Aluminum Forging
Aluminum forging is a method for processing aluminum alloys using pressure and heat to form high strength, durable products. The process of aluminum forging involves pressing, pounding, and...
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
This Article takes an In-depth look at Forging
You will learn more about topics such as:

Forging is an ancient metalworking practice with two primary forms: hot and cold forging. Hot forging dates back several centuries, whereas cold forging became prevalent during the Industrial Revolution of the 19th century. Despite the differences between these methods, they both aim to reshape metal into desired forms. The decision to use hot, cold, or warm forging depends on the metal type and the intended product's final shape.
In hot forging, metal is heated well beyond its recrystallization temperature threshold. This temperature varies depending on the metal: for steel, it's up to 1150° C; for aluminum alloys, 360° C to 520° C; and for copper alloys, it ranges from 700°C to 800°C. Keeping the metal's temperature above its recrystallization point is crucial, as falling below this point can lead to the formation of tiny crystals that strain hardens the material, rendering it challenging to work with.
Environmental conditions can impact the hot forging process, as exposure to the atmosphere can lead to oxidation. To mitigate this, forging may occur in an environmentally controlled chamber or through isothermal forging, akin to forging under vacuum conditions.
A key advantage of hot forging lies in its ability to enhance the metal's strength. Hot-forged metals, known for their excellent ductility, can be extensively deformed and reshaped, enhancing their resistance to tensile stress. The process optimizes the internal grain structure of the metal, thereby boosting the final part's strength and structural qualities.
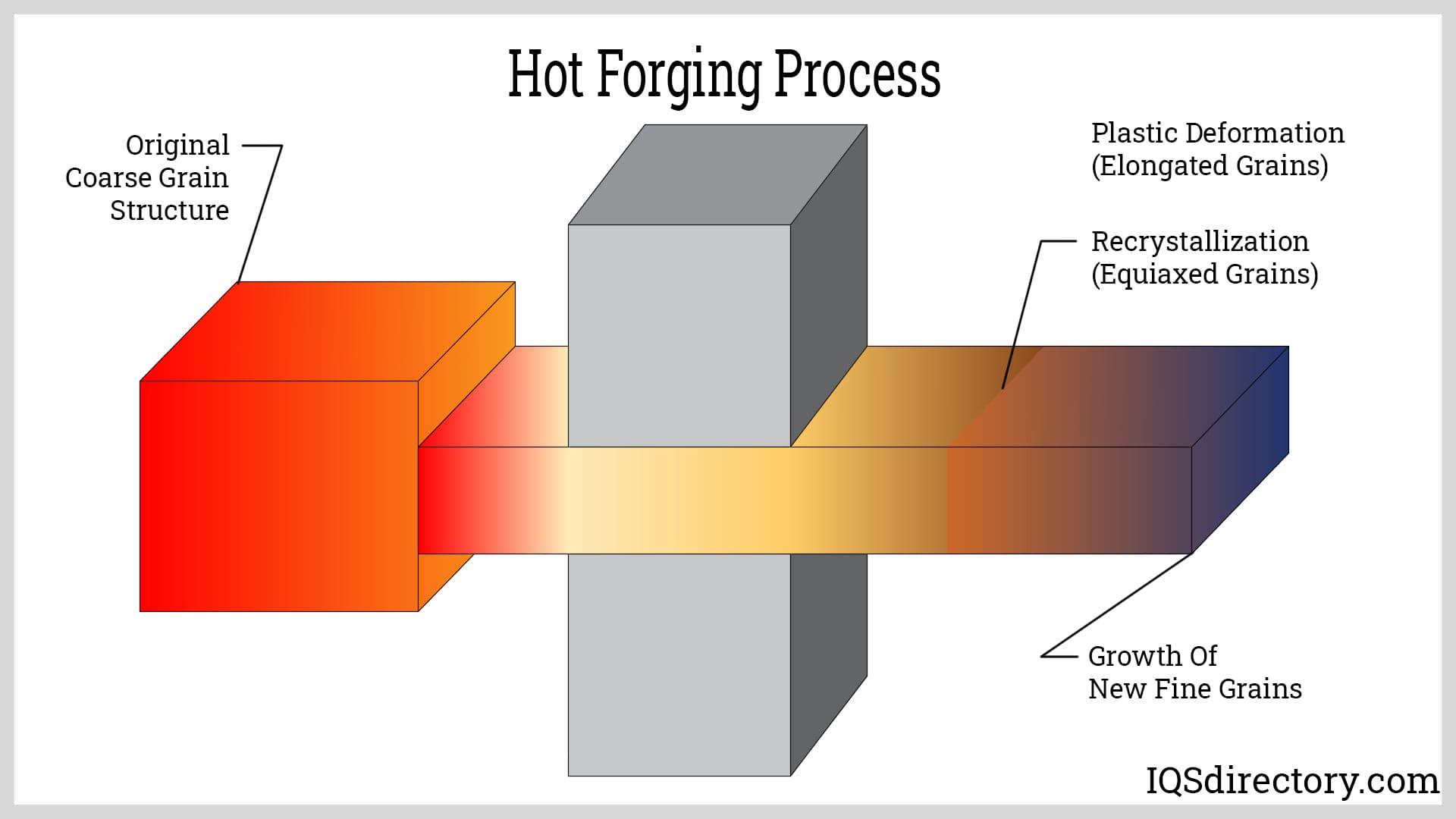
Various parts and components are produced using hot forging due to its capacity to create complex shapes with high precision. It's particularly suitable for metals with high formability, which can be readily deformed. The metal's strength and durability increase post-hot forging, which is versatile enough for crafting customized parts. Moreover, hot forged components boast superior surface finishes compatible with a range of finishing and polishing techniques.
The hot forging process offers numerous benefits, including efficient production of individual parts, albeit with somewhat lower precision compared to other methods. While it can lead to scale formation on metal surfaces, it also reduces metal stress with diminished work hardening temperatures. Additionally, it fosters uniform grain structure, boosts ductility, and addresses chemical inconsistencies in the material.
Despite the many advantages of hot forging, some drawbacks must be taken into account. During the cooling phase, there is a risk of metal warping and brittleness. Some metals are not suitable for hot forging due to potential variations in grain structure and less accurate tolerances.
Though there are a few limitations to hot forging, it remains highly effective for producing aerospace components and aircraft parts. The process enhances the malleability of metals, facilitating the crafting of intricate shapes and detailed designs required in these industries.
Cold forging, also known as cold forming, is an advanced metalworking process in which metal is shaped, compressed, or deformed at or slightly above room temperature. Unlike hot forging, this process operates at temperatures near three tenths of the metal's recrystallization point, resulting in forged components with superior dimensional accuracy and surface finish. Common cold forging techniques include squeezing, bending, shearing, and drawing. Soft, highly ductile metals—such as aluminum, copper, and select carbon steels—are ideal candidates for cold forging due to their ease of deformation and excellent final properties.
The cold forging method utilizes controlled compressive forces—applied either manually or by specialized cold forging machinery—to precisely form the workpiece. Frequently, the metal blank is pressed into a precision die that mirrors the desired final product shape. Compared to hot forging, cold forging offers significant benefits: lower energy consumption, reduced production costs, and finished parts that require minimal to no additional machining operations or surface treatment. For instance, cold forged aluminum parts often undergo subsequent heat treatment—a process known as "tempering"—to optimize mechanical strength and enhance durability.
Among the most widely used materials in cold forging processes are carbon alloy steels, stainless steels, copper alloys, and aluminum alloys. Cold forging is especially valued for mass production of small, high-volume industrial components and hardware fasteners such as bolts, screws, rivets, and nails, as well as precision automotive and aerospace parts. By eliminating the need for high-temperature heating, cold forging significantly reduces manufacturing expenses and improves overall energy efficiency, making it a popular choice for high-volume, cost-sensitive industries.
The specific cold forging technique applied often depends on the metal type, desired geometry, and mechanical properties required for the end product. Below, we outline several prominent cold forging methods, each tailored for distinct part geometries and application requirements.
Impression-die forging, a core cold forging technique, involves placing a metal blank between two dies shaped to the target form. The metal is then impacted by a hammer or press, forcing it to fill the die cavity and form with high fidelity. This approach is ideal for manufacturing complex-shaped components that demand high dimensional tolerances and consistent repeatability. Industrial applications include the production of precision automotive parts, tools, and specialty fasteners.
Also referred to as sizing, squeezing applies controlled pressure to decrease the thickness of metal workpieces while maintaining tight dimensional parameters. The squeezing process can be finely tuned by adjusting force, area, and metal type, making it invaluable for achieving custom thicknesses or precision finishes in finished parts. Squeezing enhances structural integrity and is often used for gear blanks, bushings, and bearing components.
Cold rolling (or cold roll forming) transforms thin sheets of metal, primarily steel or stainless steel, into continuous profiles with superior surface quality and tight tolerances. The process produces a wide range of cross-sectional shapes, such as floor and roof panels, C, U, or Z channel profiles, which can then be galvanized, painted, or powder coated for advanced corrosion resistance and durability. Cold rolling is a preferred process in the sheet metal fabrication and construction industries for producing high-strength, lightweight structural elements.

Drawing employs tensile forces to pull or stretch a metal blank to a predetermined thickness or shape. There are two main drawing processes: sheet metal drawing, suitable for deep-drawn housings or containers, and wire, bar, and tube drawing, which is integral to producing precision-engineered wire products, tubing, and rods required in medical devices, electronics, and automotive components. Drawing requires materials with sufficient tensile strength and ductility. While similar to cold rolling, drawing is distinguished by localized forces and intricate shape control, making it an essential method for manufacturing fine-diameter wires and seamless tubes.
In addition to these common processes, cold forging encompasses a variety of specialized techniques such as extruding, coining, and heading, which are tailored for the production of custom components with demanding specifications. The versatility of cold forging makes it a cornerstone in numerous industries, including automotive manufacturing—where it's used for steering, suspension, brake systems, axles, and chassis parts—as well as aerospace, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment sectors. Manufacturers value cold forging for its ability to deliver exceptional product consistency, high-volume scalability, and environmentally friendly manufacturing practices by minimizing material waste and reducing energy usage.
When considering cold forged parts for your next project, it's crucial to select an experienced cold forging supplier or custom metal fabricator with expertise in material selection, tooling design, and quality assurance. Look for partners who offer in-house engineering support, state-of-the-art forging equipment, and advanced finishing capabilities. This ensures you receive high-quality, precision-engineered components tailored for your application, whether you require custom fasteners, structural elements, or complex metal assemblies. To learn more about the advantages and applications of cold forging, explore our detailed guide or contact us today.
Modern forging requires advanced, reliable machines designed to produce durable metal components efficiently. These forging machines are essential across a broad spectrum of industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, oil and gas, shipbuilding, and general manufacturing. In the following sections, we highlight several of the most respected and widely used forging machine brands and models available throughout the United States and Canada, focusing on innovation, quality, and industry standards.
The Bulldog 200 by Ajax-CECO is a highly adaptable forging machine, praised for its robust frame, advanced hydraulic power, and state-of-the-art control systems. This drop forging hammer is known for its dependability and consistent performance, supporting high-volume production of forged metal components. The Bulldog 200 is used extensively for producing automotive parts, custom hot forgings, and precision machined components, ensuring exceptional surface quality and repeatability. Its sturdy design and flexible configuration make it a top choice for facilities seeking energy efficiency, reduced maintenance, and scalable forge production.
National Machinery's FORMAX Plus series sets the industry standard among cold forging and warm forging equipment with cutting-edge servo-driven technology. This equipment is engineered for rapid tool changes, lower energy consumption, and optimized throughput. Manufacturers appreciate FORMAX Plus for its unmatched precision, high productivity, and adaptability to a variety of metal forming techniques, including extrusion and heading. It stands out in sectors where fast production cycles and consistent quality are critical, such as fastener manufacturing and automotive supply chains.
Erie Press Systems offers electric forging presses that deliver notable energy efficiency, advanced programmable logic control (PLC) systems, and versatile motion profiles for forging diverse shapes and alloys. These electric forging presses are designed for optimal force output, fast cycle times, and fine control over forging parameters. They support forging applications for alloy steel, stainless, and non-ferrous metals, satisfying rigorous quality standards for aerospace and defense parts. Their reputation for sustainability and precision makes Erie Press Systems a leader in modern green manufacturing and precision die forging solutions.
Wyman-Gordon is renowned for high-performance radial forging machines that employ innovative radial die movement to create parts with superior mechanical properties and material utilization. These machines allow for closed-die forging and forging of complex geometries, resulting in parts with increased tensile strength and reduced post-forging machining. Key applications include large forged shafts, turbine components, and seamless pipe manufacturing, where strength, grain structure, and dimensional accuracy are paramount. These advanced forging machines are trusted for lean manufacturing and cost-saving metal forming operations.
The MF Series Forging Press from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries America stands out with its robust engineering, large pressing capacity, and fully automated operations. This forging equipment excels in hot, warm, and cold forging tasks, offering integrated process monitoring for enhanced production quality and traceability. Its versatility enables fast setup changes for diverse forging processes, supporting both traditional steel forging and advanced lightweight material forming (such as aluminum and titanium alloys) frequently used in aerospace and high-performance automotive components.
When investing in forging equipment, buyers should evaluate features such as tonnage capacity, energy savings, automation options, rapid tool exchange, process flexibility, and after-sales technical support. Each of the machines highlighted above delivers specific advantages for industrial forging applications, whether the need is for large-scale production, custom forming, or precision die work. For the latest information on new forging press technologies, open-die and closed-die forging machines, and turnkey forging solutions available in the US and Canada, consult directly with manufacturers or qualified industry experts. Considering total cost of ownership, training opportunities, and service packages can further optimize long-term manufacturing performance and product quality.
Hot forging heats metal above its recrystallization temperature for high ductility and reshaping, often used for complex shapes. Cold forging shapes metal at or near room temperature, providing better dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and lower energy usage.
Cold forging reduces energy consumption, lowers production costs, and delivers components with superior dimensional accuracy and surface finish. It's ideal for high-volume production of industrial components, fasteners, and automotive parts.
Hot forging enhances metal strength by optimizing internal grain structure, boosting ductility, and increasing resistance to tensile stress. Hot-forged parts are strong, resilient, and well-suited for demanding applications like aerospace components.
Forging machines are widely used in the automotive, aerospace, construction, oil and gas, shipbuilding, and general manufacturing industries throughout the United States and Canada for producing durable metal parts.
Buyers should consider tonnage capacity, energy efficiency, automation, rapid tool exchange, process flexibility, technical support, and total cost of ownership when investing in forging equipment for optimal manufacturing performance.
Cold forging is most effective for soft, highly ductile metals such as aluminum, copper, carbon steels, stainless steels, and copper alloys, due to their ease of deformation and excellent finished properties.
Cold forging provides various advantages, such as operating at room temperature without the need to heat the metal, which reduces the overall cost of parts. Additionally, it eliminates the need for costly equipment like blast and industrial furnaces used in hot forging.
Cold forging enables the rapid and consistent production of parts with excellent dimensional accuracy, making it ideal for companies that need high volumes and fast delivery. Thanks to computerized processes, each component is produced with identical precision and detail. Additionally, cold forging extends the lifespan of dies, as they are not subjected to the stress and wear associated with hot metals.
Cold forging enhances precision, creating parts with tight tolerances and consistent quality. By closely following design specifications, this method minimizes defects and the need for rework, while also producing components with a refined grain structure.
An important factor, in this era of environmental concerns, is the eco-friendliness of cold forging since parts are shaped and formed under high pressure at room temperature. Unlike other processes, cold forging ensures that there will not be air bubbles or other deformities trapped in the workpiece.
Some of the other benefits of cold forging include improved material usage, lower energy costs, and little to no finishing. With the rising costs of energy and the shortage of materials, cold forging is the solution to producing parts efficiently reducing the effect of those factors.

Aluminum forging is a method for processing aluminum alloys using pressure and heat to form high strength, durable products. The process of aluminum forging involves pressing, pounding, and...

Cold forging is a metal shaping & manufacturing process in which bar stock is inserted into a die and squeezed into a second closed die. The process, completed is at room temperature or below the...

Copper and brass forging is the deformation of copper and brass for the purpose of manufacturing complex and intricate shapes. The temperature at which copper and brass are forged is precision controlled and...
Forging is a metal working process that manipulates, shapes, deforms, and compresses metal to achieve a desired form, configuration, or appearance outlined by a metal processing design or diagram...
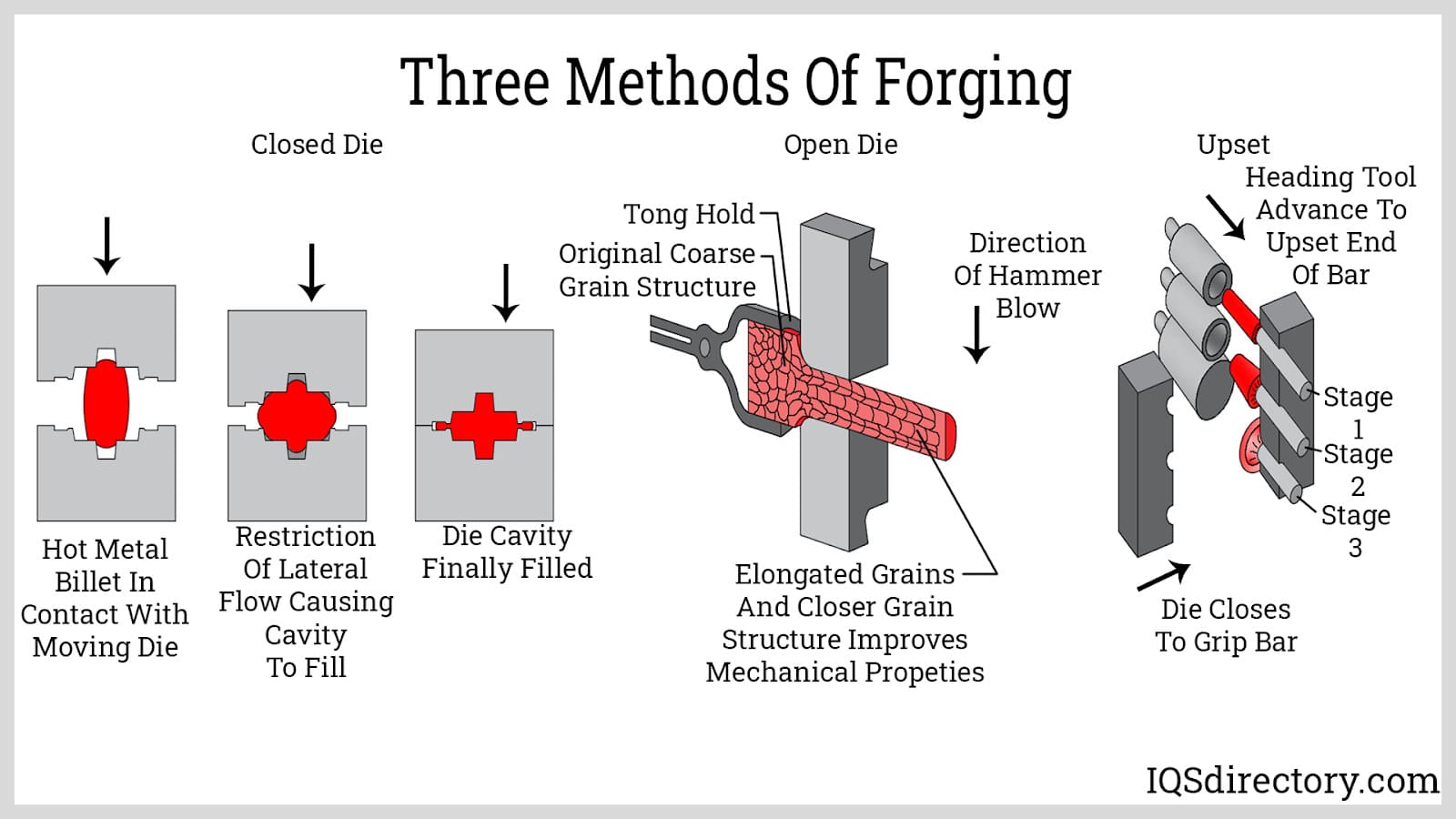
In this article, there are key terms that are typically used with open and closed die forging and it is necessary to understand their meaning. Forging is a process in manufacturing that involves pressing, hammering, or...
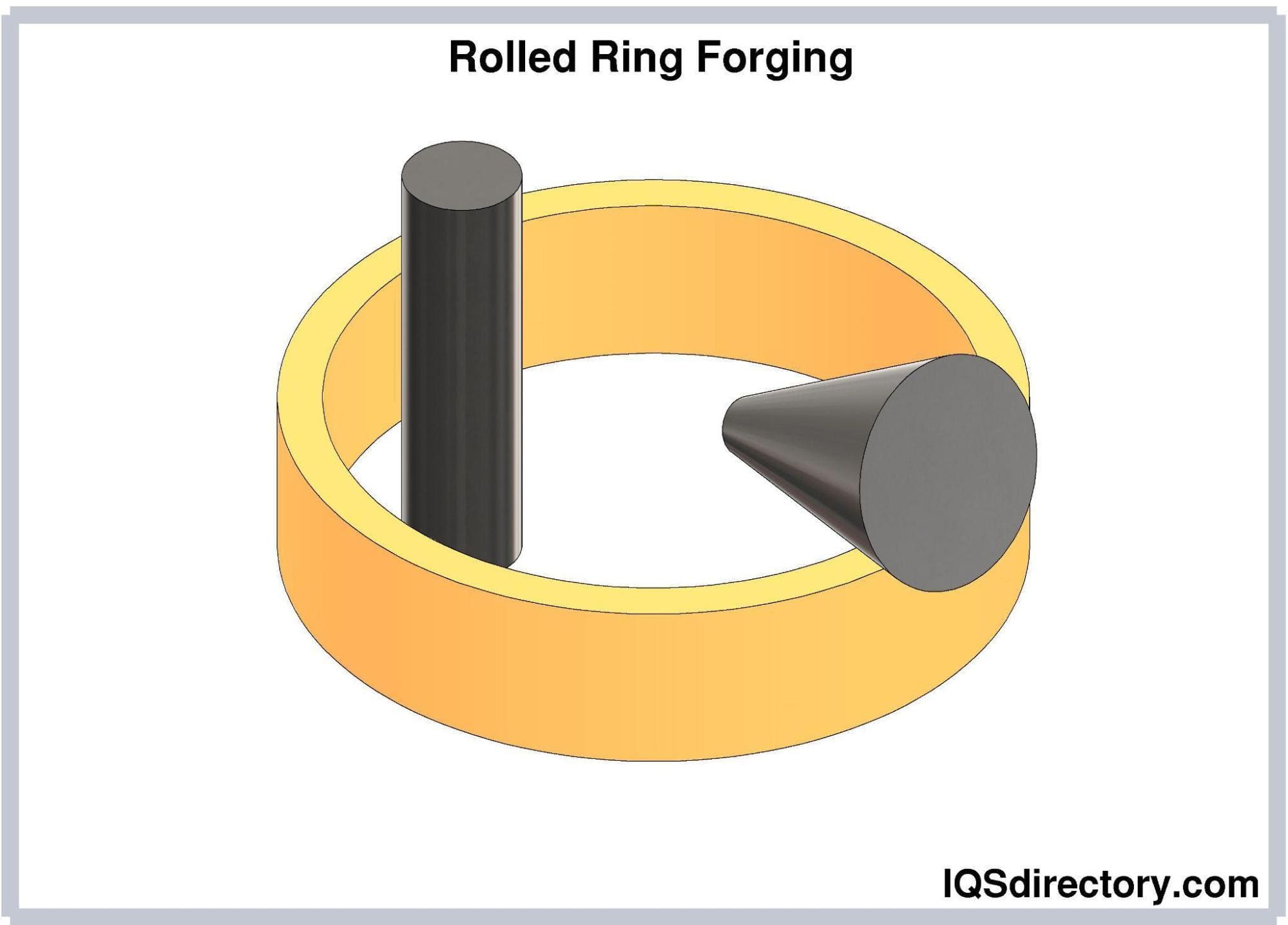
Rolled ring forging is a metal working process that involves punching a hole in a thick, solid, round metal piece to create a donut shape and then squeezing and pressuring the donut shape into a thin ring...
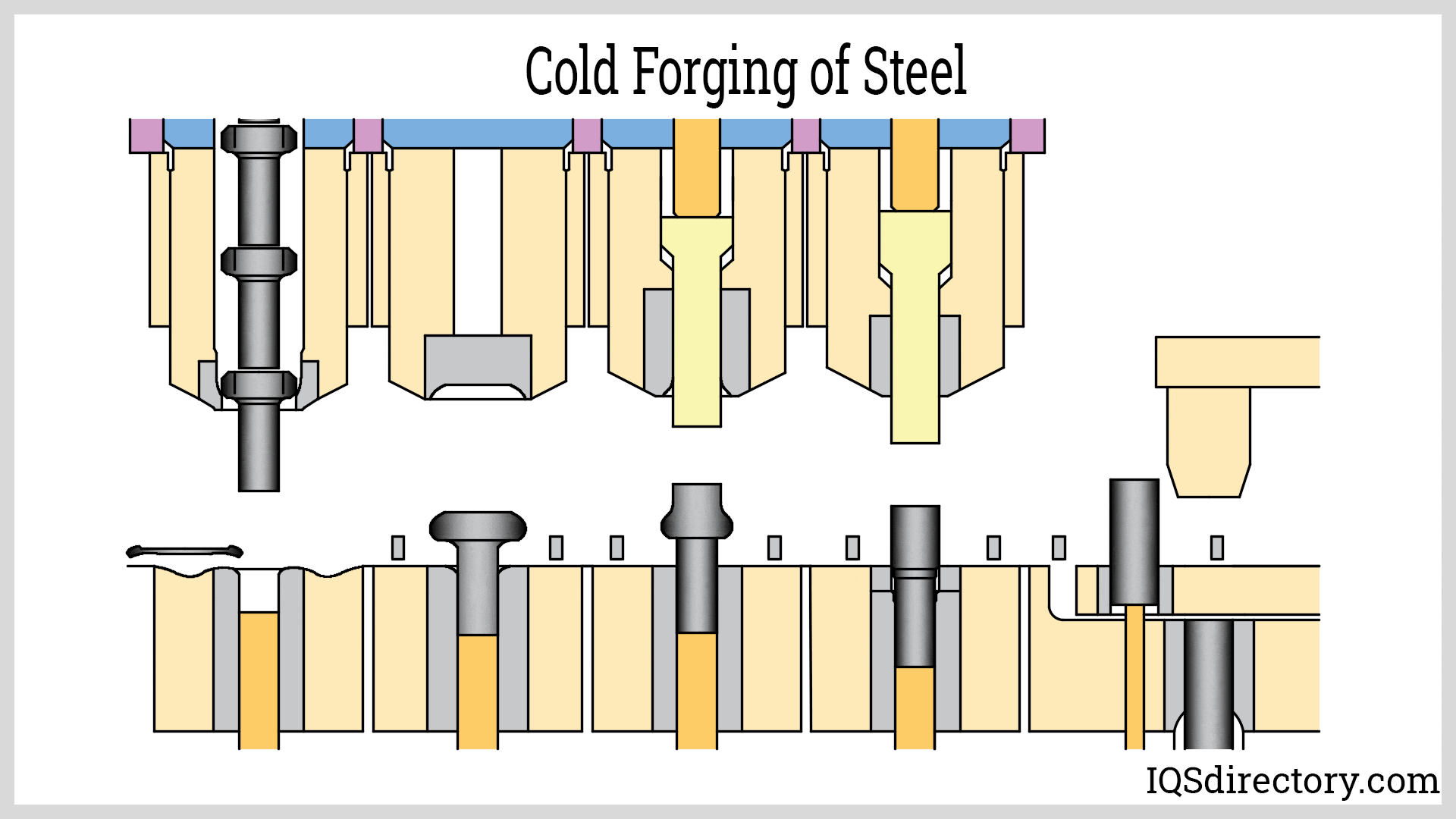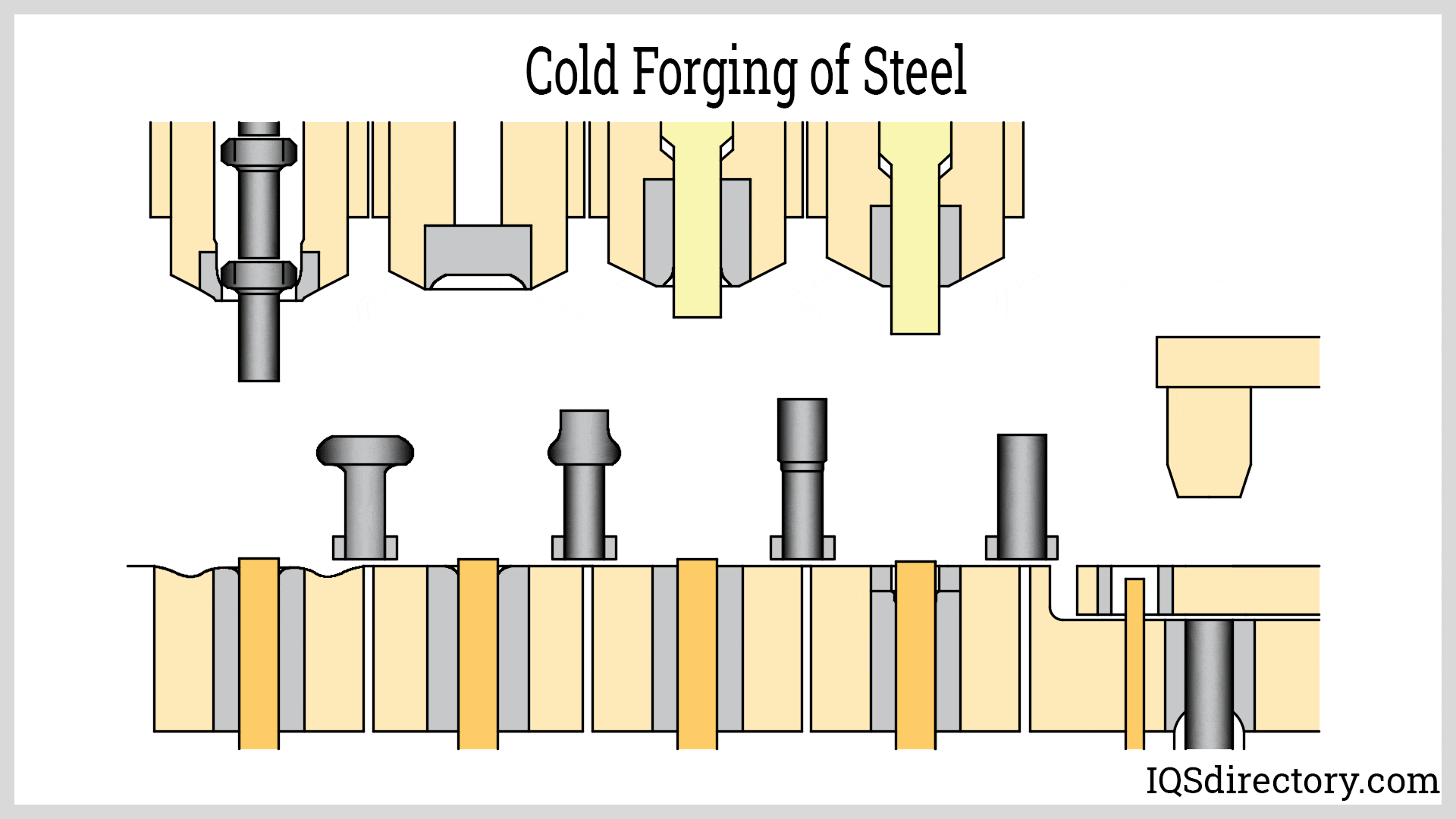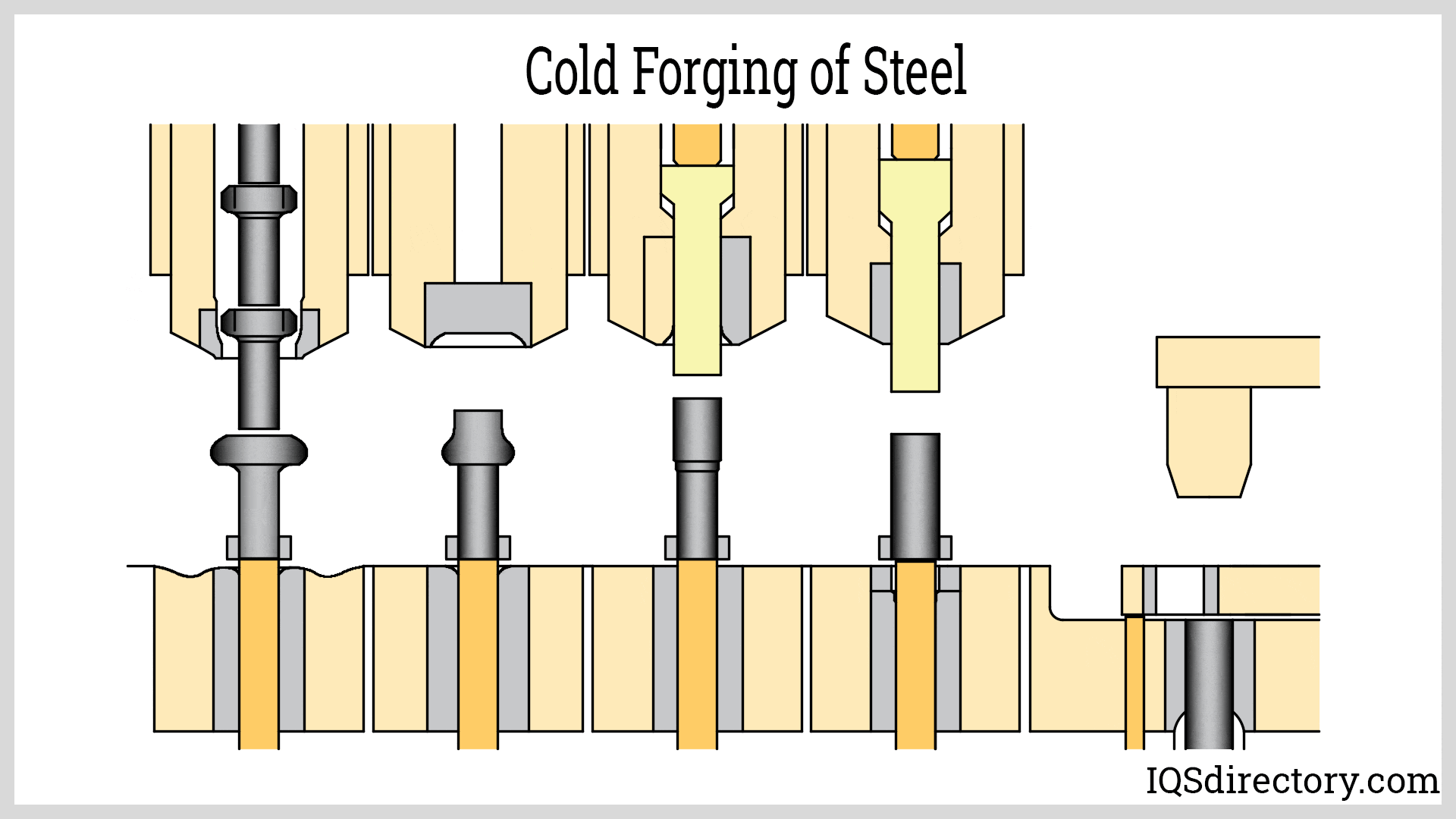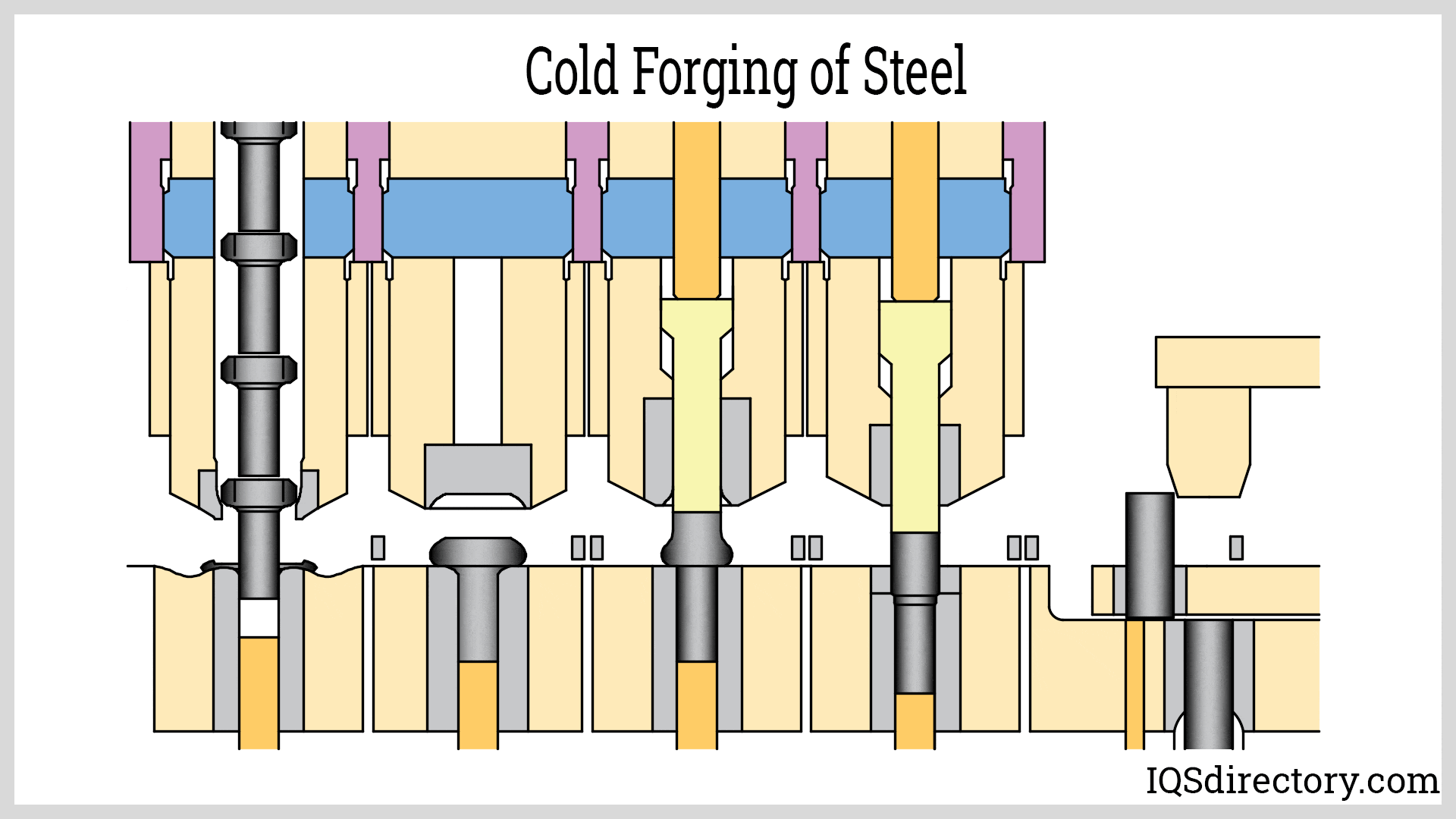
Forging steel is a manufacturing process used to shape steel by using localized compressive forces, which include hammering, pressing, and rolling. It is a widely used method for producing high quality steel products...

Aluminum casting is a method for producing high tolerance and high quality parts by inserting molten aluminum into a precisely designed and precision engineered die, mold, or form. It is an efficient process for the production of complex, intricate, detailed parts that exactly match the specifications of the original design...
Die casting is a high pressure metal casting process that forces molten metal into a mold. It produces dimensionally accurate precision metal parts that have a flawless smooth finish...
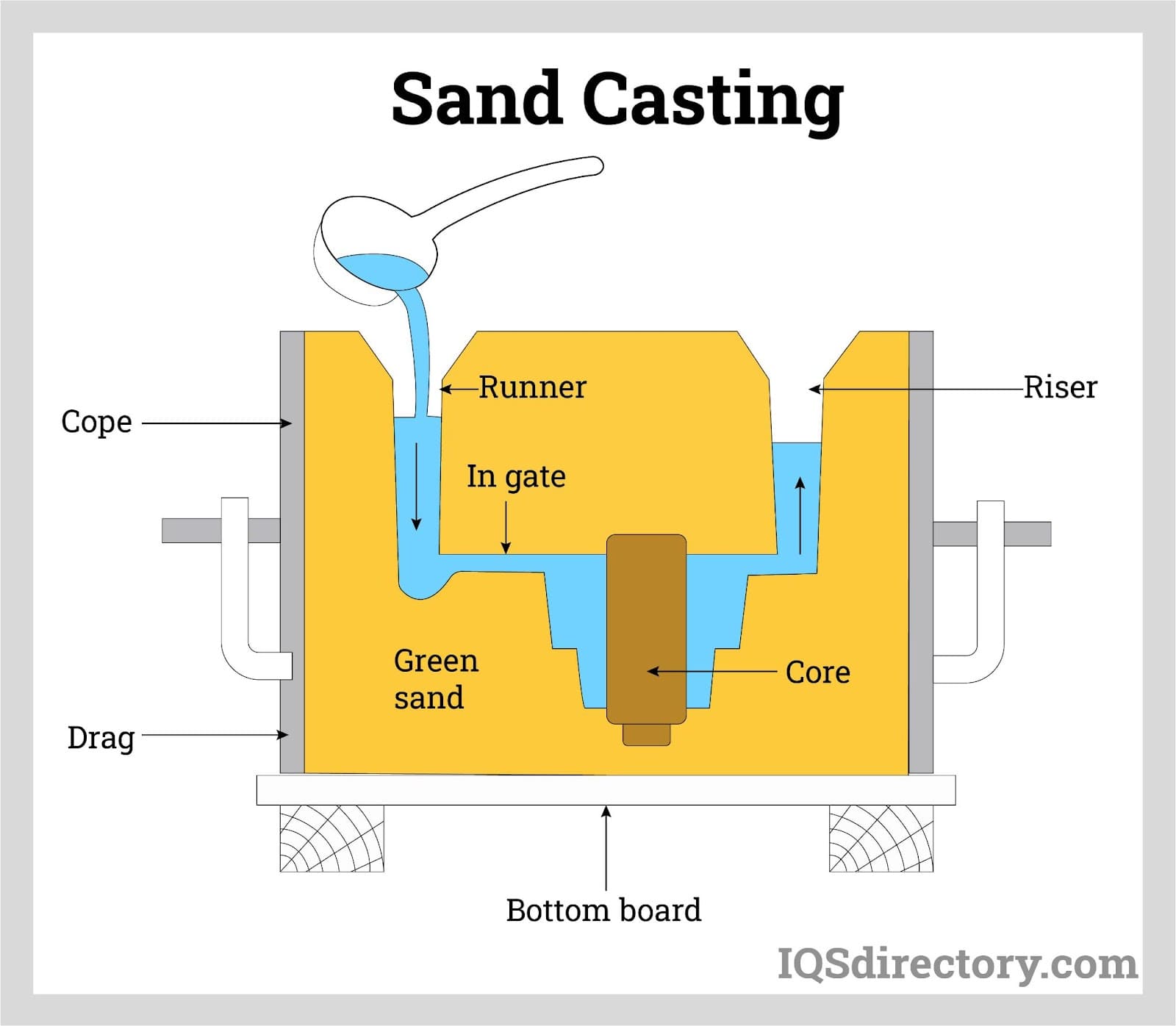
Sand casting is a manufacturing process in which liquid metal is poured into a sand mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape and then allowed to solidify. Casting is a manufacturing process in which...

Zinc die casting is a casting process where molten zinc is injected into a die cavity made of steel that has the shape, size, and dimensions of the part or component being produced. The finished cast zinc product has...
The casting process is an ancient art that goes back several thousand years to the beginning of written history. The archeological record has finds that document the use of the casting process over 6000 years ago around 3000 BC or BCE...