ISO Standards: Certifications, Compliance & Applications
Introduction
This article will give a detailed discussion on ISO standards
It is expected that after reading, one should understand:
- ISO Standards: What are ISO Standards and What is ISO Certification?
- How to Obtain ISO Certification
- Common ISO Standards in Different Industries
- Benefits of ISO Certification
- And Much More...
Chapter One: Understanding ISO Standards and Certification
Defining ISO Standards
ISO standards are comprehensive guidelines that cover a variety of management techniques, technological processes, and production procedures, all aimed at enhancing global safety and quality of life. Established in 1947, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) aims to discover best practices for both simple and intricate activities worldwide.
One of ISO's initial tasks was to create a universal measurement system, resulting in the global acceptance of the metric system. Throughout the years, ISO's scope has widened to embrace numerous fields. Today, it comprises standards governing everything from garment manufacturing and wireless connectivity to advanced industrial processes.
The name ISO stems from the Greek word "Isos" (ίσος), signifying "equal." As a global entity, ISO functions to enhance the welfare of people worldwide. It includes 163 member countries, who regularly convene to assess developments in industrial and manufacturing methodologies. During these assemblies, ISO committees and experts propose and deliberate on new standards for ratification.
ISO releases documents containing specifications, guidelines, and standards that companies use to ensure top-tier quality and acceptability in materials, products, processes, and services. Regulatory authorities depend on these standards to evaluate quality. Earning ISO certification communicates to customers, suppliers, and partners that products meet elevated standards of quality, safety, endurance, and eco-friendliness.
The inception of the International Organization for Standardization goes back to a 1946 conference in London, attended by delegates from 25 countries discussing post-war progress and reconstruction. Launching in 1947 with 67 technical and expert committees, ISO has expanded to issue over 24,500 international standards by November 2022, supported by 811 technical committees and subcommittees.

Exploring ISO Certification
ISO certification serves as an official recognition that a company has complied with established quality management benchmarks. For globally-operating companies, ISO certification can help broaden their client reach and improve their brand reputation. Displaying an ISO certification assures stakeholders that the company is reliable, credible, and committed to producing products of superior quality.
The very first ISO standard, ISO/R 1:1951, standardized a reference temperature for industrial measurements. Updated several times, its latest iteration is ISO 1:2002. A pivotal moment in ISO's history occurred in 1987 with ISO 9001's introduction, launching the first quality management standard. With increasing environmental issues in the 1980s and 1990s, ISO also developed ISO 14001 to address environmental pollution and impact concerns.
Numerous industries reap significant benefits from ISO certification. For example, healthcare organizations use it to affirm their commitment to excellent patient care. Likewise, hospitality businesses like hotels and restaurants employ ISO certification to highlight their focus on guest satisfaction.
ISO certification is highly esteemed in fields such as construction, engineering, manufacturing, and technical services, where it demonstrates proof of quality and operational excellence. Customers are more inclined to choose companies with ISO 9001:2015 certification, a standard for quality management systems signaling adherence to stringent quality standards. Such companies often satisfy additional criteria set by regulatory entities.
Obtaining ISO certification involves an extensive evaluation by an outside party to confirm that a company adheres to ISO benchmarks for quality, efficacy, and uniformity. ISO-certified companies are dedicated to delivering high-quality products promptly.
As ISO standards evolve, businesses must adapt their practices accordingly to stay compliant. The core mission of ISO is to elevate safety, quality, and security across various industries, thereby improving both industrial and public welfare.
Chapter Two: How to Receive an ISO Certification?
When a company obtains ISO certification, it has undergone a comprehensive audit by an independent third party to ensure full compliance with the relevant quality management system standards set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Achieving ISO certification demonstrates a commitment to excellence, risk management, and international best practices. The ISO also operates a Committee on Conformity Assessment (CASCO), which oversees the entire ISO certification process and ensures that certification requirements for various ISO standards—including ISO 9001 (Quality Management), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety), and other industry-specific ISO certifications—are rigorously maintained and updated.
The Committee on Conformity Assessment develops international standards, policies, and guidelines for conformity assessment bodies (CABs) and accreditation bodies (ABs). CABs are responsible for auditing and verifying that organizations meet the appropriate ISO standards through essential practices such as quality testing, inspections, risk assessments, system evaluations, audits, and ongoing performance monitoring.
An accreditation body is an independent, third-party organization that provides formal recognition of an entity’s technical competence, reliability, and capacity to consistently perform specific certification functions. As the number and complexity of ISO standards evolve and expand, the demand for credible accreditation bodies has grown globally. ABs include standards bodies, testing laboratories, inspection agencies, and certification organizations, all of which conduct impartial assessments designed to verify the integrity and compliance of the organization's management system.

To achieve ISO certification, a company must first establish, document, and implement its management system according to the relevant ISO standard. These requirements may include process control, document management, corrective and preventive actions, and risk-based thinking. Many organizations engage experienced ISO consultants or certification experts to guide them through the certification process and improve the efficiency of ISO implementation. The typical steps involved in obtaining an ISO certification are:
Creating a Management System
The journey begins with a self-assessment, during which a business reviews current procedures and benchmarks them against the specific ISO standard (such as ISO 9001 for quality, ISO 14001 for environmental, or ISO 27001 for information security). Every level of management is involved in documenting workflows, roles, and responsibilities. This thorough documentation ensures that processes align with mandatory requirements and industry-specific regulations. Once compiled, the documented management system should be distributed across departments for feedback, review, approval, and organization-wide adoption.
Implementation of the System
To effectively implement and maintain the ISO management system, it is crucial that all agreed-upon procedures are put into practice exactly as recorded. Success depends on robust internal training programs for employees, compliance audits, corrective and preventive action plans (CAPA), and systematic monitoring and measurement of performance metrics. Comprehensive reporting systems, structured management review meetings, key performance indicators (KPIs), statistical data analysis, regular inspections, risk assessments, corrective measures, and preventive actions are used to continually refine processes. Ongoing evaluations and internal audits ensure continuous improvement—an essential pillar of any ISO management system.
Checking the Efficacy of the System
After the management system has been fully implemented and reviewed internally, the organization should engage an accredited third-party auditor to conduct an external audit. The ISO audit process involves a detailed on-site assessment where auditors verify compliance with ISO requirements by conducting document reviews, employee interviews, and process observations. The auditor provides a gap analysis and a comprehensive audit report that identifies strengths, weaknesses, and recommendations for achieving and maintaining ISO compliance. Addressing any non-conformities with corrective actions is a vital step before proceeding to certification.
Identify the System
Following the external audit, the organization’s management system documentation is formally submitted for evaluation and approval. The auditor's assessment confirms whether all ISO standard requirements have been satisfied. Upon successful verification, ISO accreditation and certification is granted, often accompanied by a certificate of conformity. It’s important to note that ISO standards are continually revised, so certified management systems must undergo surveillance audits annually and full re-certification audits every three years. Regular audits support recertification and help organizations maintain ISO compliance long-term, reinforcing trust among partners, regulators, and customers.
Selecting an ISO Consultant
Engaging a knowledgeable ISO consultant or advisor is a critical step in the ISO compliance journey. The right ISO consultant brings expertise in regulatory requirements, audit preparation, and process improvement. Consultants analyze your organization’s current systems, identify gaps, and provide actionable insights for reaching ISO certification efficiently.
ISO consultants conduct an in-depth needs assessment and recommend the most appropriate ISO standard—such as ISO 13485 for medical devices, ISO 22000 for food safety, or ISO/IEC 27001 for information security management—based on the organization’s size, industry, and strategic goals. After this analysis, consultants carry out a detailed gap analysis to clarify the difference between current processes and those specified by the chosen ISO standard, ensuring a targeted and effective certification strategy.
Focused on Results
ISO consultants develop tailored implementation plans and project timelines, incorporating process optimization, internal audit schedules, team training sessions, and KPI tracking aligned with organizational objectives and budgets. These plans may include process reengineering, compliance documentation, risk management procedures, and sustainability initiatives, all geared toward achieving ISO certification and positioning the organization for ongoing operational excellence.
Reason to Hire a Consultant
The process of preparing for ISO certification introduces new demands and responsibilities, which can be time-intensive and complex, especially for first-time applicants. An experienced consultant acts as both project manager and subject matter expert, guiding the management team through each phase and streamlining the documentation and audit preparation required. The depth and scope of consultant involvement are determined by the organization’s initial level of ISO readiness, desired timeline, and available internal resources. Common consultant roles include:
- Advisory: Explaining the intent, benefits, and practical application of ISO standards; offering regulatory and industry guidance.
- Management: Overseeing the end-to-end ISO implementation process, facilitating change management, and ensuring project milestones are met.
- Implementation: Providing hands-on support and additional resources for process mapping, documentation, and internal audit facilitation.
- Ongoing support: Assisting with continuous improvement initiatives, conducting post-certification audits, and supporting future recertification needs.
Individualized Services
Each organization seeking ISO certification operates with distinct goals, workflows, and industry-specific compliance issues. Experienced ISO consultants tailor their services—whether you need ISO 9001 certification for manufacturing quality or ISO 27001 certification for information security—to address unique business challenges, facilitating a customized path to certification. By adapting ISO compliance solutions to each client, consultants maximize the impact and efficiency of the ISO implementation process.
Cost and Schedule
The cost of ISO consulting and certification services varies considerably based on several factors, including the organization's size, complexity of operations, employee involvement, scope of the management system, and pace of implementation. Small businesses may experience lower upfront costs but may require additional support for documentation and training, while large enterprises with extensive operations may face higher consulting fees due to the scale of ISO training, audit preparation, and system integration. Fee structures generally cover services such as internal and external audits, documentation support, process optimization, and staff training. Organizations should request detailed ISO certification quotes and project timelines from potential consultants to accurately estimate budget and resource allocation.
Consultant Success
The success of an ISO consultant is reflected in their track record, including successful certification projects across industries, client satisfaction scores, and third-party testimonials. Effective consultants possess comprehensive training in ISO management systems, regulatory compliance, business process reengineering, and internal auditing techniques. Their professional portfolio should include case studies, published articles, and references from organizations that have achieved and maintained ISO certification under their guidance. Due diligence should include evaluating a consultant’s credentials, such as IRCA (International Register of Certificated Auditors) or Exemplar Global certification, as well as direct knowledge of your sector.
Relevance and Experience
Consultants play an indispensable role in managing ISO implementation projects, acting as expert advisors, process owners, and internal auditors. Every phase—from initial gap analysis and process mapping to final certification audit—requires industry-specific expertise and up-to-date knowledge of ISO best practices. Top-performing ISO consultants deliver value by aligning management system frameworks with strategic business priorities, supporting digital transformation initiatives, and ensuring legal and regulatory compliance. Their effectiveness is measured by client outcomes, industry reputation, and demonstrated expertise in multiple ISO standards.
Key factors to consider when selecting an ISO consultant:
- Industry experience: Deep working knowledge of your sector, regulatory environment, and applicable ISO standards (such as ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 45001, and more).
- Proficiency in management systems: Expertise across various types of ISO management systems (quality, environmental, information security, food safety, etc.), and proven ability to design, implement, and maintain these systems.
- Certification body support: Familiarity with accredited certification bodies, audit requirements, and recertification best practices to simplify the ISO certification journey and ensure long-term compliance.
Chapter Three: What are some common ISO standards used in different industries?
ISO standards serve as internationally recognized frameworks that guide organizations across diverse industries toward best practices, regulatory compliance, and competitive excellence. These standards are crucial for organizations aiming to optimize quality, sustainability, occupational health and safety, information security, and operational efficiency. Each ISO standard adheres to a specific numbering system and addresses unique objectives. Among the most widely adopted are ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management, both of which are foundational for global certification and operational excellence. Beyond these, many specialized ISO standards address sector-specific challenges, ensuring comprehensive coverage for various industries.

ISO 9001: Quality Management Systems
Organizations leverage the ISO 9001 standard to systematically enhance the quality of their products and services, ensuring they meet stringent customer requirements and regulatory expectations. ISO 9001 is the global benchmark for Quality Management Systems (QMS), with over a million companies and organizations in more than 170 countries holding certification. This internationally accepted standard provides a set of requirements designed to support organizations in delivering reliable, compliant, and high-quality outputs across manufacturing, service, and retail sectors.
Key principles of ISO 9001 include a dedicated customer focus, top management involvement, risk-based thinking, a process-driven approach, and a strong commitment to continual improvement. Adherence to these quality management principles cultivates higher client satisfaction, increased consistency in product/service delivery, and improved operational efficiency. The ISO 9001 framework also supports strong supplier management and strengthens business reputation.
The standard supplies organizations with practical guidelines and a systematic approach to managing and optimizing core business processes. ISO 9001 lays the foundation for robust documentation, internal audits, corrective action planning, and performance measurement—a path for long-term success benefiting customers, employees, and senior management alike.

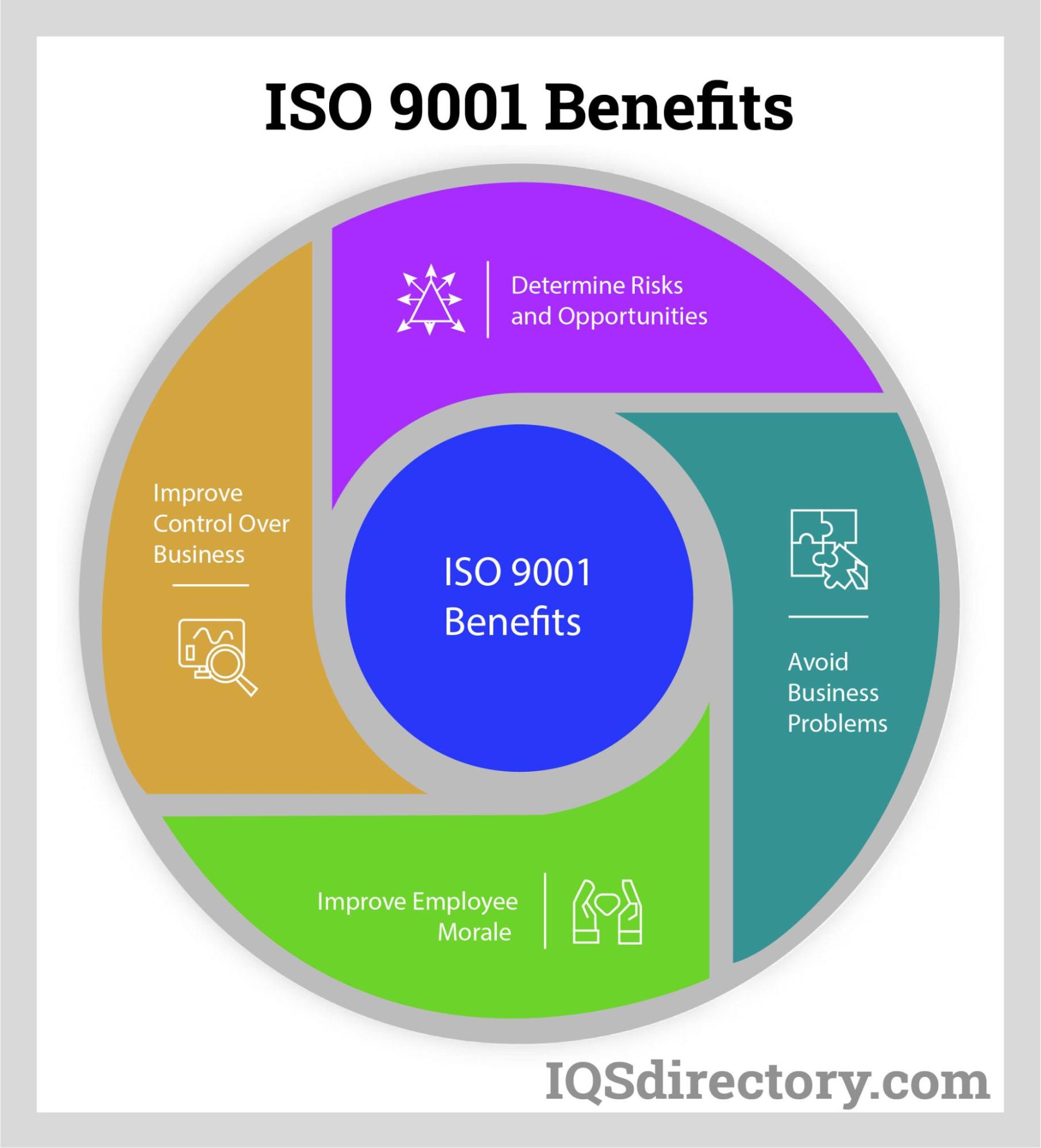
Industry Specific Applications of ISO 9001
ISO 9001 serves as a foundation for sector-specific management system standards, enabling organizations in highly regulated or specialized fields to achieve industry compliance and tailor their processes for best-in-class results. Key derivatives of ISO 9001 include:
- ISO 13485: Designed for medical device manufacturers, ISO 13485 governs all aspects of design, production, installation, and service, supporting audits and regulatory submissions in healthcare industries.
- ISO/TS 54001:2019: Tailored for the unique requirements of electoral organizations, this standard supports the integrity and quality of electoral services provided by election management bodies.
- ISO/IEC/IEEE 90003:2018: Focuses on software development, providing guidelines for applying ISO 9001:2015 principles to computer software engineering and lifecycle processes.
In addition, sectors such as aerospace (AS9100), automotive (IATF 16949), and telecommunications (TL 9000) have developed their own QMS standards derived from ISO 9001, reflecting the universal adaptability and importance of quality assurance across industries.
ISO 45001: Occupational Health and Safety
ISO 45001 establishes the international gold standard for Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems (OHSMS). This certification helps organizations of all sizes identify, mitigate, and prevent workplace hazards, thereby reducing the risk of employee injuries, occupational illnesses, and fatalities. As workplace safety becomes a top priority amid global supply chain challenges, compliance with ISO 45001 demonstrates a company's commitment to worker safety and compliance with legal obligations, such as OSHA in the United States.
Developed with input from OHSAS 18001 as well as International Labor Organization (ILO) conventions, ISO 45001 supports a proactive approach—integrating risk assessment, hazard identification, and preventive controls. Organizations that achieve ISO 45001 certification are more likely to reduce incidents, absenteeism, and insurance costs, while promoting a culture of safety and employee well-being. The adoption of this standard can enhance corporate image, attract top talent, and provide competitive advantages in supplier selection and tendering.


ISO 14001: Environmental Management Systems (EMS)
ISO 14001 defines best practices for Environmental Management Systems (EMS), enabling organizations to minimize their environmental footprint, enhance sustainability, and meet compliance requirements with evolving environmental regulations. The standard is relevant to public, private, and non-profit organizations aiming to improve their environmental performance and establish sustainable operations. Companies utilize ISO 14001 certification to manage resource efficiency, lower waste, improve recycling rates, and reduce environmental risks.

Businesses adopting ISO 14001 must assess their impact on natural resources, energy use, air pollution emissions, water and wastewater management, waste disposal practices, and climate change-related concerns. Complementing ISO 14001, ISO 14004 offers additional guidance for environmental management principles, operational improvements, and EMS efficiency.
Recent enhancements to ISO 14001 emphasize environmental leadership, integration with strategic planning, and a cycle of continual environmental improvement. Implementing this standard can help businesses identify cost-saving opportunities, increase eco-efficiency, ensure legal compliance, and attract environmentally conscious customers and partners. It is an essential part of corporate social responsibility and environmental risk management strategies, especially as organizations work toward net-zero and sustainability objectives.

ISO 13485: Quality Management Systems for Medical Device Manufacturing
ISO 13485 is the internationally recognized standard for Quality Management Systems tailored specifically to the medical device sector. It establishes rigorous regulatory requirements for the design, development, manufacture, installation, and servicing of medical devices and diagnostic tools. This management system enhances risk management, traceability, process validation, and product safety—key elements for regulatory compliance with global agencies such as the FDA, European Medicines Agency (EMA), and others.
ISO 13485 certification increases organizational credibility and streamlines product registration processes in multiple regulatory markets. It supports manufacturers, suppliers, and service providers in the medical device supply chain while ensuring effective internal audits and alignment with continuous quality and safety improvements. This standard is regularly updated every five years to address advancements in technology, regulatory expectations, and sector vulnerabilities.

ISO 22000: Food Safety Management Systems
ISO 22000 is the global standard for Food Safety Management Systems (FSMS), built to ensure food is produced, processed, and handled according to the highest levels of food safety throughout the supply chain. It combines ISO management system principles with the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) methodology to control and minimize biological, chemical, and physical hazards at every step.
This standard is applicable to all organizations in the food supply chain—from producers and processors to retailers and restaurants. Certification to ISO 22000 demonstrates an organization's commitment to food safety compliance, industry regulations, and consumer protection. The standard integrates prerequisite programs (PRPs), interactive communication, and robust systems management to ensure food safety from farm to table.

Implementing ISO 22000 streamlines compliance with national and international food safety legislation, fosters supplier-customer transparency, and reduces risks of contamination, recall, and non-conformance. Obtaining ISO 22000 certification assures stakeholders of a company's keen focus on food safety excellence, risk assessment, and hazard prevention—key factors for growth in competitive food and beverage markets.
ISO 22000 also reinforces process documentation, traceability, and continual improvement for food manufacturers, packaging companies, and logistics providers. Ensuring effective communication at every stage helps to meet evolving customer expectations, regulatory requirements, and industry best practices. Compliance with ISO 22000 gives organizations a powerful marketing tool and increased market access both regionally and globally.

ISO 27001: Information Security Management Systems
ISO 27001 is the international benchmark for implementing, operating, monitoring, maintaining, and improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS). This standard is vital for organizations that process sensitive personal data, intellectual property, financial details, and confidential commercial information in sectors such as healthcare, finance, and technology.
Certification to ISO 27001 enables businesses to identify and mitigate cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and information vulnerability risks. It supports regulatory compliance with privacy and security laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and other industry-specific mandates. ISO 27001 certification provides assurance to customers, partners, and regulators that robust information security controls and cyber risk management measures are in place.

By adopting ISO 27001 best practices, organizations boost their resilience to cyber-attacks, safeguard their reputation, and support business continuity. The certification process includes comprehensive risk assessment, development of security policies, implementation of controls, incident response planning, and internal/external audit requirements—all critical to effective IT governance.
ISO 50001: Energy Management Systems
ISO 50001 is the global standard for Energy Management Systems (EnMS), empowering organizations to systematically improve energy efficiency, reduce carbon emissions, and lower operational costs. This standard helps businesses in manufacturing, real estate, transportation, and other energy-intensive sectors to monitor, manage, and optimize energy consumption through strategic energy performance indicators and continuous process improvements.
ISO 50001 certification showcases a company's dedication to sustainability, compliance with environmental regulations, and alignment with energy efficiency initiatives like corporate social responsibility (CSR) and net-zero targets. Implementing ISO 50001 may require advanced energy monitoring systems and cross-departmental engagement to achieve optimal outcomes in energy conservation and cost reduction.

The standard delivers significant benefits, such as improved resource utilization, reduced emissions, and increased operational agility. It supports integration with other management systems, including ISO 14001 for environmental management, thereby maximizing the value of a holistic sustainability strategy. ISO 50001 is pivotal for organizations seeking to strengthen energy governance, meet regulatory demands, and enhance reputation in the marketplace.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is ISO certification and why is it important?
ISO certification officially recognizes that a company complies with internationally accepted quality management standards, communicating reliability, credibility, and a commitment to high-quality, safe, and sustainable products or services.
Which ISO standards are most commonly used across industries?
Common ISO standards include ISO 9001 (quality management), ISO 14001 (environmental management), ISO 45001 (occupational health and safety), ISO 13485 (medical devices), ISO 22000 (food safety), ISO 27001 (information security), and ISO 50001 (energy management).
What are the main steps involved in achieving ISO certification?
The process includes creating and documenting a management system, implementing procedures, conducting internal reviews, undergoing audits by an accredited third party, and receiving ongoing surveillance and recertification audits.
How does ISO 9001 differ from ISO 14001 and ISO 27001?
ISO 9001 focuses on quality management systems, ISO 14001 targets environmental management practices, while ISO 27001 addresses information security management, helping organizations safeguard quality, sustainability, and data security, respectively.
Why should organizations hire an ISO consultant during certification?
ISO consultants offer expertise in regulatory requirements, conduct gap analyses, guide efficient implementation, and support documentation and audit preparation, streamlining the pathway to certification and compliance.
Are ISO standards recognized globally, and how do they benefit companies internationally?
Yes, ISO standards are internationally recognized, trusted in over 170 countries. Certification enhances a company’s global reputation, expands client reach, and simplifies compliance with diverse international regulatory bodies.
Chapter Four: What are the benefits of ISO certification?
ISO documentation provides specifications, guidelines, practices, and processes that organizations can utilize to guarantee that materials, products, procedures, and services meet the highest quality standards. Guidelines for information security, food safety, risk management, environmental performance, and quality management contribute to enhancing a company's reputation and credibility. Adhering to ISO standards ensures excellence, consistency, and safety.
The benefits of ISO accreditation:
- Reliability: An ISO accreditation shows a company’s dependability to customers, suppliers, business partners, and the government as well as its dedication to the quality, safety, and durability of its goods and services. Included in ISO accreditation is a demonstration of adherence to and meeting the requirements of international laws and regulations as well as a commitment to excellence.
- Enhanced efficiency: To adhere to ISO standards, companies describe, record, and track their processes to determine their goals and track their development. ISO accreditation provides companies with the knowledge to optimize their operations and boost performance. Following the ISO process helps people to work effectively and efficiently, as well as to adopt new working methods quickly and successfully.
- Superior quality: ISO standards enable companies to improve the quality of their services and manage projects efficiently to reach new markets. The display of the ISO emblem promotes consumer confidence since it is associated with reliability and high quality. Compliance with ISO standards gives clients faith and confidence in a company’s goods and services.
- Better quality control: ISO complaint management and client satisfaction monitoring standards keeps clients and customers happy and reduces consumer complaints, an important advantage of ISO certification, according to research.
- Increased income: ISO certification allows a company to market its quality, which leads to an increase in revenue and sales. Large businesses demand that suppliers have an ISO certification, which is crucial for businesses looking to expand into international markets. ISO standards have become more important as world markets become more interconnected in regard to the movement of goods, services, and logistical technologies. The finest performance outcomes occur in businesses that consistently strive to enhance operations.
- Risk mitigation: The ability to anticipate hazards and turn them into opportunities is a key advantage of ISO standards. The requirements guarantee and awareness of methods for risk management and risk reduction. When issues do develop, businesses are prepared to handle them and recover quickly.
- Sustainability: In recent years, sustainability has become a major concern for companies as they focus on how their operations will affect future generations. ISO standards assist by showing an organization's commitment to addressing environmental and social issues. Businesses save money, boost their reputation, and address environmental issues by examining how they use their resources and energy as well as the quality of their waste management practices.
- Innovation: A practical outcome of ISO certification is a business’ ability to see its processes and develop new and innovative ways to approach problems. The energy and system improvement provided by ISO certification opens communications and empowers all members of an organization.
- Applies to all business sizes and types: A primary goal of the ISO is to help companies improve, regardless of their size, function, and sector. If the world is to properly deal with the issues of climate change and industrial pollution, it needs a set of standards as a guide and touchstone, which is what the ISO provides.