunnel boring heads, and wear plates for earthmoving equipment to maximize penetration and durability in harsh geological conditions.
Beyond traditional industrial uses, tungsten carbide serves as an efficient neutron reflector in the nuclear energy sector, corrosion-resistant material for precision surgical tools, hard-wearing elements in sporting equipment (such as ice spikes, cycling tire studs, and trekking pole tips), and an attractive material in jewelry manufacturing due to its metallic luster and lasting finish. Its versatility and long lifespan lead to a lower cost of ownership, reduced maintenance requirements, and higher total equipment effectiveness in sectors where uptime and reliability are mission critical.
Exposure to tungsten carbide dust can pose significant occupational health risks, including respiratory conditions such as fibrosis and chronic lung disease. Industries using tungsten carbide should institute comprehensive dust control, personal protective equipment measures, and comply with occupational health and safety regulations to safeguard workers from hazardous inhalation and minimize industrial hygiene risks.
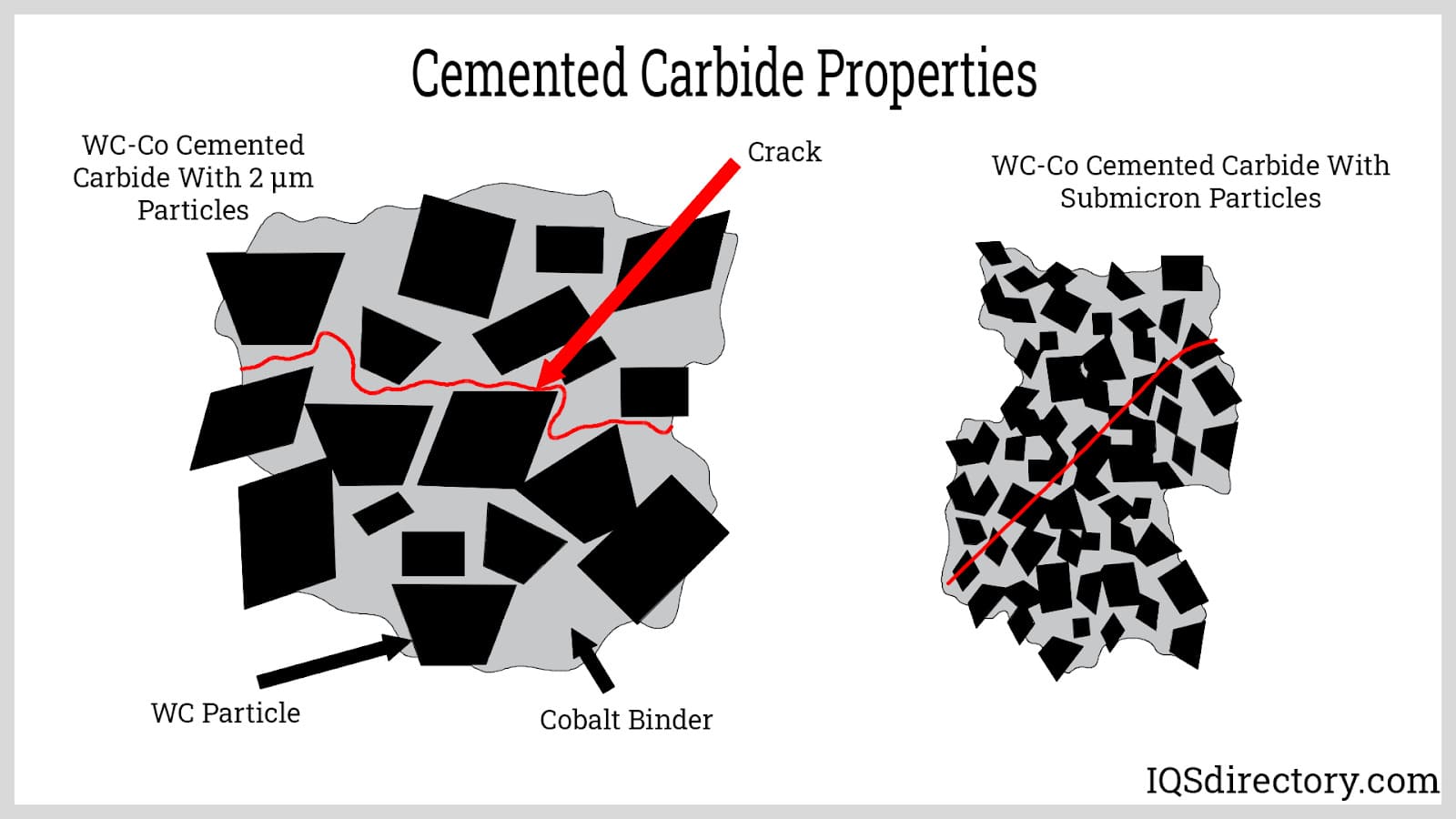
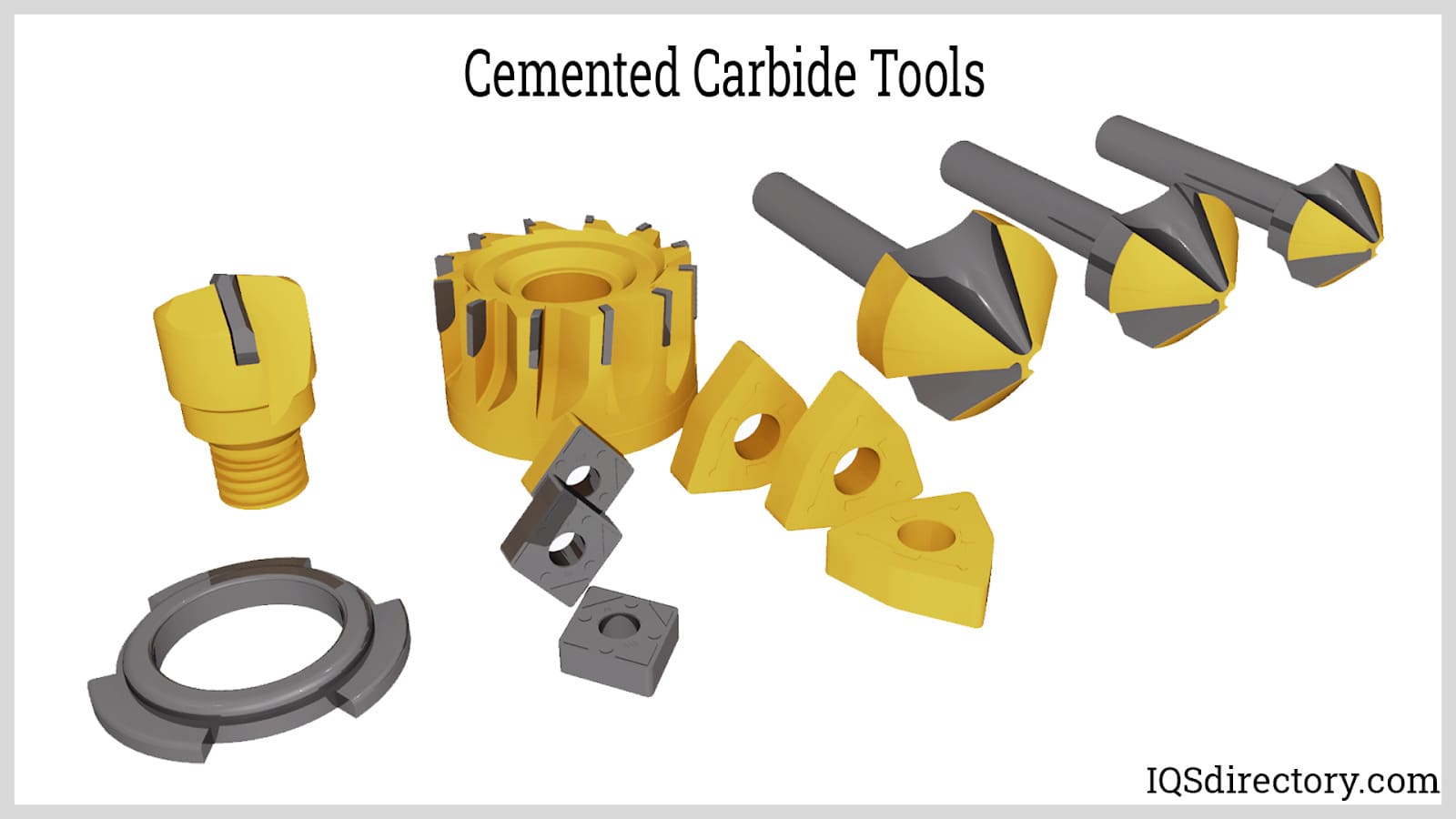
Cemented carbide is a widely utilized tungsten alloy, created by combining tungsten carbide grains with a metallic binder—most commonly cobalt. This sintered composite structure adds toughness, reduces brittleness under high pressure, and makes cemented carbide suitable for highly demanding structural and wear-resistant applications. The integration of cobalt ensures improved mechanical durability and impact resistance compared to non-cemented tungsten alloys.
Cemented carbides generally feature a composite structure composed of hard carbide particles (such as tungsten carbide or sometimes titanium carbide) serving as the aggregate, embedded within a metallic matrix composed of cobalt, nickel, or iron. This engineered composite structure, similar in concept to a grinding wheel’s abrasive grains and binder, yields a material with remarkable toughness and wear resistance.
Key production steps include hot isostatic pressing (HIP), where carbide grains are merged with molten binder metal while maintaining solid carbide phases (due to their significantly higher melting point). This creates a complex microstructure that enables the alloy’s unique properties, including fracture toughness and thermal shock resistance, ideal for high-impact and high-heat manufacturing environments.
The thermal expansion of cemented carbide is influenced by the metallic binder content, most commonly cobalt. Generally, increasing the proportion of cobalt increases the thermal expansion coefficients, affecting the alloy’s dimensional stability under temperature fluctuation. Cemented carbides retain high compressive strength, exceptional hardness, and superior resistance to deformation and impact, making them especially effective in high-speed machining and industrial cutting operations. Tailoring the binder composition allows manufacturers to optimize the alloy for specific wear, hardness, and toughness requirements.
Cemented carbide is the material of choice for indexable inserts, cutting tool inserts, metal cutting tools, mill rolls, boring and threading equipment, die-casting molds, and progressive stamping dies. Its reinforced structure ensures reduced vibration susceptibility and enhanced precision in critical machining and toolroom applications. To prolong tool lifespan and boost surface finish, cutting tools often receive specialized coatings such as titanium aluminum nitride (TiAlN), titanium carbide (TiC), titanium nitride (TiN), and aluminum titanium nitride (AlTiN)—as well as tungsten-based coatings—to provide even greater abrasion and oxidation resistance.
Heavy-duty mining and tunneling equipment are typically outfitted with cemented carbide-tipped cutting elements, known as bottom bits, which deliver unparalleled drilling and excavation capability in the world’s toughest geotechnical conditions. The alloy further finds use in hot and cold rolling mill rolls, high-performance industrial pump pistons, valve seats, wire drawing dies, and specialized components for nuclear power applications due to its high thermal and mechanical stability.
Alloyed tungsten encompasses a broad class of high-performance tungsten alloys produced by combining tungsten with various metals such as copper, nickel, and iron. These alloys are valued in specialized engineering, electronics, and industrial applications where a customized balance of density, machinability, electrical conductivity, or magnetic properties is required. For example, tungsten-nickel-iron alloys benefit from nickel’s enhancement of density, strength, and ductility, making them ideal for counterweights, defense projectiles, and high-mass components. Tungsten-nickel-copper alloys, with added copper content, are non-magnetic—critical for applications in medical imaging (such as oncology systems), electrical contact shielding, and non-magnetic sensor housings.
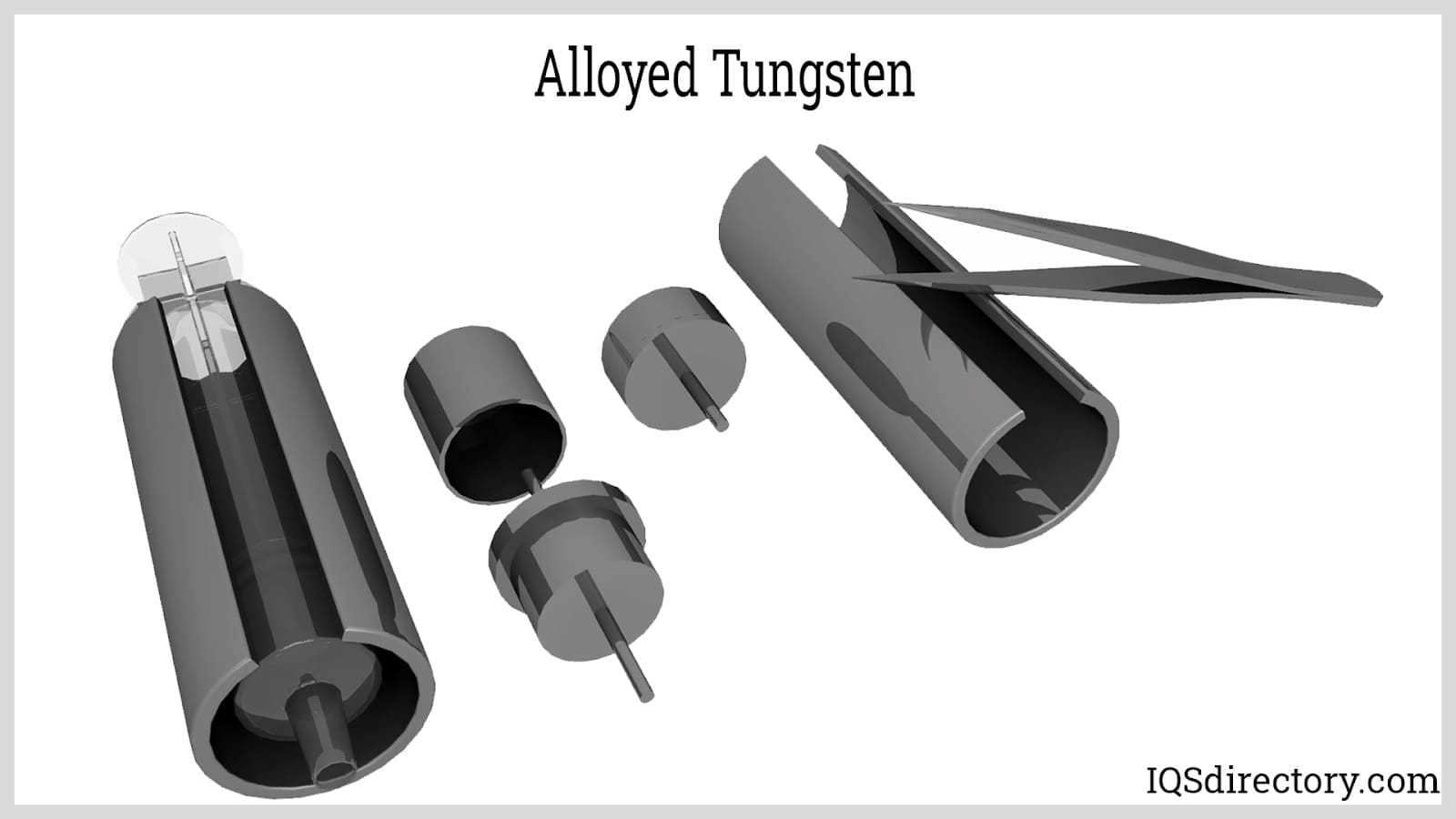

Alloys of tungsten containing copper or nickel exhibit lower tensile strengths (typically ranging from 500 to 700 MPa) and reduced ductility relative to steel; however, they provide unique characteristics such as high thermal and electrical conductivity (in tungsten-copper blends) or non-magnetic behavior (in tungsten-nickel-copper alloys). Their mass density and electrical properties make these alloys highly desirable in the manufacture of electrical contacts, EDM electrodes, thermal management systems, and heavy-metal shielding.
Tungsten-copper alloys are primarily used in high-temperature heating elements and electrical resistance heating coils, due to their outstanding stability and low thermal expansion. You’ll find these alloys in products such as water heaters, industrial furnaces, kettles, ovens, specialty resistors, and advanced stove plates. Their performance in environments with rapid temperature cycling, high electrical loads, and corrosive atmospheres makes them indispensable in both consumer appliances and advanced manufacturing facilities.

Heavy metal tungsten alloys feature exceptionally high tungsten content (up to 90% or higher), with a minor proportion of additional elements. Incorporating 2% thorium oxide into tungsten alloys, for instance, significantly enhances thermionic electron emission properties, making these high-density, heavy metal alloys essential for a variety of specialized electronics, aerospace, medical, and nuclear applications, such as radiation shielding and electrical contacts.

In its pure metallic state, tungsten displays exceptional electrical conductivity and is primarily employed in electrical, electronic, and semiconductor applications. Due to its remarkable melting point (the highest of all metals at 3,422°C), pure tungsten is indispensable for fabricating filaments in lighting, electrical contacts, heater elements, and as a crucial interconnect material in circuit boards and microelectronics.
Tungsten chemistry plays a crucial role in the production of pigment phosphors, organic dyes, catalysts, X-ray screens, lubricants, and fire-resistant coatings. Tungsten compounds and salts contribute to a diverse range of chemical and industrial processes, offering unique properties for electronic, catalytic, and material science applications.
Tungstic acid is a yellow, fine-grained powder with an ultra-small particle size and excellent chemical purity. It is highly reactive and primarily used as a sintering enhancer in the fabrication of ultra-high-temperature ceramics, advanced catalysts, and certain specialty glass coatings.
Sodium tungstate dihydrate is a high-purity, water-soluble white crystalline powder, used extensively in the synthesis of other tungsten compounds, corrosion inhibitors, catalysts, and as a starting material for electronic-grade tungsten processing. Its ability to dissolve completely in water makes it valuable for chemical and industrial manufacturing requiring high purity and low residue.
Ammonium metatungstate is a tungsten salt appearing as a water-soluble white crystalline powder and is favored in catalyst production, reactive media for electronic components, and advanced ceramics. Its complete solubility in water ensures its suitability in high-purity, precision chemical synthesis and material preparation.
Tungsten trioxide, found as either yellow or green ultra-fine powder, is highly pure and features an advanced crystal structure. It is deployed in the manufacturing of smart window coatings, gas sensors, pigment formulations, and as a precursor for producing metallic tungsten and tungsten oxide-based catalysts.
TC-1 tungsten carbide chemical is a black, fine-grained powder, commonly used in manufacturing high-density suspensions and enhancements for SPT-3, as well as in the production of strong, dense composites, abrasives, and advanced coatings designed for extreme service environments.
Tungsten, identified in 1783 through the charcoal reduction of the oxide extracted from wolframite, is an exceptionally dense and hard transition metal valued for its unique material properties. Its discovery played a pivotal role in advancing metallurgy and high-performance industrial applications. Over the centuries, tungsten has been used for a variety of purposes, including porcelain production in the ceramics industry and, more recently, as a critical element in electronics and heavy metal alloys. In many countries, tungsten is still referred to as wolfram—derived from the German "wolf rahm" ("wolf's foam"), while the name "tungsten" comes from Swedish, meaning "heavy stone." These etymologies reflect the metal's global industrial significance.
Tungsten serves as both a base element and a vital alloying agent, with tungsten carbide ranking as its most commercially significant compound. Core tungsten ores such as scheelite and wolframite supply the raw material for numerous tungsten-based alloys. Tungsten's first major technological breakthrough was as the filament in light bulbs, an enduring use due to its impressive melting point and electrical resistance.
Tungsten carbide is a robust chemical compound comprised of equal parts tungsten and carbon atoms. With its signature metallic gray appearance, tungsten carbide emerges as a fine powder that is subsequently consolidated through sintering—a process of heat-based shaping—into a dense, wear-resistant material. This allows it to be manufactured into cutting tools, industrial machinery, mining bits, abrasives, armor-penetrating projectiles, wedding bands, and high-performance jewelry. Both tungsten and tungsten carbide exhibit extremely high melting points (5,200°F / 2,870°C) and boiling points (10,830°F / 6,000°C), which are critical for applications in environments requiring high temperature resistance and thermal stability.
There are two primary types of tungsten carbide compounds: tungsten carbide (WC) and tungsten semicarbazide (W2C). Structurally, tungsten carbide is further classified into α-WC—featuring a hexagonal crystal structure—and β-WC, which forms a cubic structure stable at elevated temperatures. These unique configurations are central to tungsten carbide's industrial versatility and performance characteristics.
Tungsten's popularity in advanced manufacturing and engineering sectors has grown due to its remarkable ability to withstand extreme heat, its consistently low vapor pressure, outstanding density, and exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity. As one of the hardest elements on Earth, it provides unmatched durability for use in high-stress applications such as aerospace components, military hardware, and heavy industry. However, tungsten is inherently brittle, presenting manufacturing challenges for forming and shaping processes. To overcome this, tungsten is often alloyed with ductile metals—nickel, copper, or iron—which enhance the resulting alloy's machinability and ductility while maintaining its core strength and wear resistance. For example, tungsten-heavy alloys are used in kinetic energy penetrators, balancing superior hardness and toughness for defense applications.
While pure crystalline tungsten is more malleable and easier to process, its high cost restricts use to specialized settings, such as advanced lighting, X-ray targets, and electronic contacts. During processing, tungsten is typically heated to improve its ductility and facilitate shaping. Tungsten powder—widely produced via hydrogen reduction of tungsten oxide—is the starting material for numerous tungsten products including wire, rods, tubes, plates, and other precision components. It also serves as a critical feedstock when alloyed with powders like molybdenum, rhenium, or copper in the fabrication of electrical contacts, high-density weights, and even radiation shielding materials. Notably, when processed as tungsten carbide powder, this material forms the basis for ultra-hard cutting tools and abrasives. Although tungsten powder is highly versatile in metalworking and electronics, it must be handled with caution as it can spontaneously ignite in ambient air, posing inherent safety risks.
Tungsten carbide is engineered by chemically combining tungsten powder with carbon powder, typically via a high-temperature carburization process above 2,200°C. This synthesis results in the formation of tungsten carbide crystals, with a precise 1:1 atomic ratio of tungsten to carbon, yielding a stoichiometric compound highly valued in precision engineering. The resulting material is characterized by its extreme rigidity and outperforms most metals, including steel, in compressive and shear strength.
Compared to pure tungsten, tungsten carbide (WC) delivers enhanced mechanical performance—most notably, it is extraordinarily hard (approaching the hardness of diamond), resistant to abrasion, galling, and impact, and maintains its structural integrity across a wide temperature range. This premium wear resistance makes WC indispensable in the manufacture of hardmetal cutting tools, industrial drill bits, metal-forming dies, and mining equipment. Its superior hardness means that it cannot be effectively machined with conventional steel tools; instead, diamond or ceramic cutting tools are required.
When combined with metal binders such as cobalt or nickel, tungsten carbide forms a composite cermet structure—a ceramic-metal hybrid—that further boosts toughness, fracture resistance, and wear life. Typical applications for such sintered tungsten carbide cermets include precision machine tooling, industrial blades, ballpoint pen tips, and advanced armor plating. With a density of 15.7 g/cm³ and extreme resistance to deformation, tungsten carbide alloys are at the forefront of demanding manufacturing processes involving continuous cutting, high load, and exposure to aggressive environments where high-performance, long-lasting materials are essential.
The elastic modulus, or Young's modulus, is a critical metric in materials engineering, quantifying a metal's stiffness or rigidity. For reference, magnesium has an elastic modulus of 45 gigapascals (GPa), while tungsten achieves a remarkable 407 GPa. By bonding tungsten with carbon to produce tungsten carbide, this modulus escalates to approximately 600 GPa—placing it near diamond, the hardest natural material known, with an elastic modulus of 1,000 GPa. This quantifiable superiority makes tungsten carbide a preferred choice for ultra-hard industrial tools and machined components requiring unmatched stiffness.
The shear modulus, representing a material's response to torsion or shearing forces, is another essential design consideration. Tungsten exhibits a shear modulus of 161 GPa—twice the value of widely used steels (80 GPa). Tungsten carbide surpasses both, offering a shear modulus of 274 GPa. This provides greater resistance to deformation during machining and manufacturing operations where high torque or friction is involved, which is especially beneficial for wear parts and cutting tools facing repetitive and intensive use.
Owing to their inherent stiffness and high modulus, both tungsten and tungsten carbide are relatively brittle and best suited for compression-dominated scenarios—such as tooling, dies, and weights—rather than flexure-intensive or high-tension roles. Tungsten carbide, for instance, offers an impressive compressive strength of 2,683 MPa at room temperature and retains this strength even as operating temperatures fluctuate. By comparison, steel not only has a lower compressive strength but is also prone to more dramatic performance shifts with temperature changes, impacting long-term precision in industrial settings.
Thermal conductivity and stability are additional distinguishing features. Metals often experience variances in conductivity due to temperature-induced strain; however, tungsten demonstrates remarkable constancy, making it ideal for components such as filament wire, heater coils, vacuum tube elements, and electrodes. Its capability to retain material integrity under intense heat allows for continued operation in harsh environments where lesser metals would fail or degrade, reducing maintenance costs and improving operational uptime in critical equipment.
The signature trait of tungsten carbide is its exceptional hardness. On the Rockwell A hardness scale, tungsten carbide is rated at 94 HRA, enabling it to cut through hardened steel, resist abrasive wear, and maintain sharp edges longer than conventional tool materials. This is especially critical for users and industries searching for maximum hardness, surface durability, and minimal tool wear in their operations. A high Rockwell hardness not only underscores the toughness and longevity of tungsten carbide tools but also influences purchasing decisions for manufacturing engineers seeking to reduce tool replacement and downtime.
When evaluating whether to use tungsten versus tungsten carbide, consider the specific application requirements: for maximum wear resistance, hardness, and longevity—such as in cutting, mining, or machining—tungsten carbide is superior. For components requiring high density, strength, and thermal resilience with some flexibility, tungsten and tungsten-heavy alloys may be preferred. Understanding the superior properties of each material enables more informed product selection, increased cost efficiency, and improved performance across a range of demanding modern manufacturing, engineering, and industrial processes.
Tungsten is distinctive for its extremely high melting point (3,422°C), exceptional hardness, high density, corrosion resistance, and excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. These qualities make it the densest engineering material and crucial for demanding industrial applications.
Tungsten carbide is a compound of tungsten and carbon, offering much higher hardness (Mohs 9), outstanding wear resistance, and greater compressive strength than pure tungsten. It is ideal for cutting tools, mining bits, and applications requiring extreme durability.
Tungsten alloys are used in high-performance cutting tools, mining equipment, defense projectiles, electrodes, electronic components, heating elements, and radiation shielding. Their strength, density, and conductive properties suit demanding engineering and manufacturing scenarios.
Tungsten carbide is produced by reacting tungsten metal with carbon at temperatures between 1,400 and 2,000°C, or by alternative methods like chemical vapor deposition, yielding high-purity, fine-grain carbide for advanced industrial use.
Exposure to tungsten carbide dust can cause respiratory problems, including fibrosis and chronic lung disease. Strict dust control, protective equipment, and adherence to safety regulations are vital in industries using this material.
Tungsten carbide and cemented carbide are favored for toolmaking due to their extreme hardness, high wear resistance, and stability at elevated temperatures, ensuring long-lasting cutting edges and efficient manufacturing performance.
Tungsten, like other metals, is available in various forms and shapes to facilitate shipping and meet customer needs. These forms include bars, sheets, and foil, which are produced from the extraction of tungsten ore. Tungsten also comes in different alloys, each tailored for specific applications and processes.
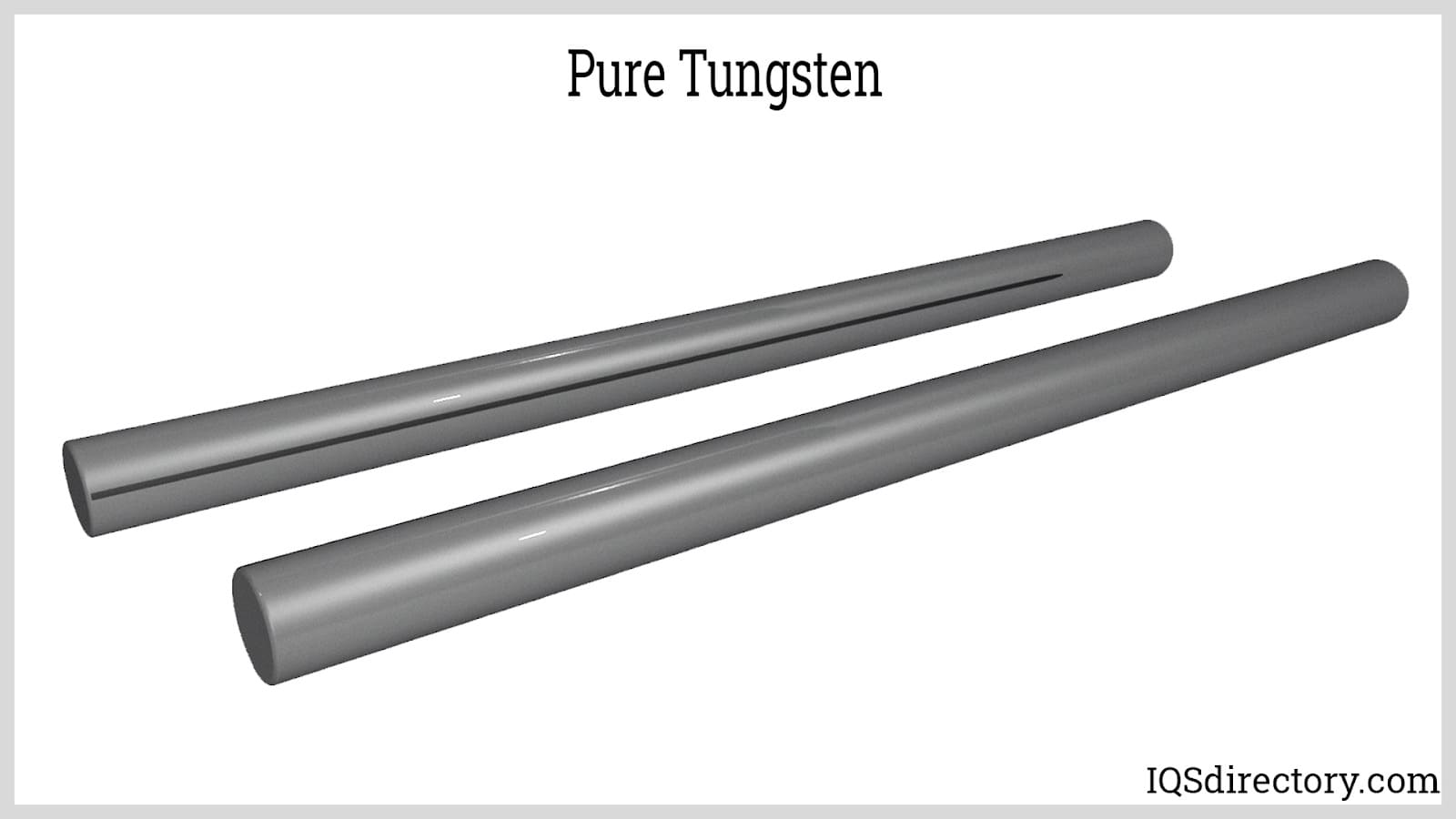
Tungsten bars are composed of 99.9% pure tungsten powder that has been shaped into various forms. These bars retain all of tungsten's properties, including its high density and resistance to high temperatures. When alloyed with other metals, tungsten bars can be produced in six different alloys and customized for specific applications.
As one of the rare metals found in the Earth's crust, tungsten has a density comparable to gold and is 1.7 times denser than lead. Working with pure tungsten bars can be challenging due to their extremely high melting point of 3,422°C (6,191.6°F). However, tungsten bars are known for their stability under various conditions, including exposure to water, air, and sulfuric acid. They do oxidize when exposed to the atmosphere.
Tungsten bars are produced through powder metallurgy. In this process, tungsten ore is first reduced to a fine powder and then chemically processed to create tungsten oxide. The tungsten is extracted from the oxide through heating, forming pure tungsten, which is then pressed into molds. After shaping, the bars are sintered to further consolidate and bind the metal powder.
Once processed, tungsten bars are sent to manufacturers for the production of various components such as cathodes, wire, pins, electrodes, stainless steel additives, and heating elements. Producers aim to supply tungsten in the appropriate form to meet the specific requirements of their customers.
Tungsten foil is a thin, smooth metal sheet with a black metallic sheen, produced by rolling tungsten sheets through cold or hot processes to achieve the desired thickness. The manufacturing of tungsten foil starts with tungsten bars that are rolled into flat sheets, which are then further processed to create the foil. The process includes vacuum annealing furnaces to strengthen the tungsten.
Stamped and drawn tungsten foil is utilized in high-temperature applications such as heat shielding, heating elements, and furnaces. It is also used in semiconductors due to its low thermal expansion coefficient and low electrical resistivity. Tungsten foil typically ranges in thickness from 0.05 mm (0.002 in) to 1 mm (0.04 in) and has a purity of 99.9%. It is available in widths from 100 mm to 400 mm (4 in to 16 in) and lengths from 400 mm to 1500 mm (16 in to 59 in).
Tungsten foil is silver gray with a metallic luster, a melting point of 3410o C (6170o F), and density of 19.35g/cm3. It is used to manufacture electric light source parts, medical shields, current collectors for aluminum ion batteries, heating elements, and heat shields. Additionally, tungsten foil is used to make tungsten evaporation boat.
Similar to tungsten sheets and foil, tungsten plates are flat pieces made from tungsten powder. The manufacturing process involves extracting tungsten from its ore, grinding it into pure tungsten powder, and then molding it into plates using heat and pressure. After shaping, the plates are annealed to improve their strength. While tungsten plates and sheets are similar, they are distinguished by their thicknesses.
Processing pure tungsten plates is challenging due to tungsten's exceptionally high melting point. Every step in the process must be carefully controlled to prevent damaging the plates. During the rolling process, manufacturers must precisely heat the rollers to match the specific rolling conditions.
Tungsten plates are available in a range of sizes and thicknesses, with most being cast. The standard thicknesses start at 6.35 mm (0.25 in), though custom thicknesses can be produced for specific applications. Tungsten plates are commonly used for shipping due to their manageable size and ease of handling.
Tungsten plates are utilized across various industries, including aerospace, construction, and electronics. They are used to manufacture turbine blades for generators and aircraft engine components because of their high melting point and exceptional strength. Additionally, tungsten plates are processed into radiation protection materials due to their density, radiation absorption properties, and resistance to corrosion.
Tungsten rods are cylindrical extrusions available in various lengths to suit different applications. They come in a range of diameters, shapes, sizes, and tungsten grades. Their widespread use is attributed to their remarkable strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. Tungsten rods can be machined, ground, and shaped to create a diverse range of parts and products.
Tungsten rods are available in various shapes such as round, square, rectangular, octagonal, hexagonal, and oval, depending on the manufacturer and intended use. However, a notable challenge with tungsten rods as raw materials is the difficulty in fabricating them into finished products due to tungsten's high melting point.
Tungsten rods have many uses and are a critical part of engineering designs and industrial manufacturing. A common use for tungsten rods is as cutting tools, which is superior to cutting tools made of aluminum or steel. In medicine, tungsten has been perfected to be used as implants and in medical procedures that require exposure to extreme temperatures due to sterilization. The factor that makes tungsten rods the first choice for manufacturing, production, and industrial applications is its exceptional wear resistance, which makes it perfect for operations that require repeated use of a tool.
Tungsten sheet is a flat form of tungsten that is thicker than foil but thinner than tungsten plate. It is produced from tungsten slabs refined during processing. Tungsten sheets are distinguished from foil and bars by their thickness, which ranges from 1.5 mm to 2.2 mm (0.06 in to 0.09 in). Tungsten material thicker than 0.25 mm (0.1 in) is categorized as tungsten plate.
The surface of tungsten sheets can vary, including finishes such as shiny, matte, satin, or rolled, depending on their thickness. The sheets are produced by isostatically pressing and sintering high-purity tungsten powder into ingots using powder metallurgy techniques. Before reaching the final finish, the ingots are deformed and heat-treated. The resulting blanks are then further processed by hot or cold rolling into sheets.
Tungsten sheets, like tungsten plates and foils, are prized for their radiation shielding properties and are used in manufacturing electronics, cables, and shipbuilding materials. They are particularly valuable for specialty applications that leverage their unique attributes. Tungsten sheets are often preferred over other high-density metals such as lead, tantalum, and uranium. Lead and uranium are avoided due to their toxicity, while tantalum, though a viable alternative, is very costly compared to tungsten.
This section will explore the uses and benefits of Tungsten metal.
Tungsten is commonly employed in making filaments for incandescent light bulbs. However, these bulbs are being gradually replaced in many places because they are not energy-efficient and convert more energy into heat than into light. When an electric current flows through the filament, it heats up and emits light. Tungsten’s ability to endure high temperatures allows the filament to remain functional and continue glowing despite the intense heat.

Tungsten is frequently used in the production of cutting tools. It can be fashioned into blades or combined with other elements such as nickel, copper, or carbon to enhance its properties. Tools made from tungsten or its alloys are exceptionally hard and can endure high temperatures, allowing them to operate for extended periods without melting or deteriorating.
Tungsten is also utilized in drilling and boring equipment. The metal’s exceptional hardness makes it ideal for drill bits and heavy-duty earth-boring machinery. Additionally, tungsten is used in dental drills. Cemented carbide, a tungsten-based material, is commonly employed in high-speed tools for mining refineries and other demanding applications. Due to its durability, tungsten is also popular in the creation of jewelry.
Calcium and magnesium tungstate are employed in fluorescent lighting applications. Tungsten is also utilized as a catalyst in the reduction of certain complex compounds. Additionally, tungsten plays a role in the production of magnetrons used in microwave ovens. Old television sets with cathode ray tubes incorporate tungsten due to its ability to endure the high temperatures generated over time.
Tungsten is employed in applications where high density is essential. Common uses include producing counterweights, ship anchors, and tail ballasts for engines in rockets, airplanes, and other vehicles.
Tungsten finds several important military uses. Its strength and hardness make it suitable for producing armor-piercing ammunition. Tungsten or its alloys are sometimes used in the manufacture of missiles, grenades, shells, and large rounds designed to penetrate heavily fortified targets such as tanks or bunkers.
Tungsten (IV) sulfide serves as a lubricant capable of enduring extremely high temperatures, making it ideal for use in high-speed tools.
Advantages of utilizing tungsten metal include:
Among all pure metals, tungsten boasts the highest melting point at 3,244°C. This exceptional property allows it to be utilized in environments with extremely high temperatures where other metals would fail.
Tungsten has a high density of 19 g/cm³, attributed to its microcrystalline structure. This characteristic makes it valuable in applications that need substantial mass within compact dimensions.
Among all pure metals, tungsten has the lowest coefficient of thermal expansion. Unlike steel, tungsten remains highly stable at elevated temperatures and does not change in form or size.
Due to its excellent conductivity and general inertness, tungsten is commonly employed in electrical devices that operate under high levels of radiation. It also serves as an ideal material for electrodes in the electrolysis of various substances.
Tungsten's exceptional resistance to corrosion allows it to be used in diverse applications where corrosion is a concern. It performs well in outdoor environments exposed to water and acids. Typical uses of tungsten include fishing lures, ship construction, and certain types of jewelry.
Despite its strength, tungsten can be drawn into extremely thin wires without breaking. For example, the filaments in light bulbs are made from tungsten, allowing them to endure high temperatures while remaining functional.
In its pure form, tungsten is quite brittle and can easily fracture. It cannot withstand stretching, compression, or twisting without losing its shape. This fragility is due to its rigid structure, which limits its ability to be manipulated without failure.
Inhaling tungsten can irritate the mucous membranes and the lungs. It is considered highly toxic, and uncontrolled exposure could pose significant risks to both human health and the environment.
Tungsten is a valuable metal with a high cost due to its unique properties. Its rarity and the growing demand contribute to its continued high price.
Tungsten is a dense metal, which makes it challenging to work with. For example, tungsten jewelry can be quite heavy, often causing discomfort for the wearer. Similarly, in the production of earth-boring equipment, the metal's weight results in high transportation costs due to the difficulty of moving such heavy machinery.
Although tungsten is expensive, it does not retain its value upon resale. Unlike gold, which can be fashioned into various jewelry pieces and resold at a value close to its original purchase price, tungsten does not hold the same resale value.
Compared to other metals, tungsten has the following specific applications and uses:
Tungsten and its alloys are used to manufacture durable tools for cutting and crushing. Unlike steel, which can wear out and break when used on tougher materials, tungsten offers superior longevity and strength, making it the ideal choice for heavy-duty applications.
While tungsten is a good conductor of electricity, its high cost, weight, and brittleness make it less favorable compared to other metals. Copper, aluminum, and steel are generally preferred for electrical conduction due to their more advantageous properties.
Although tungsten is a hard and tough metal, it is not ideal for use in the construction industry. Its brittleness makes it unsuitable for large structural applications. Instead, lightweight and strong materials such as reinforced steel are more appropriate for building projects.
ATI offers a wide range of metals, including various types of tungsten, known for their high performance and superior quality. In addition to standard metals, ATI manufactures specialty metals to fulfill specific customer requirements and industrial demands. With over 25 years of experience, the company processes tungsten in the Dallas, Texas area.
Betek specializes in manufacturing tungsten carbide tools, systems, and wear protection. The company produces high-quality tools tailored to specific industrial applications, ensuring a longer lifespan and reducing the need for frequent tool replacements. While focusing on current needs, Betek is also committed to future innovations to address evolving demands and requirements.
Buffalo Tungsten produces tungsten and tungsten carbide powders of the highest quality. They offer a range of powders including fine, coarse, crystalline, ultra-high purity, high density, low grade, and granulated tungsten. Their powders boast a purity of 99% with particle sizes ranging from 10 microns (µ) to 50 µ. The company also provides ultra-high purity 5N tungsten metal powder, with a purity level of 99.999%. Buffalo Tungsten enhances the density, particle size, and flow characteristics of their powders through additional processing.
Starck Solutions manufactures high-quality tungsten chemicals, metal, and tungsten carbide. Their product range includes various tungsten forms, from tungstate to tungsten carbide, available in both ultrafine and coarse grain sizes. The company is committed to adhering to the highest standards in tungsten production and works closely with customers to develop innovative, customized solutions that meet and exceed their requirements.
Federal Carbide produces a variety of tungsten products, including tungsten heavy alloy, tungsten carbide, tungsten carbide seal rings, and tungsten heavy metal alloy radiation shields. Their tungsten heavy alloy items are available as machinable blanks or custom parts tailored to specific customer requirements. Their product range spans the full spectrum of the tungsten market, including components for engines, helicopter rotors, firearms, and golf club weights. Federal Carbide emphasizes providing the hardest man-made metal, tungsten carbide, at the lowest cost with fast and efficient delivery. The company's commitment to hard work and quick responses to customer needs underpins its goals.
In summary, tungsten is a naturally occurring metal found on earth. It is a very unique metal as it has a very substantial chemical structure. It has a very high melting and boiling point and is a very dense metal with an over the top weight and density. Despite all these excellent characteristics, tungsten is a very brittle metal and cannot be used as would other metals like copper and iron.

Aluminized steels are steels that have been hot-dip coated with pure aluminum or aluminum-silicon alloys. This hot-dip coating process is termed hot-dip aluminizing (HAD)...

Aluminum 1100 is the softest of the aluminum alloys, which makes it easy to shape and form into a wide range of products for industrial and home use. It can be cold and hot worked but is frequently shaped by...

The term "aluminum coil" describes aluminum that has been flattened into sheets where their width is significantly higher than their thickness and then "coiled" into a roll. Stacks of individual aluminum sheets are difficult to...
Aluminum piping and tubing is silvery-white, soft, and ductile. The metal belongs to the boron group. Aluminum is the third most abundant element present on earth. Aluminum has low density. When exposed...
Beryllium Copper is a versatile copper alloy that is valued for its high strength and hardness, combined with good electrical and thermal conductivity. It is a non-ferrous, non-magnetic, and non-sparking metal alloy...

A variety of copper-zinc alloys are referred to together as brass. Different ratios of brass and zinc can be used to create alloys, which produce materials with various mechanical, corrosion, and thermal properties...
Copper is a ductile, malleable, and reddish-gold metal with the capacity to effectively conduct heat and electricity. Brass and bronze, two commonly used alloys, are created when copper is combined with...
The copper sheet is a highly malleable and workable metal with outstanding electrical and thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. Copper (Cu) is a reddish, very ductile metal that belongs to Group 11 of the periodic table...

Metals are a group of substances that are malleable, ductile, and have high heat and electrical conductivity. They can be grouped into five categories with nickel falling in the category known as transition metals...

Stainless steel grade 304 is an austenite stainless steel that is the most widely used and versatile of the various grades of stainless steel. It is a part of the T300 series stainless steels with...

Stainless steel is a type of steel alloy containing a minimum of 10.5% chromium. Chromium imparts corrosion resistance to the metal. Corrosion resistance is achieved by creating a thin film of metal...
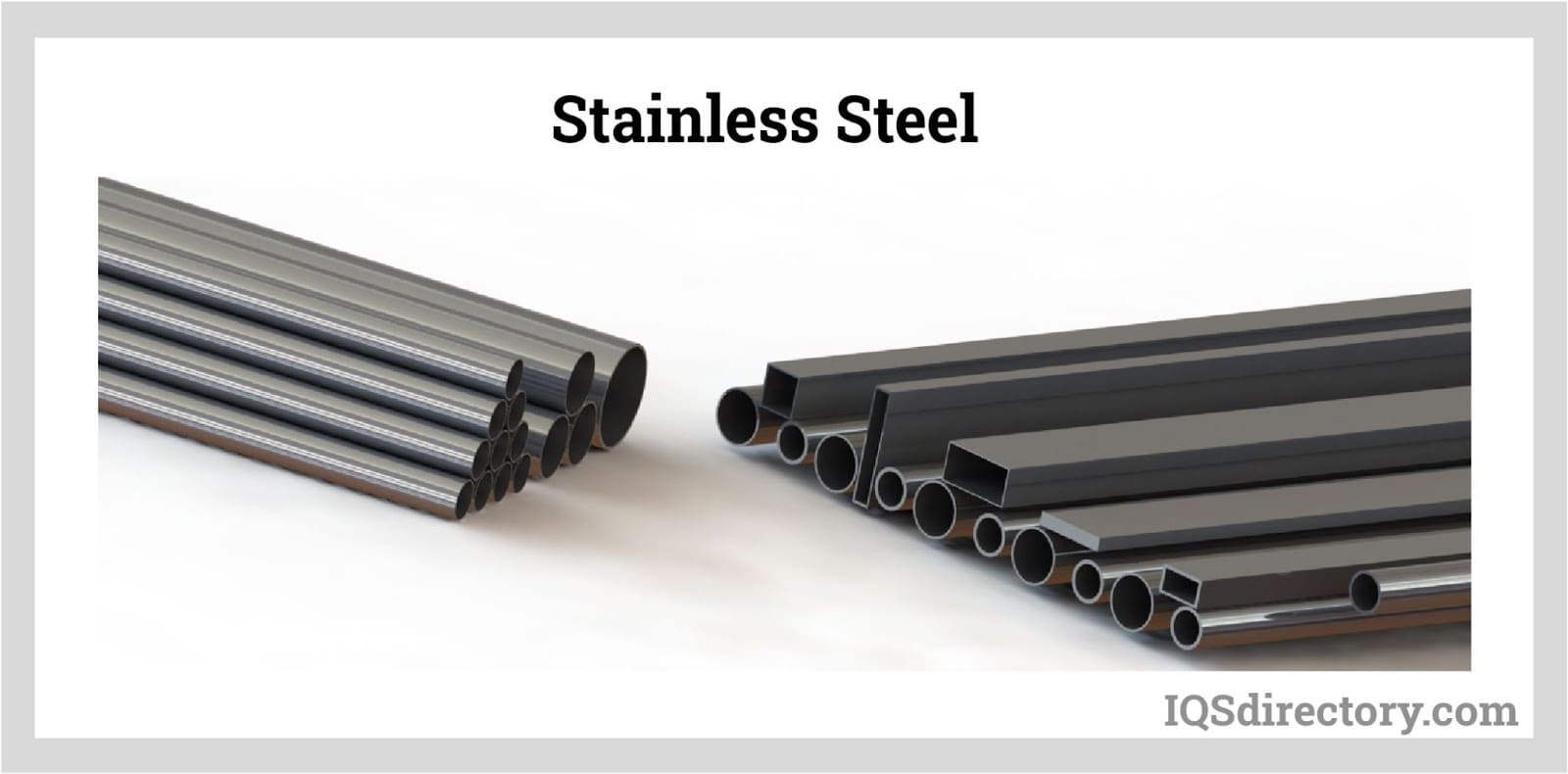

Stainless steel grades each consist of carbon, iron, 10.5%-30% chromium, nickel, molybdenum, and other alloying elements. It is a popular metal used in various products, tools, equipment, and structures that serve in many industrial, commercial, and domestic applications...
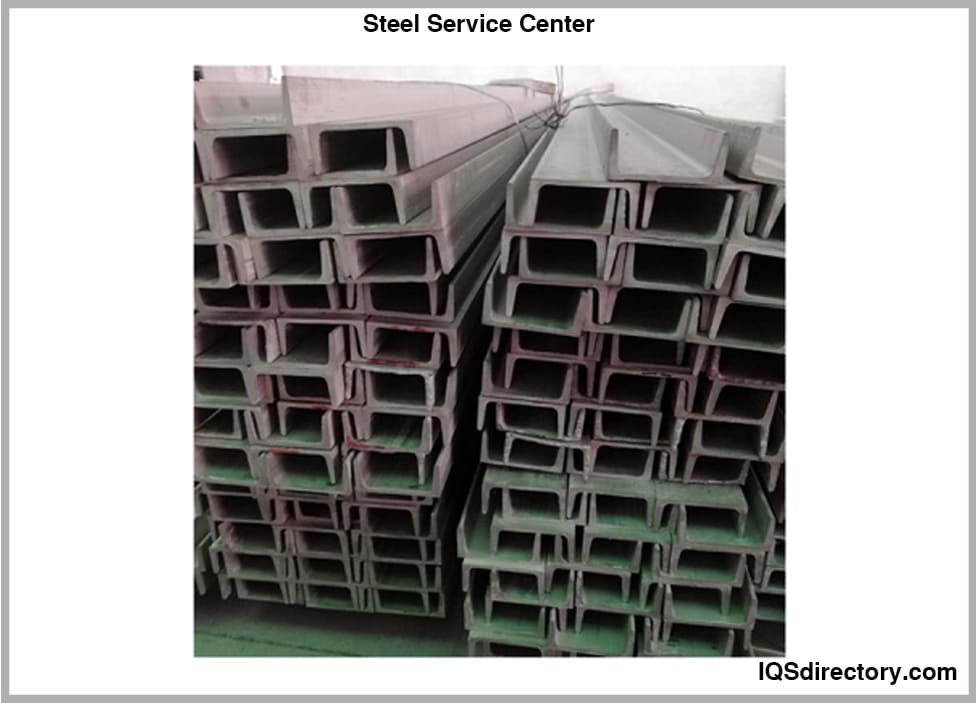

Steel service centers are companies that specialize in procuring steel directly from mills and manufacturers and supplying them to the customers. They are fundamental to the steel supply chain...

Stainless steel can be fabricated using any of the traditional forming and shaping methods. Austenitic stainless steel can be rolled, spun, deep drawn, cold forged, hot forged, or stippled using force and stress...

Stainless steel tubing is a multifaceted product that is commonly utilized in structural applications. Stainless steel tubing diameters and variations vary greatly based on the application requirements and are...

Titanium metal, with the symbol Ti, is the ninth most abundant element in the earth‘s crust. It does not occur in large deposits, yet small amounts of titanium are found in almost every rock...
Aluminum is the most abundant metal on the Earth’s crust, but it rarely exists as an elemental form. Aluminum and its alloys are valued because of their low density and high strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and corrosion resistance...