Broaching
Metal production encompasses operations aimed at reshaping metals to meet product specifications. Central to these methods is cutting, a process far more intricate than mere sizing of metal pieces. Metal cutting encompasses diverse operations aimed at removing excess material from a workpiece to meet precise design specifications. These operations utilize specialized machines engineered for efficient and accurate performance.
Various cutting processes such as broaching, CNC machine cutting, expanded metal processing, laser cutting, stamping, etching, and perforation shape metals to meet specific application requirements, ensuring efficient and precise operations.
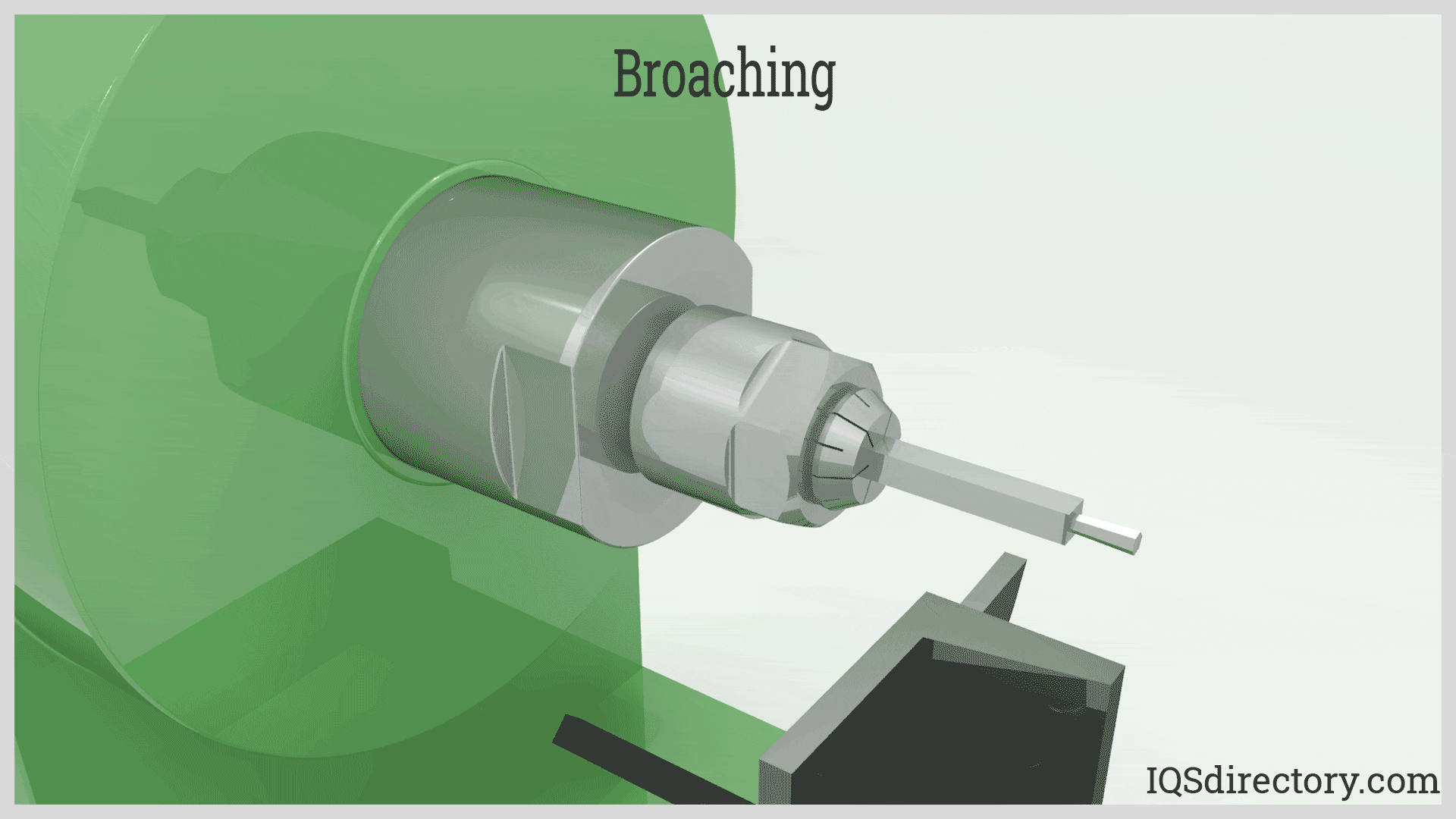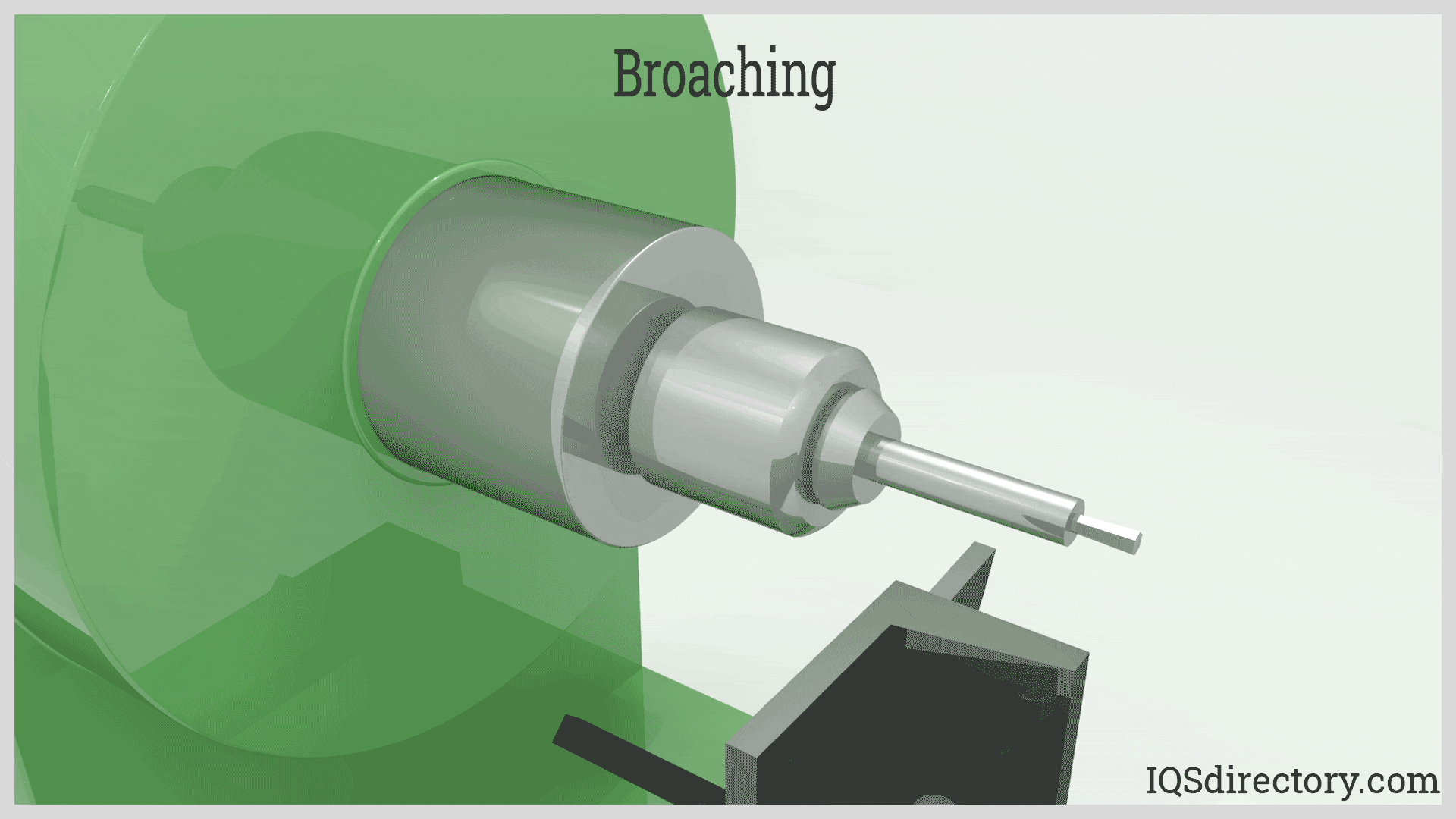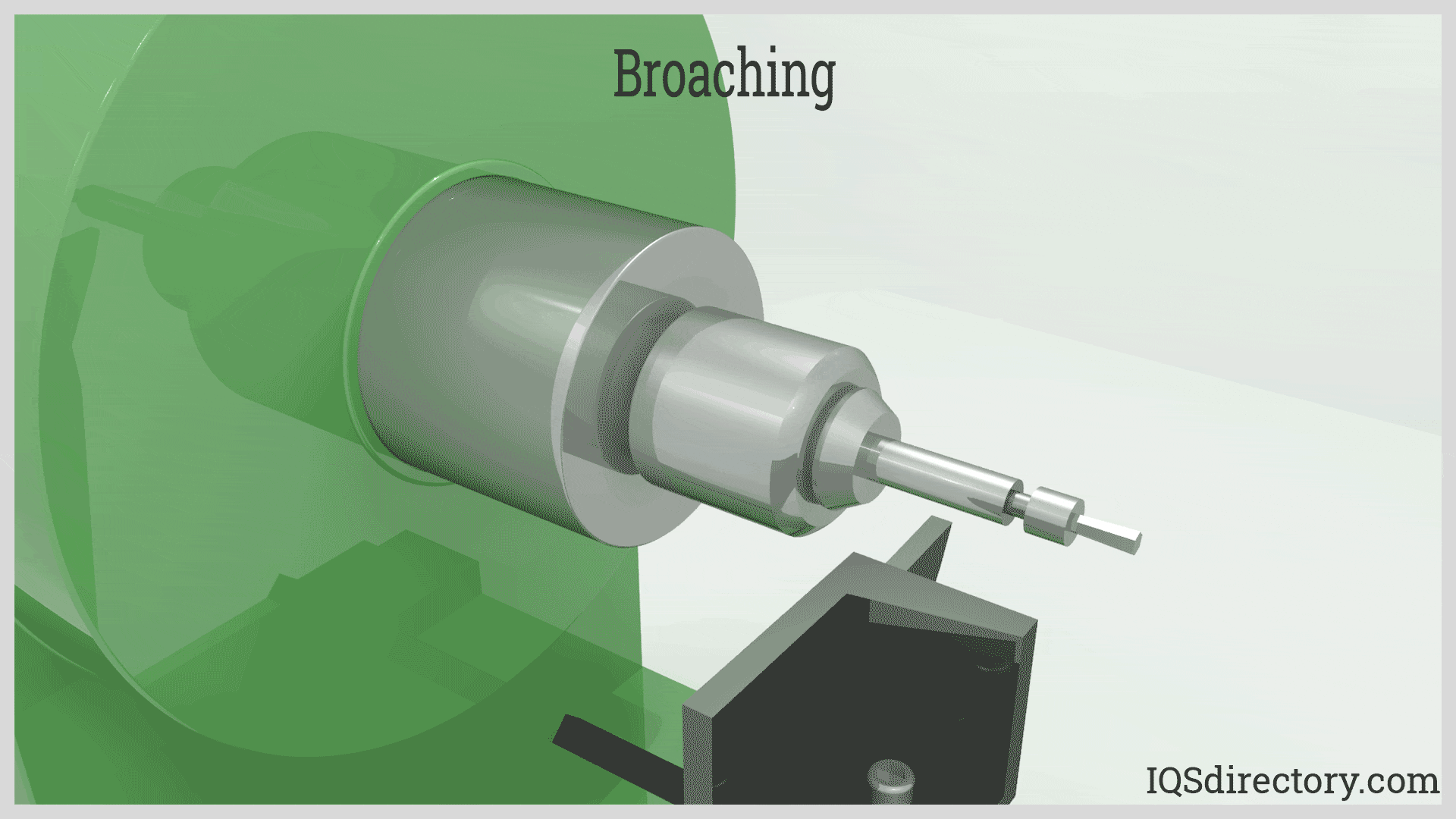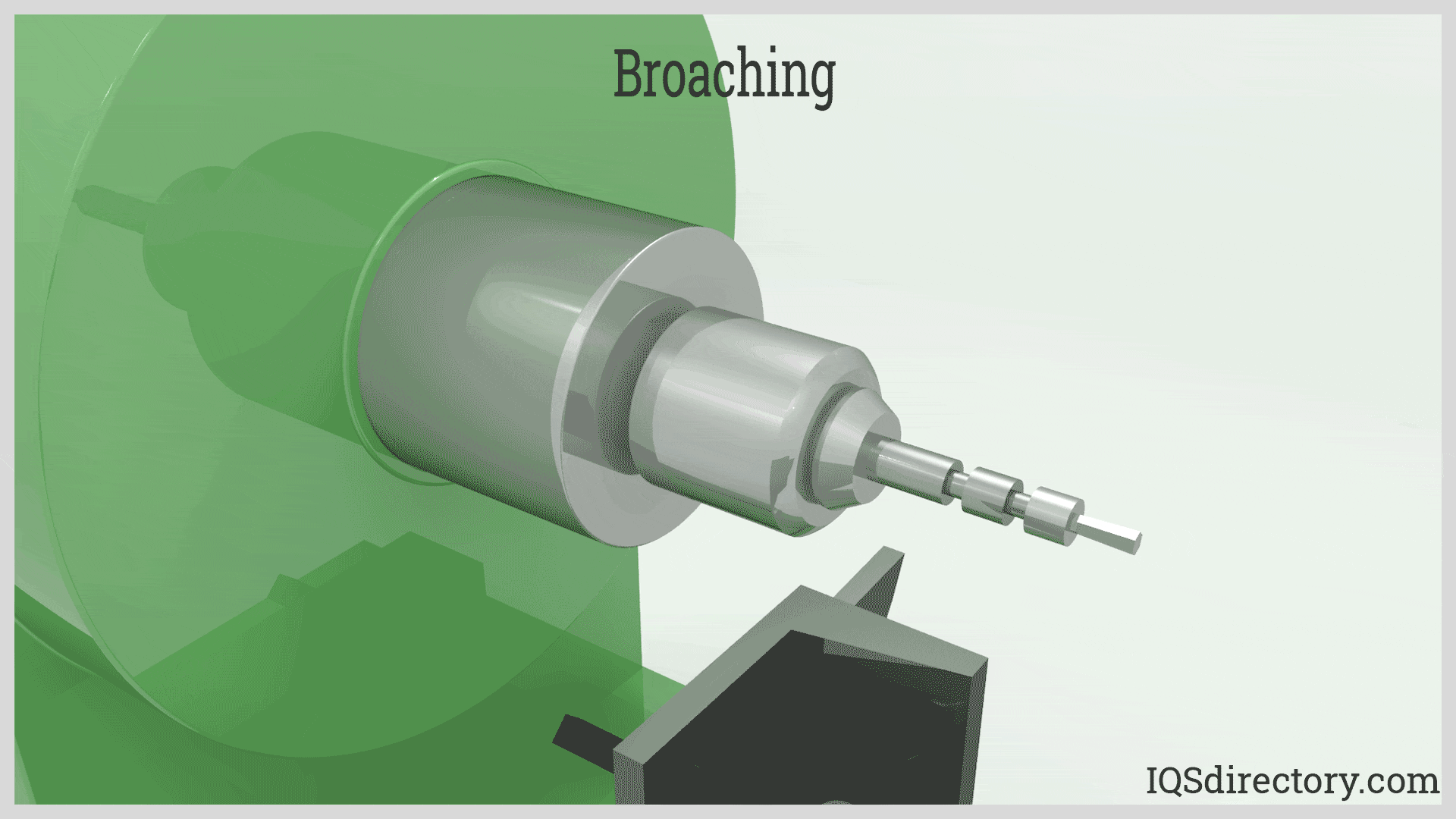
Broaching efficiently removes material using a sharp toothed broach. It involves two types: linear, which moves directly against the surface, and rotary, where the broach rotates during operation. Products made through broaching include gears, fasteners, threading, pulleys, sprockets, and bushings. Broaching can be applied to a wide range of materials, including plastics, copper, and various grades of steel, offering versatility in manufacturing.
CNC processes are employed for a diverse range of manufacturing functions, prominently including cutting. The method offers significant advantages through direct programming of machine instructions, ensuring swift and efficient cutting operations across various types.
The expanded metal process is a distinctive method for metal cutting. Metal sheets or coils are expanded to form a mesh, which is then cut with a knife to create specific designs. This process involves simultaneous stretching and cutting of the metal to achieve the desired mesh design.
Laser cutting is typically integrated into CNC processes due to its exceptional precision and accuracy, achieving exacting tolerances. "Laser" stands for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation," referring to the highly focused beam used. CNC programming further enhances the precision of laser cuts, ensuring near-flawless results.
Metal etching is a creative method for shaping metal surfaces into designs, shapes, or patterns through the use of grooves and fine lines. Techniques vary and may involve chemicals, acids, stamping, photofabrication, water jet cutting, and lasers. When executed by skilled craftsmen, metal etchings achieve high precision and a smooth finish.
Metal fabrication encompasses various processes aimed at shaping, configuring, transforming, and manipulating metals. Cutting is a crucial aspect of these processes, essential for sizing and shaping pieces during fabrication.
Similar to etching, stamping alters metal surfaces to create designs or patterns. Unlike etching, stamping employs diverse processes such as cutting, bending, drawing, and blanking, each requiring specific tools or dies. A key advantage of stamping is its capability to swiftly and efficiently manufacture finished products.
Stamping, akin to etching, transforms metal surfaces into designs or patterns using a variety of processes including cutting, bending, drawing, and blanking, each utilizing specific tools or dies. Its significant advantage lies in the ability to efficiently produce finished products with speed and precision.
Perforating is a process similar to expanding but does not involve stretching metals to create patterns. Perforated metal serves various purposes, from decorative pieces to protective covers for machines. This process involves punching metal sheets with force to create uniquely shaped holes.
An advanced and highly precise machining process is the Swiss screw machine, which efficiently removes excess material from parts by rotating them against cutting tools. This method is renowned for its precision and has become essential in modern metal production.
A fundamental aspect of metal fabrication involves shaping and manufacturing tubes into a diverse range of diameters, sizes, and lengths. Tube fabrication includes processes such as bending, enlarging, and cutting tubes from various metals to create parts, components, and products.
Water jet or hydro cutting utilizes high-pressure water to remove excess material from metals. This process incorporates various abrasives to enhance cutting efficiency. Known for its exceptional accuracy and precision, water jet cutting is widely favored in manufacturing.
Broaching is a cost-effective method for precision metal removal that can cut nearly any material, although it is commonly used for softer metals. It is utilized to cut external (flat, round, or contoured) surfaces and internal features such as splines, gears, sprockets, keyways, slots, or serrations. Broaching operations are typically carried out in specialized job shops.
Broaching primarily serves the industrial sector, producing items such as gears, threaded fasteners, pulleys, sprockets, wrenches, and bushings. Materials commonly broached include copper, aluminum, brass, various steel grades, plastic, and wood.
Learn more about broaching.
CNC machining is a manufacturing process that employs specialized computer programs to automate the design and production of highly precise parts across various industries.
CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control, encompassing a variety of manufacturing processes used to efficiently produce large or small volumes of precise, identical parts throughout the production process.
Learn more about cnc machining.
Expanded metal encompasses all metals or alloys that have undergone a machining process where a sheet or coil is cut and drawn simultaneously to form an open grid pattern. This method is an economical alternative to perforated metals, producing no waste since the material is slit, not punched. Additionally, it requires fewer raw materials as each component can be stretched up to ten times its original length.
Learn more about expanded metals.
Laser cutting is a low-distortion, hot cutting process primarily using a CO2 laser to cut materials, typically metals. "Laser" stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. The laser beam is an extremely focused radiation wavelength, preventing dissipation like conventional light beams.
Laser cutters are often controlled by precision programs that direct the cutting process with minimal human intervention. These programs obtain machining details from CNC systems using CAD designs.
Technicians may also use an "assist gas," such as nitrogen or carbon dioxide, with laser cutting to prepare newly cut surfaces for painting or corrosion resistance coating. CO2 laser cutting, a gas assist technique, is currently considered the most powerful wave laser globally.
Learn more about laser cutting.
Metal etching, also known as metal engraving, involves creating grooves, fine lines, or designs on metal parts or sheets. This can be achieved through various methods, with the most common being mechanical machining, chemical machining, or acid etching.
Today, metal etching is primarily performed using chemical machining, mechanical machining, or acid etching. Additional techniques include photo etching (photofabrication), stamping, water-jet cutting, laser engraving, electro discharge machining (EDM), and mechanical milling. Laser etching is preferred for its precision and minimal need for touch-ups. EDM achieves tight tolerances by exposing the metal to streams of corrosive electromagnetic discharge. Post-etching, manufacturers can smooth or polish the metal to remove any imperfections, burrs, or marks.
Learn more about metal etching.
Metal fabricators are companies that transform metals into usable products, encompassing a wide range of metalworking processes. Common fabrication techniques include metal bending, welding, stamping, and punching. Fabricated metal parts are typically made from pre-processed metals rather than raw, unprocessed materials. Standard raw materials used by metal fabricators include plate metal, tube stock, formed and expanded metal, welding wire, welding rod, and castings.
While virtually any metal or alloy can be used to create a part or product, materials like steel, stainless steel, and aluminum are more commonly utilized. Other frequently used metals in fabrication processes include bronze, brass, and titanium.
Learn more about metal fabrication.
Metal stamping is a metal forming method that uses a press to shape sheet metal into a tool or die. It can incorporate other processes like bending, drawing, blanking, and cutting. Utilizing various tools and dies, metal stamping can produce a wide range of metal products. This process is ideal for manufacturing large quantities quickly and efficiently at a low cost, with parts that are repeatable and capable of achieving precise tolerances.
Learn more about metal stampings.
Perforated metals are produced through a metal stamping process that creates patterns of holes in sheet metal. Various metals, including steel, aluminum, brass, and titanium, can be perforated for diverse applications such as structural, design, and filtration purposes. Lightweight metals like aluminum are often used for decorative purposes, while perforated steel is commonly utilized for architectural support. Perforation patterns vary, with options such as staggered and straight patterns, and holes come in multiple shapes and sizes.
Learn more about perforated metals.
Specialty screws and fasteners are often produced using screw machining, or Swiss screw machining. However, turned parts play pivotal roles across various industries, serving as precision medical tools, automotive components, laboratory instruments, electronics parts, appliance elements, military components, and more. These applications typically demand precise turning and machining processes for their construction.
Learn more about screw machine products.
Sheet metal refers to thin, broad sheets of metal typically used as a base material in various industries including aerospace, automotive, communications, computing, construction, electronics, food processing, military, and pharmaceuticals.
The transformation of sheet metal into finished products is known as sheet metal fabrication. This process involves numerous techniques such as bending, drawing, flanging, punching, shearing, spinning, and stretching. Each method aims to produce durable, high-quality parts and products while optimizing material and labor efficiency.
Learn more about sheet metal fabrication.
Tube fabrication, also known as pipe fabrication, employs diverse techniques to shape, bend, enlarge, and cut tubes of various sizes and metals for manufacturing parts, components, and consumer products. Tubes fulfill various functions such as containment, support, transportation, and protection. Although tube fabricators typically do not form raw metal into tubes, their services are crucial in the overall manufacturing process of tubes and pipes.
Trained engineers utilize specialized equipment such as swaging machines, mold bending tools, hydraulic tube benders, and CNC mandrel bending machines for tube cutting, flaring, swaging, and bending processes. These techniques are critical for enhancing tubing strength and preventing material distortion.
Learn more about tube fabrication.
Water jet cutting is a subtractive manufacturing process that shapes new forms or refines existing ones. This method provides manufacturers and fabricators with a resource-efficient alternative to traditional hot-cutting techniques such as laser and plasma cutting. Water jet cutters excel in accurately shaping intricate designs from metals, plastics, and in some cases, glass and ceramics.
Waterjet cutting services cater to a diverse clientele spanning aerospace, automotive, communications, food processing, and industrial equipment manufacturing industries, alongside lumberyard workers and artists. This method is favored for its ability to produce clean cuts without burrs or imperfections, unlike traditional blade cutting processes. Moreover, as a cold-cutting technique that avoids heat-induced risks such as warping, discoloration, and related damage, waterjet cutting is highly valued across these sectors and beyond.
Learn more about water jet cutting.