Industrial Hoses
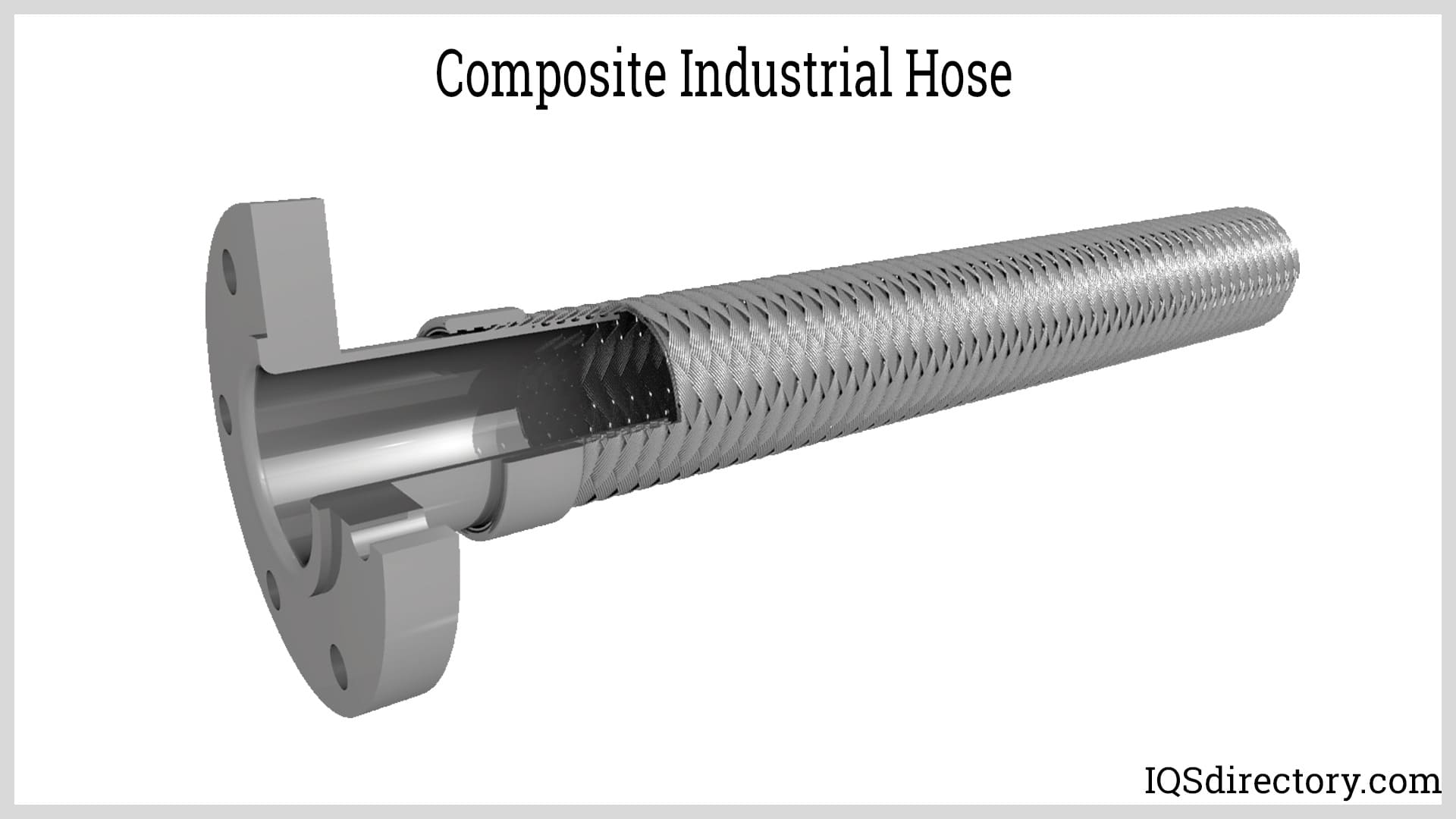
An industrial hose is a durable and precision constructed hose used to transfer and transport liquids, gases, and other materials for industrial applications. They are made of materials that...
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
This article will take an in-depth look at nylon tubing.
The article will bring more detail on topics such as:
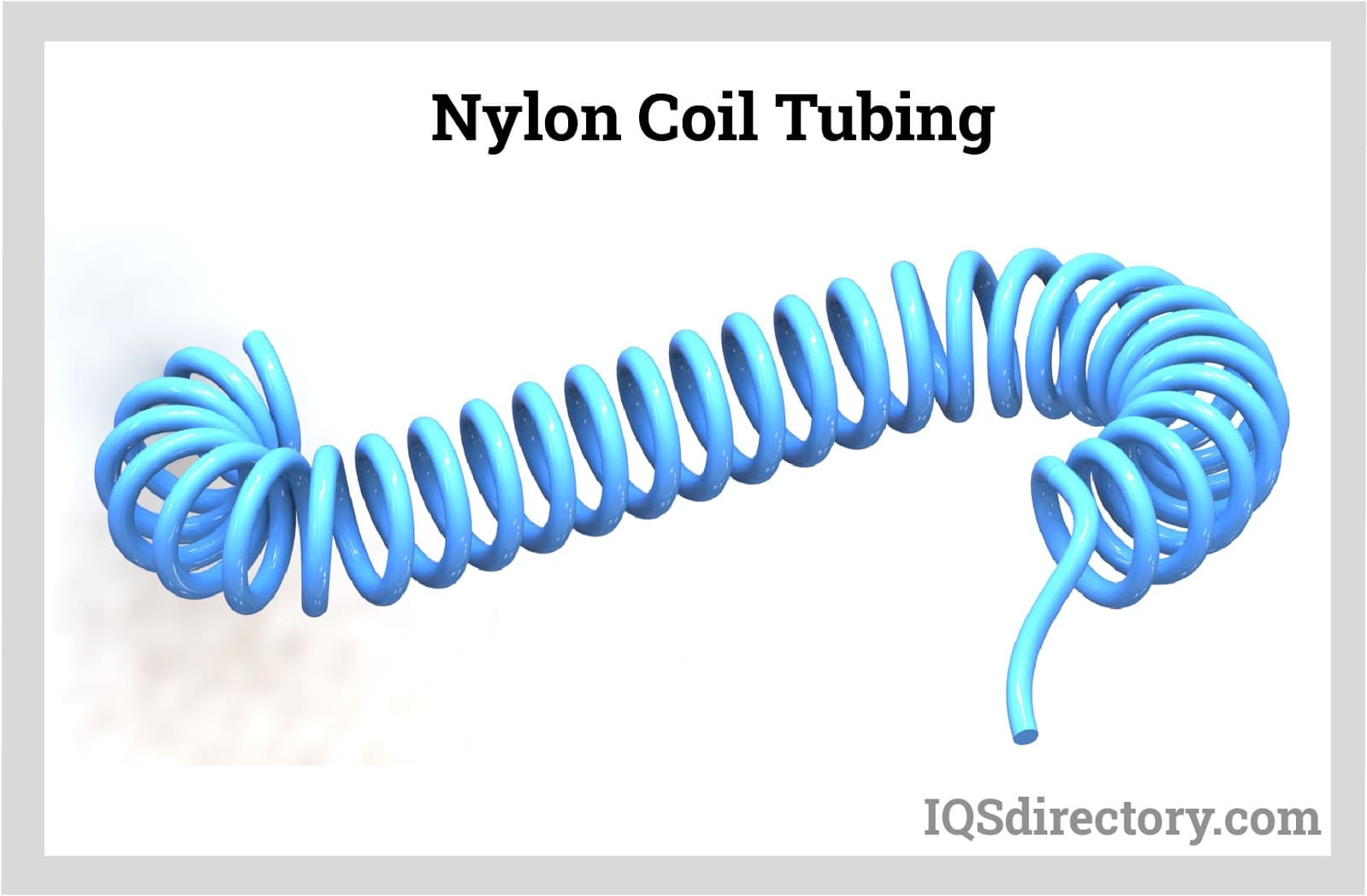
This part delves into the world of nylon tubing, discussing its production techniques and operational foundations.
Known as polyamide tubing, nylon tubing is manufactured from polyamide resin, providing outstanding resistance to abrasion. It's engineered for applications involving high pressure and temperature conditions. Notably versatile, certain nylon variants resist chemical-induced degradation effectively.

Its UV stabilization makes nylon tubing perfect for sunny and warm settings. Its exceptional flexibility allows integration into complex configurations. Due to its elastic memory, nylon tubing endures frequent bending without cracking.
Even in subzero temperatures, nylon tubing maintains impact resistance and absorbs minimal moisture, retaining its dimensions and shape. Additionally, it successfully withstands solvents, alkalis, petroleum products, greases, oils, and numerous molds and fungi.
Nylon tubing is invaluable in industrial applications, spanning robotics, hydraulic systems, brake and air lines, fuel and vacuum lines, oil and chemical processing, and tool lubrication. It's also integral to food processing and pneumatic mechanisms using compressed air for operational automation.
Compared to other nylon resins, nylon plastic tubing presents a reduced bend radius and a lighter weight wall. The special characteristics of nylon tubing originate from its molecular structure, setting it apart from other plastics like polycarbonate. With a melting point around 374°F (190°C), it remarkably surpasses the thermal resilience of many other resins.
Furthermore, nylon's crystalline composition enhances its durability against wear and chemical exposure. The nylon tubing comprises hollow channels crafted from solid nylon. Though commonly utilized in textiles, solid nylon excels as a material for fabricating plastic tubes and other similar products.
Crafting nylon tubing involves either plastic extrusion or plastic co-extrusion, elaborated in detail hereunder.
The initial step in nylon tubing creation is the plastic extrusion method. In this stage, raw materials—commonly small beads or nurdles—are delivered from a hopper into the barrel of an extruder. Additives, including colorants and UV stabilizers, are introduced either into the extruder or mixed with resin beforehand.
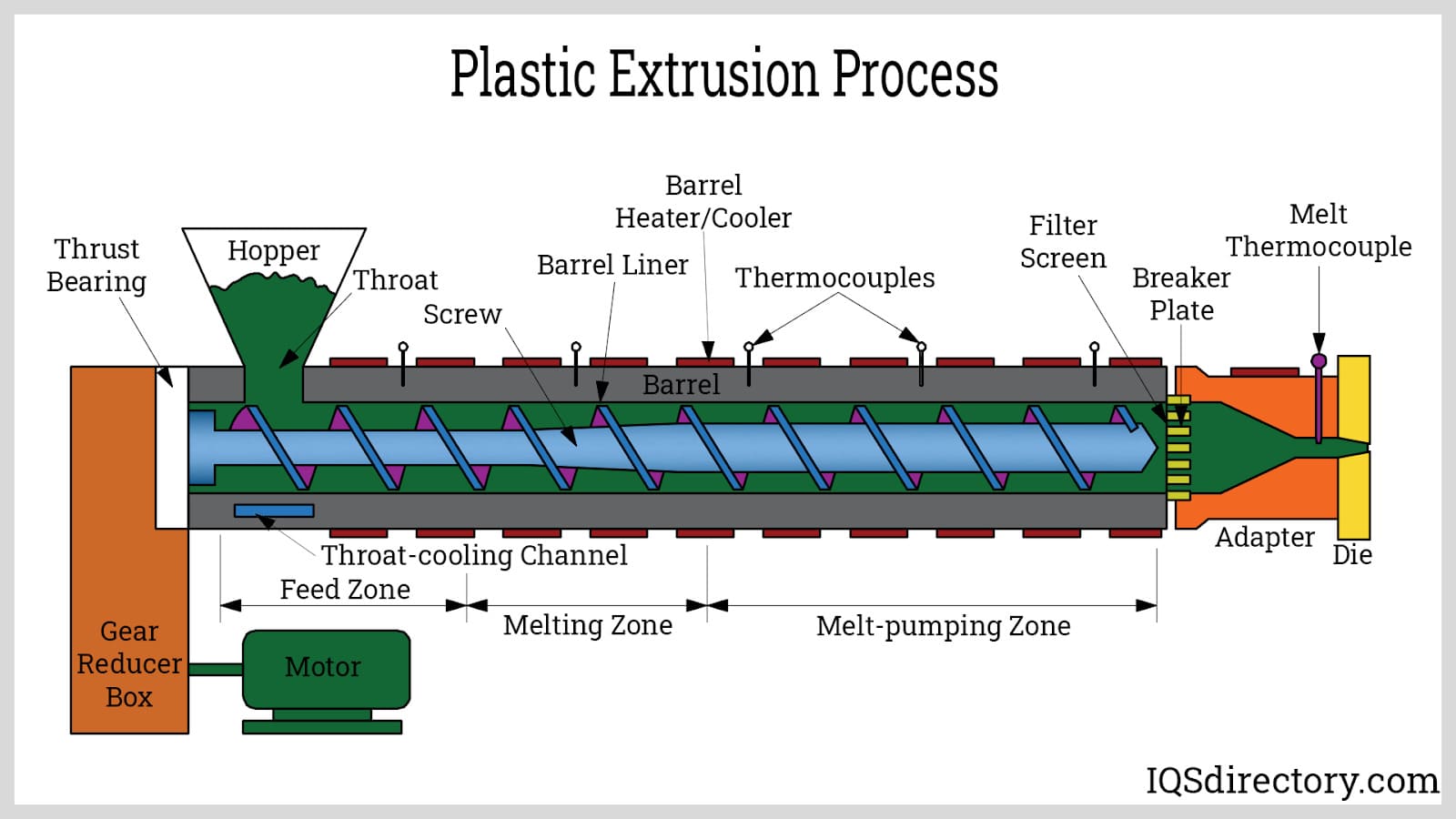
While similar to plastic injection molding, extrusion is a continuous operation. The related technique, pultrusion, pulls products through a die for reinforcement rather than extruding melted polymers.
Initially, material enters the feed throat at the barrel's back, where it meets a rotating screw, often running around 120 rpm, propelling the plastic beads into a heated barrel. Extrusion temperatures frequently surpass the barrel's set temperature due to viscous heating.
In extrusion setups, a designated heating profile with multiple PID-controlled zones raises the material's temperature as it traverses the barrel, averting overheating and degradation.
Further heat is generated through internal pressure and friction within the barrel.
Efficient extrusion lines can regulate melt temperature via pressure and friction, occasionally eliminating the need for heating elements. Many setups feature cooling fans and cast-in cooling coverings to manage excess heat when air cooling is insufficient.
Upon exiting the barrel, the molten plastic traverses a screen pack to filter contaminants. Reinforced by a metal breaker plate, this setup withstands high pressures, essential for maintaining uniform melting and mixing. Adjusting the number and mesh size of screens, among other aspects, allows control of pressure.
Screen packs and breaker plates also minimize rotational memory, reducing longitudinal memory. Once past this phase, the molten plastic reaches a die, shaping the final product. Precise die engineering ensures even flow and precludes residual stresses that can warp profiles during cooling. While a variety of shapes is possible, continuous profiles are the domain of this process.
Once extruded, the product cools, usually in a water bath. Given plastic's insulating properties, it cools slowly compared to metals. A controlled vacuum within the water bath prevents collapse of newly formed tubes or pipes.
For products like sheeting, cooling often involves cooling rolls, while thin films sometimes use air cooling initially, as in blown film extrusion. In addition, plastic extruders reprocess sorted, blended, and cleaned recycled plastic materials effectively.
Nylon rods aren't always purely nylon—they may be co-extruded with materials like metals. This adapted extrusion method combines multiple materials in a single product through individual extruders melting specific polymers for incorporation.
Upon melting, materials enter the die at consistent speeds, forming distinct layers. Co-extrusion combines unique material properties to create enhanced characteristics unattainable by individual polymer use.
To economize material or fortify the rod's core, producers may co-extrude with a different plastic or material. Low-cost co-extrusion materials suffice where minimal strength is required.
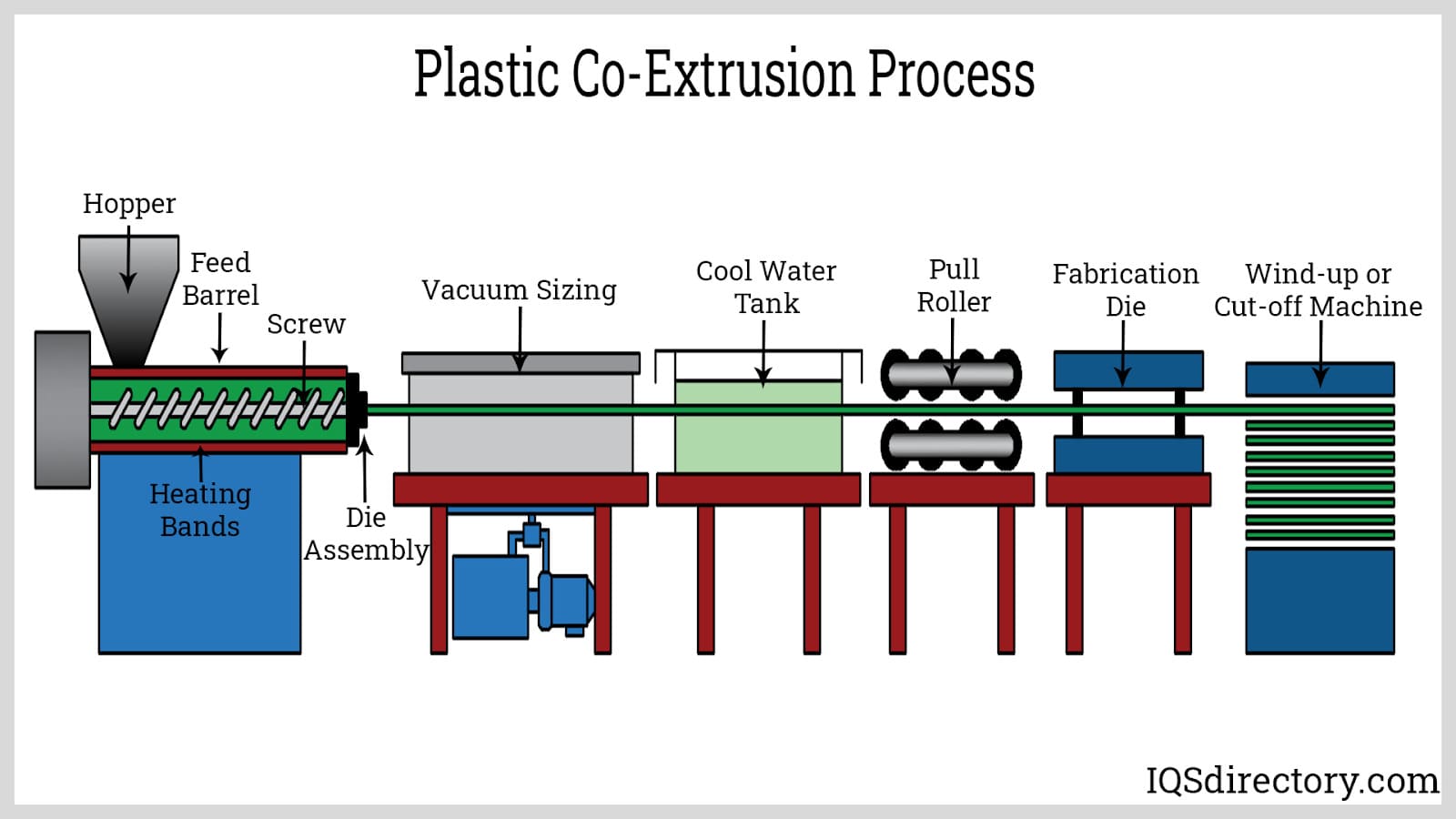
For enhanced structural support, a metal core may be included. Moreover, co-extrusion seeks to bolster wear resistance and cut down oxygen permeation.
Pultrusion, akin to extrusion, continuously creates tubing profiles but involves drawing fiber reinforced by thermoplastic resin through a die, unlike extrusion's polymer melting. Polymerization proceeds within the die, efficiently yielding corrosion-resistant, low thermally conductive plastic tubing.
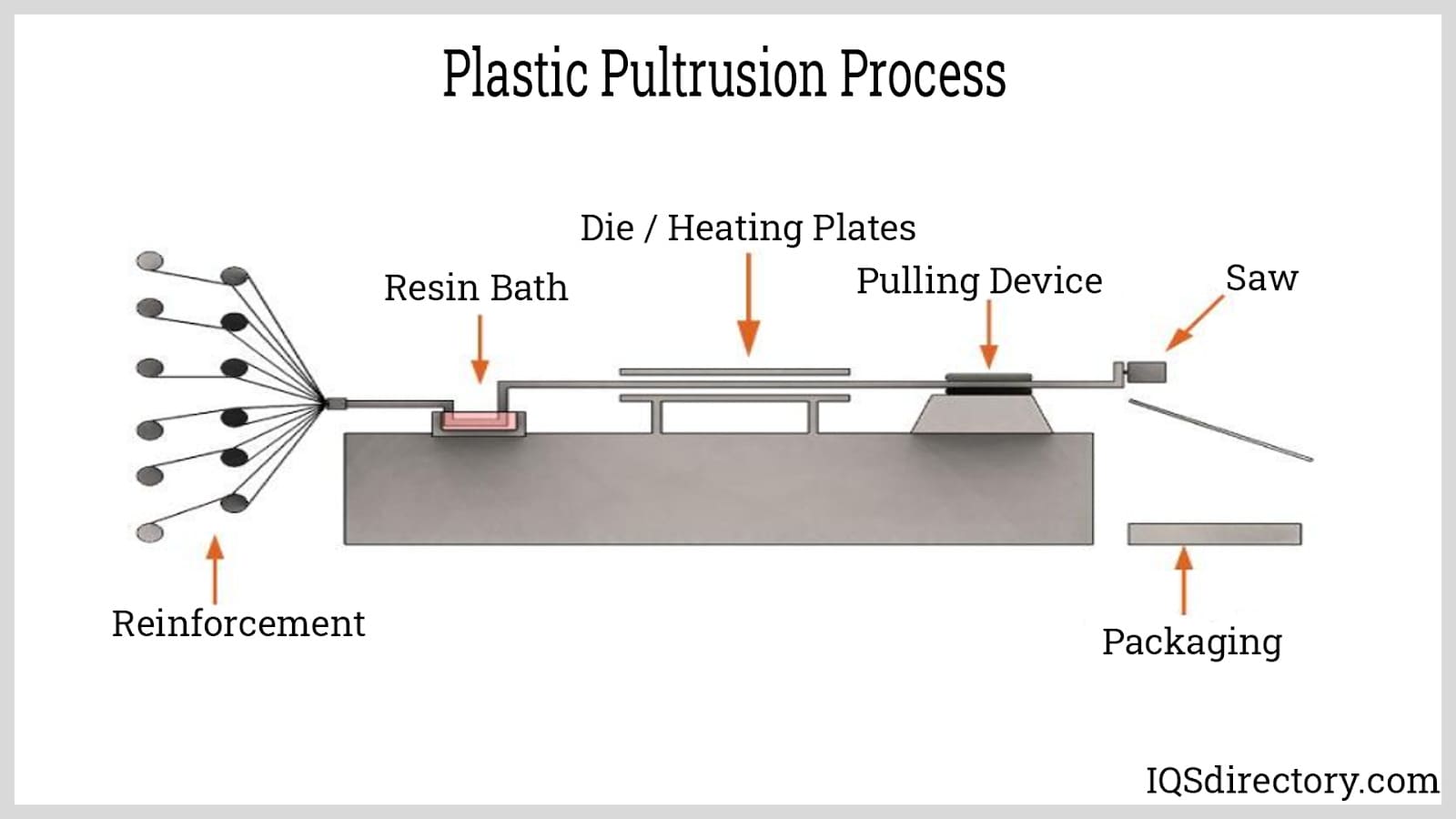
Radius pultrusion, a pultrusion variant, facilitates two or three-dimensional curved profiles with minimal distortion. This is advantageous for complex textile reinforcements in specialized applications.
On occasion, manufacturers employ secondary processes for their plastic rods, like drilling, painting, deburring, powder coating, labeling, finishing, and notching. The rods come transparent or in varied, custom colors.

Extruded nylon tubing's versatility and wide material options make it a preferred choice among manufacturers, offering cost-effective, swift, and enduring results.
Nylon and polyurethane are prominent tubing materials, each with distinct benefits. Polyurethane's flexibility suits tight bends, like in robotics, and finds application under medium pressures. Contrastly, nylon excels in high-pressure settings, resists stress cracking, and offers superior chemical and heat resistance compared to polyurethane. Both demonstrate commendable abrasion resistance.
In the United States and Canada, a wide range of advanced extrusion machines are used to produce high-quality nylon tubing. These nylon tube extrusion systems play a critical role in today’s manufacturing industries—especially in sectors such as automotive tubing, aerospace tubing solutions, medical device tubing, and food and beverage processing. Nylon tubing is valued for its excellent abrasion resistance, chemical compatibility, flexibility, and durability, making it an optimal choice for transporting fluids, compressed air, and gases in demanding applications. Below, we explore some of the leading nylon tube extrusion machines and highlight their unique features, efficiency, and benefits for industrial manufacturers.
Key Features: The DSREV Extruder is a highly regarded solution for nylon tubing manufacturing due to its remarkable reliability and productivity. This polymer extrusion machine incorporates cutting-edge PLC-based control systems for exact temperature and pressure management, ensuring highly uniform tube dimensions and consistent wall thickness—essential for strict quality control, especially in medical grade nylon tubing and fuel line production. The system is exceptionally energy efficient, supports fast line speeds, and offers extensive material compatibility, including performance polymers and engineering plastics beyond nylon such as PA12, PA6, and polyurethanes (PU) for co-extruded tubing requirements. This makes the DSREV ideal for manufacturers seeking consistent output and operational cost savings.
Key Features: Conair MedLine® Co-Extruders are trusted for producing multi-layer nylon tubing, enabling manufacturers to combine a variety of polymer layers for optimal barrier properties, flexibility, or chemical resistance. These extrusion machines excel at manufacturing medical catheters, pharmaceutical tubing, and food-grade tubing where custom performance is required. With user-friendly touchscreen controls, in-line quality monitoring, and seamless integration with downstream equipment like laser measurement systems and automatic cutters, these co-extruders support high-volume, continuous nylon extrusion with minimal operator intervention.
Key Features: The Nylon Tube Extrusion Line from Allied Supreme Corp. is custom-engineered for nylon tube extrusion applications. Its advanced temperature and pressure control allow for tight tolerances, while its robust design ensures high-output production cycles and minimal downtime. These lines accommodate different grades of nylon resin, including nylon 6 (PA6), nylon 12 (PA12), and specialty blends. Their flexibility makes them suitable for producing a wide range of flexible pneumatic tubing, automotive fuel hoses, and high-pressure hydraulic lines often required in the OEM and aftermarket sectors.
Key Features: AET’s Nylon Tubing Extruder stands out for its precision-engineered screw and barrel design, optimized for efficient melting, mixing, and extrusion of nylon and related thermoplastics. Its high-performance output and excellent process stability make it a preferred choice for tight-tolerance industrial tubing such as instrumentation tubing and high-pressure hydraulic tubing. The ease of operation, simplified maintenance, and modular design allow manufacturers to easily switch between different tube sizes and wall thicknesses with minimal production downtime—key considerations for contract manufacturing and custom extrusion operations.
Key Features: American Kuhne provides specialized nylon tube extrusion lines designed to accommodate the unique processing characteristics of engineering-grade nylons. These extrusion lines deliver precise dimensional control and superior product consistency, whether manufacturing small-diameter medical microtubing or large-bore industrial hoses. Customization options allow producers to meet diverse application requirements ranging from chemical transfer hoses to high-purity water lines. American Kuhne’s solutions are scalable, integrating seamlessly with downstream take-offs, cooling baths, laser inspection, and automated winding systems.
When considering which nylon tubing production equipment to invest in, it’s essential to prioritize machines that align with your desired tubing specifications, raw material needs, production volume, and compliance standards—such as FDA, USP Class VI, or ISO 9001 certifications for regulated industries. For the most current information on the top nylon tube extruders and suppliers in the United States and Canada, we recommend consulting directly with equipment manufacturers, extrusion experts, and authorized distributors. This ensures you have access to the latest advancements in extrusion technology, tailored recommendations for your specific application, and reliable ongoing support for your nylon tubing manufacturing operations.
Nylon tubing, also known as polyamide tubing, is available in a wide range of types engineered to meet diverse industrial requirements. Variants include high-pressure nylon tubing for demanding fluid transfer, flexible or ultra-soft nylon tubing for tight-radius installations, coiled nylon tubing for retractable applications, Department of Transportation (DOT) approved nylon tubing for brake lines, standard nylon tubing for general use, durable mini nylon coils, as well as specialty formulations like nylon 6 and nylon 66 tubing. Choosing the right nylon tubing type is essential to optimize chemical resistance, flexibility, pressure rating, and long-term performance for specific industrial, automotive, pneumatic, or hydraulic applications.
The most prevalent form of nylon tubing is produced from nylon 6 resin, renowned for its superior moisture absorption characteristics and thus heightened corrosion resistance compared to other grades of polyamide tubing. Nylon 6 is made from a single caprolactam monomer, comprising six carbon atoms— a feature that defines its name. This standard nylon tubing is trusted for applications requiring chemical resistance, rigidity, and low weight, making it a popular choice in the pneumatics and water treatment sectors, as well as for industrial air lines and instrumentation tubing.
DOT nylon tubing is engineered to rigorously meet Department of Transportation (DOT) and SAE J844 specifications for pneumatic and hydraulic brake systems. Manufactured from an engineered polyester-blended polyamide formulation, DOT nylon tubing offers enhanced flexibility, kink resistance, and long-term durability compared to standard grades. As a result, it is especially suited for use in vehicle brake lines, trailer air lines, and over-the-road trucking applications, where safety, reliability, and regulatory compliance are critical.
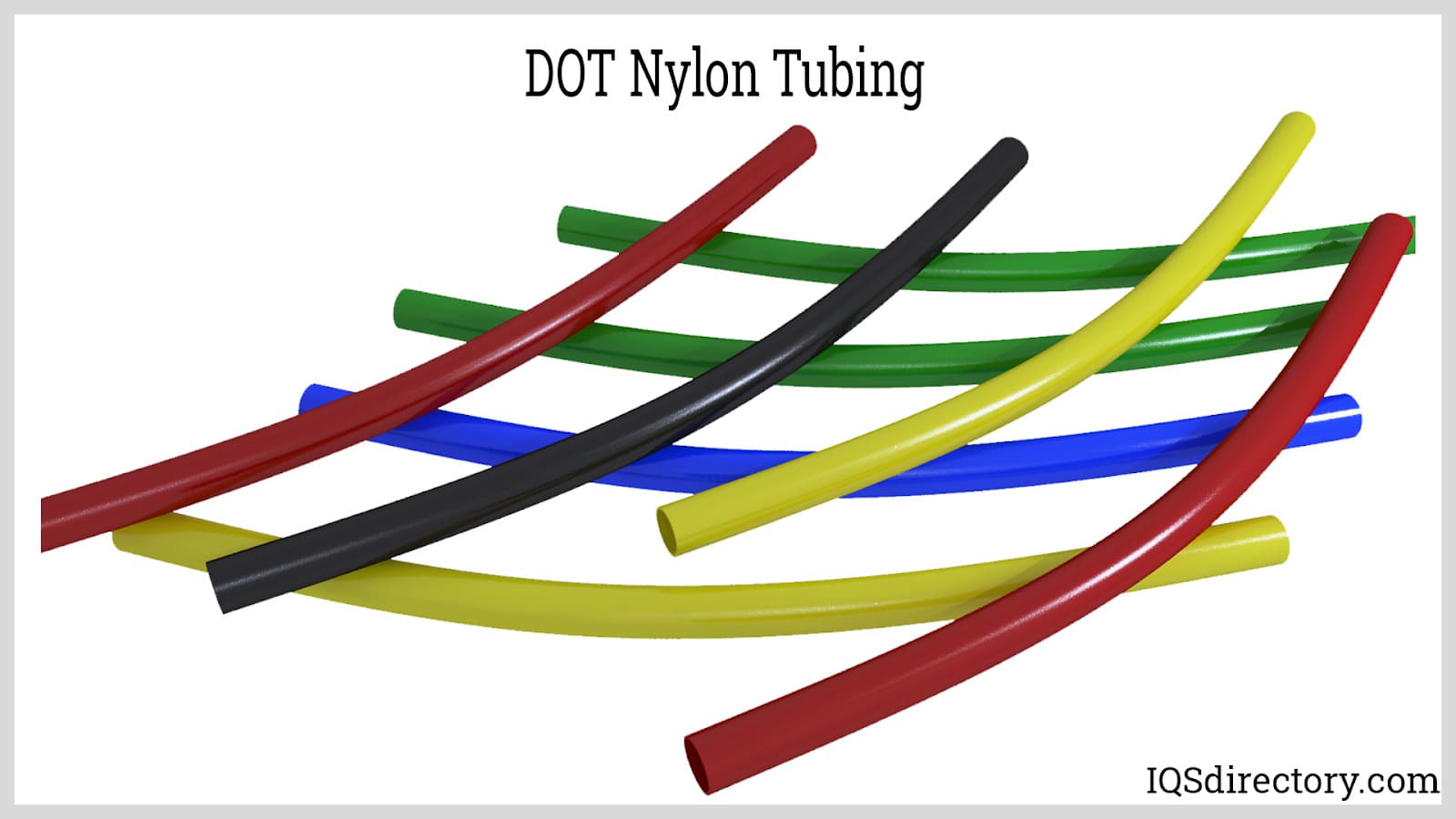
DOT nylon tubing withstands extreme operating conditions, with a typical temperature range of -85°F (-65°C) to over 200°F (93°C). Its lightweight, fatigue-resistant design ensures long service life in automotive pneumatic lines. With excellent dimensional stability, abrasion resistance, and vibration dampening, DOT tubing is a top choice for heavy-duty vehicles, air brake systems, and roadside repair applications alike.
High-pressure nylon tubing is specifically engineered for environments where consistent exposure to aggressive chemicals, hydraulic fluids, alkalis, and certain acids is common. Known for high tensile strength and rigidity, this type of polyamide tubing offers exceptional resistance to abrasion, heat, and vibration. High-pressure nylon tubing excels in maintaining safe fluid and gas containment under temperatures that often exceed those tolerated by standard polymers.

This robust nylon tubing is ideal for applications such as brake lines, hydraulic hoses, pneumatic robotics, vacuum systems, air compressors, and high-pressure gas transfer lines. With pressure ratings typically reaching up to 800 psi, and heat tolerance up to 200°F (93°C), high-pressure nylon tubing is trusted for industrial automation, OEM equipment, and process manufacturing, offering long-term durability, chemical compatibility, and consistent flow characteristics.
Flexible nylon tubing, often called super soft nylon or nylon air hose, is produced from nylon 11 resin. This bio-based material, derived from castor beans, provides enhanced flexibility, kink resistance, and superior mechanical properties. Super soft nylon tubing is also recognized for its excellent chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and durability against impact, abrasion, heat, and moisture, making it highly versatile.

Applications for flexible nylon tubing include fuel and oil lines, pneumatic controls, lubrication systems, gas detection equipment, refrigeration and coolant lines, as well as automation and robotic assemblies. It is frequently chosen as an alternative to polyurethane or PVC tubing when those materials cannot withstand tough environmental conditions. The flexibility, resilience, and low moisture absorption rates ensure reliable long-term operation in both indoor and outdoor installations.
Nylon coils are formed by winding nylon tubing into spiral configurations, creating a retractable tubing solution ideal for environments where frequent extension and retraction are required. Coiled nylon tubing is widely used for compressed air delivery, fluid transfer, and instrumentation where workspace efficiency is crucial. The spring-like memory of the coils allows them to automatically retract, reducing trip hazards and simplifying hose management in production, lab, or assembly settings.
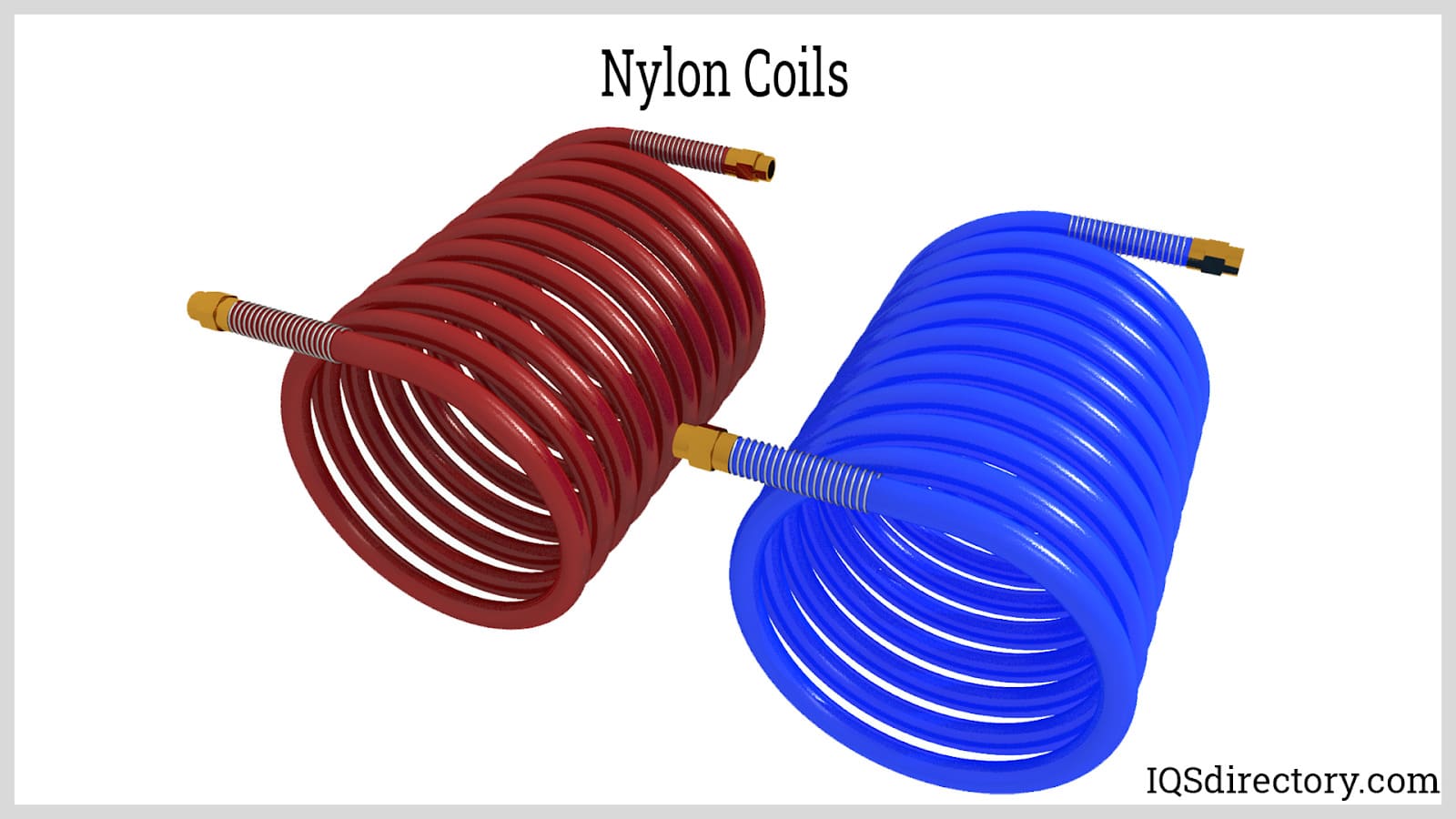
Thanks to their non-marring design, nylon coils are commonly used in automotive brake coils for semi-trucks, as well as in agricultural equipment for livestock feeding and watering. The versatility and space-saving benefits make nylon coils a preferred choice in pneumatic tool supply, robotics, and automated machinery applications.
Nylon mini coils are compact, tightly wound versions of coiled nylon tubing, offering high levels of flexibility, maneuverability, and pressure capability. Featuring pigtails at each end for easy connection to pneumatic or hydraulic circuits, these mini coils deliver the same recoil memory benefits as their larger counterparts, but in a smaller footprint.
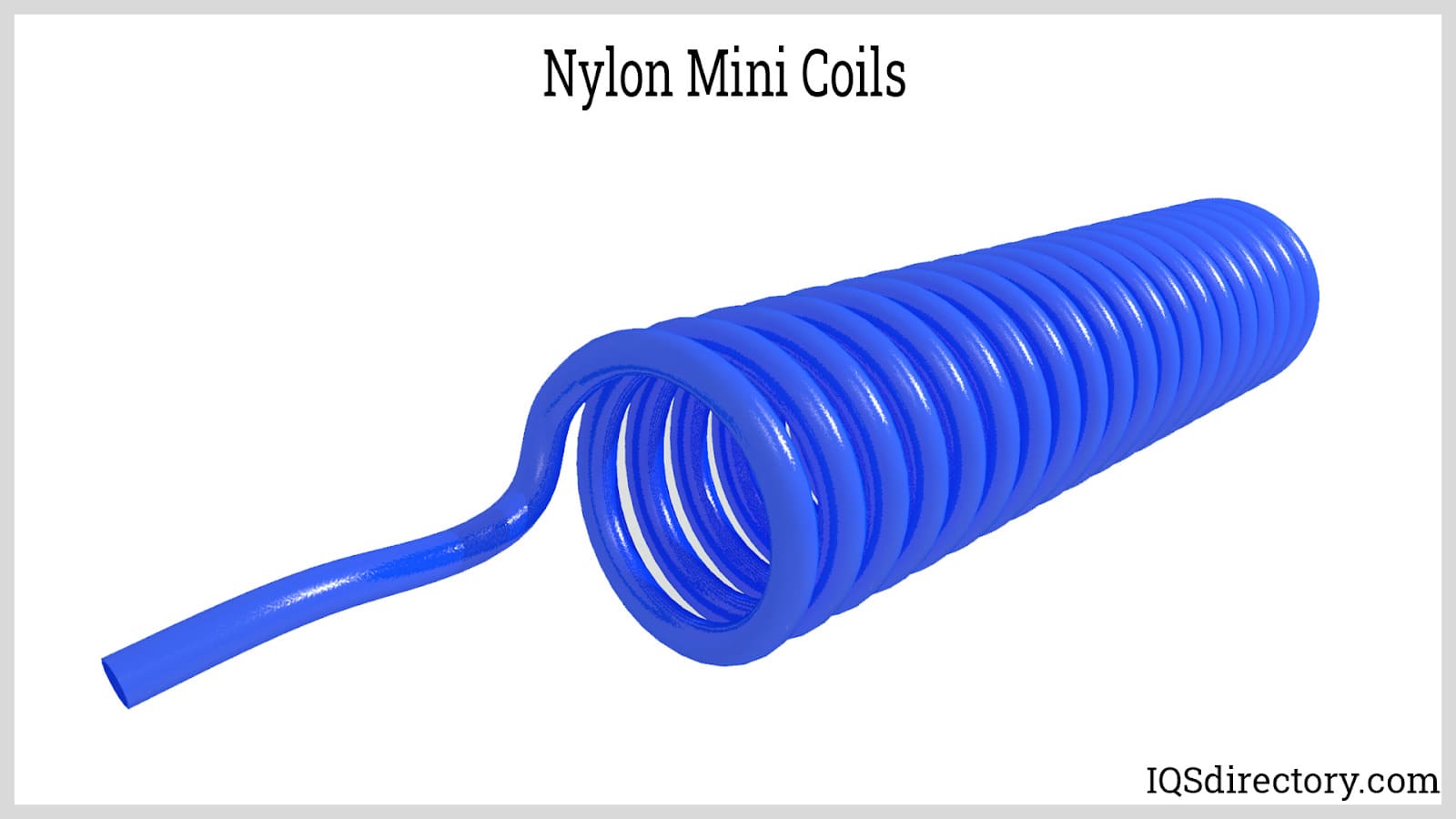
Engineered for high-pressure operation—up to 298 PSI—nylon mini coils are abrasion-resistant and suitable for tight, space-constrained environments. They excel in control circuits, pneumatic automation, robotic arms, laboratory equipment, and compact pneumatic hand tools, offering streamlined routing, easy installation, and reduced risk of kinking or entanglement.
Their coil memory ensures fast, safe retraction to the original shape after extension. Mini nylon coils also provide advantages in motion control, timing circuits, and applications requiring frequent movement without excess slack or tangling.
Nylon 6 and nylon 66 represent two of the most widely utilized types of engineering-grade nylon tubing, each offering unique mechanical and chemical properties. Nylon 6, composed of a single monomer with 6 carbon atoms, provides high stress and impact resistance, lower shrinkage during molding, and ease of color customization. Nylon 66, synthesized from two different monomers, is characterized by a highly crystalline structure, delivering excellent resistance to acids and chemicals, superior heat tolerance, and greater water absorption capacity than nylon 6.
Both nylon 6 and 66 tubing provide essential qualities such as ease of machining, smooth bore for optimized flow, superior electrical insulation, mechanical strength, vibration absorption, fatigue resistance, and durability under x-ray and gamma ray exposure. Nylon 6 tubing finds applications in military and defense, gears, firearms manufacturing, and under-hood automotive components, while nylon 66 tubing is often selected for chemical processing, hot water applications, and environments exposed to harsh acids or elevated temperatures.

Customized nylon tubing is engineered to meet exact project or product requirements, delivering unique performance characteristics tailored for specific industries. Customization options include size, color, wall thickness, reinforcement, multi-layer construction, additives (such as UV inhibitors), and even FDA or NSF approval for food and beverage applications. Custom nylon tubes can be designed to provide precise pressure ratings, abrasion resistance, or enhanced flexibility depending on end-use needs.

Nylon tubing can be manufactured in wide-ranging custom colors, including neon, red, blue, orange, and other shades. Color-coding nylon tubing facilitates visual identification in complex fluid or air delivery systems, simplifies troubleshooting, and supports process safety compliance—an essential consideration in laboratories, manufacturing, and food processing environments.
With custom cutting options, nylon tubing is precision-cut to meet your project's specific length and installation requirements. This promotes accuracy in assembly, minimizes waste, lowers production costs, and ensures seamless integration with push-to-connect fittings or custom-designed connectors.
Custom-coiled nylon tubing maximizes efficiency and minimizes clutter in pneumatic and hydraulic installations. By tailoring coil diameter and retractability, users can optimize hose reach, return force, and fit, ensuring reliable performance over extended service life in both stationary and mobile applications.
Advanced co-extrusion manufacturing enables the creation of multi-layer nylon tubing, blending different polymer materials for enhanced functionality. For example, coextruded nylon tubing can feature a chemical-resistant inner layer with an abrasion-resistant outer layer, enabling use in high-corrosive environments or demanding process lines. This provides versatility, improved durability, and the integration of multiple performance attributes in a single nylon tube.
Formed nylon plastic tubing can replace more expensive injection molded parts in complex assemblies. Custom-formed sections eliminate common problems like space limitations and kinking, and streamline installation for OEMs and system integrators across numerous industries, including automotive, appliance manufacturing, and medical device production.
Bonded nylon tubing consists of two or more color-coded or sized tubes fused together in a flat or round profile. This integrated design streamlines routing, simplifies replacement or line tracing, and eliminates confusion in multi-line pneumatic or hydraulic assemblies. The tubes can be separated quickly, without tools or residue, making changeout fast and efficient.
Nylon tubing can be manufactured from a variety of specialty nylon resins, such as nylon 6, nylon 66, nylon 11, or nylon 12, each imparting differing properties:
Comparing nylon grades ensures that your tubing selection provides the optimal combination of flexibility, durability, stress and impact resistance, chemical compatibility, and thermal performance. By consulting with a nylon tubing supplier or technical specialist, you can specify tubing that aligns precisely with your operational requirements, ensuring safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in your fluid management systems.
Nylon tubing is resistant to abrasion, chemicals, UV rays, impact, and wide temperature ranges. Its flexibility, dimensional stability, and low moisture absorption ensure reliable performance in demanding applications such as hydraulics, pneumatics, and fluid handling.
Nylon tubing is created through plastic extrusion, co-extrusion (multi-material), and pultrusion for reinforced profiles. Secondary processes such as drilling, painting, cutting, and coiling are also applied for customization and specific application requirements.
Nylon tubing types include standard, DOT-approved, high-pressure, flexible (super soft), coiled, mini coils, nylon 6, nylon 66, and customized tubing. Each type is engineered for certain pressure, flexibility, chemical resistance, and industry standards.
Top machines in the United States and Canada include Davis-Standard DSREV Extruder, Conair MedLine® Co-Extruders, Allied Supreme Corp. Nylon Tube Extrusion Line, AET Nylon Tubing Extruder, and American Kuhne Extrusion Lines.
Co-extrusion enables nylon tubing to combine multiple polymers or a metal core, creating multi-layered tubes with specific benefits like increased structural support, reduced oxygen permeation, chemical resistance, or cost-effective material use.
Yes, nylon tubing can be tailored by color, size, wall thickness, reinforcement, multi-layer construction, additives, or forming techniques. This ensures optimal pressure ratings, compliance, and integration for specialized applications.
This chapter will explore the various applications and advantages of nylon tubing.
Nylon tubing is valued for its lightweight and flexible characteristics, making it suitable for a range of applications. It is commonly used in pneumatic systems, including aircraft control mechanisms. Additionally, nylon tubing is employed in automotive fuel lines, refrigerator water lines, and other applications requiring resistance to cracking and heat. In certain cases, nylon tubing can serve as a substitute for metal tubing due to its advantageous properties. Some types of nylon tubing are FDA-approved, making them suitable for use in the food and beverage industry as well.
Nylon tubing is also used in medical technology, aerospace, filtration, irrigation, refrigerants, and laboratories. Nylon tubing has become very useful in industries and some of its application areas include robotics, hydraulic hoses, and fuel lines, in different varieties of vacuum lines, vapor lines, brake lines, air lines, oil processing lines, chemical processing lines, and tool lubricating systems. Nylon tubing can be included in pneumatic systems which make use of compressed air so as to supply power to machinery automatically. Nylon tubing can also be used in printers and agricultural equipment.

Nylon tubing made from nylon 12 polymers exhibits excellent properties, including high resistance to abrasion, cold temperatures, and heat. In the pneumatic sector, its precise tolerance allows for seamless compatibility with push-in and compression fittings.
In the brewery and beverage industries, nylon tubing is used for carbon dioxide gas lines and can withstand high temperatures. It is lightweight, heat-stabilized, and resistant to stress cracking. The advantages of nylon tubing include its strength, flexibility, light weight, resistance to corrosion and chemicals, dimensional stability, and a tight bend radius.
Nylon tubing, also known as polyamide tubing, is a type of tubing made from polyamide resin that has a strong resistance to abrasion and is used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications. The processes of plastic extrusion and plastic co-extrusion are used in the production of nylon tubing. Nylon tubing products are hollow channels made up of solid nylon. This type of tubing is also very versatile, and some of its varieties will not even degrade when used in chemical solutions. Nylon tubing contains UV stabilization, which be handy when they are being used in warmer areas and where there is a direct exposure to sunlight. Nylon tubing is also very flexible and can be used to fit into many different complex designs.

An industrial hose is a durable and precision constructed hose used to transfer and transport liquids, gases, and other materials for industrial applications. They are made of materials that...

Plastic tubing is a form of tubing that is manufactured from a mixture of a polymer with a variety of chemicals to form a material that can be solid or flexible. Since its first use in...
Poly tubing is a highly flexible, lightweight, and durable tubing that is produced from polyethylene, a polymer that is made from the polymerization of ethylene. It is a very versatile form of tubing that has break and crack resistant walls...

PVC is a tough chemically resistant synthetic polymer of vinyl chloride used especially for making pipes, films and electrical insulation. It is made by polymerizing vinyl chloride, and...

Rubber tubing, also known as rubber hose or piping, is made from a combination of natural and synthetic rubber. This versatile material is widely used for transporting and circulating liquids and...
Silicone tubing is a very tough elastomer that exhibits high strength, flexibility, and resistance. Silicone tubing can be stretched without tearing and is highly versatile. It cannot be weakened with repeated bending and twisting due to...
Plastic channels are plastic products that have linear extruded profiles. They have a constant cross-sectional shape across their axis. They are long and narrow structures, and their depth is relatively short. These products serve a variety of functions and uses...
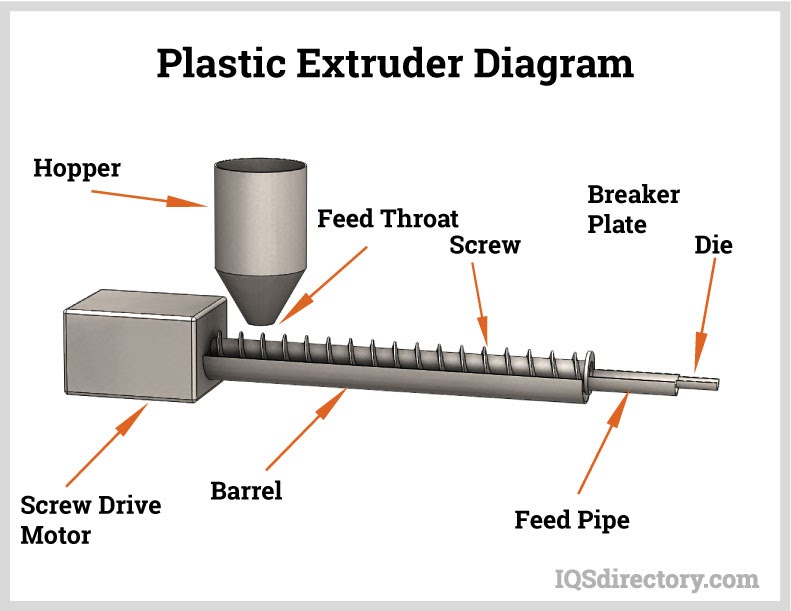
Plastic extrusion, also known as plasticating extrusion, is a continuous high volume manufacturing process in which a thermoplastic material -- in a form of powder, pellets or granulates -- is homogeneously melted and then forced out of the shaping die by means of pressure...

Plastic materials are objects artificially made from organic compounds called polymers along with other additive components. They possess excellent formability, making them extremely versatile for many different fabrication and manufacturing processes...

A plastic tank is a large capacity liquid or granular storage unit that can be vertical, horizontal, below or above ground, as well as movable. They are designed to hold several gallons of a variety of substances for long periods without experiencing wear, weathering, or deterioration...
A plastic rod is a solid plastic shape made by the process of plastic extrusion or plastic co-extrusion. These have a contrast of plastic tubing and hollow plastic profiles. Plastic rods are found in various industries, including...

Plastic trim products are extruded linear profiles that can be made to any length. Because of its ability to attach, hold, and seal, plastic trim has many applications. Plastic, HDPE, LDPE, butyrate, PVC, acrylic, and...

A plastic water tank is a large capacity container designed to store water for household, agricultural, irrigation, and industrial manufacturing use. There are various types of water tanks produced to meet the needs of specific applications, with...

A poly tank is a plastic storage tank used to store, transport, and collect water, other liquids, and granular or powder materials. They are made of polyethylene or polypropylene and are a cost effective, lightweight, and easy to handle...
A coupling is a device that is used to transmit power between two shafts connected together at their ends. Couplings serve one primary purpose: to join two pieces of rotating equipment together, while...