Work Benches
Workbenches and workstations are equipment or furnishings that create an efficient space in which people perform a set of specific duties, whether in offices, plants, or manufacturing processes.
While industrial equipment manufacturers often refer to "workstations" and "workbenches" interchangeably, there is a small difference between the two terms:
In this context, the term "workstation" refers to entire work areas and units. This includes items like assembly tables, chairs, storage benches, racks, laminar flow benches, cleanroom work benches, and office tables. While "workbench" (or work table) often refers to the same items, it more specifically refers to assembly tables, storage tables and lab work tables; “workbenches” focuses instead on work surface areas, as opposed to entire units with furniture, shelving, and storage. Going forward, however, expect to read references to both workbenches and workstations.
Quick links to Work Benches Information
The History of Work Benches
Since they’re based on tables, it’s a little difficult to say when people began using workbenches. However, we do know that they were around at least by 50 A.D., in Rome. Roman workbenches were low (much lower than modern workbenches), thin, and very simply constructed. To use them, workers often had to sit down. Humans continued to use workbenches in one form or another over the centuries, without significant change, until the time of the French workbench of the 17th and 18th centuries, which relied mostly on stops to hold pieces in place.
In the 20th and 21st centuries, workbenches became more ergonomic and mobile. Also during this time, manufacturers began equipping workbenches with electronic elements, like lights and power strips.
Designing Work Benches
Workbenches are produced with work surface areas as the focus. They range widely in dimensions, per their applications, including if workers will be sitting or standing. It’s extremely important that workbenches are able to withstand the loads and everyday rigors of their applications. For that reason, manufacturers sometimes choose to partially or fully weld workstations. For precision, they can use laser welding. At other times, they take a more modular approach, producing workbenches that you can assemble on-site.
The most heavy-duty workbench models are made from stainless steel or heavy-gauge steel. In addition, you can purchase a work bench that features a steel frame and legs, with other components made from other materials. For example, common workbench top materials include plastic laminate, ESD laminate, high-pressure laminate, maple wood, plywood, and particle board. Of course, you can also always get a steel workbench top. Decisions about work bench material are mostly related to the application. For example, for use in a lab, you might consider a stainless steel workbench. This is because stainless steel is corrosion resistant and easily sterilized.
The primary design aspects that go into work bench manufacturing are ergonomics and increased productivity. Workbenches and workstations are ergonomically designed with shelves, reels or laminar flow for the assembly of industrial parts; sometimes, industrial workstations are also designed with units of specialized assembly furniture, like benches, chairs, shelves, and accessories.
With accessories and furniture options like these, the options for custom workbench design are nearly endless. In addition to their physical design features, like adjustable height, workbenches can be designed for applications requiring ultra-sterility, such as lab work or cleanroom environments.
Work Bench Applications
Manufacturers create workbenches to help workers accomplish tasks efficiently. They offer a space for organization and order.
The ergonomic design of workbenches is useful, if not essential, to applications in many different industries. Workers who rely on work areas provided by work bench manufacturers include office workers, call center staff, factory workers, clean room workers, assembly line workers, machinists, operators, and air traffic controllers, among others.
Note: Within the context of industrial manufacturing, workbench applications do not include woodworking or hobbyist projects.
Work Bench Features
As a whole, workbenches are pretty simple. You put things on them; you store things in them; you work at them. However, individually, they work all kinds of different ways. For example, some are manually height adjustable; others allow you to turn a hand crank in order to achieve height adjustment; still, others do not adjust at all. Some work only where they are placed, while others can be wheeled around to new spots.
Workbenches are essentially tables; at first glance, they are not unique. However, the ways in which they can be made unique are too many to count.
Work Bench Installation
Typically, workbenches and workstations, particularly modular workbenches, come with in-depth instructions on installation. If you have questions, ask your manufacturer.
Standards and Specifications of Workbenches
All workbenches, whether it’s a heavy duty workbench or a modular workbench, must meet the standard requirements of OSHA. You’ll also want to make sure that your workbench has been guaranteed with ANSI certification and ISO certification. From there, most requirements relate to your application and industry.
Ways to Increase Productivity
At some time in the past, every office manager has probably recognized that their employees are not working at their fullest capacity or potential. Even the best performing workers seem to be affected by poorly designed workspaces. Employee-engagement activities have not fulfilled the promise of maximum productivity and new and tenured employees are equally stifled by office furniture, lighting, and other environmental factors.
However, a multitude of science-based research has concluded that, by redesigning your office work station, you can not only engage new employees but also reinvigorate the careers of your most loyal staff members.
Setting daily goals for your employees, encouraging them to take frequent breaks, and streaming music throughout the office can achieve short-term gains in productivity. However, broader changes in furniture configuration are a more lasting approach to improving your office culture.
To get you started, here are a few ideas and simple techniques for boosting motivation and improving employee performance.
- Natural Lightening for Employees
- On earth, there is no better and larger source of energy than the sun. If your office configuration does not allow your employees to experience direct sunlight throughout the day, encourage walks outside or even install special lighting to achieve the same effect. Sunrays are a very important source of mood-boosting energy.
- Maintain a Standard Office Temperature
- Temperature also plays a major part in determining the interest level and productivity of staff members. Make sure that your air conditioning units are well maintained and that you employ proper ventilation techniques. Monitor office temperature settings to ensure that all workers enjoy a constant temperature.
- Play Music
- Some people are motivated by music or other background noise when working in an office setting. However, if you choose to stream constant music to your base of employees, take their preferences into consideration and avoid music containing a lot of dialogue or other distracting elements.
- Feng Shui or Vastu
- Feng Shui is Chinese and Vastu is from India. Both of these ancient arts (based on science) have proven mood enhancing properties. Most modern furniture design firms can incorporate Feng Shui and Vastu principles as an added measure of employee engagement.
A Note on Choosing Your Manufacturer or Supplier
You will find that there are many companies that can offer you workbenches, and that, thus, it is hard to discern between them. Our advice? Go with a company that makes you their number one priority. Find the supplier that demonstrates respect for your timeline, budget, requirements, and restrictions. The right manufacturer for you isn’t the manufacturer with the most accolades, but rather the one with the best customer service record. Find the one by browsing those companies we have listed near the top of this page.
Accessories for Work Benches
Workbench manufacturers offer so many accessories; you can be sure that they have what you need. Some examples of common and sought-after accessories include drawer units, cabinets, casters, workbench software, adjustable shelf units, power outlets, lights, integrated electrical components, privacy screens, locks, footrests, and more. Any of these accessories may be of use to you, depending on your application. To get the best workbench for your application, discuss your specs and preferences with your supplier at length.
Work Bench Images, Diagrams and Visual Concepts
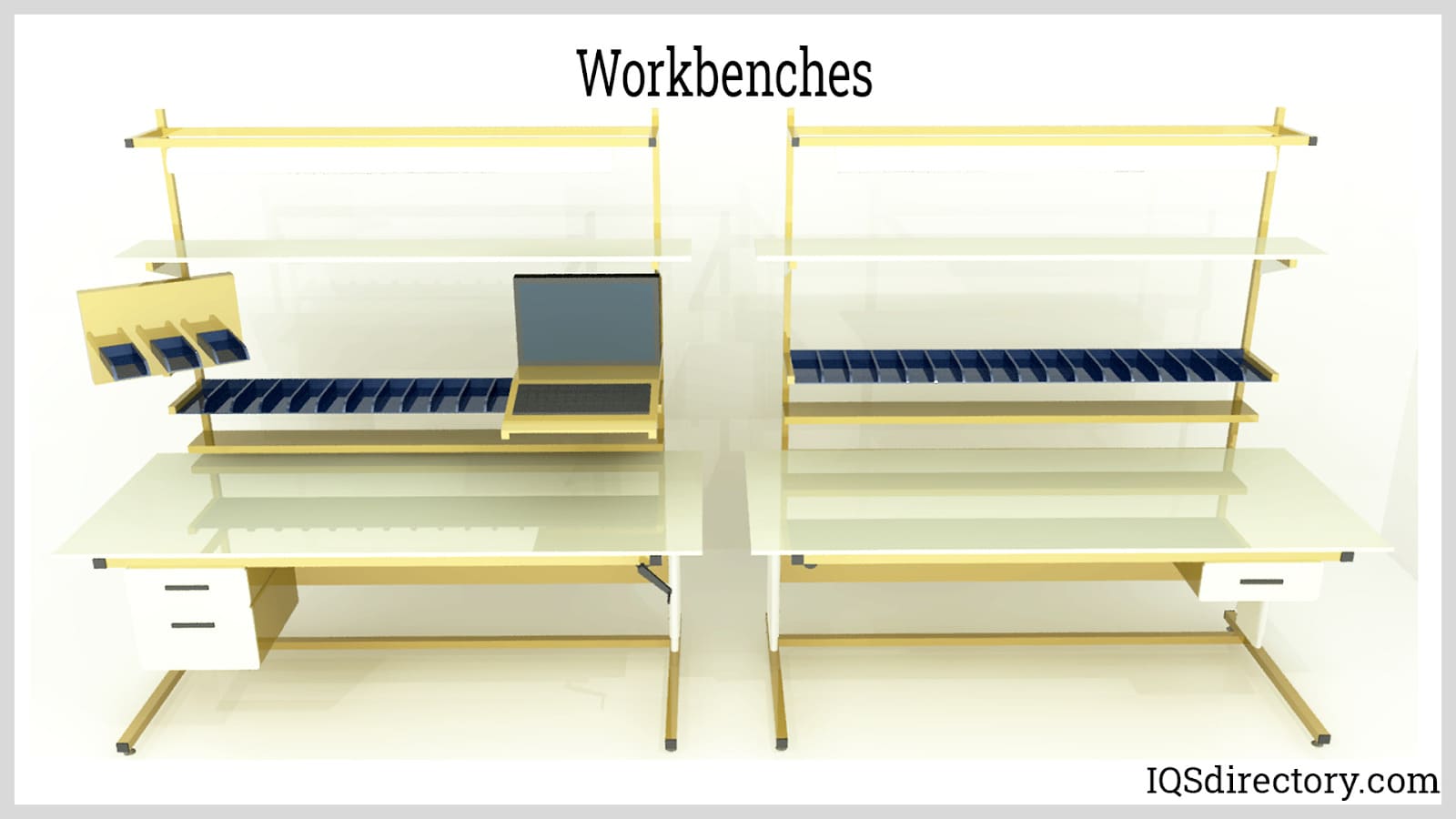 A sturdy flat, smooth, molded surface which comes in a variety of sizes and designs.
A sturdy flat, smooth, molded surface which comes in a variety of sizes and designs.
 An adjustable work bench that allows the user to adjust and regulate the height of the workbench.
An adjustable work bench that allows the user to adjust and regulate the height of the workbench.
 Easier access increases efficiency and productivity.
Easier access increases efficiency and productivity.
 Electric availability allows for the operation of tools, testers, monitoring equipment, and electrical components.
Electric availability allows for the operation of tools, testers, monitoring equipment, and electrical components.
 Moisture control depents on the useage of the workbench, if the components are susceptible to humidity.
Moisture control depents on the useage of the workbench, if the components are susceptible to humidity.
 Laminate is an all purpose surface that is designed to be exceptionally smooth that does not trap dust, dirt, oil, or chemicals and is nonconductive, resistance to oil, stains, and diluted chemicals.
Laminate is an all purpose surface that is designed to be exceptionally smooth that does not trap dust, dirt, oil, or chemicals and is nonconductive, resistance to oil, stains, and diluted chemicals.
 ESD laminate tops are designed to be durable, resistant to humidity and abrasions, and compliant with ESD standards.
ESD laminate tops are designed to be durable, resistant to humidity and abrasions, and compliant with ESD standards.
Work Bench Types
- Adjustable Workbench
- You can, for example, alter adjustable work benches in order to fit the needs of the workers, changing the height of work benches desks, chairs, and in some cases, desk drawer units, cabinets, and keyboard platforms.
- Cantilever Workbench
- A work bench designed with a rigid rear steel panel and a rigid front beam. These heavy duty industrial workbench features are meant to strengthen the structure of the workbench, which is typically used in warehouses and material handle and storage facilities. In addition to individual workbenches, there are many workstation assemblies available in conjunction with them. These include modular workstations, computer workbenches, command operation centers.
- Command Operating Centers
- Common in information technology fields, accommodate technological equipment for organizing computer and electronic equipment, including display monitors, keyboards and processors, in a readily accessible structure.
- Computer Workbenches
- Encompass a wide range of products including equipment, furnishings and accessories used to create practical and efficient work spaces for industrial and personal computer use.
- CPU Holders
- Workstation accessories which are often primary components of computer workstations, keeping valuable central processing units up off the floor, away from dust, dirt and damage and providing easy, ergonomic access to workers and technicians.
- Ergonomic Workstations
- Consist of furniture that can be adjusted to overcome repetitive strain injury, carpal tunnel syndrome and musculoskeletal disorder, which can be caused by uncomfortable and static workstations. Adjustable ergonomic workstation designs conform to special needs.
- Industrial Workbenches
- Sturdy tables used in the construction and repair of industrial products and have adjustable shelves, drawers and height. Workbenches are common in the woodworking and automotive industries.
- Industrial Workstations
- Accommodate a variety of industrial applications, including shipping and receiving, packaging and mail sorting. Industrial workstations, which improve organization and efficiency, are available in a variety of setups containing drawers, shelves and side tables.
- Lab Furniture
- Includes the various pieces that are used in laboratory work stations.
- Lab Workbenches
- Often simply called a lab bench, is a work table that provides the space and surface to conduct tests and procedures, store lab equipment, and create workstations for technicians or students in a scientific laboratory.
- Metal Workbenches
- Provide a rugged, durable and efficient space where multiple or specific tasks may be carried out in industrial, commercial and residential environments.
- Modular Workstations
- Or cubicles, have components that can be rearranged into different configurations.
- Mobile Workbench/Mobile Workstation
- Also known as mobile workstations or portable workbenches, are movable, task-oriented workbenches. They can be adapted to new applications and surroundings, and ensure practicality and efficiency.
- Modular Workbench
- Contain components that can be rearranged. Modular shelves, drawers, and cabinets can be situated in various configurations to suit the needs of workers.
- Modular Workstation
- Equipped with adjustable shelves, tables, and bins which workers can arrange to optimize their work space. Like the portable workbench, modular workstations ensure practicality and efficiency.
- Packing Tables
- Workstations or workbenches for packaging products for shipping or distribution; packing tables have various features and accessories to speed workflow while maintaining an ergonomically safe working environment.
- Packaging Tables
- Packaging tables and assembly tables are a type of industrial furniture, created for the purpose of increasing the speed and quality of processes of the same name. In this context, the first of these two processes, packaging, may be defined as the coordinated system of readying goods and products for transport, warehouse storage, logistics, sale and end use.
- Portable Workbenches
- Non-stationary, task driven workspaces designed to provide efficient and mobile units in a variety of industrial, commercial and residential environments.
- Shipping Tables
- Used in distribution centers as workstations for packaging, labeling and shipping products. Tables may have adjustable features and ergonomic design for safe, efficient workflow.
- Steel Workbenches
- Task driven workspaces made of a number of steel alloys and designed to provide a rugged, durable and efficient work environment in industrial, commercial and residential settings.
- Technical Furniture
- Creates a workstation that is able to hold large amounts of computer and electronic equipment and is sturdier than regular office furniture.
- Tool Benches
- Come in a variety of sizes and styles, but they usually have a large surface that you can use to work on projects and set up equipment. The most convenient feature of a tool bench is that it has built in storage compartments like cabinets, drawers and shelves where tools and other important instruments or parts can be organized and securely locked up.
- Work Stations
- Spaces designed for specific tasks.
- Workshop Benches
- Useful in a variety of workshop settings where you need to set up equipment, put the finishing touches on a project, or work something that involves lots of tools. Because workshop benches come in a wide variety of sizes and styles, you can easily find one that meets your needs.
- Workstation Furniture
- A broad category that includes all furnishings, such as seating, tables and cabinets, needed and implemented in a given work area to promote organization, safety and productivity in industrial, commercial and domestic occupational environments.
Work Bench Terms
- Anthropometry
- The study of the relative measurement of bodily dimensions, including height, weight, and girth; these measurements are considered when analyzing workstations.
- Anti-Fatigue Mats
- Cushioned padding that reduces strain placed on legs and feet during standing.
- Biomechanics
- The study of the effects of biology and movement on the human body. Particular attention is paid to muscular movement.
- Bursitis
- Inflammation of the bursa, small lubrication-secreting sacs located between bones and tendons, caused by overexertion.
- Carpal Tunnel
- The fibrous tunnel that runs through the wrist, or carpal, bones, carrying necessary tendons to the hand.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- A repetitive strain injury (RSI); Common symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome include numbness, burning, tingling, and wrist and hand pain. The disorder afflicts those who use their wrist in repetitive actions on a regular basis, including typists, computer workers and some sports players and musicians.
- CPU Holder
- A sliding, swiveling bracket used to hold computers' central processing units in order to maximize workspace utility and to provide easy, ergonomic access to CPU ports.
- DeQuervain’s Tenosynovitis (DeQuervain’s Disease)
- A repetitive strain injury (RSI) caused by inflammation of the tissues surrounding tendons on the radial side of the wrist. Like carpal tunnel syndrome, this disorder affects those who use their wrists repetitively; the disorder can be treated with splints, medication, cortisone injections and in advanced cases, surgery.
- Engineering Controls
- Any physical alteration of a production facility including workstations, equipment or other applicable parts of the work area to lower or avert risk factor exposure
- Epicondylitis
- A form of tendonitis of the elbow caused by overstressing the joints in the elbow. Symptoms include pain during various wrist and arm movements, and treatments include cold and heat therapy, braces, massage therapy, steroid injections and laser treatments.
- Extension
- The stretching of a joint, usually through straightening.
- Median Nerve
- The main nerve running down the arm into the forearm. The median nerve is responsible for supplying the hand with feeling and movement.
- Musculoskeletal System
- The system containing bones, tendons, muscles, ligaments and cartilage.
- Nerve
- Fibers that transmit signals or impulses between the brain and body parts; these impulses direct feeling and movement of the body.
- Neutral Position
- The bodily position in which muscles remain relaxed, not stressed. During extended activity, neutral positions decrease the likelihood of strain and injury.
- Pacing
- Regulating the workers movement rate through various work environment methods, such as pay inducements, peer pressure or production pressure, a continuously moving conveyor at a constant speed.
- Redesign
- This refers to both an alteration to current production equipment of workplaces to render them appropriate for additional workers, or, a reassessment of the patterns of occurrence of tasks. The redesign is more costly to implement than the integration of ergonomic standards in the preliminary job design.
- Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
- Also referred to as Cumulative Trauma Disorder (CTD), this is a term given to disorders resulting from the overuse or misuse of a group of muscles.
- Static Loading (Static Exertion)
- Exertion whereby the same stance is maintained throughout the duration of the action.
- Tendon
- Body part responsible for connecting muscles and bones as well as relaying movement from muscles to bones.
- Tendonitis
- Inflammation of the tendons; usually occurs in conjunction with tenosynovitis.
- Tenosynovitis
- Inflammation of the protective coverings guarding the tendons.
- Trigger Finger
- Inflammation of finger tendons that causes the finger to stick in a particular position. Trigger finger is caused by overuse or misuse of the tendons.