Cardboard Tubes
Cardboard tubes, or paper tubes, are cylindrical products fabricated from wood pulp which has been made into different varieties of cardboard such as fiberboard, paperboard, kraft paper and paper-adhesive composites. Cardboard tubes are used for a wide variety of functions in different industries and are typically fabricated from ribbons of cardboard wrapped around a mandrel in the desired dimensions.
Quick links to Cardboard Tubes Information
The History of Cardboard Tubes
The history of cardboard tubes largely tracks the history of cardboard in general. While heavy paper had been used by the Chinese as a packaging material for centuries beforehand, the earliest cardboard box dates to the late 1800s.
By 1903, cardboard tubes and cardboard cores were already being produced, though cardboard packaging in general only grew popular several years later with the Kellogg brothers' adoption of cardboard boxes for cornflakes.
Over the next century, the use of cardboard accelerated, especially with the growth of chemistry and industrial manufacturing methods to produce stronger cardboard more efficiently.
Modern production differs little from earlier methods except in the quality of the base materials and the degree of automation.
Benefits and Advantages of Cardboard Tubes
- Lightweight Advantage
- Being produced from paper, cardboard tubes are naturally very lightweight compared to similar structures and products.
- Relatively Strong for Weight.
- While cardboard may not be the strongest material out there, it's weight relative to its weight is respectable for many applications.
- Versatility of Cardboard
- Basic cardboard tube designs work for a huge variety of applications, with only minor modifications necessary for specialized applications.
- Inexpensive Tubing
- Few other materials can be made into cylinders with similar properties at as low a price as cardboard tubes.
- Easy to Degrade
- While not a benefit in all applications, many will find the relative ease of disposing of lighter grade cardboard tubes to be beneficial.
- Environmentally Friendly
- While not all cardboard tubes can be produced in environmentally friendly ways, the material is relatively easy to recycle and produce from recycled materials. This allows it to be environmentally friendly to a greater degree than many alternatives.
Design Factors of the Tubes
- Strength of a Tube
- The strength-to-weight ratio of a tube depends on a variety of factors. The base paper, adhesives used, layering, resins and curing, and the length of the tube all factor into the general resilience of your end product. Make sure you determine your specific strength requirements in advance, so you can work with your cardboard tube manufacturer to produce acceptable results.
- Length of Cardboard
- Cardboard tubes can be any length, but rarely exceed four feet for most common applications. Narrower tubes may look more like rings than tubes, such as the cardboard tubes used as structural support for tape.
- Interior Diameter Tube
- Cardboard tubes are exclusively described according to their interior inch diameter, never their exterior dimensions. If you need a specific exterior measurement for your application, make sure you communicate carefully with your manufacturer to avoid mistakes about what a tube inch or inch diameter describes.
- Cardboard Tube Thickness
- The thickness of a cardboard tube will usually be a factor of its base material and how many layers are used during production. Resins, adhesives, and other coatings may also influence the final thickness of your cardboard tubes.
- Production Cost
- Generally speaking, stronger cardboard tubes will cost more to produce. You may also need to factor in the weight of shipping heavier cardboard tubes in your budget. For this reason, it's best to aim for 'strong enough' instead of a cardboard tube as strong as possible.
- Weight of Cardboard Tubes
- If you need to keep weight particularly low, make sure you work with your manufacturer to find the best combination of materials and process to create the lightest tube that meets your standards for strength and other physical factors. You can find a convenient list of cardboard tubing manufacturers at the top of this page.
- Sealants or Cures
- If you need your cardboard tubes to be moisture resistant, waterproof, or otherwise more resilient than the basic paper materials from which they are crafted, you'll need special sealants and treatments applied during manufacture to create a non-porous material.
Tube Characteristics
Cardboard tubes are primarily notable for their relatively high strength-to-weight ratio, convenient shape for various purposes, and low production and shipping costs. In many applications, the relative ease of taking cardboard tubes apart also plays a role in their value, i.e. to get a support out of the way after concrete has set. This cardboard can then be shredded by special equipment and recycled to make another product.
Cardboard Creation Process
Most cardboard tubes are spiral wound and strengthened with adhesive additives. Firstly, large sheets of cardboard or paperboard are cut into thin ribbons which are then coated in adhesive and wrapped on an angle around a mandrel of the desired shape. Numerous layers of cardboard can be added to the forming mandrel, depending on the desired strength of the tube. All paper tubes are measured and defined by their interior dimensions rather than exterior, and while they can vary greatly, most tubes are no longer than 48 inches in length to ensure structural integrity. For heavy duty applications when high strength, waterproof and resistant cardboard is needed, adhesives or interior waterproof sealing layers can be added to the tube fabrication process. The wood pulp-resin mix is formed and cured, and may be followed by further curing in an oven. While post forming heat treatments take place, the pulp and adhesives coalesce to provide a stronger product. The finished product is more durable and holds its shape better in humidity or when affected by elements of weather. These are important features, especially for the storage or transportation of products which in addition to regular transit damage, can be further damaged or ruined by elements of moisture or air.
Cardboard Tube Images, Diagrams and Visual Concepts
 Paper tubes consist of paper or paperboard sheet layers wound together to for a cylindrical shape and bonded with adhesives.
Paper tubes consist of paper or paperboard sheet layers wound together to for a cylindrical shape and bonded with adhesives.
 The different varieties that pape tubes are used for.
The different varieties that pape tubes are used for.
 Different methods used for storing paper tubes to prevent damage.
Different methods used for storing paper tubes to prevent damage.
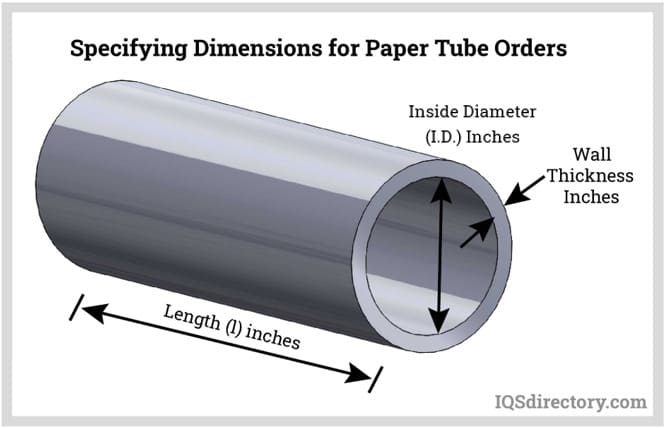 Paper tubes are measured according to the inner diameter (ID), wall thickness and length, which should be based on the products dimensions.
Paper tubes are measured according to the inner diameter (ID), wall thickness and length, which should be based on the products dimensions.
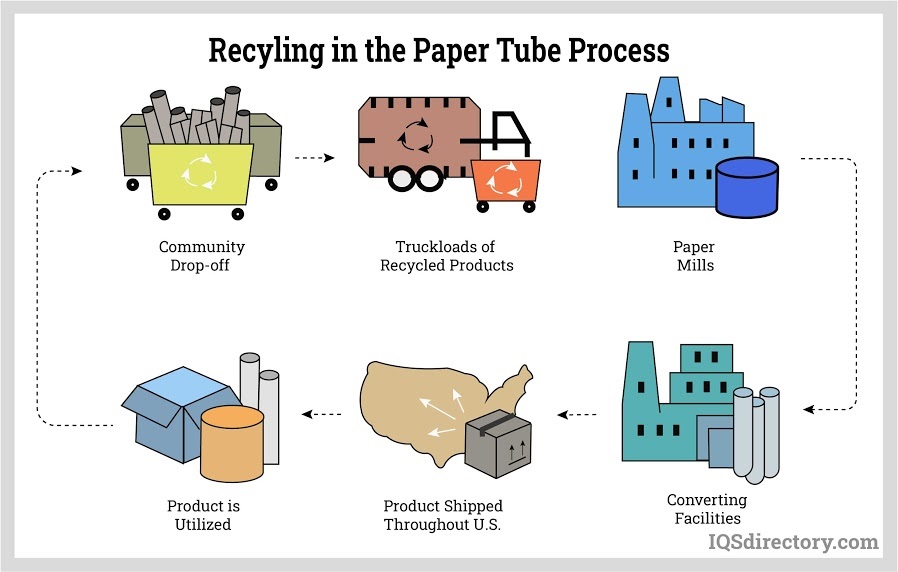 The recycling process used to recycle paper tubes for new usage.
The recycling process used to recycle paper tubes for new usage.
Cardboard Tube Types
- Cardboard Tubes
- Any tube made from spiral wound cardboard material. They serve many purposes from cores for various products to storage containers and shipping purposes.
- Coin Bank
- A small paper tube used to hold specific monetary amounts of coins of the same denomination.
- Corrugated Tubes
- Tubes made from composite paperboard, which is a layer of fluted material sandwiched between two layers of linerboard.
- Construction Tubes
- Or construction cores, are cardboard tubes used to help form and create concrete construction components. Most commonly these products are utilized to fabricate concrete columns for load bearing applications but can be used for many other industrial and commercial applications.
- Convolute Tubes
- "Roll longitudinally upon itself” or “to form into a twisted, coiled, or rolled shape.” So, convolute tubes are simply those cardboard tubes that have been rolled in on themselves.
- Fiber Tubes
- Tubes made from fiberboard and can be used for individual roll storage, to protect sensitive fabrics from crushing, to separate secure small lots, to provide a location for return goods and to make “bottom” rolls accessible when an entire roll is not cut.
- Mailing Tubes
- Cardboard tubes that paper products are rolled up into for compact shipping that does not bend or crease the material being shipped.
- Shipping Tubes
- Also called mailing tubes, are tubes, potentially having graphic advertisements printed on them, which are used for the express purpose of shipping items that fit conveniently in a tube. End cap materials include wood, metal or paper.
- Sonotube
- A large, water-resistant cylinder paper form used in concrete pouring applications.
- Paper Tube Cores
- Tubes that are typically spiral wound and used for any material that requires a center, including such things as paper towels, fax paper rolls, tape and film products.
- Paper Cans
- Composite containers typically made from paperboard material with an inner liner that provides a protective barrier. Thicknesses and sizes vary, as do types of closures and label options.
- Spiral Wound Paper Tubes
- Have longer cores.
Uses for Cardboard Tubes
Cardboard tubes can be made to fit a broad range of products, and are made in different levels of structural strength and thickness, depending on the level of protection required. Most commonly used for mailing tubes and shipping tubes, cardboard tubes are readily available for papers, posters, documents and pieces of artwork which are able to be rolled into a cylindrical shape. These poster tubes are able to withstand the pressure and stress that occurs during transit as they are formed from a material such as high quality kraft paper. Kraft tubes are strong and are often used in shipping and packaging. Other common uses for cardboard tubes include: paper cores providing structural strength to items such as rolls of fabric, paper towels or toilet paper, and electrical wires, coin banks for collecting money and donations, caulking tubes for construction projects, grease cartridges for use in the automotive and mechanical industry and paper cans which are used widely in packaging for foods, cosmetics and merchandise. Another specific use for cardboard tubing is by contractors and construction industries that use large, heavy duty and highly durable cardboard tubes, called Sonotubes®, for concrete pillar forming. You can find Sonotube® manufacturers and concrete tube producers here on IQS Directory.
For transportation, storage or mailing of fragile items, thicker cardboard should be used. Mailing tubes are designed to be strong enough to guard against denting, bumping and breaking during transit, and therefore it is important to purchase the correct size of tube to ensure the contents are not moving around more than is necessary inside the tube. Both ends of shipping tubes are typically closed with a plastic plug, one of which is removable, but may be sealed for postal or transportation purposes, especially of confidential documents or medical and scientific products. Or, the tubes themselves may fold in and close at either end. The measurements given to classify tubes are the interior dimensions of the tube, taking into consideration the wall thickness and closing space at each end. Shipping and mailing tubes are often stronger than boxes or other containers and the cylindrical shapes make an ideal shipping container as there are many products that it is preferable not to fold such as posters, artwork, large maps or blueprints etc.
The most common ways cardboard tubes are used range broadly in terms of function, size and industry. Tubes can be coated in colorful, customizable printed paper or foil. For food processing items, product information and logos can be printed out the outside of the tube. For gift packaging and holiday themed postal tubes, colors, patterns and designs can be incorporated into the cylindrical shape. Cardboard tubes are often manufactured from recycled paper and those made from more durable board can be used over again, making them a cost-efficient alternative to metal, plastic, glass and wood packaging. They are comparably cost-effective because cardboard materials are easier for manufacturers to cut, purchase and dispose of than most other materials. Cardboard tubes also rival plastic and metal tubes in strength-to-weight ratio, making them an ideal solution for mailing, shipping, storing and distributing almost any material. Heavy-duty cardboard tubes are difficult to dent and break, therefore mailing and shipping tubes offer superior protection from rough handling. However, cardboard is a porous material and therefore for specific applications such as those for electrical wiring or food processing, layers of non-porous material may need to be added to the interior or exterior of the tube as a barrier against moisture. Despite this drawback, cardboard tubes are tough, flexible and renewable, and therefore provide a great commercial and industrial solution to many tubing needs.
Cardboard Applications
The applications of cardboard tubes are somewhat limited due to their simplicity, but those applications make them of value to any number of industries and fields.
- Shipping Tubes
- Cardboard mailing tubes, postal tubes, and shipping tubes for documents, posters, and various other small items.
- Structural Cores as Support
- Paper cores serve as structural supports for paper towels, wrapping paper, issue paper, textiles, and similar materials.
- Grease Cartridges
- Certain grease cartridges used in mechanical and automotive fields are made of cardboard tubes.
- Paper Cans
- Paper cans for certain foodstuffs, cosmetics, and assorted other goods.
- Construction Cardboard
- Heavy duty cardboard can be used as structural support for concrete pillars and similar structures.
- Support in Horticulture
- They are frequently used as supports for plants, as inexpensive alternatives to pots, and as containers for garden goods.
- Cardboard Storage
- Used for inexpensive storage for assorted goods and materials.
How Cardboard Tubes are Made
Production of cardboard tubes usually begins with the production of cardboard in ribbon form. The base cardboard may be paperboard, fiberboard, kraft paper, or any number of composites and laminates. These ribbons are then coated with strengthening adhesives and wrapped in a spiral around a mandrel to form a cylindrical shape.
Many forms of specialized tube will have additional adhesives, coatings, and sealants applied during this process or shortly after it. The heaviest applications may involve resin coating and oven curing or other heat treatments. This results in cardboard with greater water resistance, chemical resistance, and general moisture tolerance.
Cardboard Innovations: Emergency Road Signs
Cardboard tubes have a somewhat limited use. They are used for packaging, as the center holder for materials like paper and plastic, for forming concrete and other liquid-to-solid materials, and even as pots for flowers. However, these few uses are about all the tubes are used for.
Recent innovations, however, have brought about a new use for cardboard tubes. Cardboard is an inexpensive, but sturdy, material that is ideal for the new application. This new design uses a cardboard tube to house an emergency sign for doctors, emergency personnel, and travelers. The tube is home to a thin, flexible, plastic emergency sign. The sign is used to indicate car trouble along the road. The sign can say anything the owner requests, which is particularly useful for a variety of industries. Inside the tube, the plastic sign is green with white letters. This makes it reflective in the night just like road signs, for maximum visibility.
The first use of the signs was in the United Kingdom. In fact, the company that invented the signs actually created them after a local doctor's car died along the highway and the doctor was unable to get to work. No one stopped to help the doctor get to her final destination, because they were unaware that the car belonged to a doctor. The sign was invented to help prevent situations like that from occurring again.
A cardboard tube manufacturer was commissioned to make the case for the sign to keep costs low and to help make the sign lightweight and easily portable. The sign fits into any small space in the car- ready for any emergency. Owners can choose between a variety of sign colors if they do not want to use the green and white combo.
Cardboard Standards and Specifications
Because of the wide variation in applications for cardboard tubes, there are few if any concrete standards or compliance factors to consider. Instead, you'll want to carefully familiarize yourself with the specific regulations or standards associated with a particular use before you contact a manufacturer.
Working with a manufacturer familiar with your application can also help, as they'll usually understand the specific needs and specifications required to meet compliance requirements.
Things to Consider When Purchasing Cardboard Tubes
When choosing a cardboard tube manufacturing team, make sure you look for the right manufacturer for your project—not just the best-reviewed or cheapest manufacturer in your region. A good fit will save you more money, time, and other resources than anything else.
- Specific Applications of Tubes
- Because there are so many unique applications for cardboard tubes, it's going to be best if you do your research and find a manufacturer familiar with your specific application. At the very least, references from production jobs similar to your type of application. When you find a team that knows what you need and expect, you won't have to worry about mistakes, missteps, waste, or general inefficiency in production.
- Manufacturer Flexibility
- It's a good idea to work with a cardboard tube manufacturer willing to work with you to customize products to your exact needs, rather than one that will try to foist one-size-fits-all solutions on your company to avoid changing settings on a slit machine. A good manufacturer helps you maximize your efficiency and efficacy instead of their own at your expense.
- Scheduling Delivery
- It's very important that you clarify schedules early in your negotiations with any manufacturer, just to make sure you'll have your cardboard tubes when you need them for your project or product. It's also important that scheduling be realistic and based upon a detailed understanding of your needs, shipping requirements, and other factors.
- Product Transparency
- Make sure you know what you're getting for what you pay. If you're buying cardboard tubes for a specific purpose, make sure you understand what, if any, caps, storage solutions, sealants, and other secondary items are included in your quote. A failure to determine the exact details of quotes when ordering cardboard tubes can create huge problems with your budget or production.
Proper Care for Cardboard Tubes
While cardboard tubes are used for their inexpensive, disposable nature in most cases, that doesn't mean you can afford to have them damaged before or during use. To make sure your cardboard tubes properly fulfill their function, be alert to these issues:
- Effects of Moisture
- Outside of specially treated heavy-duty cardboard made from non-porous material, moisture will ruin nearly any cardboard tube. Make sure you keep your tubes in a dry environment, or wrap them in protective plastic or other insulating barriers if they're to be used somewhere moist or wet.
- Upright Storage
- Because cardboard tubes aren't particularly sturdy, make sure to store them such that they won't end up crushed or bent. In most cases, they're best stood upright rather than piled horizontally.
- Heat Sources
- Be careful with your cardboard tubes around sparks, flames, and other sources of high heat; they're made up of paper, wood, and glue in most cases, and thus highly flammable.
- Secure From Pests
- The glue and paper of cardboard is a favorite treat for many pests, so make sure you store your cardboard securely to avoid problems or spray in advance as protection.
Use and Installation of Tubes
Cardboard tubes are perhaps the easiest product you'll ever use for any purpose. Just make sure the relative fragility of the product is considered in handling and management, and you won't have any particular problems. Cardboard tubes meant for use in high-speed manufacturing or sorting machinery should be engineered with those applications in mind.
Cardboard Tube Accessories
- End Caps
- Cardboard tubes intended for use as containers for shipping, storage, or similar applications require fittings to seal their ends. You'll need caps, plugs, or seals matching the size of your tube.
- Sealants
- While cardboard can be strengthened and reinforced during the production process, you can also apply various sealants and coatings after the fact to insulate against moisture, specific chemicals, pests, etc.
Cardboard Tube Terms
- Composite or Paperboard Can
- A package comprising a body with two ends made from a variety of materials and available in many shapes and sizes. The container bodies are paper tubes and various liner materials to achieve barrier requirements and a printed label for package graphics of paper tubes.
- Corrugating Medium
- The fluted middle portion of a corrugated boxes or paper tubes that are made from paperboard and typically produced on a Fourdrinier machine as a single layer, using varying combinations of virgin and recycled fibers.
- Cylinder Paperboard
- The paperboard produced from recycled fibers on a cylinder machine consisting of multiple plies that are bonded together in the papermaking process.
- End Closure
- Rigid metal caps, film caps, plastic caps, paper caps or paper structures that are mechanically attached to the end of a package or a layered plastic film, foil or paper membrane heat-sealed to the end of a rigid package.
- Engineered Carriers
- Paper tubes, Cardboard Tubes, and cores of paper or plastic that serve as product carriers for film tubes, paper tubes, tape tubes, textile tubes, metal tubes and more. The carrier tubes are highly engineered to permit take-up of these materials at extreme speeds.
- Fiberboard
- A composite material made from compressed wood fibers and glue.
- Fourdrinier Machine
- A machine divided into a wet end, a press section, a drier section and, typically but not always a calendar section that is employed in the manufacture of all grades of paper tubes and board.
- Kraft Paper tube
- A coarse paper made from a type of chemical wood pulp, whose color is dark brown but may be bleached to lighter shades of cream. Taking its name from the German word for strong, this paper is typically used for wrapping and packaging.
- Mandrel
- The core elongated mold around which resin-impregnated fiber, paper, fabric, tape or filaments are wound to form pipes, tubes or structural shell shapes.
- Membrane Closure
- A flexible material attached to the end of a rigid package with a peelable heat seal. This material can be a coax plastic film or a layering of plastic film, foil or paper with a heat-seal coating.
- Paperboard
- A subdivision of paper that is generally heavier in basis weight, thicker and more rigid than paper. All sheets of 12 points (0.012) or more in thickness are considered paperboard with some exceptions, such as blotting papers, felts and drawing paper in excess of 12 points, while some corrugating medium, chipboard and linerboard of less than 12 points are still categorized as paperboard.
- Recovered Paper
- Paper and paper derivatives separated, removed or diverted from solid waste disposal for the purpose of sale, use, reuse or recycling, whether or not such material necessitates further separation and processing.
- Spiral Winding
- The process in which a ribbon of cardboard, coated with adhesive is wrapped in a helix pattern around a set round mandrel to produce spiral wound paper tubes. It's done at an angle that will produce a continual flow of product that can be cut to any specification.