Nylon Tubing

Nylon tubing, also known as polyamide tubing, is a type of tubing made from polyamide resin, which has a strong resistance to abrasion. It is used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications...
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
This section examines the nature of silicone tubing, delving into its characteristics and the technological process employed for its production.
Silicone tubing, a resilient elastomer, is celebrated for its robustness, adaptability, and resistance. Remarkably durable, it retains its flexibility even when subjected to repeated bending and twisting. Due to its safe and non-toxic attributes, it's highly suitable for medical-grade uses, making it a top pick in healthcare environments.

Renowned for its ability to function under a vast temperature range and accommodate sudden climate fluctuations, silicone tubing is incredibly versatile. It is indispensable in various sectors where the transfer of liquids and gases is crucial. Due to its exceptional properties, it often emerges as the preferred tubing material across numerous applications.

Offering excellent UV and heat resistance, silicone is ideal for industries such as electronics and aerospace. Its facile cleaning and sterilization make it perfect for high-hygiene environments like medical, pharmaceutical, and food production sectors. Available in an array of sizes and grades, including high-temperature variants, silicone tubing meets diverse industry needs.
High-temperature silicone tubing withstands extreme thermal variations, making it superior to plastic or rubber options. FDA-approved food-grade tubing ensures stability, heat resistance, and non-stick characteristics, ideal for the food and beverage sectors. Medical-grade silicone tubing adheres to rigorous purity and non-toxicity standards necessary for medical fields.
Silicone tubing is crafted using the well-established rubber extrusion technique.
Favored for its efficiency and capability to create vast volumes promptly, the extrusion method is prevalent among rubber producers. It starts with heating and curing a silicone compound, which is then pre-shaped into slabs or strips.
This prepared silicone is introduced into a screw extruder. The extruder exerts pressure to push the compound through a steel die, held firmly by the extruder head. The die then molds the silicone into tubing as it passes through, followed by continuous curing in a heated curing oven.
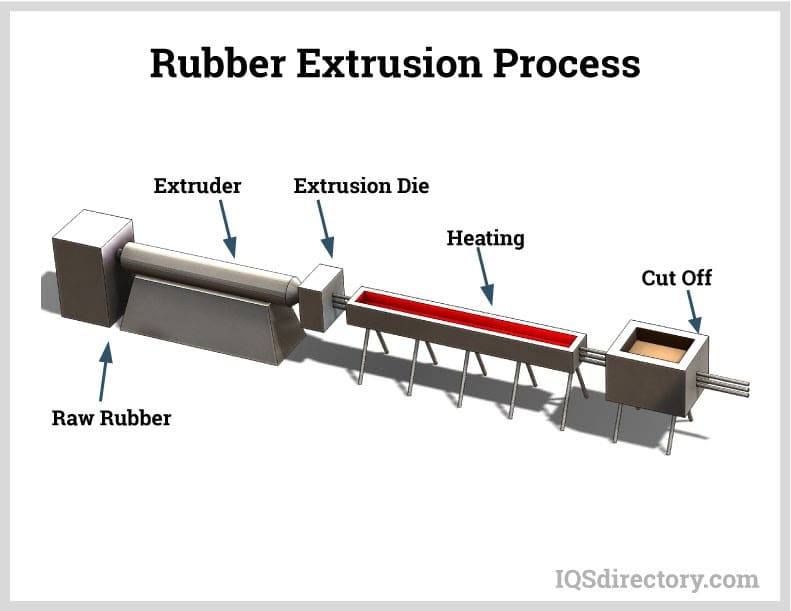
The curing process employs various oven types, such as salt bath cures, steam vulcanization, and infrared cures. Sometimes, the silicone is further vulcanized by immersion in salt water. The primary challenge lies in selecting raw materials that perform optimally under specific conditions, ensuring the final product conforms to specifications.
The key distinctions between extrusion and molding include product shape, application, and production orientation. Extrusion is ideal for creating extended, circular shapes, whereas molding handles irregular forms but in limited lengths.

For tubing longer than 50 feet, extrusion requires re-sulfurization of the vulcanization tunnel. With extrusion, lengthy silicone tubes are produced continuously. Conversely, the solid-liquid injection technique involves liquid glue, reminiscent of plastic injection molding, starting with high-temperature sulfurization.
Post-injection, the product is de-molded. While this yields complex structures, it results in lower tubing hardness compared to extruded alternatives. Soft and smooth, injection silicone tubing suits the power industry for its unique attributes.
With exceptional resistance and insulating features, silicone is highly valued in the power sector. The solid-liquid injection process crafts set and irregular shapes, whereas extrusion generates extended tubes, both capable of meeting high-voltage demands in power systems.
In the healthcare industry, silicone tubing extrusion frequently pairs with the injection process. Extrusion is mainly for standard pipings like drains, while injection suits non-regular shapes. Despite higher costs associated with injection, including raw materials and equipment, extrusion remains a budget-friendly choice for producing standard pipes.
The dimensions of silicone tubing are instrumental in determining its use. Small tubing, with thin walls, is utilized in electrical sleeving; medium tubing, often employed for fluid and powder transport, is key in industries requiring precision and hygiene. Large tubing is utilized in applications demanding durability, like air ducts.
In the pharmaceutical and food industries, medium tubing is prized for hygiene. Platinum-cured silicone tubing, devoid of ketones and peroxides, finds widespread application in medical, food, dairy, and vending industries, ensuring taste preservation and product integrity. Moreover, cured silicone tubing serves as a versatile, food-compatible solution.
The different types of silicone tubing are:
Silicone peroxide-cured tubing, also known as peroxide cured silicone hose, is available in translucent formats and comes in a wide range of diameters. This type of silicone tubing is typically used in industrial applications where ultra-high purity, medical-grade standards, and repeated sterilization are not critical requirements. It is well-suited for general pump transfer, insulation, and protective sleeving applications where the primary requirements are flexibility, UV resistance, and durability rather than stringent cleanliness or precise dosing.

Silicone peroxide tubing is often used in automotive, appliance, and general industrial applications due to its ability to withstand temperatures up to 392°F (200°C) and excellent dielectric properties. Additionally, its cost-effectiveness compared to platinum-cured silicone tubing makes it a practical choice for applications prioritizing affordability and performance over purity. However, it's worth noting that peroxide-cured tubing may exhibit slight yellowing over time, particularly in high UV or ozone environments. For applications where this is a concern, platinum-cured alternatives are preferred.
Platinum-cured silicone tubing, sometimes referred to as high-purity silicone tubing or medical-grade grade silicone hose, offers several advantages over peroxide-cured options, making it a top choice for food, beverage, pharmaceutical, and biomedical industries. It boasts higher tear strength, superior flexibility, and can operate within a broad temperature range of -40°F (-40°C) to 392°F (200°C), ensuring reliability even under fluctuating temperature extremes. Platinum cured silicone offers ultra-low extractables and excellent chemical resistance thanks to its modern manufacturing process, which eliminates peroxide by-products. This ensures the tubing remains clear, non-yellowing, and tasteless.
Platinum-cured silicone tubing is available in several formats, including translucent, black, or white. Its purity, biocompatibility, and low leachables make it ideal for peristaltic pump applications and critical fluid transfer where sterility is required. This tubing is widely used in non-invasive medical devices, bioprocessing equipment, and laboratory settings, as well as food and beverage processing where taste, odor, and product safety are paramount. Further, its compliance with USP Class VI, FDA, and NSF-51 standards adds an additional layer of quality assurance for regulated industries.
Silicone dairy tubing, specifically engineered for the dairy industry and milk processing equipment, stands out due to its outstanding resistance to mechanical wear-and-tear and repeated cleaning cycles. Most silicone dairy tubes are manufactured using platinum-cured silicone, which provides greater purity and avoids by-products associated with peroxide curing. These features help maintain product integrity and prevent contamination of milk and other dairy fluids during automated milking, transfer, and pumping operations.

Dairy-grade silicone tubing maintains its high flexibility and elasticity over time, even after prolonged use, cleaning, and sterilization. Its extra-smooth inner bore enhances fluid flow rate and promotes high levels of hygiene by minimizing material buildup or bacterial residue. As a result, silicone dairy tubing is widely adopted in automated milking systems, cream separators, cheese making, and other sanitary processing equipment within the dairy industry.
Silicone fuel hoses, also known as silicone fuel lines, are highly popular in the radio-controlled (RC) car, airplane, and boat hobby industries. These specialty silicone tubes are extremely resistant to aggressive fuels such as methanol and nitro blends, which helps preserve fuel purity and maximize performance. Their outstanding flexibility and resilience allow secure routing through tight, confined compartments commonly found in RC models.

Silicone fuel tubing is available in a wide variety of vibrant colors, making it easy for users to color-code or customize the appearance of their RC vehicles and equipment. However, it is crucial to remember that these hoses are formulated specifically for RC fuels and are not compatible with gasoline (petrol) or diesel engines found in full-scale vehicles or industrial machinery.
High-temperature silicone hoses and high-temperature silicone tubing are engineered to withstand prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures, harsh thermal cycling, and aggressive environmental conditions. These hoses are often marked with a temperature rating number, such as “550”—indicating the maximum continuous service temperature in degrees Fahrenheit (up to 550°F or 288°C for specialized grades). Selecting the proper high-temperature silicone tubing is critical for thermal management systems, exhaust gas transfer, and hot air ducts commonly found in the automotive, aerospace, and processing industries.
It is important for users to distinguish between a hose’s thermal resistance and its flammability. While a hose may withstand high temperatures, it is not inherently flameproof. The term “burn point” specifies the ignition threshold when directly exposed to an open flame. For applications involving direct fire exposure or requiring compliance with flammability standards, confirm the hose is certified as flame retardant or self-extinguishing for maximum safety and compliance with industry standards.

Depending on your unique requirements, high-temperature silicone hoses may offer exceptional flexibility for routing around tight radii in restricted spaces. While silicone hoses generally exhibit impressive flexibility, repeated extreme bending may cause flex fatigue, eventually resulting in tears after prolonged cycling. Additionally, high-temperature silicone tubing demonstrates resilience against numerous harsh chemicals and thermal degradation, tolerating brief exposure to certain oils, solvents, and industrial gases. Always verify the manufacturer’s chemical compatibility chart before specifying for critical process applications.
Food-grade silicone tubing is one of the most preferred solutions for food and beverage transfer, processing, and dispensing. This form of silicone tubing is formulated from ultra-pure silicone elastomer compounds and engineered to prevent the migration of harmful chemicals, plasticizers, and additives into consumable products. As it contains no BPA, phthalates, or latex, food-grade silicone is an ideal choice for reducing exposure to potential health hazards. Additionally, its non-porous and odorless nature ensures there is no transfer of flavors or unwanted odors, preserving food integrity during handling and transport.
Food-safe silicone tubing is renowned for its superior stability across a broad temperature range. It is suitable for use in everything from refrigerated lines to high-temperature food processing plants. The material meets stringent food contact regulations, including FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 and NSF-51, supporting both commercial and industrial food system requirements.

Food-grade silicone offers clear advantages over more traditional plastic and rubber tubing:
Food-grade silicone tubing is commonly used in beverage dispensers, water filtration systems, commercial kitchen appliances, dairy processing, and pharmaceutical production settings where reliability and hygiene are essential.
Medical-grade silicone tubing, also known as platinum-cured medical tubing, is specifically formulated to meet stringent requirements for hygiene, biocompatibility, and safety. These tubes must comply with United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP) Class VI, ISO 10993, and FDA standards, ensuring suitability for medical devices, fluid delivery systems, and critical pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Medical silicone tubing provides excellent flexibility, kink resistance, and is manufactured in cleanroom environments to provide consistent purity. Top use cases include intravenous (IV) lines, peristaltic pump transfer, laboratory sampling, catheters, wound drainage systems, as well as biotechnology and cell culture operations.
Key advantages of medical-grade silicone tubing include:
The unique chemical inertness and flexibility of medical-grade silicone tubing make it an indispensable choice for use in hospitals, research laboratories, and pharmaceutical production. Platinum curing methods ensure it is odorless, tasteless, free of extractables, and suitable for sensitive biological or pharmaceutical uses.

In silicone tubing systems, shear refers to the force that acts parallel to a surface and results from the movement of fluids at differing speeds. High shear forces within connectors or junctions can cause turbulence, damaging delicate cells, increasing extractables, and ultimately compromising critical products in bioprocessing, biopharmaceutical manufacturing, and downstream applications.
Excessive shear stress on cells may lead to the release of proteases, DNA, or host cell proteins—adversely impacting culture viability, reducing product quality, and interfering with process measurement equipment. To control shear, process engineers often utilize purpose-designed overmolded connectors and junctions with exceptionally smooth internal transitions, which support laminar flow, minimize dead volume, and prevent areas of product entrapment.
Overmolding is a molding process used to fabricate leak-resistant, seamless silicone connections in configurations including Y’s, T’s, crosses, and reducers. Overmolded junctions maximize total product recovery and prevent the formation of turbulent eddies inside silicone tubing assemblies, supporting cell-saving and yield-optimizing operations.
Barbed fittings, while commonly used for ease of installation, may create turbulence, backflow, and high shear regions inside the tubing. This increases the risk of product loss, contamination, and reduced efficiency—particularly problematic for sensitive biomedical and pharmaceutical fluids. By contrast, overmolded connectors enhance sanitary design, support strict process validation, and are widely adopted in regulated single-use manufacturing workflows.
This specialized range of colored silicone tubing features robust, thick-walled construction derived from premium silicone rubber, making it not only visually distinctive but also suitable for high vacuum and negative pressure applications. Available in a wide palette of colors, colored silicone tubing is routinely used for process color coding, media separation, or safety indication in laboratories, food processing, and industrial automation.

Additionally, colored silicone tubing serves as protective sleeving for electrical wires and cables in the electronics sector, offering both insulation and burn resistance. Its customizable appearance and technical versatility have made colored silicone tubing a popular choice for OEM equipment manufacturers, laboratories, and process engineers seeking visibility and differentiation in complex installations.
General-purpose silicone tubing, also referred to as multipurpose silicone tube or flexible silicone hose, is ideal for applications where maximum compound purity and pressure resistance are not required, but thermal resistance, electrical insulation, and material flexibility are still necessary. This type of tubing is valued for its easy handling, excellent resilience, and affordability.

Common uses for general-purpose silicone tubing include household appliances, laboratory equipment, aquarium airline systems, craft projects, and do-it-yourself (DIY) repairs. Its tolerance for a wide range of operating temperatures and general chemical resistance make it suitable for many non-critical fluid transfer, venting, and insulating needs found in homes, workshops, and hobby settings. For applications requiring compliance with regulatory standards (such as NSF, FDA, or USP VI), always confirm product specifications with the supplier or manufacturer.
This section explores the diverse applications and key benefits of silicone tubing across major industries. By highlighting the distinct properties that set silicone tubing apart, you'll gain insight into why it is the material of choice for critical applications requiring durability, flexibility, and biocompatibility.
Silicone tubing serves a wide range of purposes across multiple sectors, thanks to its unique blend of flexibility, chemical resistance, and safety. Below, we detail its most common and important uses:
Medical-grade silicone tubing is essential in the healthcare and life sciences industries due to its outstanding durability, non-reactivity, and sterilization compatibility. Its biocompatibility, a core requirement for medical tubing, helps prevent toxicity, irritation, or allergic responses, making it suitable for direct contact with bodily fluids and tissues. As a result, silicone tubing is relied upon in life-saving medical implants, drains, catheters, oxygen supply lines, IV infusion sets, peristaltic pump systems, and feeding tubes where safe, sterile fluid transfer is crucial.

The physical properties of medical silicone tubing—including high purity, kink resistance, and transparency—make monitoring and precise delivery in medical devices easier. Modern manufacturing utilizes continuous extrusion and platinum-cured processes for superior consistency and cleanliness, allowing for sizes ranging from delicate microbore capillary tubes to robust tubing suited for bulk fluid transfer. This versatility meets the strict regulatory requirements of the healthcare industry.
In laboratory and analytical settings, silicone tubing's flexibility, non-contaminating properties, and resistance to a broad range of chemicals make it indispensable for sample conveyance in instrumentation, chromatography, fluid handling, and peristaltic pump applications. Its ability to maintain sterile flow paths and withstand repeated sterilization cycles underpins its value for high-precision instruments such as spectrometers and chemical analyzers.
Silicone tubing is a preferred material for electrical insulation due to its high dielectric strength, thermal stability, and flame resistance. This makes it indispensable in protecting electrical wiring and components within the electronics and automotive sectors. In automotive engineering, silicone hoses are used in engine coolant systems, turbocharges, and vacuum lines, where they outperform standard rubber hoses under high heat and vibration. Silicone's resistance to cracking, ozone, and chemical exposure ensures enhanced reliability for automotive and industrial machinery.

Due to its non-toxic, taste-free, and chemically inert characteristics, food-grade silicone tubing is commonly used in water filtration and purification systems. It ensures that potable water systems remain uncontaminated, supporting applications in residential water purifiers, laboratory filtration units, dialysis machines, and municipal water processing where pure and safe water transfer is essential.
Silicone tubing meets stringent health and safety regulations for contact with food, beverages, and dairy products. Its resistance to extreme temperatures and food-grade certification make it ideal for beverage dispensing lines, dairy process piping, commercial kitchen equipment, and brewing operations. As an FDA-approved and BPA-free solution, it prevents flavor carryover and withstands repeated cleaning cycles—critical requirements in food and beverage industries.
In the aerospace and defense sectors, high-performance silicone tubing is widely used due to its resistance to high pressure, extreme temperatures, and aggressive environmental stressors. It serves in aircraft environmental control systems, fluid conveyance, oxygen lines, and vacuum seals for both spacecraft and military vehicles. Silicone's ability to retain properties in fluctuating altitudes and atmospheres also enhances safety and performance for aerospace contractors.

Additional common applications for silicone tubing include:
Choosing silicone tubing offers a comprehensive range of performance and safety benefits, making it the top choice for demanding, critical, and high-purity applications:
Silicone tubing maintains excellent flexibility across an exceptionally broad temperature range, retaining resilience and pliability from deep-freeze conditions to high-heat environments. This property proves vital in dynamic systems or where repeated bending occurs—unlike many standard rubber hoses, silicone tubing will not harden or crack even after years in service.

With a standard operational temperature window from -130°F to 600°F (-90°C to 315.5°C), silicone tubing excels in applications exposed to both subzero and extremely high heat while resisting thermal degradation, UV radiation, and ozone-induced aging. This durability ensures reliable long-term use in outdoor equipment, harsh industrial settings, and sensitive aerospace systems.
Silicone tubing delivers superior tensile strength and tear resistance compared to other flexible tubing materials like PVC or latex, minimizing the risks of leaks or ruptures. This structural integrity drives its adoption in plumbing, commercial kitchens, food processing, and beverage dispensing, where hose reliability is paramount. Its crack and fatigue resistance allow for prolonged use in demanding facilities such as breweries, chemical plants, aquariums, and water treatment plants.
Suppliers offer silicone tubing in a vast selection of colors and transparent grades, aiding process organization, safety coding, and fluid visibility for monitoring applications. Custom color-matching and labeling options cater to specific industry needs.
Both food-grade and medical-grade silicone tubing feature a seamless, non-stick surface that resists bacterial buildup and particle accumulation. This smoothness is essential to maintaining sterility and hygiene in sectors including biomedical labs, food processing, and analytical research.
Silicone tubing withstands repeated cleaning, sterilization, and exposure to a wide array of chemicals, including mild acids, alkalies, and cleaning agents. It does not support mold, fungus, or bacterial growth, further reinforcing its place in pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and sanitary liquid handling applications.
Available in an extensive range of hardness values (from soft 20 Shore A to firm 90 Shore A), silicone tubing allows engineers to choose the optimal durometer for pressure, vacuum, or flexibility requirements. This customization enhances performance in both sensitive and rugged applications.
Silicone tubing provides excellent pliability, tightly bending without kinking or collapsing. Its flexible nature enables seamless installation in confined or complex layouts—ideal for laboratory, medical, and microfluidic setups where precision matters.
Because silicone tubing is repeatedly sterilizable via autoclaving and resists UV, ozone, and various chemicals, it excels in continual-use environments that demand high cleanliness and minimal maintenance. Its antimicrobial properties help prevent contamination in critical applications.
Silicone tubing can be extruded, molded, or injection-formed to precise dimensions required by OEMs, medical device manufacturers, and industrial system designers. Whether for small-bore analytical lines or large-diameter process hoses, customization is consistently achievable.
Silicone tubing is easy to clean and sterilize, resisting degradation when repeatedly exposed to disinfectants, detergents, or high temperatures. Unlike other materials, it does not become brittle or lose flexibility over time, resulting in lower replacement costs and greater system uptime.
Its chemically inert nature ensures that silicone tubing does not impart any taste, odor, or toxic substances to conveyed media. This makes it safe and highly recommended for systems involving food, potable water, beverages, as well as sensitive pharmaceuticals and laboratory reagents.
It is important to note that while silicone tubing boasts many advantages, it is not suitable for concentrated fuels or oils, as prolonged exposure can degrade the tubing and compromise system safety.
With its unmatched safety, chemical compatibility, flexibility, thermal stability, and range of customizable options, silicone tubing remains a top choice for engineers, manufacturers, and facilities managers seeking reliable, high-performance solutions for fluid transfer, insulation, and protection across modern industries.
Silicone tubing types include peroxide-cured, platinum-cured, dairy, fuel, high-temperature, food-grade, medical-grade, colored, and general-purpose. These serve applications from medical and food processing to automotive, laboratory, and electronics, each optimized for specific purity, durability, or flexibility needs.
Platinum-cured silicone tubing offers ultra-low extractables, superior flexibility, clarity, and complies with strict FDA, NSF-51, and USP Class VI standards, making it ideal for sterile environments where biocompatibility, flavor preservation, and chemical purity are essential.
Medical-grade silicone tubing is biocompatible, flexible, inert, and sterilizable. Its transparency supports flow monitoring, while its resistance to kinking and chemical interaction ensures safe, reliable use in devices like IV lines, catheters, and peristaltic pumps.
High-temperature silicone tubing withstands extreme heat, thermal cycling, and chemical exposure. With ratings up to 550°F (288°C) for specialized grades, it is used in automotive, aerospace, and industrial systems for thermal management and exhaust applications.
Yes. Food-grade silicone tubing is BPA, phthalate, and latex-free, offers no taste or odor transfer, withstands high and low temperatures, and meets FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 and NSF-51 standards, ensuring maximum food safety and compliance.
In dairy and food sectors, platinum-cured and food-grade silicone tubing ensures hygienic milk transfer, beverage dispensing, and food processing. Its purity, flexibility, and repeated sterilization capability support sanitary operations and product integrity.
This chapter will cover methods for cleaning, sterilizing, and connecting silicone tubing.
Regular cleaning of silicone tubing is essential in food production environments, such as homebrewing setups or soft drink dispensing systems. Silicone tubing is easy to clean and can be thoroughly sanitized by boiling, which removes any residue inside the hoses. This regular cleaning is necessary to prevent buildup, blockages, and unpleasant odors.
For other applications, like those in the automotive industry, frequent interior cleaning of silicone tubing may not be required. A simple method for cleaning silicone tubing is to use hot soapy water, either wiping down the tubing or flushing it through.
Silicone’s high heat resistance means that the water temperature is not a concern during cleaning. However, certain cleaning agents can negatively react with silicone tubing, leading to damage and discoloration. It is important to avoid using WD40 or petroleum-based cleaners on silicone tubing.
Silicone tubing is widely used in medical instruments and equipment due to its ease of sterilization. Several sterilization techniques commonly employed in medical laboratories are available. The most prevalent method is gamma irradiation, although this process may alter the silicone's properties, increasing its tendency to kink. Another option is electron beam irradiation, which can produce similar physical effects.
Another effective sterilization method is ethylene oxide. This technique works well because silicone tubing absorbs ethylene oxide, but it is crucial to ensure that the ethylene is fully removed before the tubing is used in medical applications.
The methods of joining silicone tubing are:
Isopropyl alcohol (IPA) is commonly used to lubricate silicone tubing, facilitating its movement over barbed fittings. IPA is hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture. When used with silicone tubing, IPA should be applied in its pure form. It is readily available and generally affordable.

IPA is effective because it evaporates cleanly without leaving residue on medical devices. However, its main drawback is the slower drying time, which can make the process more time-consuming and increase production costs. To accelerate drying, techniques such as applying low temperatures to the silicone tubing can be used.
Another approach for joining silicone tubing involves using silicone oil-based lubricants. This method is often favored by engineers due to its intuitive nature, as using silicone fluid with silicone tubing ensures material compatibility. However, there are significant drawbacks to using silicone oil.

One major drawback of using silicone oil-based lubricants is their tendency to create a mess. The oil does not evaporate and is designed to remain on surfaces indefinitely. Since silicone easily migrates to other surfaces, controlling the application to specific parts of a device can be challenging. This often leads to a time-consuming process, as more cleanup is required after the coating and joining are complete.
Additionally, the risk of contamination increases during the coating process because the oil can attract and trap dust and dirt from the surrounding environment. Even in a clean room, the likelihood of contamination remains high. Moreover, medical-grade silicone, which is necessary for such applications, is more expensive compared to lower-grade silicones used in other industries.
The silicone swelling process is similar to how a sponge absorbs water. When silicone tubing absorbs a solvent, it expands like a sponge and then contracts as the solvent evaporates, eventually returning to its original size. This process creates a tight seal around metal parts or barbed fittings, making the attachment of silicone tubes or parts to barbed fittings both quick and straightforward.
Typically, silicone only needs to expand by 1 to 2% for effective fitting, and the entire swelling process can be completed in less than a minute. To begin, the end of the silicone that will connect to the barbed fitting is dipped into a swelling agent. The tubing or part begins to swell almost immediately upon immersion. The duration it remains in the solution dictates the extent of swelling, which can be timed precisely in high-volume operations to optimize efficiency.
Once removed from the solvent, the swelling agent starts to evaporate right away. As the solvent evaporates, the part returns to its original dimensions. Compared to other methods, the silicone swelling process—both the expansion and the subsequent recovery—can be completed very quickly.
Barbed fittings utilize serrations or ridges to grip the interior surface of the connecting tubing, creating a secure seal without causing damage to the tubing wall. Commonly referred to as hose barbs or hose barbed connectors, these fittings are popular due to their ease of installation.
The secure connection provided by barbed connectors makes them suitable for low-pressure applications, typically up to 200 psi, involving fluids, gases, and airflow. The effectiveness of the seal relies on the interaction between the connector’s surface and the tubing wall.
Push-to-connect fittings function similarly to barbed fittings but lack the barbs or ridges. These fittings use a uniquely shaped connector into which the tubing is inserted. A securing ring within the connector keeps the tubing firmly in place. For a proper fit, the tubing must be cut to a clean, uniform 90° end. The gripper ring in the connector not only secures the tubing but also allows for easy removal when needed.

PFA compression fittings offer a more secure and tighter connection compared to push-to-connect fittings. Constructed from PFA fluoropolymer, these fittings are designed for use with rigid and semi-rigid tubing. They operate by compressing the outer diameter of the tubing to create a secure seal.
Unlike barbed fittings, compression fittings engage with the outside of the tubing, requiring the tubing wall to be robust enough to handle the applied pressure. A PFA compression fitting consists of four main parts: the body, the ferrule, the gripper, and the nut. For a proper fit, the tubing must be cut to a clean 90° angle.
To assemble the fitting, start by sliding the nut onto the tubing. Next, place the gripper over the tubing and inside the nut, with its smaller end facing the nut. Then, insert the ferrule into the nut, positioning its larger end towards the gripper. With these components in place, push the body of the fitting over the tubing and towards the nut as far as possible.
Once all parts are assembled, thread the body of the fitting onto the nut and tighten it carefully with a wrench. It is crucial to tighten the fitting with care to avoid over-tightening, which could deform the fitting.
Compression fittings are available in various forms, including Ts and elbows, making them suitable for diverse applications. Although they are more expensive than other types of fittings, they are essential for high-pressure situations.

As mentioned above, silicone tubing is a tough elastomer that exhibits many good properties, including high resistance to temperature ranges, high flexibility, good wear and tear resistance, and resistance to UV and ozone. These benefits make silicone tubing a popular choice in a variety of applications, such as in the medical and food industries. Its high flexibility and strength make it a better choice over other rubber materials that can be used in its place. One of the other benefits that make silicone tubing a popular choice in the medical field is that it is easy to clean. This can be easily done by boiling it to remove the dirt that builds up in the material. The flexibility and high tensile strength of silicone tubing make it suitable for various applications in the medical, automobile, dairy, food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries. Because of the different grades in which silicone tubing is available, careful considerations must be made when opting for silicone tubing for a specific type of application.

Nylon tubing, also known as polyamide tubing, is a type of tubing made from polyamide resin, which has a strong resistance to abrasion. It is used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications...

Plastic tubing is a form of tubing that is manufactured from a mixture of a polymer with a variety of chemicals to form a material that can be solid or flexible. Since its first use in the 1950‘s, plastic tubing has revolutionized industrial processes and has found a use in a wide variety of applications...
Poly tubing is a highly flexible, lightweight, and durable tubing that is produced from polyethylene, a polymer that is made from the polymerization of ethylene. It is a very versatile form of tubing that has break and crack resistant walls...

PVC is a tough chemically resistant synthetic polymer of vinyl chloride used especially for making pipes, films and electrical insulation. It is made by polymerizing vinyl chloride, and...
Plastic channels are plastic products that have linear extruded profiles. They have a constant cross-sectional shape across their axis. They are long and narrow structures, and their depth is relatively short. These products serve a variety of functions and uses...
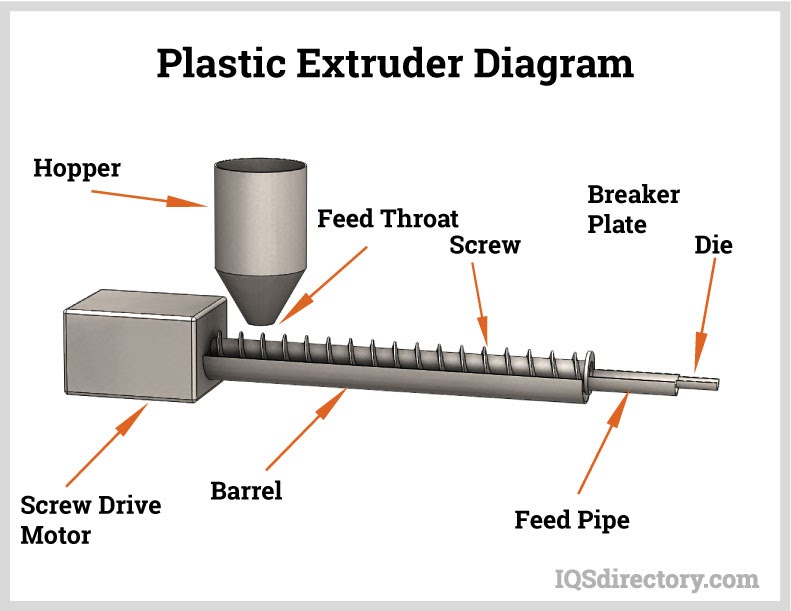
Plastic extrusion, also known as plasticating extrusion, is a continuous high volume manufacturing process in which a thermoplastic material -- in a form of powder, pellets or granulates -- is homogeneously melted and then forced out of the shaping die by means of pressure...

Plastic materials are objects artificially made from organic compounds called polymers along with other additive components. They possess excellent formability, making them extremely versatile for many different fabrication and manufacturing processes...

A plastic tank is a large capacity liquid or granular storage unit that can be vertical, horizontal, below or above ground, as well as movable. They are designed to hold several gallons of a variety of substances for long periods without experiencing wear, weathering, or deterioration...
A plastic rod is a solid plastic shape made by the process of plastic extrusion or plastic co-extrusion. These have a contrast of plastic tubing and hollow plastic profiles. Plastic rods are found in various industries, including...

Plastic trim products are extruded linear profiles that can be made to any length. Because of its ability to attach, hold, and seal, plastic trim has many applications. Plastic, HDPE, LDPE, butyrate, PVC, acrylic, and...

A plastic water tank is a large capacity container designed to store water for household, agricultural, irrigation, and industrial manufacturing use. There are various types of water tanks produced to meet the needs of specific applications, with...
A coupling is a device that is used to transmit power between two shafts connected together at their ends. Couplings serve one primary purpose: to join two pieces of rotating equipment together, while...
Silicone rubber molding is a method for shaping, forming, and fabricating silicone rubber parts and products using a heated mold. The process involves compressing or injecting silicone rubber into a mold...