Electric Actuators
Electric actuators are devices capable of creating motion of a load, or an action that requires a force like clamping, making use of an electric motor to create the force that is necessary...
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
This article will take an in-depth look at 12V linear actuators
The article will bring more detail on topics such as:
In this chapter, we delve into the mechanics and functioning of 12V linear actuators, examining their operation and various uses.
A linear actuator transforms rotational motion into linear movement, enabling the actuation of machinery or materials through pushing, pulling, lifting, lowering, sliding, or tilting actions. These devices provide dependable, low-maintenance motion control that is both eco-friendly and secure. Powered by a 12-volt DC source, 12V linear actuators are characterized by three main types: screw, wheel and handle, and cam. Screw-type actuators achieve movement as the screw mechanism winds and unwinds.
In wheel and handle actuators, motion results from the tension of a belt or chain attached to a shaft. Meanwhile, cam actuators employ an eccentric circle to shift the shaft. The definition of a linear actuator may vary by industry. Often, it is understood as a device engineered to transform rotary force into linear movement, with initial forces derived from motors or hand cranks.
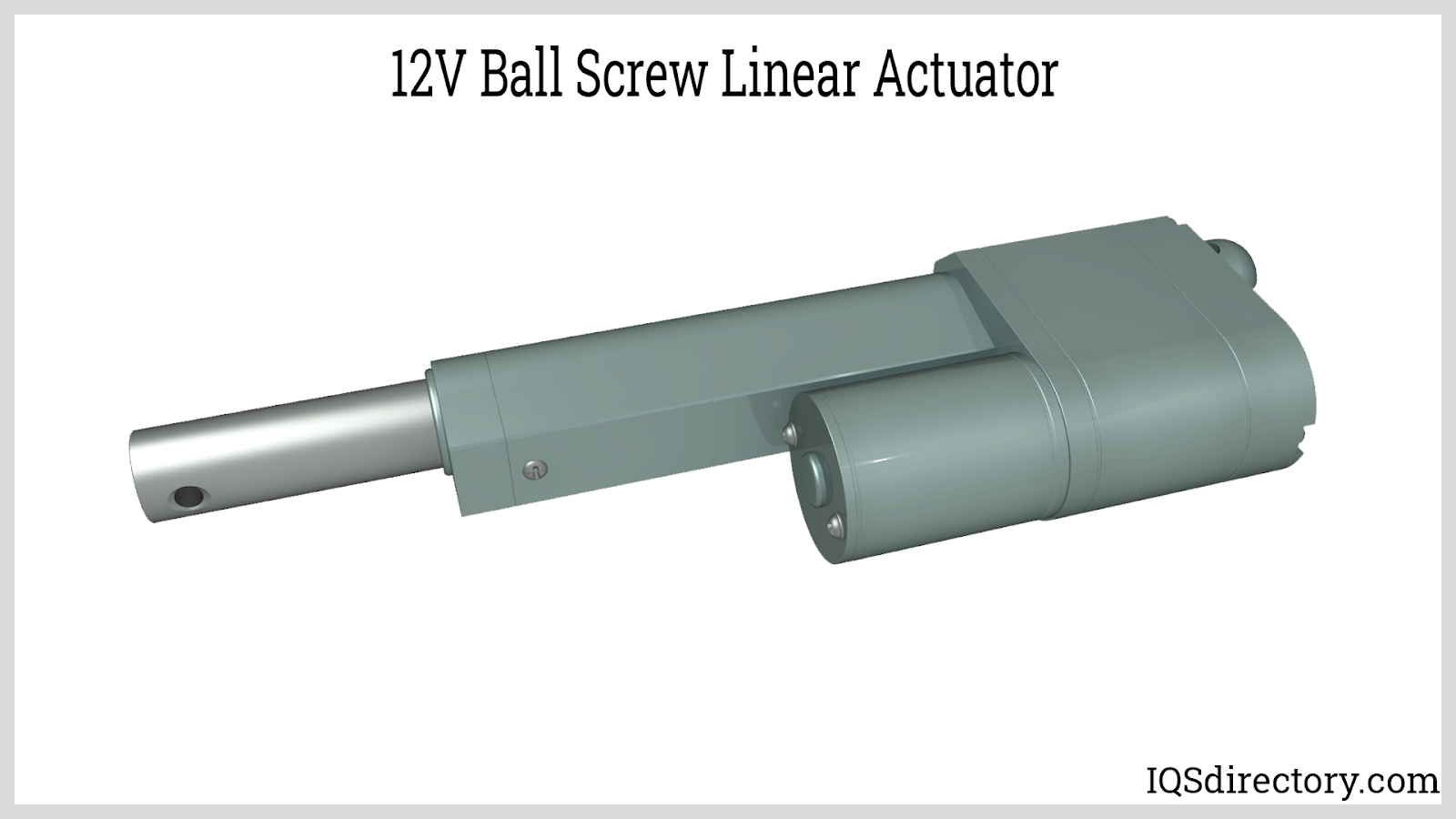
At the heart of a 12V linear actuator lies a compact DC gear motor that applies a screw-drive mechanism and gears to electromechanically manage heavy loads. Due to their robustness, ease of installation, and compact nature, these 12V DC actuators are exceptionally versatile. Each actuator includes two wires (positive and negative), mounting holes at each extremity, and built-in limit switches. With stroke lengths ranging from 1 inch to 24 inches, these actuators can exert force capabilities of 15 lbs, 50 lbs, or 150 lbs. Customization of these actuators in terms of specific sizes, currents, and speeds is common to meet distinct client needs.

Linear actuators move in a straight trajectory, with various methods achieving such motion. They are integral to numerous applications, from facilitating wheelchair access and toys to complex space technology equipment.
A DC motor powers these actuators, typically using a 12V DC voltage. In brush DC actuators, a switch can reverse the motor’s polarity, altering the actuator's motion. Servo and stepper motors necessitate control electronics to electrically manage current direction within the motor. For proper BLDC and servo motor commutation, rotor feedback is crucial, using devices like Hall effect sensors or encoders.
An actuator's control electronics may be integral or externally accessible. The force applied by an actuator is influenced by its speed, with a trade-off between the two: reducing the actuator's speed through a gearbox enhances the force output. Differentiation among actuators can be seen in the screw and shaft length, which determines stroke length.
The actuator's speed is determined by the gears between the motor and the screw. Stroke length is controlled using devices like limit switches, encoders, linear potentiometers, or LVDT sensors. Microswitches at the shaft's ends may control the stroke, responding to the screw’s movement for precise management.
This chapter will cover the key design considerations for 12V linear actuators, including important technical factors and performance features to evaluate when selecting the ideal actuator for your specific industrial automation or motion control application. By understanding the main aspects that influence the reliability and efficiency of 12V electric actuators, you can make better purchasing decisions for your automation systems, robotics projects, or manufacturing processes.
The duty cycle determines how frequently and for how long the actuator will operate within a given period. Since power is lost through heat, the duty cycle is determined by the actuator's temperature while it is in motion. By adhering to the duty cycle recommendations, you can prevent motor overheating and component damage in the actuator, enhancing the lifetime and reliability of your linear actuator system. There is variance in the duty cycles of actuators because they are not all created equally. Factors such as actuator age, mechanical load, external loading characteristics, and ambient temperature can all influence duty cycle ratings. Actuators designed for high-duty or continuous use are often equipped with specialized motors and thermal protection features.
While actuator speed is a key factor, it is also crucial to consider the weight or mass that needs to be moved, since an actuator's travel speed will decrease as the required force increases. Speed is usually measured in millimeters per second (mm/s) or inches per second (in/s), and load ratings are specified in newtons (N) or pounds (lbs). By calculating the required duty cycle in conjunction with weight and speed specifications, you’ll be able to size the actuator appropriately for your application and avoid premature wear or mechanical failure. Consider applications like motorized standing desks, lifting platforms, or robotics arms, which all demand tailored speed and force profiles.
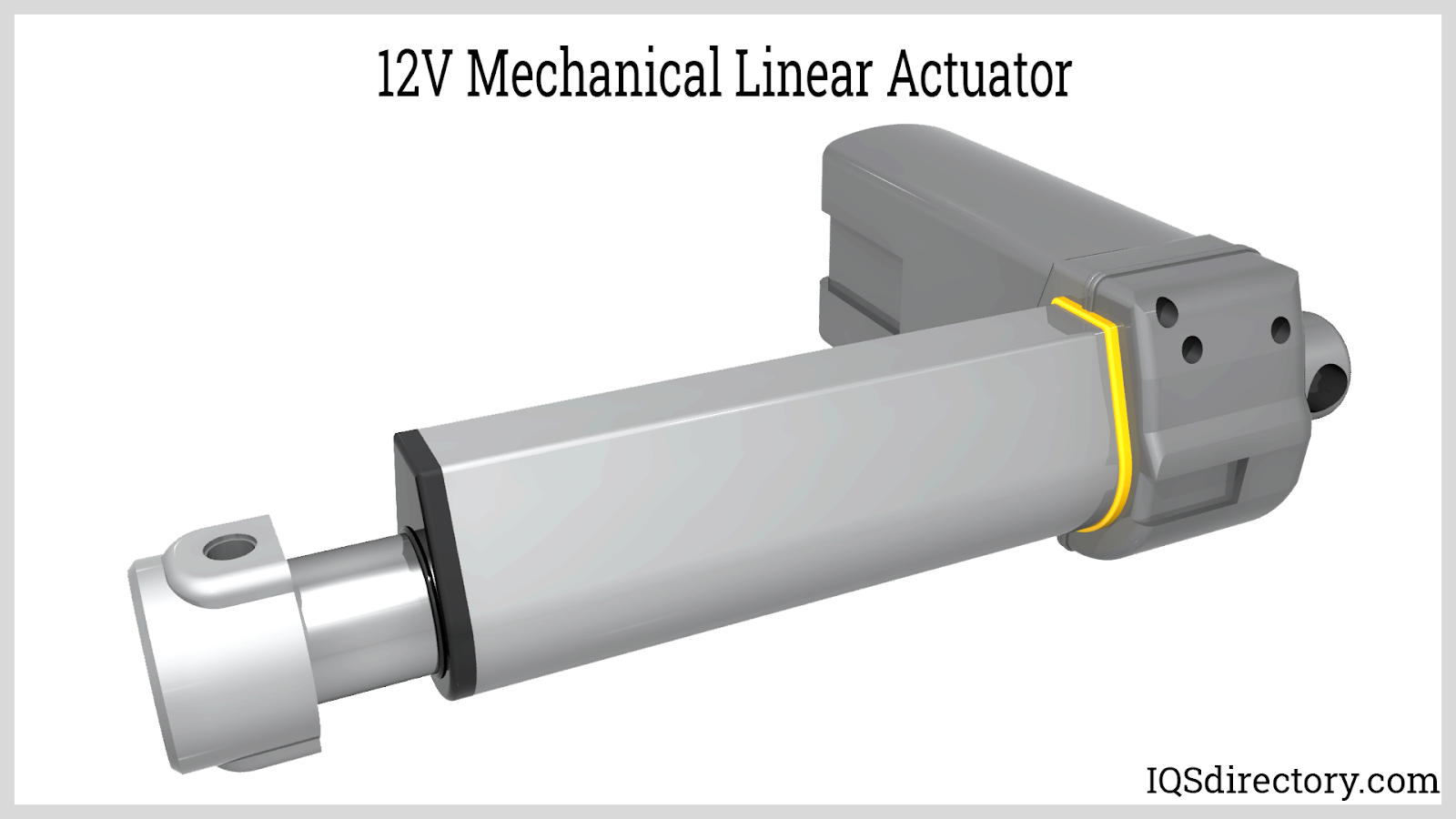
Before you purchase a 12V linear actuator, thoroughly review all technical specifications, including input voltage, peak force, stroke length, and speed ratings. Take into account the actuator's duty cycle, precision, ease of control (such as remote control systems), and available mounting options for seamless installation. For highest reliability and long-term success, consider working with experienced linear actuator suppliers who can provide custom solutions, engineering support, and access to high-quality, durable actuators for a wide range of industries—including manufacturing automation, automotive, marine, agriculture, and smart home systems.
12V linear actuators are widely used electromechanical devices that create push or pull force using a low-voltage power supply. These compact actuators are engineered for diverse automation tasks across industrial, automotive, marine, robotics, home automation, and manufacturing environments. The variety of 12V linear actuators ensures compatibility with different load and speed requirements, precise position control, and integration with smart control systems. Below, discover the most common types of 12V linear actuators, their unique mechanical designs, and key application advantages.
The primary function of mechanical or electromechanical linear actuators is to convert rotational motion into smooth, reliable linear motion. Typically, this conversion is achieved through mechanical mechanisms such as screws, wheels and handles, belts, racks, or cams—all foundational elements in linear actuator assemblies. These actuators are integral for controlled, repeatable movement in machinery and automation systems.
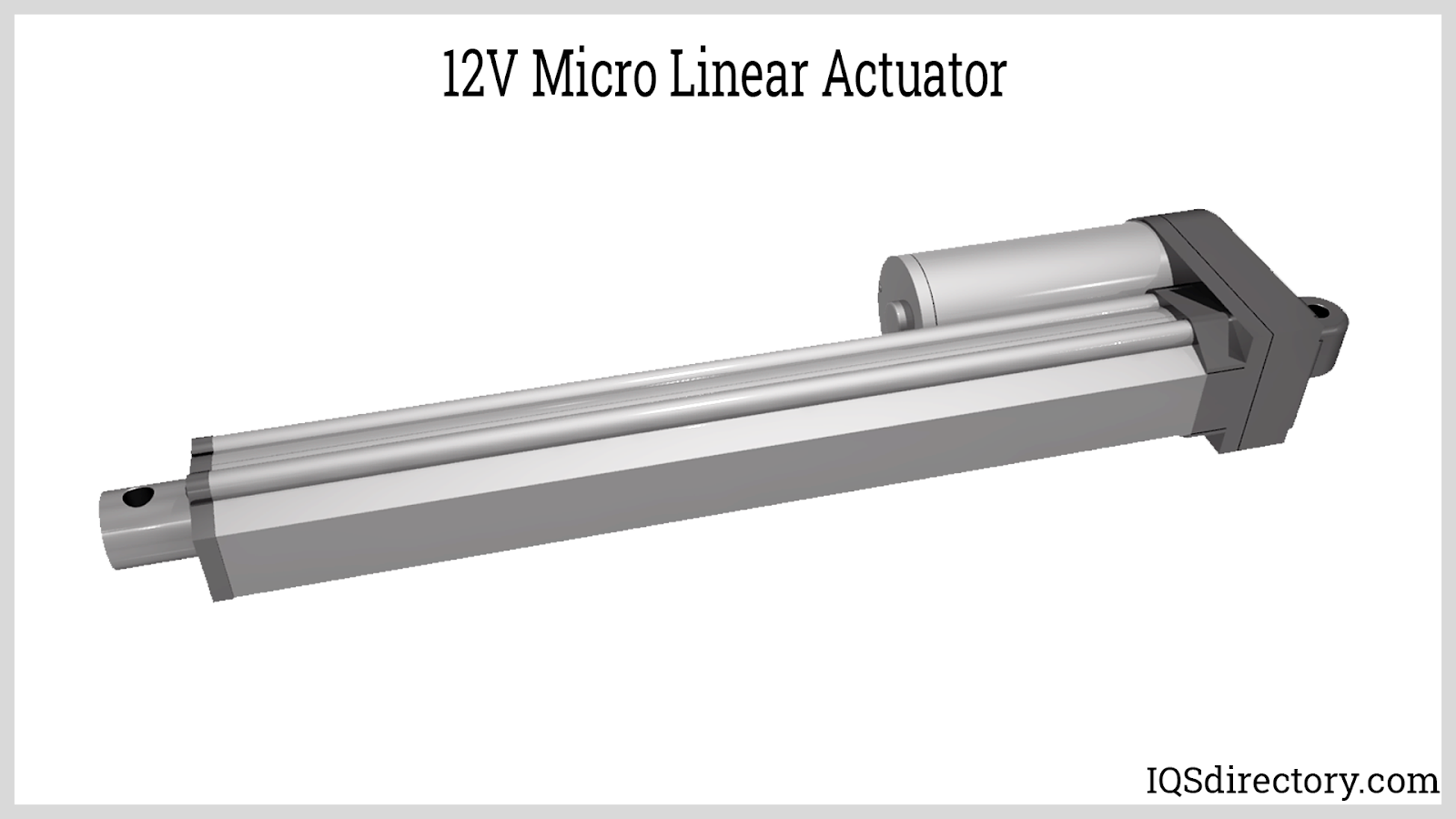
Mechanical linear actuators are driven by either AC or DC motors, with 12V DC options being especially prized for portable or battery-operated applications. In screw-type mechanical linear actuators, a variety of screw threads—including ball screws, lead screws, and roller screws—are utilized for higher efficiency and greater load capacity. The actuator typically consists of a rotating screw shaft, guided by a stator and nut, that generates precise linear travel along its main axis.
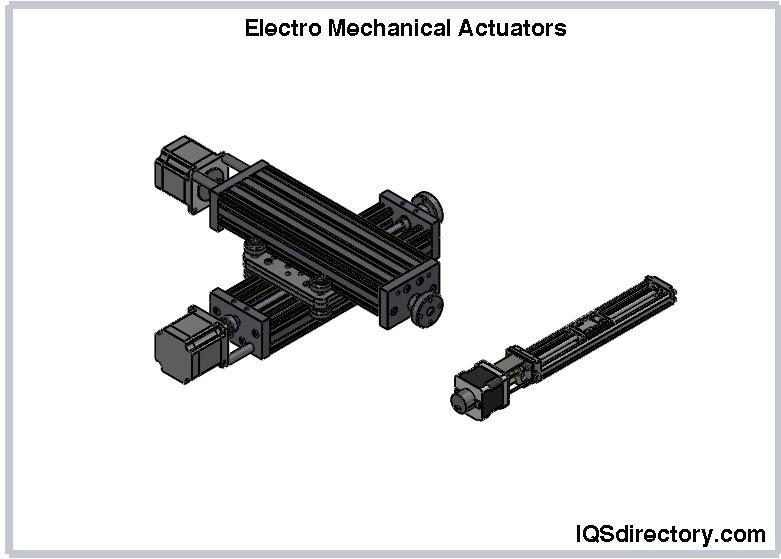
The wheel and handle style employs drive mechanisms like belts, chains, or cable assemblies attached to the shaft, often supported by recirculating ball bearings, cam follower guides, or plain linear bearings for smooth movement. These actuator types are optimal for applications requiring long stroke lengths and higher operating speeds, making them popular in automotive, packaging, and industrial automation sectors. The cam-driven variant uses an eccentric wheel to produce thrust for repetitive processes such as pressing, stamping, or switch actuation.
A servo linear actuator integrates a feedback-based motion control system via a servo controller, enabling precise position, speed, and force regulation. By continuously monitoring sensor input, the controller compares real-time actuator positioning against desired setpoints and automatically adjusts movement to correct deviations—delivering exacting performance.
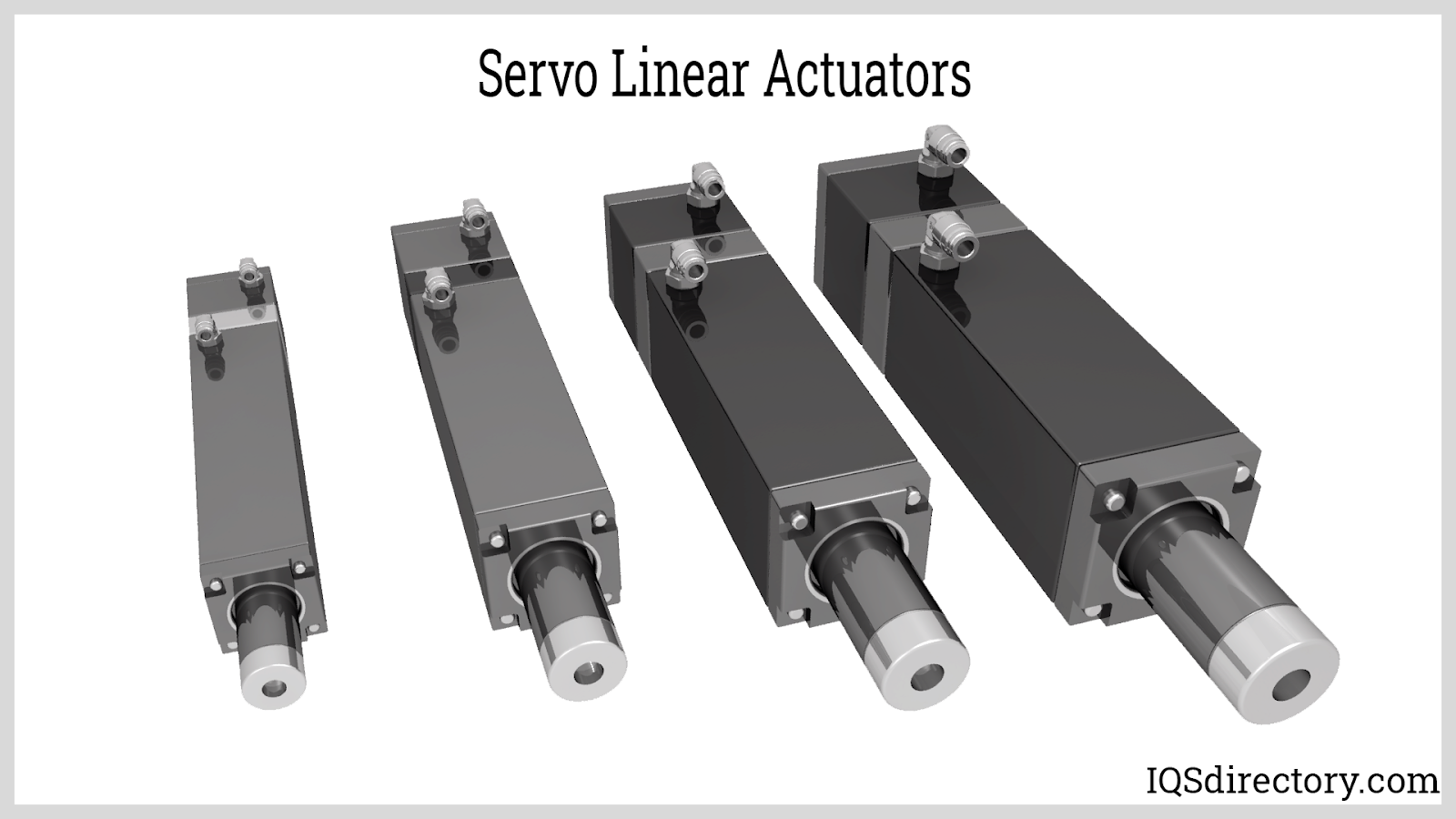
Servo actuators excel in demanding applications where high accuracy and repeatability are essential, including robotics, laboratory equipment automation, medical devices, CNC machines, and advanced industrial automation. Their capacity for fine-tuned adjustments makes them indispensable in tasks such as beam steering, satellite tracking, and camera positioning. As technology advances, servo linear actuators with intelligent motion algorithms are becoming more pervasive in smart manufacturing, Industry 4.0 environments, and unmanned systems.
Lead screw linear actuators transform rotary motion from an electric motor—often a stepper or brushless DC motor—into smooth, linear travel. Their defining feature is the combination of a power screw and a matching nut, typically crafted with precision-rolled threads for strength, long lifespan, and minimized friction. These actuators are preferred for precise load control, vertical lifting, and applications with moderate speed requirements.
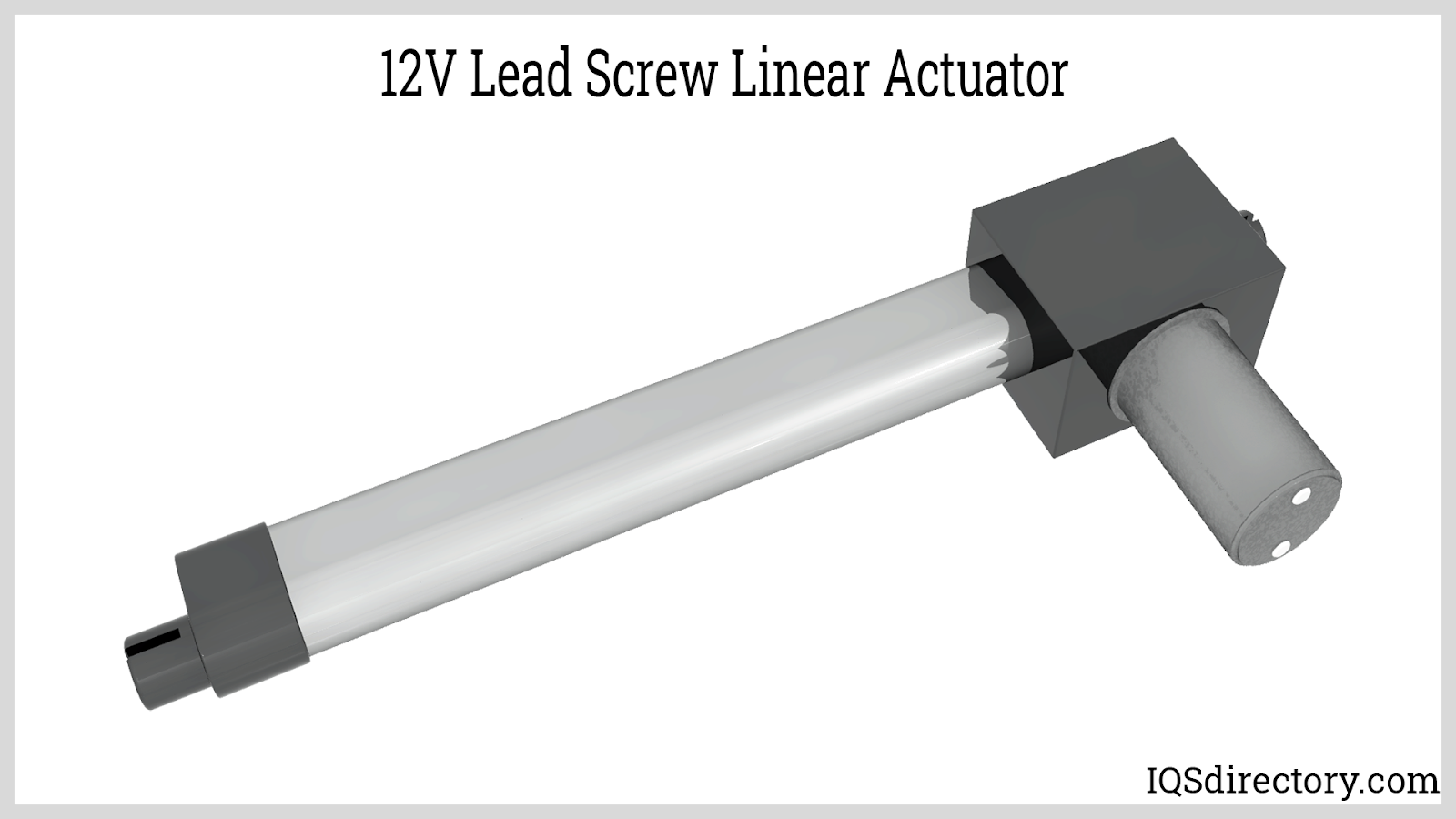
To ensure reliable and low-wear operation, the nut material is often selected for its self-lubrication properties or is made from polished metal treated with special lubricants. Lead screw actuators are compatible with open-loop control systems and can be paired with integrated position sensors for enhanced feedback. 12V linear actuators equipped with various motor types provide flexible solutions for industrial automation, laboratory instruments, and medical devices that demand accurate, repeatable stroke motions.
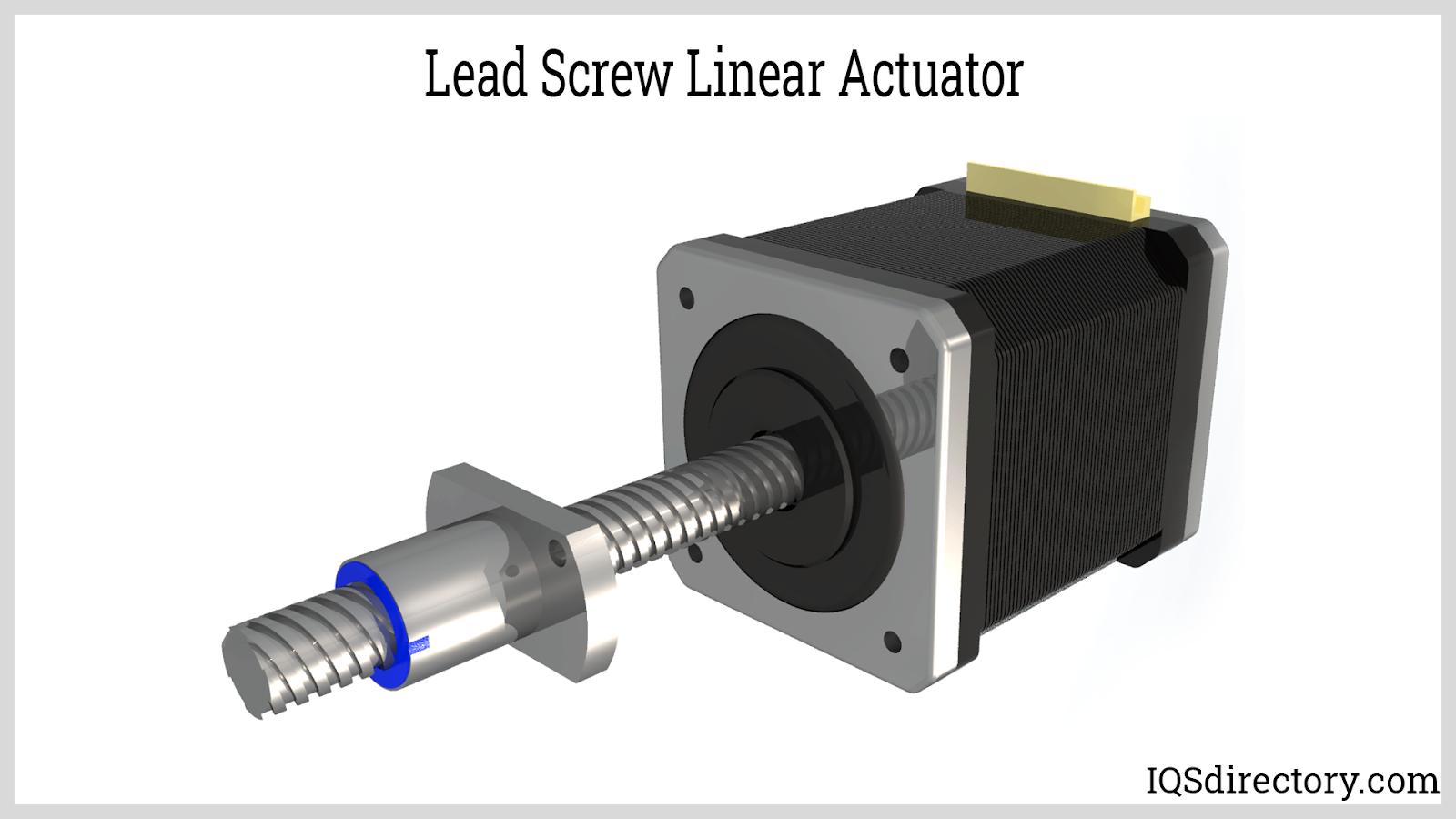
A threaded rod and a corresponding nut are part of the lead screw actuator's construction. The motor turns either the rod or the nut by mounting them directly, connecting them through gears or a belt, or both. The component that has to be moved is connected to the element that is not a part of the motor.
Electric linear actuators are electromechanical devices that convert electrical energy into controlled mechanical movement in a straight line. Standard in industrial automation, process control, and heavy equipment, these actuators use AC or DC motors—including compact, energy-efficient 12V variants—for precise actuation of valves, dampers, gates, and positioners. They offer superior control, reliability, and adaptability compared to pneumatic or hydraulic solutions.
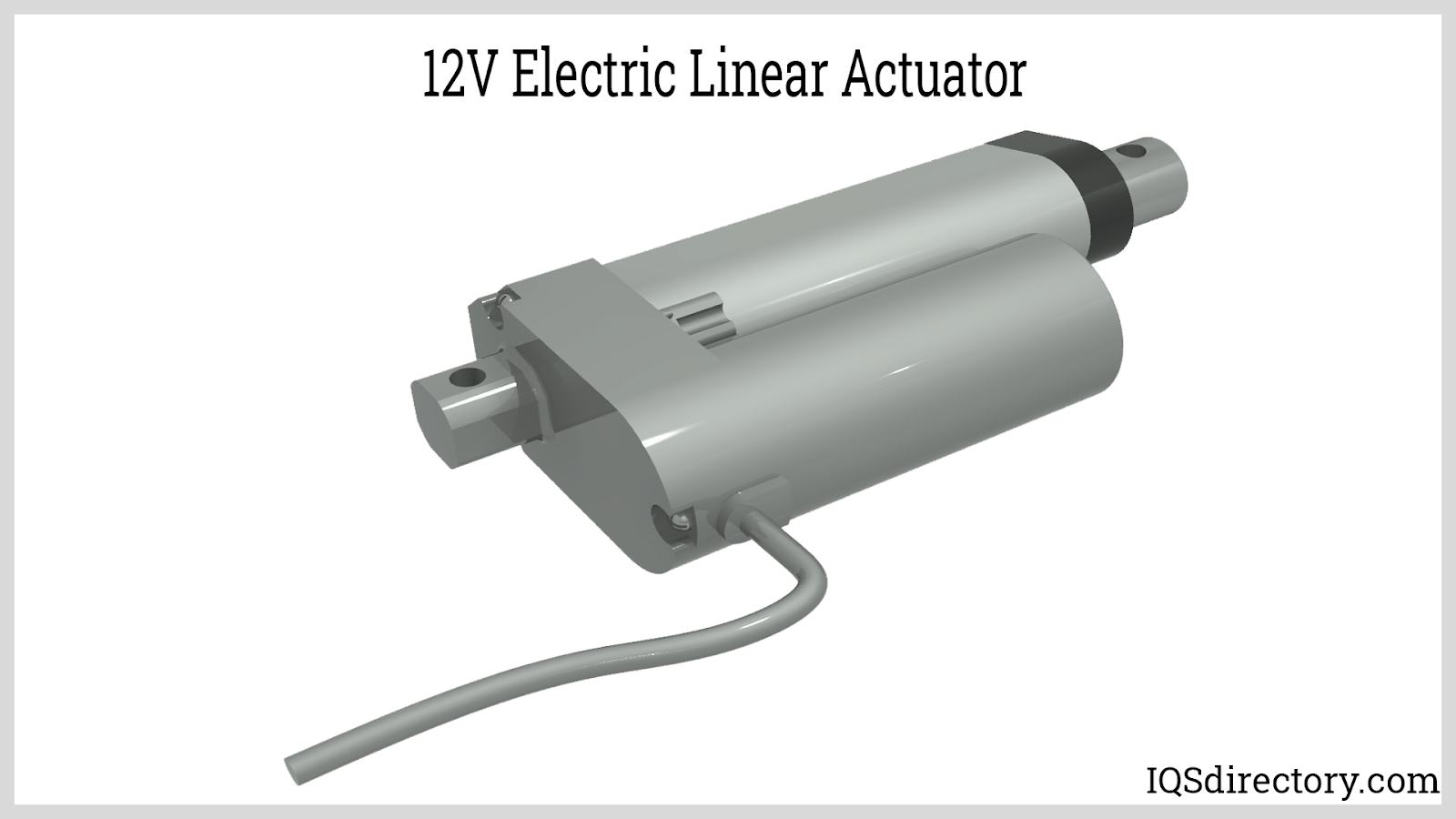

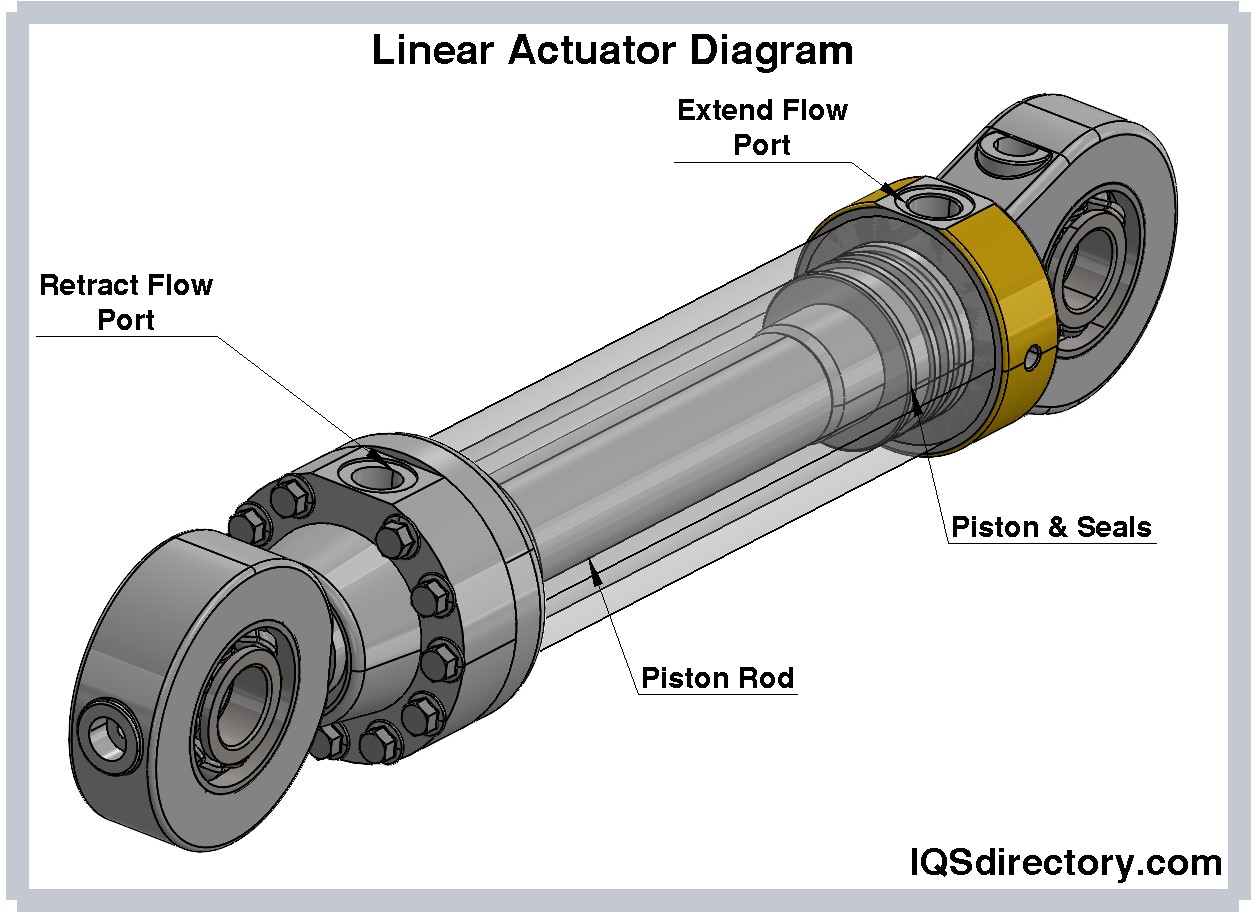
The essential components of an electric actuator include an electric motor, actuating screw, driving nut, and a set of internal or external gears. As the nut rotates along the screw, electrical energy is transformed seamlessly into mechanical motion for automated opening, closing, lifting, or adjusting. Applications range from window lifts and hospital beds to manufacturing line automation and smart home systems, thanks to their efficiency and low-maintenance requirements. Electric rotary actuators also deliver powerful performance for quarter-turn valve applications, such as operating butterfly and ball valves.
Like hydraulic linear actuators, pneumatic linear actuators operate using pressurized air to drive a piston within a sealed cylinder. This method eliminates the need for hydraulic fluids, offering greater speed and environmental adaptability. The force output is determined by the piston diameter and the supplied air pressure, granting versatility for light to medium-duty automation tasks.
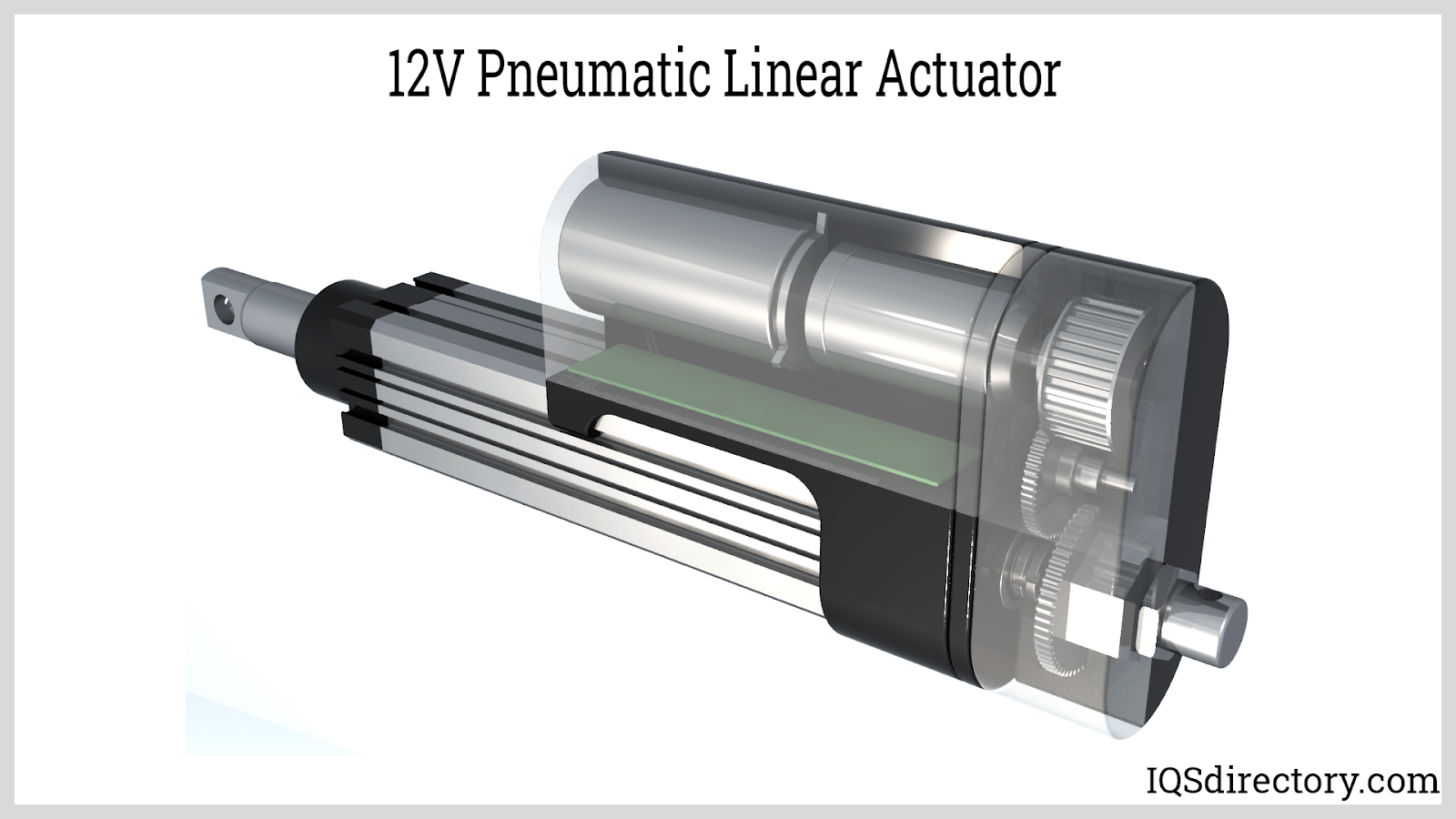
As pressure increases, the actuator provides higher thrust and faster actuation, making pneumatic linear actuators ideal for repetitive, high-speed operations in packaging, food processing, and assembly lines. Unlike electric actuators, pneumatic variants are inherently resistant to magnetic disturbances and are chosen where explosion-proof or intrinsically safe designs are critical. They are engineered to operate reliably in extreme temperature ranges, from -40°F to 250°F, and require minimal maintenance.
Ball screw linear actuators—sometimes called ballscrew drives—convert rotary motor input into linear movement using a helical ball screw and ball nut. These actuators are renowned for their outstanding precision, high-efficiency movement, and durability, achieved by recirculating hardened ball bearings between the screw and nut. This micro-machined design minimizes friction and enables high thrust output with minimal wear, even under continuous operation.
Ball screw actuators typically outperform regular lead screw actuators in high-duty cycle and heavy-load environments. Their superior repeatability, longer service intervals, and controlled backlash make them ideal for CNC machinery, aerospace manufacturing, robotics, and advanced optical equipment.
The speed and force characteristics of a ball screw actuator are defined by the lead and pitch of the screw. Lower lead values generate greater thrust at lower speeds, while higher pitch allows faster nut travel for each revolution. The intricate ball bearing assembly travels along specially machined raceways in the nut, reducing backlash and ensuring longevity. Drive options include belt drives, direct coupling, or worm gear mechanisms for various application needs.
Ball screw linear actuators are essential for industrial motion control, manufacturing aircraft and medical devices such as dialysis machines. They support substantial dynamic loads, provide smooth positioning, and are trusted for critical automation where reliability and accuracy are required.
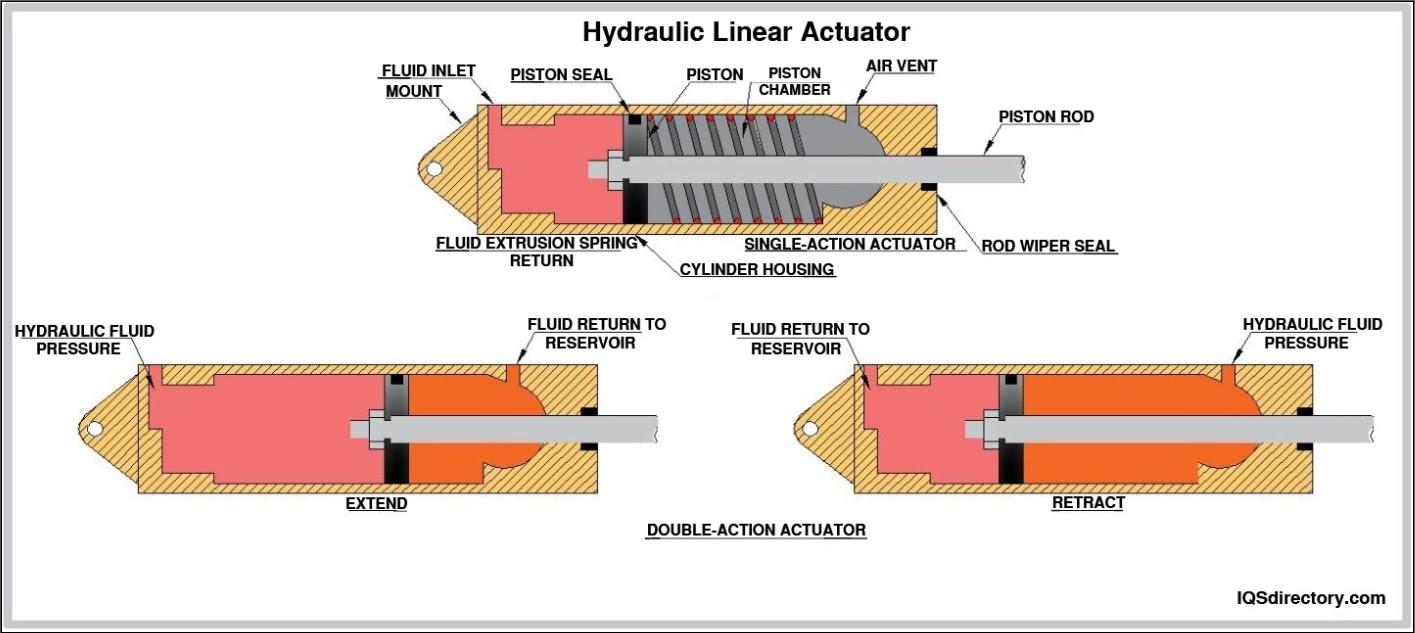
Hydraulic linear actuators are engineered for maximum force output and are often used where extremely high power and heavy lifting are required. Operating through an incompressible hydraulic fluid inside a sealed cylinder, these actuators share core components with hydraulic motors—namely, a piston, cylinder, and control valves—to convert fluid pressure into linear force. Common applications include industrial equipment, construction machinery, and lifting or pressing systems where loads reach thousands of pounds or more.
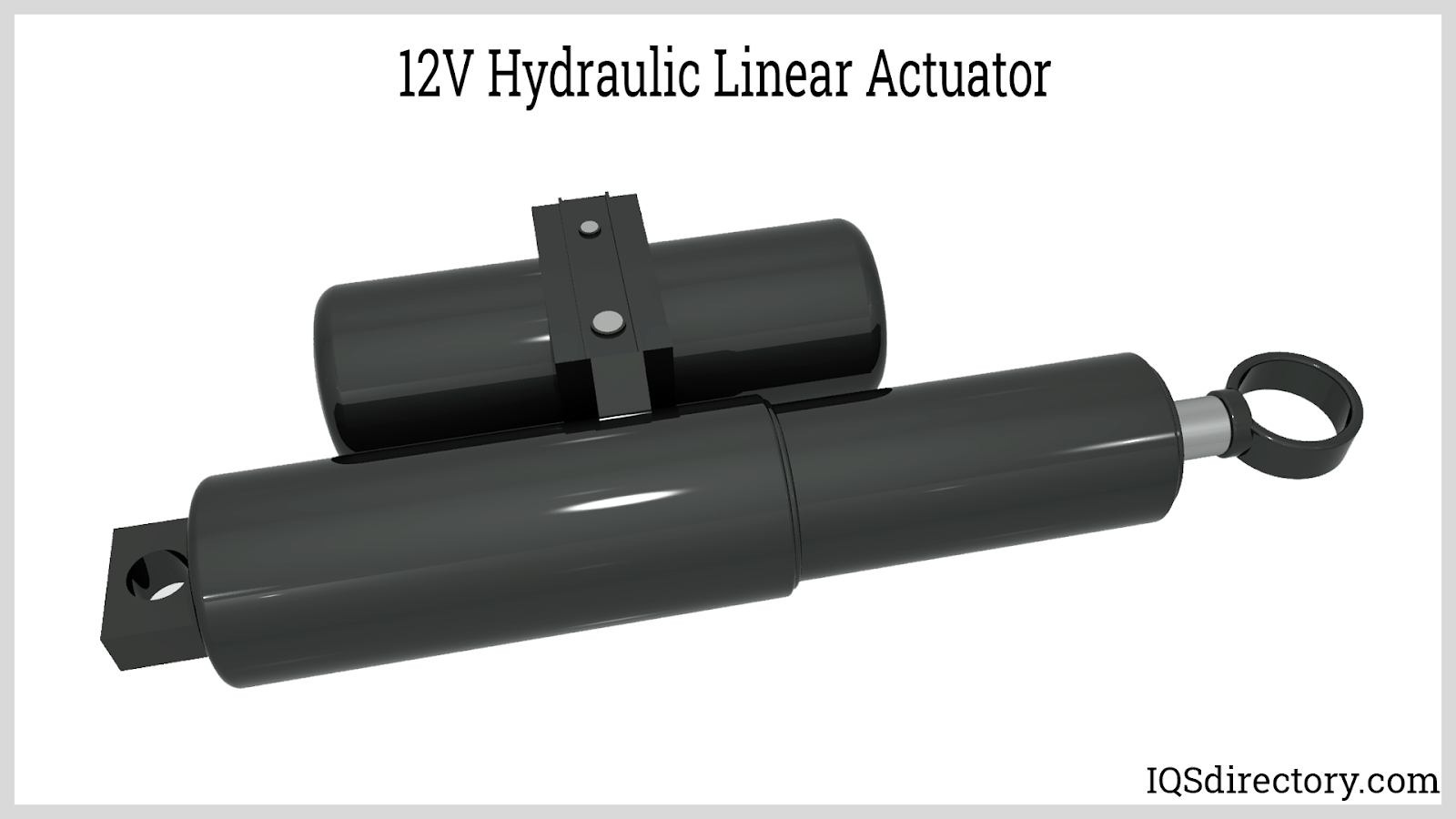

By varying the flow and pressure of hydraulic oil, users achieve precise adjustment of actuator speed and positioning. Different grades of hydraulic fluids optimize operation for temperature stability and lubrication. Hydraulic linear actuators are lauded for their exceptional accuracy, reliability, and adaptability—they can behave like an articulated arm in demanding environments. Industries select hydraulic actuators for their load capacity, shock absorption, and surefire performance under the harshest conditions.
Choosing the Right 12V Linear Actuator: When selecting a 12V linear actuator, consider the application's required load, duty cycle, stroke length, speed, and available space. Popular use cases include precise motion in home automation, ergonomic furniture, automated manufacturing, robotics, and vehicle automation tasks (such as adjustable seats or tailgates). For high-cycle operations, prioritize actuators with robust bearings and enhanced sealing to extend service life. Working with an experienced supplier ensures integration with programmable controllers and compatibility with IoT, PLC, and wireless control interfaces, expanding future automation capabilities and reliability.
A 12V linear actuator is an electromechanical device that uses a 12-volt DC source to transform rotational motion into linear movement, enabling pushing, pulling, lifting, or tilting in various automation applications.
Common types include screw-driven actuators, wheel and handle actuators, cam actuators, servo linear actuators, lead screw, ball screw, electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic linear actuators—each suited for specific loads and precision needs.
Key considerations include required force, speed, stroke length, duty cycle, efficiency, environmental conditions, available installation space, and application-specific precision or load capacity requirements.
Environmental factors such as exposure to dust, moisture, or extreme temperatures necessitate actuators with appropriate IP ratings or corrosion-resistant materials for reliable, safe operation in challenging settings.
12V linear actuators are widely applied in manufacturing automation, robotics, healthcare equipment, automotive systems, smart homes, agriculture, marine, and laboratory automation, offering versatile and precise motion control.
Yes, manufacturers offer customized 12V linear actuators tailored for specific sizes, currents, speeds, and control electronics to meet the diverse demands of industrial and specialized automation projects.
This chapter will explore the applications and advantages of linear actuators, including 12V linear actuators.
The following applications are ideal for 12V linear actuators:
Linear actuators have a variety of applications, including:
The many applications for a linear actuator have increased workplace automation. It reduces production costs while streamlining manufacturing. For the best material handling, electric linear actuators have evolved into a crucial and essential instrument. Loads are moved from point A to point B via linear actuators. The capacity to halt the action mid-stroke is an additional feature of the electromechanical version. Industrial, high-speed, and micro models are a few of the other kinds of actuators used in material handling.
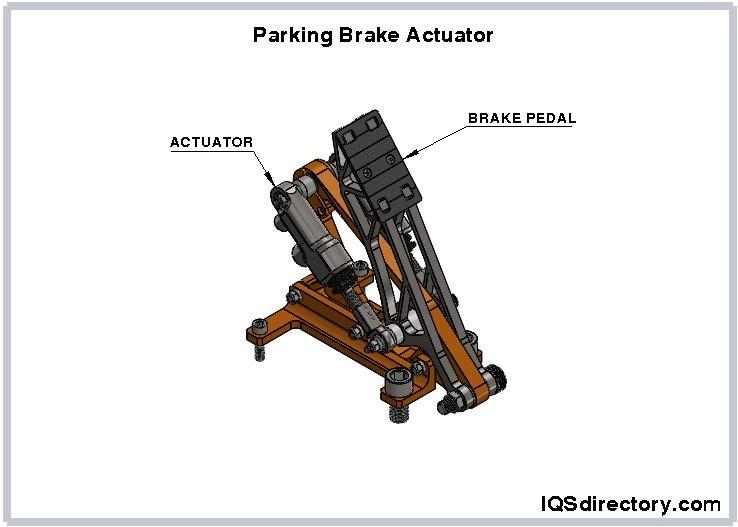
In order to lift, lower, slide, or tilt machines or materials, a linear actuator converts rotational motion into push or pull linear motion. They provide clean, safe, and effective motion control that doesn't require any maintenance. 12 Volt DC voltage sources are used to power 12 Volt linear actuators. The three different varieties of linear actuators are the screw, wheel and handle, and cam. The kind of screw is determined by the upward and downward motion of the screw winding and unwinding. Benefits, design considerations and applications need to be understood when choosing 12V linear actuators.

Electric actuators are devices capable of creating motion of a load, or an action that requires a force like clamping, making use of an electric motor to create the force that is necessary...
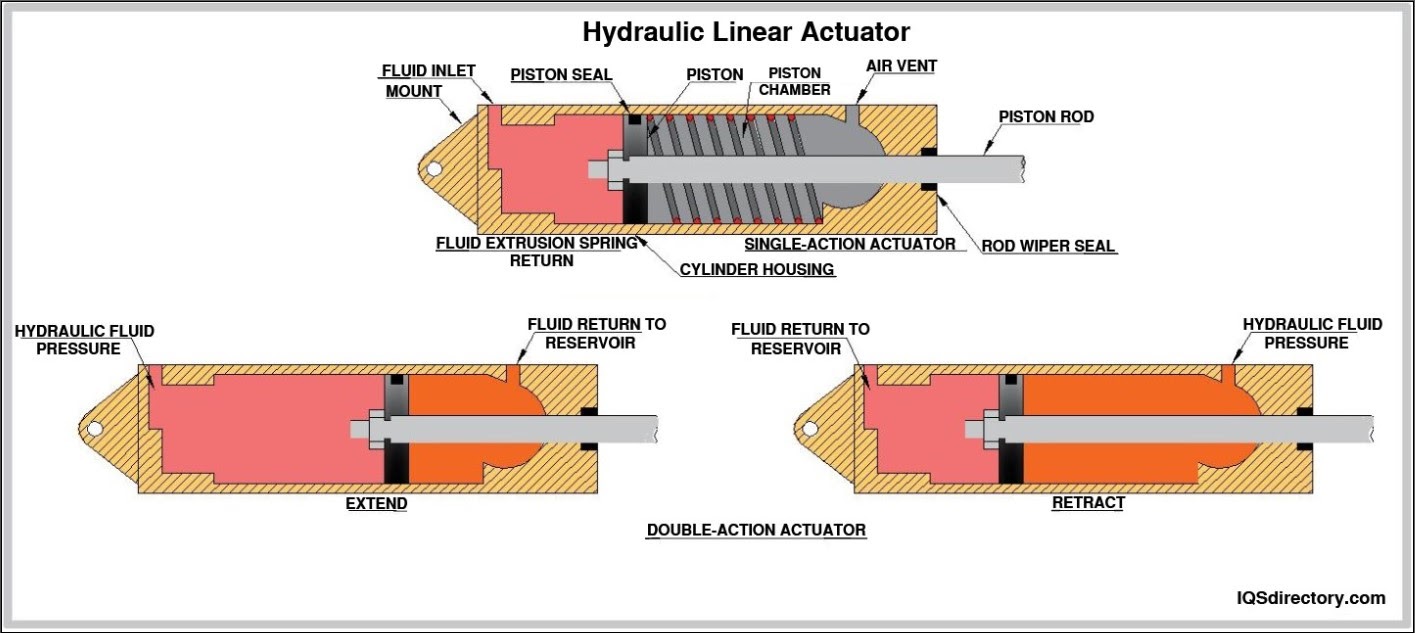
A linear actuator is a means for converting rotational motion into push or pull linear motion, which can be used for lifting, dropping, sliding, or tilting of machines or materials. They provide safe and clean...
High-precision, linear motion goods are essential components at the core of several items which are generally used in machine tools and equipment for manufacturing semiconductors. These items are utilized...
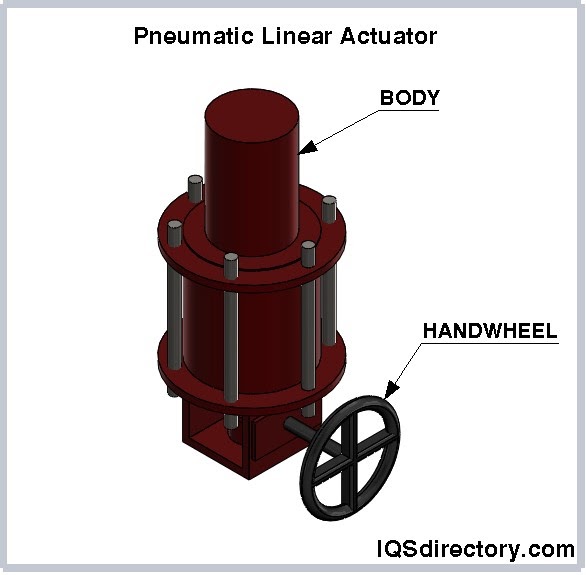
A linear actuator actuates, moves, in a linear, straight, line to complete or start a process. There are a variety of terms used to describe a linear actuator such as ram, piston, or activator. They are very common in...
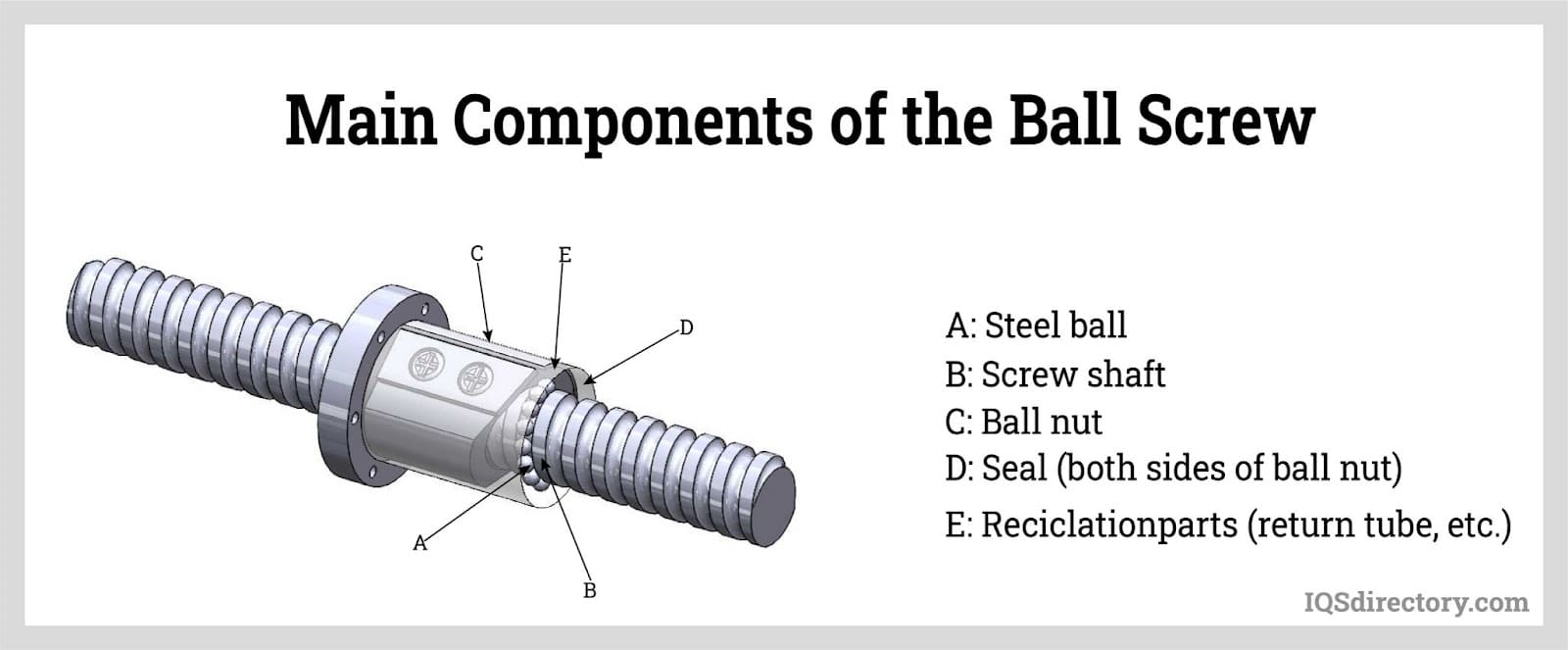
Ball screws are mechanical linear actuators that consist of a screw shaft and a nut that contain a ball that rolls between their matching helical grooves. The primary function of ball screws is to convert rotational motion to linear motion. Ball nuts are used in...
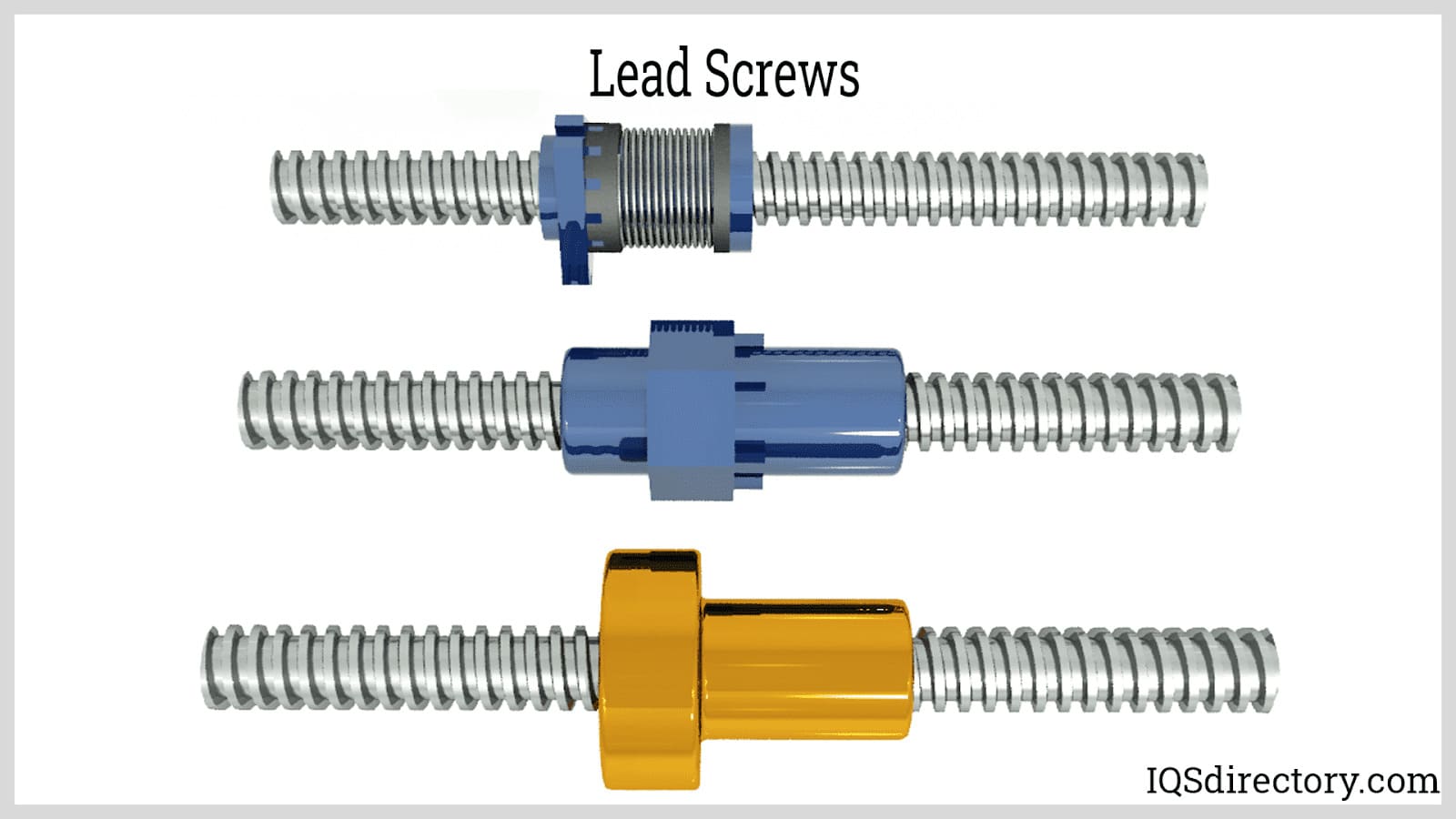
A lead screw is a kind of mechanical linear actuator that converts rotational motion into linear motion. Its operation relies on the sliding of the screw shaft and the nut threads with no ball bearings between them. The screw shaft and the nut are directly moving against each other on...
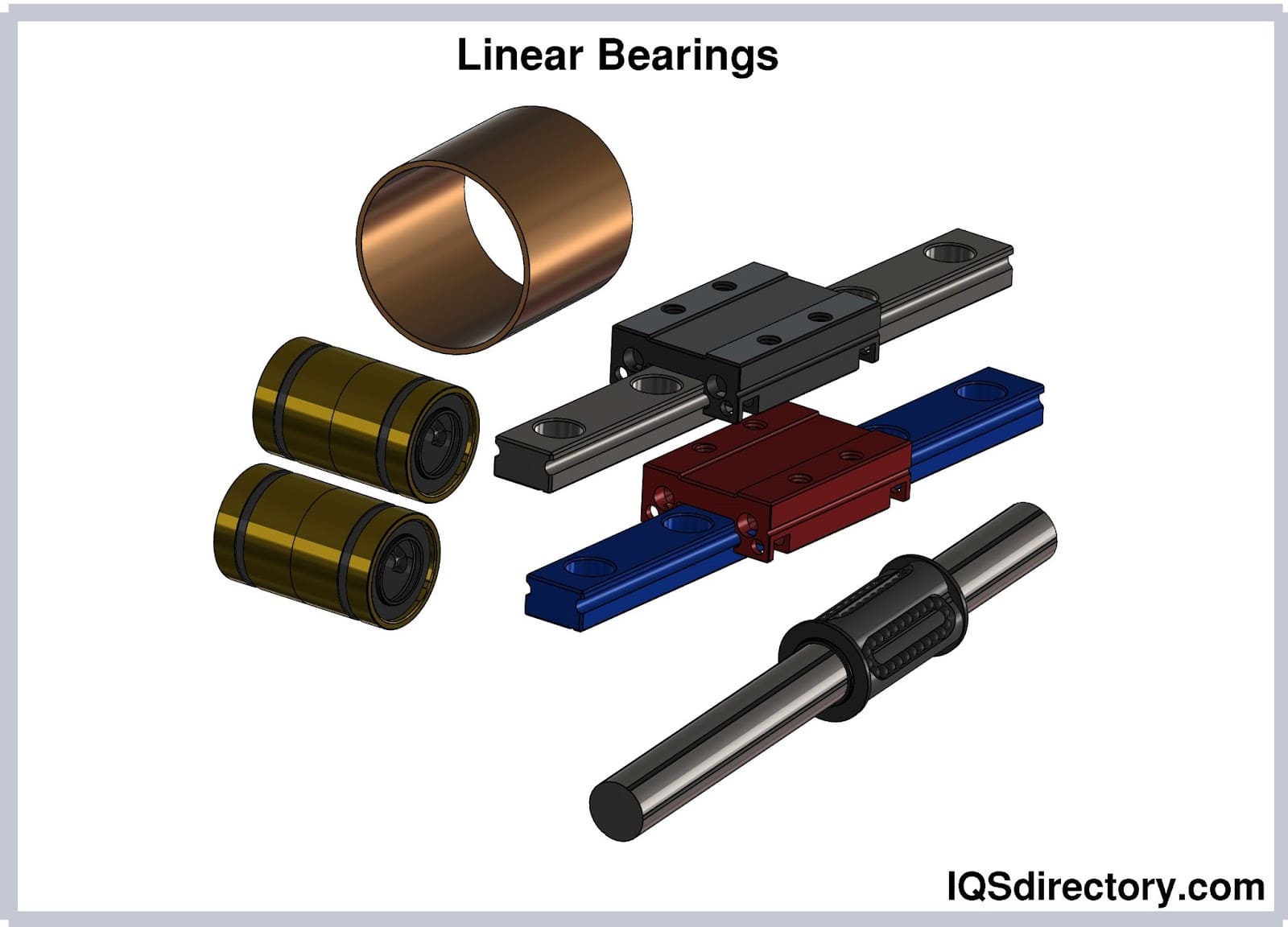
Linear bearings are a type of bearing that "bear" or support the load of the carriage during its single-axis linear movement and provide a low friction sliding surface for the guide rails. In a linear guide, the carriage is the component that travels in a straight line, back and forth, along the length of the guide rail...
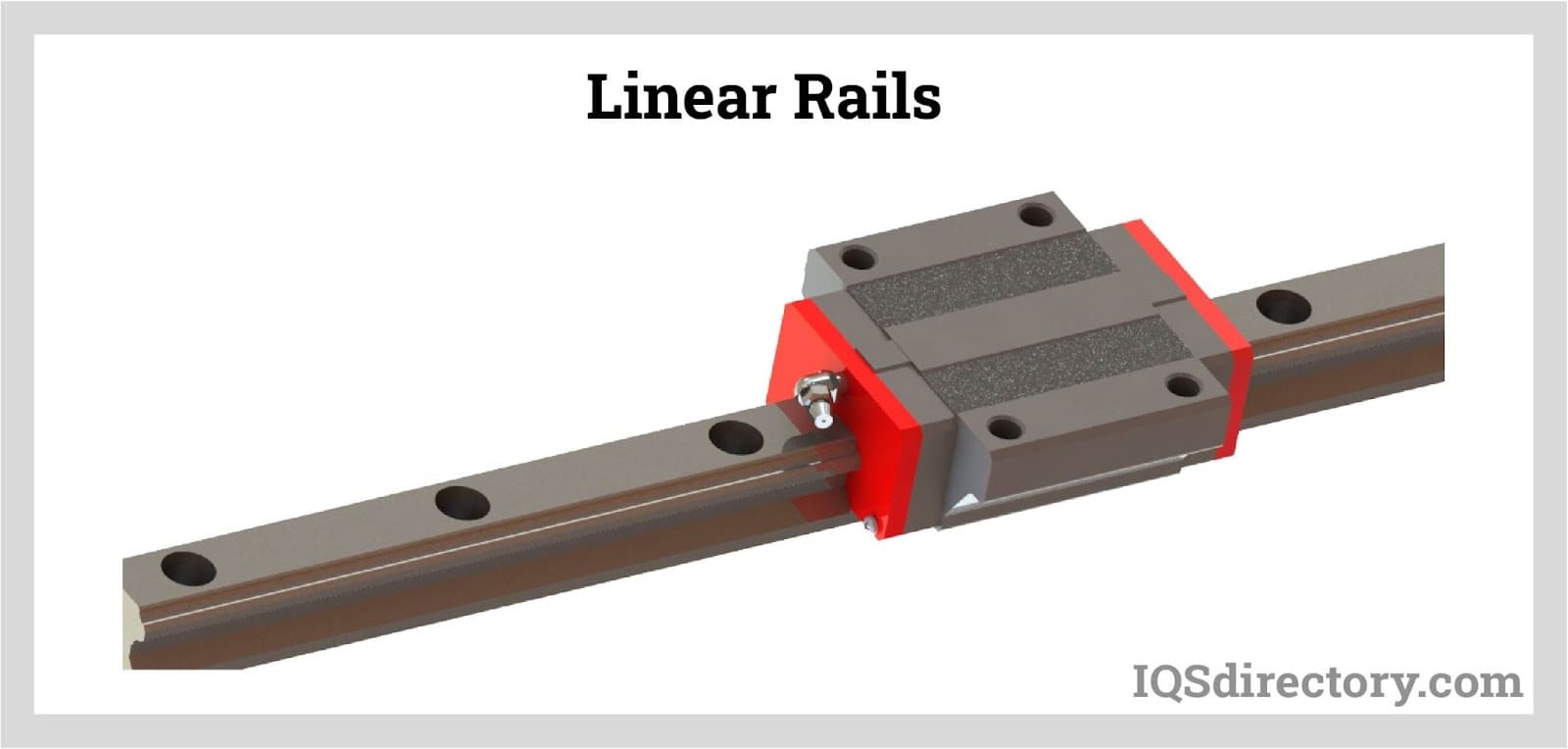

Linear Rails are ideal for moving items through a production process with great precision and as little friction as possible if creating, packing, and distributing products. Linear Rail is a type of gadget that...
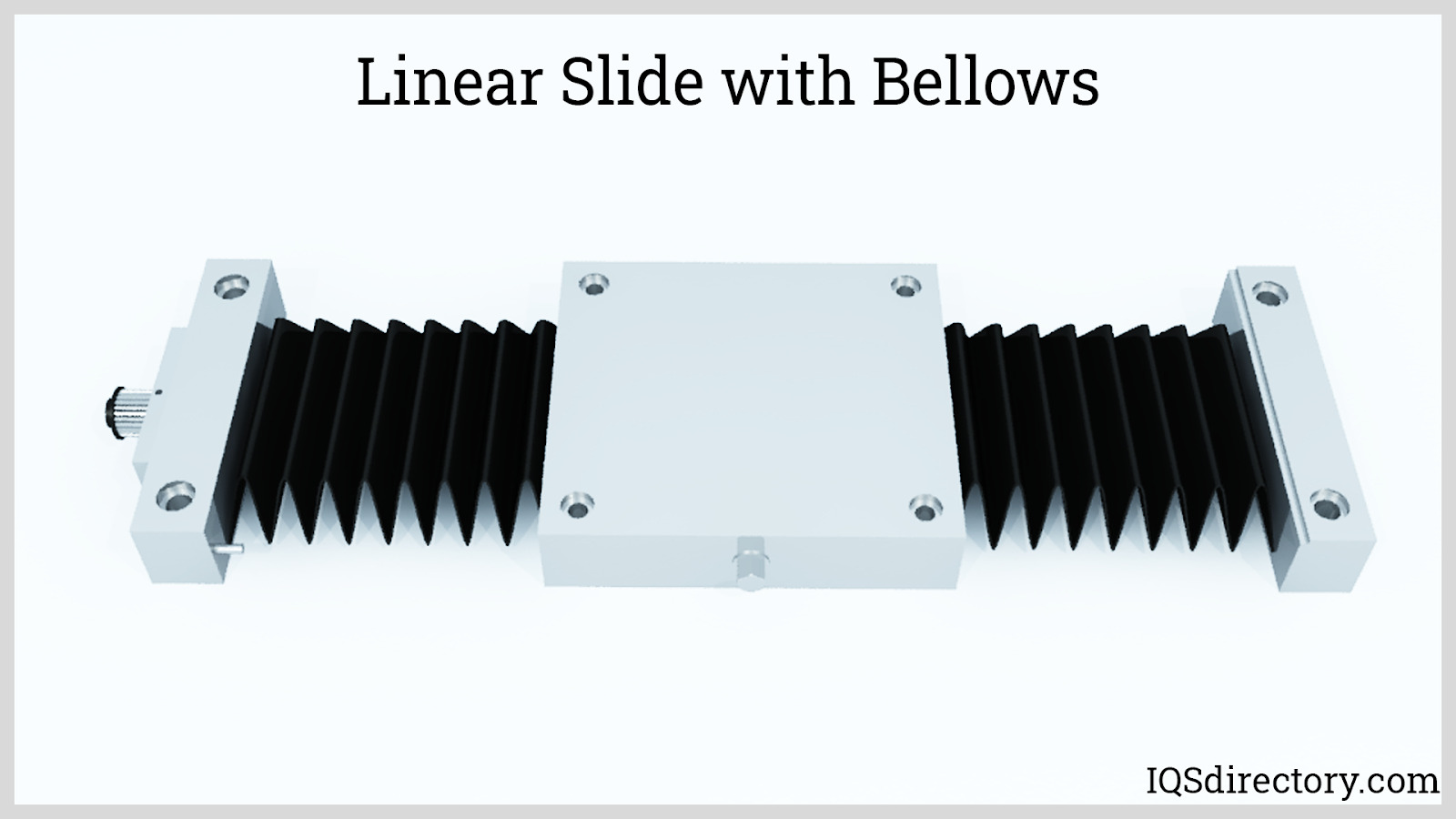
Linear slides, also referred to as linear guides or linear-motion bearings, are types of bearings that allow smooth and near-frictionless motion in a single axis. Machine tools, robots, actuators, sensors, and other...
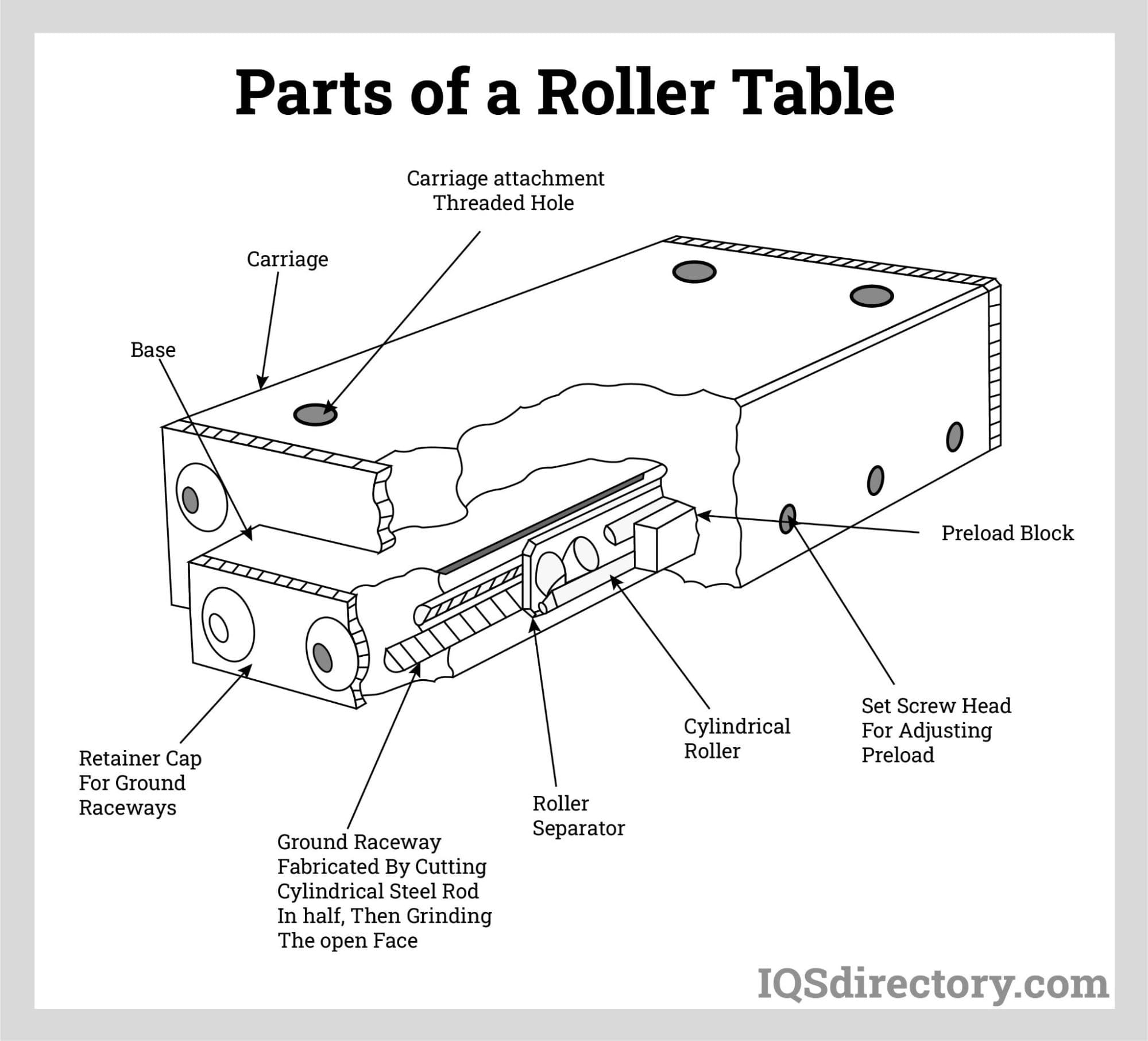
A roller table is a small, stiff, limited linear guide device with an integrated cross-roller guide. Electrical or mechanical drive systems are frequently used to move a roller table, making it easy to transfer heavy loads...