Industrial Hoses
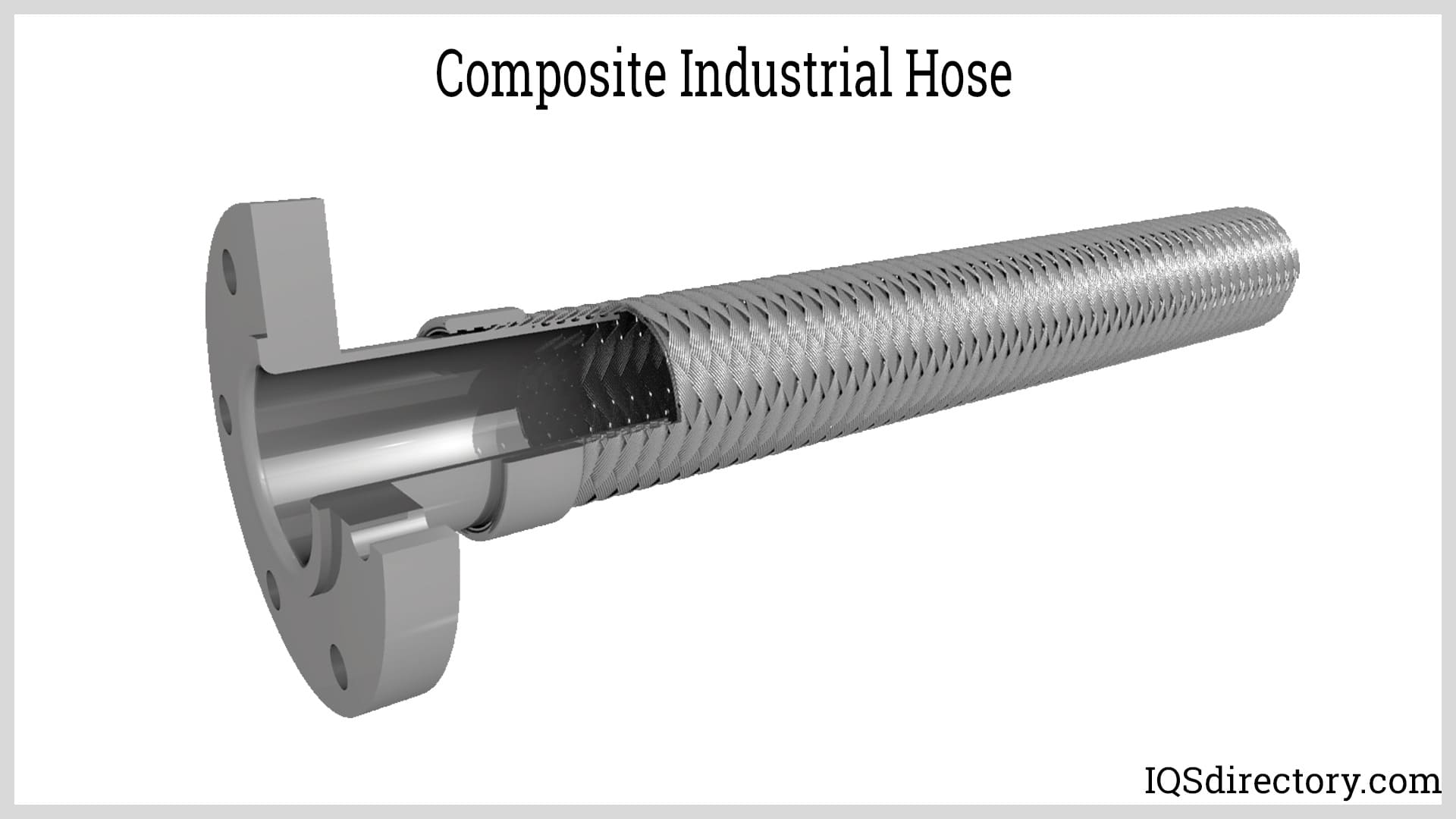
An industrial hose is a durable and precision constructed hose used to transfer and transport liquids, gases, and other materials for industrial applications. They are made of materials that...
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
Here is everything you need to know about the manufacture of plastic tubing and its use.
You will learn:

Plastic tubing is manufactured from a blend of engineered polymers and specialized chemical additives, resulting in a material that can be produced in either rigid or flexible forms. First introduced in the 1950s, plastic tubing quickly transformed industrial manufacturing and fluid handling processes and has since become a critical component across countless commercial, medical, and industrial applications.

Known for its versatility, durability, and adaptability, plastic tubing is available in a wide range of wall thicknesses, inner and outer diameters, tolerances, and strength ratings. It can be produced from multiple plastic materials, each selected to meet specific performance requirements such as chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, flexibility, pressure handling, and regulatory compliance for specialized applications.
The flexibility, chemical resistance, durability, and overall versatility of plastic tubing make it indispensable across a broad range of industrial, commercial, and residential applications. Engineered for consistent, long-term performance, plastic tubing is widely used in manufacturing, agriculture, healthcare, automotive systems, food processing, and fluid transfer operations. Compared to traditional materials such as steel, copper, and aluminum, plastic tubing offers significant advantages, including high tensile strength, lightweight construction, corrosion resistance, and superior cost efficiency. Because plastic tubing is easier to manufacture, install, and maintain, it remains a preferred solution for fluid handling, protective conduit, and transport applications.
Pneumatic tubing is a specialized category of plastic tubing designed for compressed air systems and pneumatic control applications. This flexible tubing is engineered to withstand continuous pressure, vibration, and repetitive cycling commonly found in factory automation, robotics, and industrial machinery. Manufactured from materials such as polyurethane, nylon, and polyethylene, pneumatic plastic tubing delivers reliable airflow and long service life in demanding environments. It performs well in outdoor and industrial settings, operating in temperature ranges from approximately -4° F to 140° F (-20° C to 60° C). Most pneumatic tubing is rated for working pressures up to 115 PSI at 68° F (20° C), making it suitable for compressed air lines, pneumatic actuators, and air-powered tools.

Plastic mailing tubes are commonly used to protect and transport documents such as blueprints, architectural drawings, posters, and marketing materials. These rigid tubes, typically manufactured from polyethylene or polycarbonate, feature thick walls that resist crushing, moisture intrusion, and handling damage during shipping. Available in a wide variety of diameters and lengths, plastic mailing tubes provide a durable and reusable alternative to cardboard options. Transparent designs and secure end caps enhance visibility, tamper resistance, and overall shipment security.

Plastic tubing is a core component of pneumatic tube systems used throughout the banking and financial services industry. These systems rely on heavy-duty plastic tubing to transport carriers containing documents, currency, and coins between tellers and drive-through stations. The smooth interior surface of banking tubing reduces friction and supports high-speed, reliable transport while minimizing system blockages. Manufactured from durable PVC or polycarbonate, banking tubing is engineered for continuous use, impact resistance, and long-term operational safety.

Plastic tubing plays a critical role in agricultural operations, particularly in irrigation systems, fertigation, drainage, and livestock watering. Its lightweight construction, resistance to corrosion, and UV stability allow it to be installed across large areas with minimal maintenance. Common materials such as polyethylene tubing, PEX piping, and flexible PVC enable efficient water distribution while reducing installation costs. These properties make plastic tubing an essential tool for improving crop yields, conserving water, and supporting modern farming efficiency.

Plastic tubing designed for liquid transfer supports clean, safe, and efficient movement of fluids in residential, commercial, and industrial environments. Food-grade plastic tubing—approved for potable water and beverage dispensing—is manufactured from materials such as silicone, polyurethane, polyethylene, nylon, and PVC to ensure taste neutrality and sanitation compliance. In industrial and chemical processing, specialized tubing formulations resist acids, solvents, and aggressive chemicals. Applications range from aquarium systems and laboratory equipment to breweries, water treatment plants, and pharmaceutical production lines, where precise temperature and pressure ratings are essential.

Plastic tubing is widely used in automotive applications due to its lightweight construction, chemical compatibility, and resistance to heat and vibration. Reinforced nylon, PTFE, and high-density polyethylene tubing are commonly used for fuel lines, vacuum systems, coolant routing, and windshield washer fluid delivery. Plastic tubing helps reduce vehicle weight, improves fuel efficiency, and supports compliance with evolving emissions standards while maintaining durability under harsh operating conditions.

Marine plastic tubing is engineered to perform reliably in both freshwater and saltwater environments. Commonly used for bilge pumps, livewell systems, fuel lines, and water circulation, marine-grade tubing offers resistance to salt, oils, chemicals, and UV exposure. Flexible PVC tubing is frequently selected for its durability and compliance with marine safety standards. These materials provide long service life even under constant exposure to moisture, sunlight, and fluctuating temperatures.

Medical plastic tubing is essential in healthcare and laboratory environments, enabling safe and sterile transfer of fluids, gases, and medications. Manufactured to strict quality standards, medical-grade tubing offers biocompatibility, chemical resistance, clarity, and flexibility. Common applications include IV lines, catheters, peristaltic pumps, and diagnostic equipment. Materials such as medical-grade PVC, silicone, and thermoplastic elastomers meet rigorous USP Class VI and ISO requirements, ensuring patient safety and consistent performance.

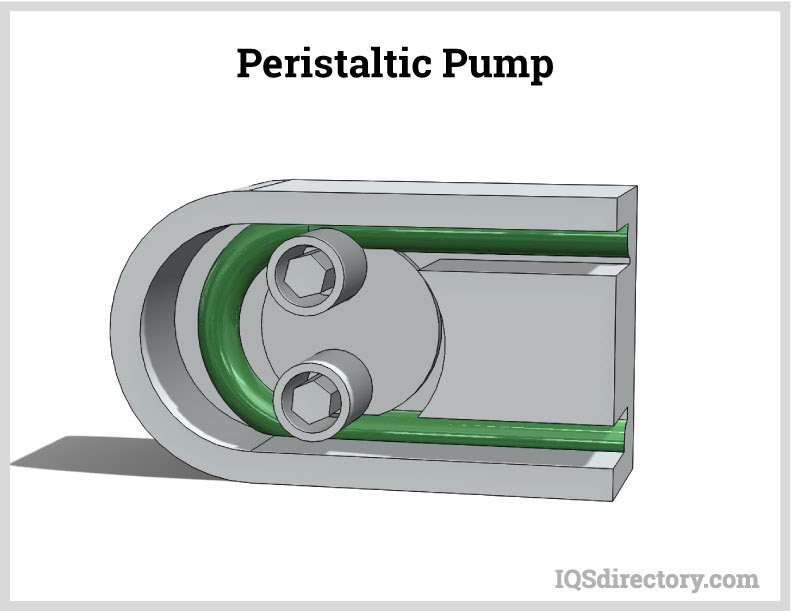
Peristaltic, or roller pumps depend on flexible plastic tubing to deliver precise, contamination-free fluid transfer. As rollers compress and release the tubing, liquids are moved accurately without contacting pump components. This makes peristaltic pumps ideal for pharmaceutical manufacturing, food processing, biotechnology, and laboratory analysis. Tubing materials such as silicone, thermoplastic elastomers, and specialty compounds are selected based on chemical compatibility, sterilization requirements, and pressure performance.
Beyond these applications, plastic tubing is widely used in HVAC systems, aquaculture, beverage dispensing, laboratory research, and industrial automation. When specifying plastic tubing, important considerations include material compatibility, pressure and temperature ratings, regulatory certifications, flexibility, and environmental exposure. Manufacturers offering engineering support, customization options, and compliance with industry standards help ensure dependable, cost-effective tubing solutions tailored to specific operational needs.
Plastic tubing is manufactured using two primary processes: extrusion and pultrusion. These modern plastic tubing manufacturing methods are used to produce a wide range of tubing sizes, wall thicknesses, and custom plastic tubing profiles for industrial, laboratory, medical, and commercial applications. In extrusion, molten plastic is pushed through a die to form precise tubing shapes and continuous lengths. In pultrusion, reinforced material is pulled through a die and cured into a rigid tubular profile. Both methods support high-volume production, consistent dimensional tolerances, and engineered tubing designs ranging from flexible tubing and rigid plastic tubing to multi-layer conduit and reinforced composite tubes.
The plastic extrusion process converts raw polymer into high-quality plastic tubing through controlled heating and shaping. The polymer resin—often supplied as pellets, granules, flakes, or powder—is fed from a hopper into the extruder barrel. Inside the barrel, a rotating screw moves the material forward while heat and friction melt it into a uniform flow. The molten polymer is then forced through a die to create the tubing’s diameter, wall thickness, and cross-sectional profile, supporting consistent performance and repeatable production.
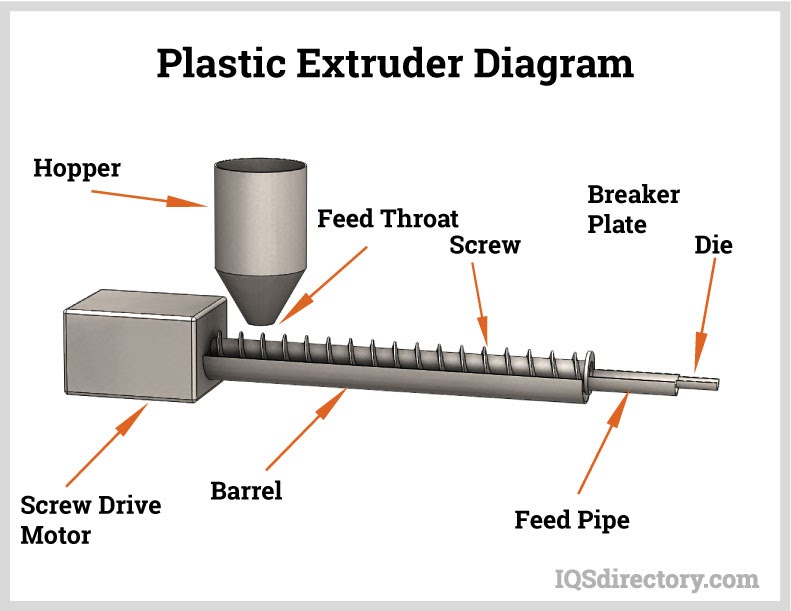
By controlling temperature zones, screw speed, pressure, and puller tension, manufacturers can produce flexible and rigid tubing with uniform wall thickness, smooth internal surfaces, and strong structural integrity. Extrusion is widely used to produce medical tubing, pneumatic tubing, food-grade tubing, laboratory tubing, and industrial fluid transfer lines. Through coextrusion, multiple materials can be combined into a single tube to add performance layers such as chemical resistance, improved flexibility, abrasion protection, or a rigid core with a flexible outer jacket for demanding service conditions.
Modern extrusion lines rely on computerized controls and in-line measurement systems to keep the tubing’s cross-section and tolerances within specification. This continuous monitoring supports better quality, less scrap, and reliable compliance with application requirements, making extrusion a preferred process for custom tubing used in water distribution, irrigation, medical devices, automation, and flexible hose assemblies.
The pultrusion process is a continuous manufacturing method used to produce reinforced plastic tubing, composite conduit, and structural tubular profiles. Unlike extrusion, pultrusion pulls reinforcement fibers—often fiberglass or carbon fiber—through a resin bath or impregnation system and then through a heated die. As the material is pulled through the die, it cures into a rigid tube with a consistent cross-section, delivering excellent mechanical strength, stiffness, and long-term dimensional stability.
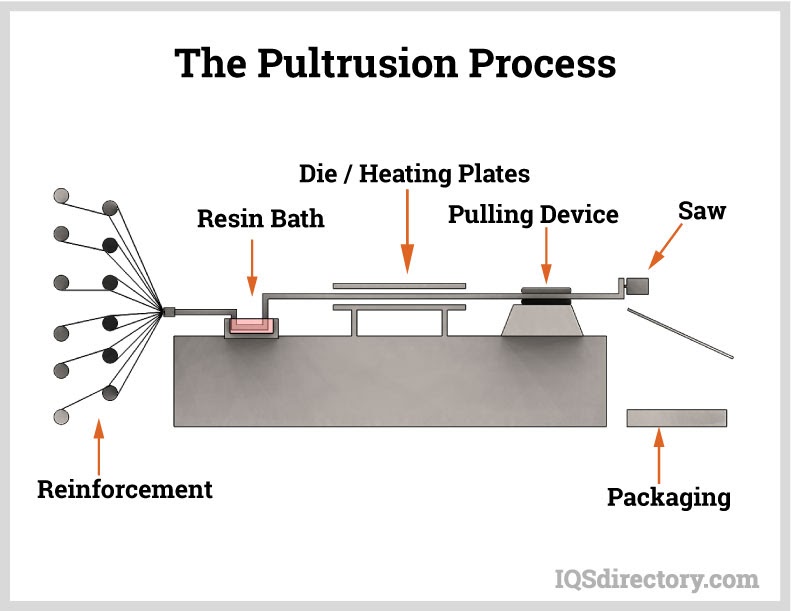
Pultrusion is commonly selected for applications requiring corrosion resistance, high strength-to-weight performance, and dependable operation in harsh environments. Pultruded tubing is often used for electrical insulation, construction supports, industrial components, and fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) piping where chemical compatibility, weathering resistance, and long service life are critical.
The performance, durability, and best-use fit of plastic tubing depend heavily on the polymer or compound selected. Different plastics offer distinct strengths in flexibility, clarity, chemical resistance, temperature stability, and compliance requirements, helping manufacturers match tubing materials to specific industrial, commercial, and regulated applications.
Acrylic tubing is valued for its optical clarity, UV stability, and strong impact performance at a fraction of the weight of glass. Acrylic tubes are commonly chosen for applications requiring visibility of flow or contents, including laboratory viewing sections, displays, lighting components, and architectural features. Its non-corrosive behavior, clean appearance, and suitability for many food-contact and retail environments make it a popular choice where aesthetics and transparency matter.

Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) tubing is one of the most widely used tubing materials due to its affordability, versatility, and broad chemical compatibility. Known for chemical resistance, corrosion resistance, abrasion performance, and flexibility, PVC tubing is used for fluid transfer, air lines, irrigation, and general-purpose applications. It is frequently selected for beverage systems, aquaculture, laboratories, and light chemical handling, and it can be produced to meet FDA and NSF requirements when specified for regulated uses.

The primary advantage of CPVC over standard PVC is improved temperature capability and resistance to more aggressive chemicals. CPVC tubing is commonly used in hot water systems, industrial chemical transfer, and process piping where higher temperature and pressure stability are required.

Fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) tubing is commonly produced via pultrusion using glass fibers with polyester or vinyl ester resin. FRP tubing provides excellent corrosion resistance, weathering performance, UV stability, and high tensile strength. Its electrical insulation properties and structural rigidity make it a dependable option for industrial supports, electrical applications, antenna components, and demanding outdoor environments.

Nylon tubing is lightweight, tough, and highly resistant to corrosion, abrasion, and many chemicals. It is commonly used for pneumatic control lines, air brake systems, and fuel-related tubing due to its flexibility, elastic memory, and durability. Nylon’s performance in low temperatures and its low moisture absorption make it a strong option for long-term mechanical and industrial service.
Polycarbonate tubing combines high impact strength with clarity and flame resistance, making it useful for protective guards, visibility-based industrial components, and specialized processing applications. It maintains structural integrity over a broad temperature range and can be machined without readily cracking, supporting use in equipment covers, shielding, and technical components requiring both strength and visibility.
Polyethylene (PE) tubing is widely used for its flexibility, smooth surface, chemical resistance, and cost efficiency. It is common in water lines, beverage systems, laboratory fluid handling, and general chemical transport where lightweight tubing and dependable performance are priorities. Polyethylene tubing is often selected as a food-safe option when appropriate grades and compliance requirements are specified.
Polystyrene tubing is lightweight and commonly used for low-stress applications that benefit from clarity and reliable barrier performance. Its moisture and vapor resistance can make it useful in laboratory, medical, and packaging environments where controlled transfer of air or liquids is needed with predictable dimensional stability.

Silicone tubing is known for outstanding biocompatibility, cleanliness, flexibility, and non-toxicity, making it a trusted material in medical, pharmaceutical, and food processing environments. It maintains elastic performance across a wide temperature range from -100°F to 500°F (-73°C to 260°C) and is frequently specified for peristaltic pumps, sterile fluid transfer, and laboratory applications requiring dependable compliance and purity standards.

Vinyl tubing, commonly made from PVC compounds, is widely used for its transparency, flexibility, and broad chemical compatibility in low-pressure applications. It is frequently used for potable water, air, aquarium systems, beverage dispensing, and general-purpose laboratory setups where visibility and ease of handling are important. When specified correctly, vinyl tubing can also support light chemical transfer needs.

Polypropylene tubing offers excellent chemical resistance, higher temperature capability, and greater rigidity than many polyethylene options. It is often used in laboratories, chemical handling, sterilizable assemblies, and applications requiring stable performance at elevated temperatures. Polypropylene tubing can remain effective up to about 275°F (135°C), making it a practical choice for medical, analytical, and industrial environments.
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) tubing is valued for its high strength-to-density ratio, impact resistance, and reliable performance under pressure. It is widely used for water supply lines, air distribution, and chemical conveyance where abrasion resistance and long service life are important. HDPE tubing is commonly selected for municipal, industrial, and environmental applications due to its durability and cost efficiency.

PTFE (Teflon®) tubing is chosen for extreme chemical resistance, non-stick performance, and dependable operation across a wide temperature range from -390°F to 500°F (-234°C to 260°C). PTFE tubing is often used in analytical instrumentation, laboratory systems, semiconductor manufacturing, and aggressive chemical processing because it resists cracking, degradation, and chemical reaction under harsh conditions.
EVA tubing is known for flexibility, impact resistance, and reliable low-temperature performance. Its resistance to grease, oils, and UV exposure, along with FDA-appropriate options, makes it useful in medical, laboratory, and food processing applications. EVA tubing is often selected for fluid transfer and cold-environment use where softness and compliance are priorities.

Polyurethane (PU) tubing is preferred for high flexibility, excellent abrasion resistance, kink resistance, and strong shape memory. It is commonly used in pneumatic systems, robotics, automation, and industrial environments where tubing must handle motion, vibration, and repeated bending. PU tubing also offers strong resistance to oils, fuels, and many solvents, making it a dependable choice for demanding service conditions.
Choosing the right plastic tubing depends on application factors such as chemical compatibility, pressure rating, temperature range, flexibility, and any required regulatory compliance. Many manufacturers offer custom tubing solutions including coextruded constructions, reinforced tubing, specialty profiles, and engineered compounds to support performance, durability, and safety. When evaluating tubing options, consider the operating environment, expected service life, and relevant certifications (such as FDA, NSF, or USP Class VI) to ensure the tubing is appropriate for its intended use.
For additional information on selecting or specifying plastic tubing for a particular industry or use case, consult with a supplier or manufacturer experienced in tubing materials, processing methods, and compliance requirements for your application.
Plastic tubing is lightweight, corrosion resistant, and cost effective while still offering strong tensile performance and reliable durability, making it a practical alternative to steel, copper, and aluminum for many fluid transfer and conduit uses.
Plastic tubing is widely used in manufacturing, agriculture, healthcare, automotive systems, food processing, banking pneumatic systems, marine applications, laboratories, HVAC, and industrial automation for fluid movement, protection, and process support.
Plastic tubing is commonly produced by extrusion or pultrusion. Extrusion forms tubing by forcing molten polymer through a die, while pultrusion pulls reinforced fibers and resin through a die to create rigid composite tubing with consistent profiles.
Common materials include acrylic, PVC, CPVC, fiberglass, nylon, polycarbonate, polyethylene, polystyrene, silicone, vinyl, polypropylene, HDPE, PTFE, EVA, and polyurethane, each chosen for specific needs such as clarity, flexibility, chemical resistance, temperature performance, or compliance.
For chemical handling, materials such as PTFE, polypropylene, CPVC, and certain PVC and polyethylene formulations are often selected due to strong resistance to acids, solvents, and corrosive fluids, depending on temperature and concentration.
Medical and food applications commonly use compliant materials such as silicone, medical-grade PVC, polyurethane, EVA, and selected polyethylene or polypropylene grades, depending on cleanliness needs, sterilization methods, and required certifications.
Across the United States and Canada, manufacturers have access to a wide range of equipment for plastic tubing production. These plastic tubing machines play a central role in modern manufacturing by enabling consistent, high-throughput output for products used in irrigation systems, medical tubing, automotive fluid handling, industrial automation, and many other end uses. Below are examples of widely recognized machine platforms used for extrusion, injection molding, and blow molding in tubing and tubular component manufacturing.
Features/Characteristics: Davis-Standard's Thermatic® series extruders are valued for flexible plastic tubing extrusion across many materials, diameters, and wall thicknesses. They are designed to support stable melt processing, repeatable dimensional control, and high output, making them well suited for manufacturers producing consistent tubing for industrial, automotive, and general-purpose applications.
Features/Characteristics: Milacron's TP series extrusion machines are known for efficient plastic tubing manufacturing with strong process precision. Advanced control features help operators tune temperature, pressure, and line speed for consistent wall thickness and tighter tolerances. The TP series is often selected for its throughput, reliability, and maintenance-friendly design in high-demand production environments.
Features/Characteristics: Conair's MedLine® extruders are engineered for medical tubing production where cleanliness, process stability, and quality assurance are priorities. These systems emphasize controlled processing and hygienic operation to support consistent tubing dimensions and reduce contamination risks, aligning with the expectations of medical and healthcare manufacturing environments.
Features/Characteristics: Arburg's ALLROUNDER series injection molding machines are widely recognized for precision, repeatability, and versatility. While primarily used for injection molded parts, certain tooling approaches can support tube-forming or pipe-style molding for specialized plastic tubing components. These machines are commonly chosen when consistent, high-volume production and tight dimensional repeatability are required for complex designs.
Features/Characteristics: Wilmington Machinery's Series III blow molding machines are designed for producing hollow plastic parts and tubular forms used in containers and related products. They focus on consistent wall thickness control, dimensional accuracy, and fast cycle times, making them a strong fit for high-volume manufacturing where repeatability and production speed are critical.
Because extrusion technology, automation, and control systems continue to evolve, machine capabilities and model offerings can change over time. For the most current guidance on plastic tubing extrusion lines and related production equipment in the United States and Canada, compare current specifications and options directly with machine manufacturers, authorized suppliers, and qualified industry integrators.
Given the wide range of materials and applications for plastic tubing, selecting the right type for a specific use requires careful consideration of the desired properties. While plastic is a versatile and durable material, the challenge lies in determining the specific features needed for the application.
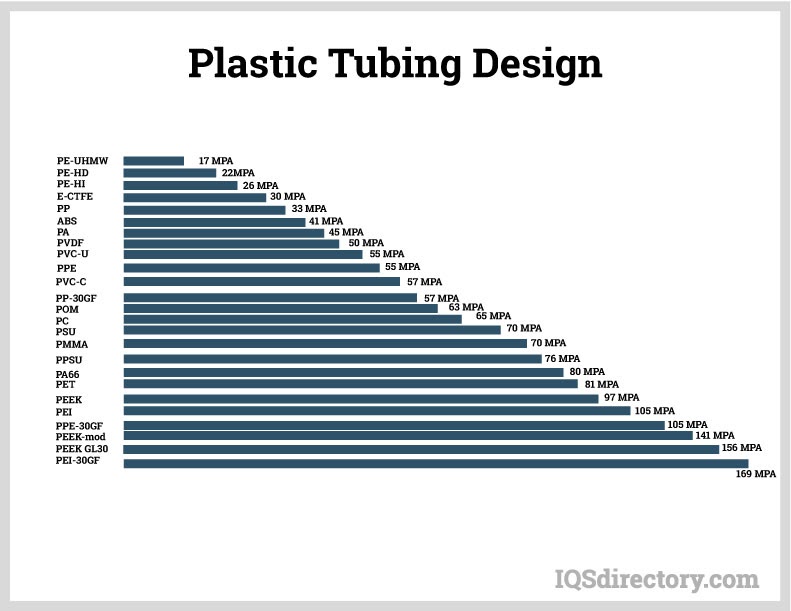
Assessing the mechanical properties of a material, including its tensile strength, is crucial when selecting the appropriate plastic. Tensile strength measures how much stress a plastic can withstand before breaking, and it varies between 12,400 psi and over 20,000 psi. The chart below provides a comprehensive list of various plastics and their tensile strength in megapascals at 73°F (23°C).
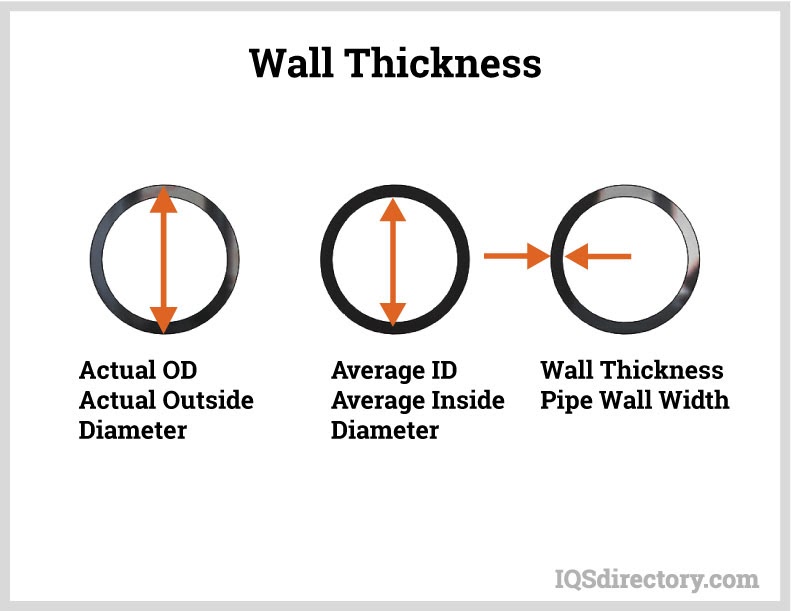
Tubing is measured by its inside diameter (ID) and outside diameter (OD), which can range from 0.125" to 4" (0.3 to 10 cm). The difference between the ID and OD represents the wall thickness, which is a key factor in determining the strength of the tubing.
Wall thickness is calculated by subtracting the inside diameter (ID) from the outside diameter (OD) and then dividing the result by two.
The flexibility of plastic tubing depends on the material used in its manufacture. PVC, polyurethane, and silicone are all flexible materials, with silicone being the most flexible of the three.

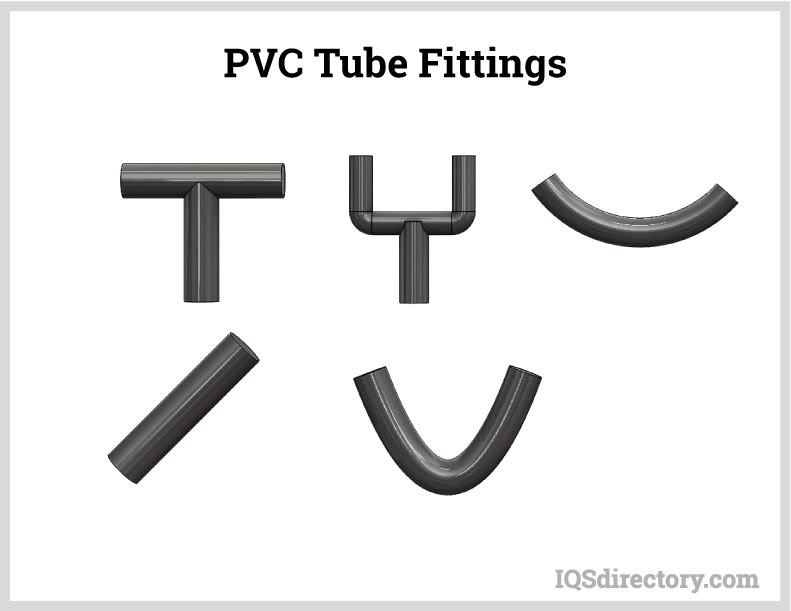
Plastic tubing fittings come in various types, including compression, push-to-connect, quick turn, threaded, barbed, socket, and flanged. The choice of fitting should be based on the specific application and how the tubing will be used.
Plastic tubing is available in an almost limitless range of colors, including translucent and clear options.
Plastic tubing can be manufactured to any length, tailored to the specific needs of the application. It can range from just a few inches to several hundred feet.

When comparing the cost of plastic tubing to steel or stainless steel in terms of tensile strength, steel and stainless steel are significantly stronger. However, the primary advantage of plastic tubing is its cost. While a few stainless steel tubes may cost as much as hundreds of flexible plastic tubes, plastic offers a more economical alternative.
The durability and strength of plastic tubing are influenced by its wall thickness and the resin blend used. The strength of plastic tubing is directly related to the amount of stress it can withstand. Plastic can endure significant stress before failing, making it quite resilient.

All plastics are resistant to corrosion, but the degree of resistance varies depending on the type of polymer used. Polyolefins and PVC are among the most corrosion-resistant plastics. Polyolefins include polyethylene and polypropylene, which are available in various densities and molecular structures to facilitate design versatility.

Resins used for plastic tubing can be manufactured with antimicrobial properties integrated into the pellets. This feature is essential for applications such as food storage, coolers, water tubes, and medical tubing. The antimicrobial additive helps prevent contamination and ensures that the tubing remains sanitized.

Plastic products can potentially be toxic, with the level of toxicity depending on the type of resin used in their production. When deciding to manufacture plastic tubing, it is important to consider the potential toxicity of the materials as part of the design process.
The characteristics of plastic tubing are determined by the polymer material, tubing design, and manufacturing process. Although surgical tubing, industrial tubing, and fluid transfer tubing serve very different purposes, most plastic tubing products share a set of core performance characteristics that make them reliable across a wide range of applications.
Plastic tubing functions as a hollow shaft engineered to convey gases, liquids, powders, or granular and flaky materials. While round tubing profiles are the most common, plastic tubing can also be produced in square, rectangular, or custom hollow shapes to meet specialized flow, structural, or installation requirements.

Plastic tubing is manufactured from a wide variety of polymers, each selected for specific performance traits. These polymers provide strength, flexibility, chemical resistance, corrosion resistance, and cost efficiency. Common materials include PVC, polyethylene, polyurethane, nylon, silicone, and PTFE, allowing tubing to be tailored to demanding industrial, medical, and commercial environments.
The mechanical strength, flexibility, wall thickness, and transparency of plastic tubing can be precisely engineered based on the polymer and manufacturing method. This adaptability makes plastic tubing one of the most widely used components in modern manufacturing, supporting applications that range from medical devices and laboratory systems to drainage, irrigation, and industrial fluid handling.

Plastic tubing can be manufactured with optical clarity comparable to glass, while offering significantly greater impact resistance and durability. Clear plastic tubing allows visual monitoring of fluid flow, making it ideal for laboratory, medical, food processing, and diagnostic applications.

Plastic tubing can be engineered to perform under a wide range of temperatures, pressures, and chemical exposures. Many plastic tubing materials naturally resist corrosion and chemical attack, reducing the need for additional coatings or treatments when transporting aggressive fluids or gases.
While plastic tubing does not match the tensile strength of steel or stainless steel, it delivers excellent durability for most applications. Plastic tubing can absorb impact, vibration, and repeated flexing without cracking, allowing it to maintain performance even after sustaining surface damage.

Most plastic tubing materials are recyclable and can be reprocessed into new products. At the end of its service life, plastic tubing can be ground into pellets or resin and reused in extrusion processes, supporting sustainability initiatives and reducing material waste.

The variety of materials used to manufacture plastic tubing matches the diversity of its types, ranging from highly sanitary tubes for cleanrooms and surgical environments to drainage tubes for sewage and waste removal. Plastic tubing is engineered to meet specific application requirements and can be molded, shaped, and configured to suit various conditions.
Corrugated tubing is used in chemical processing, corrosive environments, laboratories, and for high-purity fluid and solvent transfer. It is highly flexible, allowing it to be extended or compressed without altering the inside diameter (ID). Corrugated plastic tubing can be manufactured in any length and with various IDs to meet specific needs.
Heat shrinkable tubing is used for insulating wiring. It is applied around the wire and then shrinks to fit tightly. This tubing is resistant to fuels, lubricants, acids, and solvents, even at high temperatures.

Medical plastic tubing is manufactured to the exacting standards of the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and the National Sanitation Foundation (NSF). USP Class VI defines the requirements for biological reactivity, while NSF 51 outlines the use of plastics with food products. Medical tubing has to be translucent, able to be sterilized and reusable, and nonreactive with bodily fluids or tissues.
Square plastic tubing is less common but is occasionally used for its aesthetic appeal. It serves similar functions to cylindrical tubing and can transport liquids and gases. Its strength also makes it suitable for manufacturing lawn furniture.
Hard or rigid plastic tubing is manufactured from various materials and is used both as a conduit and as construction material. It has a wide range of industrial applications due to its durability and structural integrity.

Small diameter tubing, or miniature tubing, is used in applications where standard tubing is required but on a smaller scale. It is made from materials such as polycarbonate, polypropylene, polyethylene, polystyrene, and PVC. This type of tubing is commonly used in electrical components, swab sticks, medical products, and dispensing tubes, and it can be produced in various lengths.

Centrifuge plastic tubing consists of cylindrical tubes used in centrifuge machines to analyze and separate materials. These tubes are high-strength and precision-engineered to safely contain a variety of substances. Due to their cost-effectiveness, plastic centrifuge tubes are more commonly used than their glass counterparts.

The regulations governing the production of plastic tubing primarily focus on its use in the food industry and for water transport. In addition to government regulations, various organizations establish and oversee guidelines for materials that come into contact with the public.
The FDA regulates products that come into contact with food or beverages. Given the significant role plastic tubing plays in the food industry, the FDA has set regulations to ensure cleanliness and sanitary standards for food processing tubing. Materials used in plastic tubing are tested for composition, additives, and properties. If they meet the FDA’s standards, they are deemed FDA compliant. FDA CFR 21 encompasses regulations for materials used in medical applications as well.
The USDA oversees equipment used in the production of meat and poultry products. Its Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) provides guidelines that align with FDA requirements listed in CFR 9, ensuring safety and compliance in food production.
The 3A-Dairy group is a voluntary organization dedicated to improving the quality, standards, and equipment used in dairy product production. Its main focus is on enhancing sanitary conditions during production. The organization collaborates with food handling manufacturers to improve their methods and awards a 3-A Sanitary Standards, Inc. compliance seal to those who meet its criteria.
The NSF was established to standardize sanitation and food safety requirements, with over 80 standards for public health and safety. It covers all aspects of food production and includes critical examination and testing of equipment that contacts drinking water, such as plumbing systems, water treatment chemicals, and filters.
NSF Standards relevant to Plastic Tubing include:
The USP (United States Pharmacopeia) is a public standards authority for medicines and healthcare products, establishing criteria for quality, purity, strength, and consistency. USP Class VI standards specifically assess the toxicity of materials and their potential risks to human health. Tubes that come into contact with body tissues or muscles undergo rigorous testing and evaluation to ensure they meet these standards. The USP employs various tests to determine whether a material complies with its safety and performance requirements.

An industrial hose is a durable and precision constructed hose used to transfer and transport liquids, gases, and other materials for industrial applications. They are made of materials that...
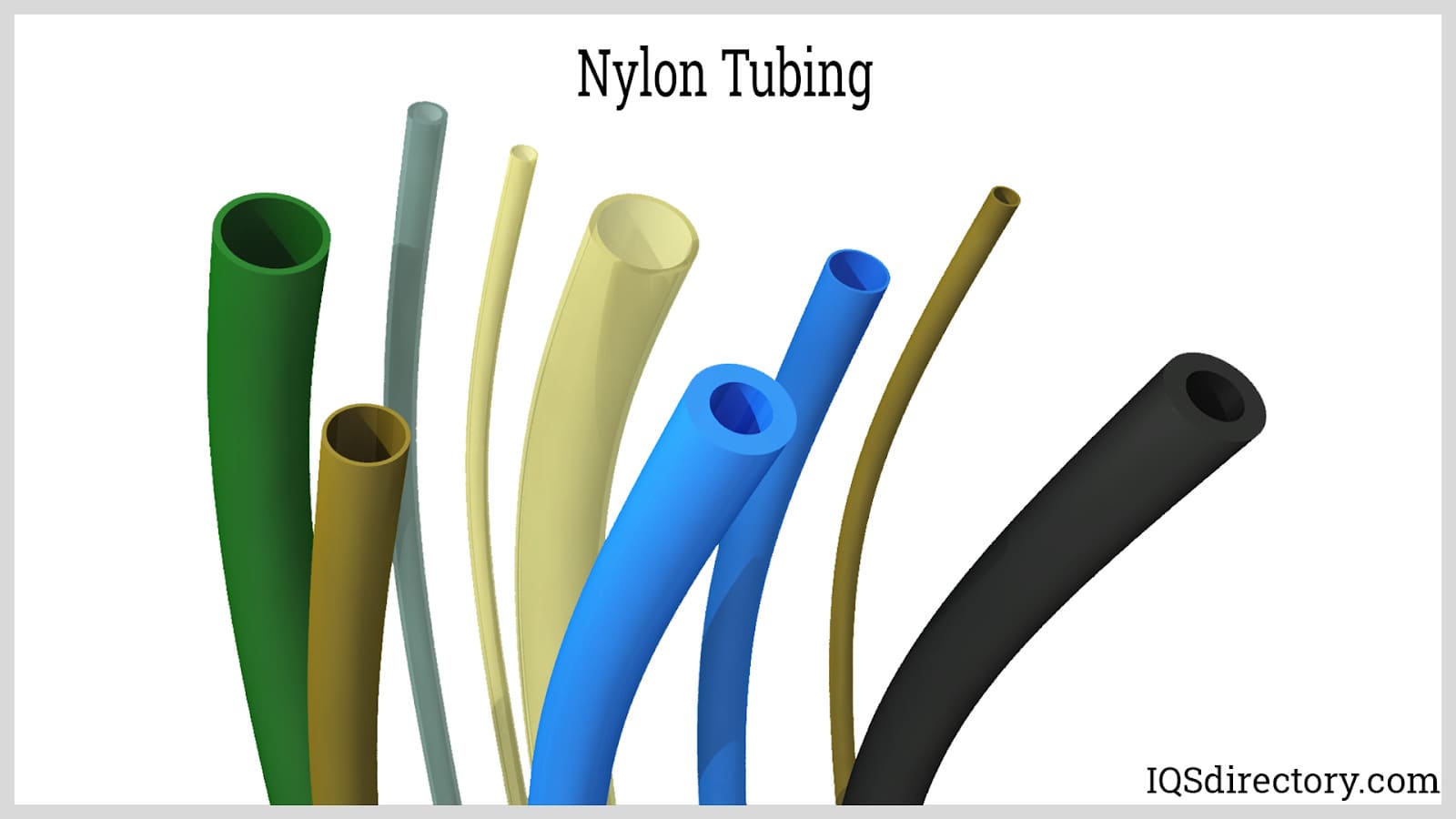

Nylon tubing, also known as polyamide tubing, is a type of tubing made from polyamide resin, which has a strongresistance to abrasion. It is used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications...
Poly tubing is a highly flexible, lightweight, and durable tubing that is produced from polyethylene, a polymer that is made from the polymerization of ethylene. It is a very versatile form of tubing that has break and crack resistant walls...

PVC is a tough chemically resistant synthetic polymer of vinyl chloride used especially for making pipes, films and electrical insulation. It is made by polymerizing vinyl chloride, and...
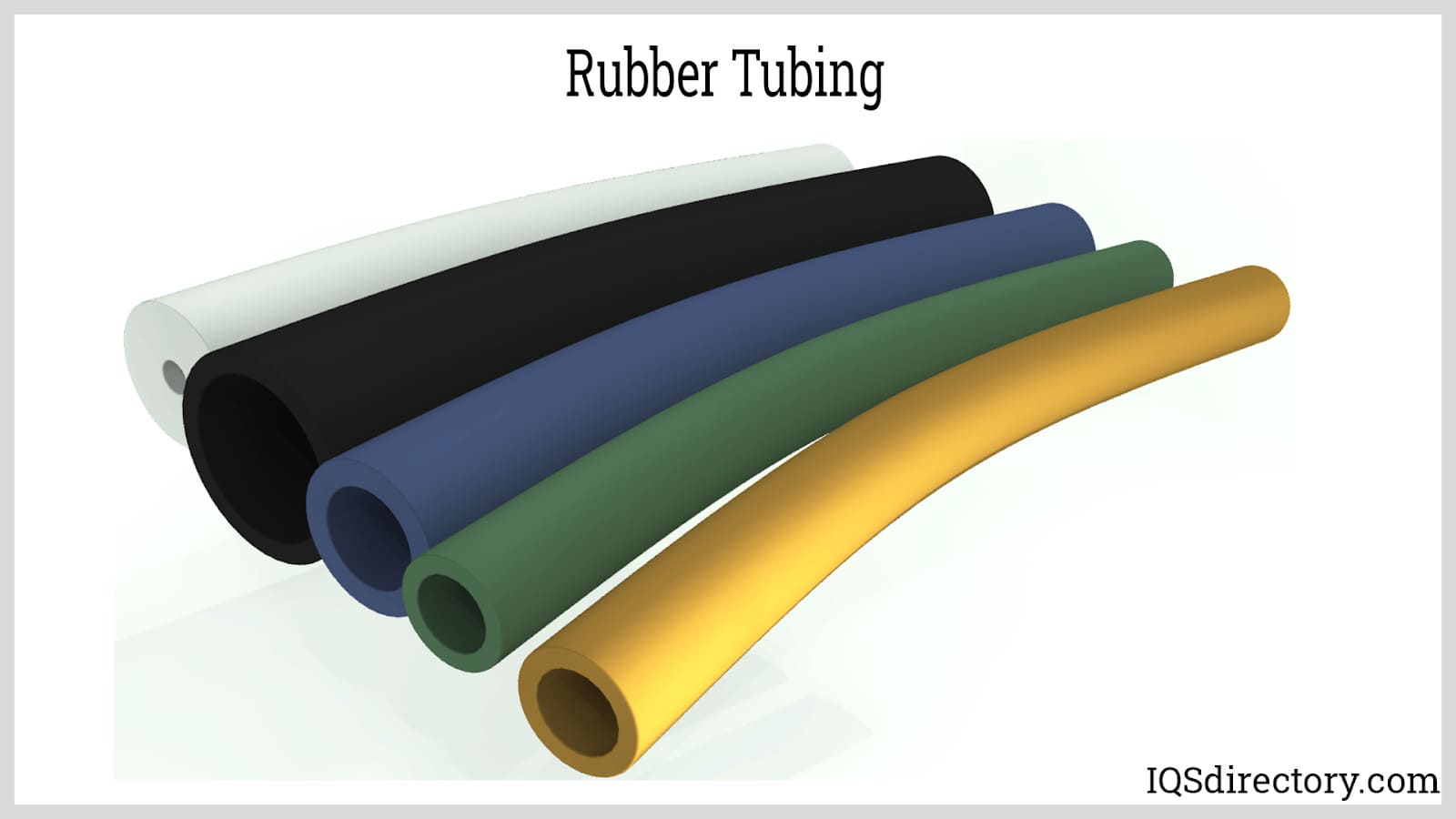

Rubber tubing, also known as rubber hose or piping, is made from a combination of natural and synthetic rubber. This versatile material is widely used for transporting and circulating liquids and...
Silicone tubing is a very tough elastomer that exhibits high strength, flexibility, and resistance. Silicone tubing can be stretched without tearing and is highly versatile. It cannot be weakened with repeated bending and twisting due to...
Plastic channels are plastic products that have linear extruded profiles. They have a constant cross-sectional shape across their axis. They are long and narrow structures, and their depth is relatively short. These products serve a variety of functions and uses...

Plastic extrusion, also known as plasticating extrusion, is a continuous high volume manufacturing process in which a thermoplastic material -- in a form of powder, pellets or granulates -- is homogeneously melted and then forced out of the shaping die by means of pressure...

Plastic materials are objects artificially made from organic compounds called polymers along with other additive components. They possess excellent formability, making them extremely versatile for many different fabrication and manufacturing processes...

A plastic tank is a large capacity liquid or granular storage unit that can be vertical, horizontal, below or above ground, as well as movable. They are designed to hold several gallons of a variety of substances for long periods without experiencing wear, weathering, or deterioration...
A plastic rod is a solid plastic shape made by the process of plastic extrusion or plastic co-extrusion. These have a contrast of plastic tubing and hollow plastic profiles. Plastic rods are found in various industries, including...

Plastic trim products are extruded linear profiles that can be made to any length. Because of its ability to attach, hold, and seal, plastic trim has many applications. Plastic, HDPE, LDPE, butyrate, PVC, acrylic, and...

A plastic water tank is a large capacity container designed to store water for household, agricultural, irrigation, and industrial manufacturing use. There are various types of water tanks produced to meet the needs of specific applications, with...

A poly tank is a plastic storage tank used to store, transport, and collect water, other liquids, and granular or powder materials. They are made of polyethylene or polypropylene and are a cost effective, lightweight, and easy to handle...
A coupling is a device that is used to transmit power between two shafts connected together at their ends. Couplings serve one primary purpose: to join two pieces of rotating equipment together, while...