Rubber-to-Metal Bonding
Rubber’s distinctive property to form strong, lasting bonds with a variety of metals increases its durability and functionality. Numerous industries, including automotive and electronics, rely on rubber-to-metal bonding to manufacture tough, integrated components. This advanced bonding technique merges several parts into unified assemblies, delivering reliable metal adhesion for demanding uses.
In the molding process, rubber-to-metal bonding involves the mechanical fusion of rubber to a metal insert. This essential technique supports the production of a wide spectrum of goods across industrial, commercial, and healthcare markets.
Rubber-to-Metal Bonding FAQs
What is rubber-to-metal bonding used for?
Rubber-to-metal bonding is used to create durable, integrated components for automotive, aerospace, and industrial equipment. It enhances strength, vibration control, and environmental resistance, making it vital for engine mounts, gaskets, rollers, and medical devices.
How does the rubber-to-metal bonding process work?
The process fuses rubber to a metal insert using heat, pressure, and bonding agents. During molding, adhesives and primers help the rubber chemically adhere to the metal surface, forming a single, unified assembly that resists stress and corrosion.
What metals are commonly used in rubber-to-metal bonding?
Steel, aluminum, brass, copper, and bronze are frequently used metals. These materials offer excellent adhesion and can endure the high temperatures and pressures required during bonding and curing processes.
Which methods are used for bonding rubber to metal?
Common methods include vulcanizer curing, chemical curing, induction heating, and exhaust steam curing. Each method ensures strong adhesion depending on part size, metal type, and production volume requirements.
Why are water-based adhesives preferred for rubber-to-metal bonding?
Water-based adhesives are environmentally friendly alternatives to solvent-based formulations. They provide strong sealing capabilities and maintain durability under varying industrial conditions while meeting environmental safety standards.
What are typical products made using rubber-to-metal bonding?
Typical products include engine mounts, rubber rollers, gaskets, bearings, reinforced tires, seals, and medical instrument handles. These bonded parts combine flexibility with structural strength for demanding applications.
What factors influence the success of a rubber-to-metal bond?
Proper surface preparation, adhesive selection, curing temperature, and clean handling are critical. Any contamination or incorrect mixture ratio in bonding agents can weaken adhesion and reduce long-term performance.
Quick links to Rubber-to-Metal Bonding Information
Design of Bonding Processes
The ability of rubber to bond with a wide range of materials is central to its versatility for bonding solutions. Metals like bronze and brass bond effectively with rubber, though the success depends on the specific metal composition. Environmental guidelines have led to a shift from solvent-based adhesives to water-based options. These environmentally friendly adhesives offer similar sealing capabilities, maintaining durability under various conditions.
Rubber can also be bonded to glass, fabrics, and many plastics, but metals remain the top choice for bonded parts. Metals such as steel, aluminum, copper, beryllium, and brass provide excellent adhesion. The chosen metal must endure the high heat and pressure during bonding. Both natural and synthetic rubbers—including silicone, neoprene, and nitrile—are utilized in these processes.
Examples of rubber-to-metal bonded products consist of:
- Silicon Bonding
- Often crafted into surgical instrument handles
- Rubber Lined Rollers
- Engine Mounts
- Gaskets
- Reinforced Tires
- Bearings
- Rubber Lined Tanks/Pipes
- Conveyor Belts
- Electrical Cables and Plugs
Producing metal-rubber composites involves applying rubber to metal with specialized adhesives. This process depends on three main components:
- Rubber Materials
- Includes any type of styrene-butadiene or silicone rubber capable of filling molds without premature cross-linking, and prevents rapid migration of rubber elements to the uncured surface.
- Metal Substrate (Coating)
- The metal used in rubber-to-metal bonding, which may be aluminum, brass, or other alloys, is selected based on the application's requirements.
- Bonding Agents
- Typically composed of solvent or water-based formulations, these include a phenolic-style resin primer and a topcoat made from polymers and other compounds.
- Steel has been the predominant metal in rubber-to-metal bonding, but aluminum alloys and polyamides are increasingly popular for their light weight and cost advantages, while still offering strength and durability.
Vulcanizer curing places a rubber-coated metal component in a steam vulcanizer, applying pressure to cure the bond. This achieves strong adhesion and high density, enabling the product to withstand corrosive agents.
Chemical curing uses a special agent on the lining's surface, which permeates over time at room temperature. Heat can speed up this process. This method is mainly used for repairing tanks or lining large vessels.
Induction heating is an accurate, energy-saving approach that heats targeted areas without altering the metal’s properties, making it ideal for continuous production lines.
Exhaust steam curing introduces live steam into a sealed vessel, ensuring the lining remains intact and firmly bonded. This is especially beneficial for large tanks that are difficult to transport.
 Rubber to metal bonding demonstrates a chemically prepared rubber part securely attached to a metal surface.
Rubber to metal bonding demonstrates a chemically prepared rubber part securely attached to a metal surface.
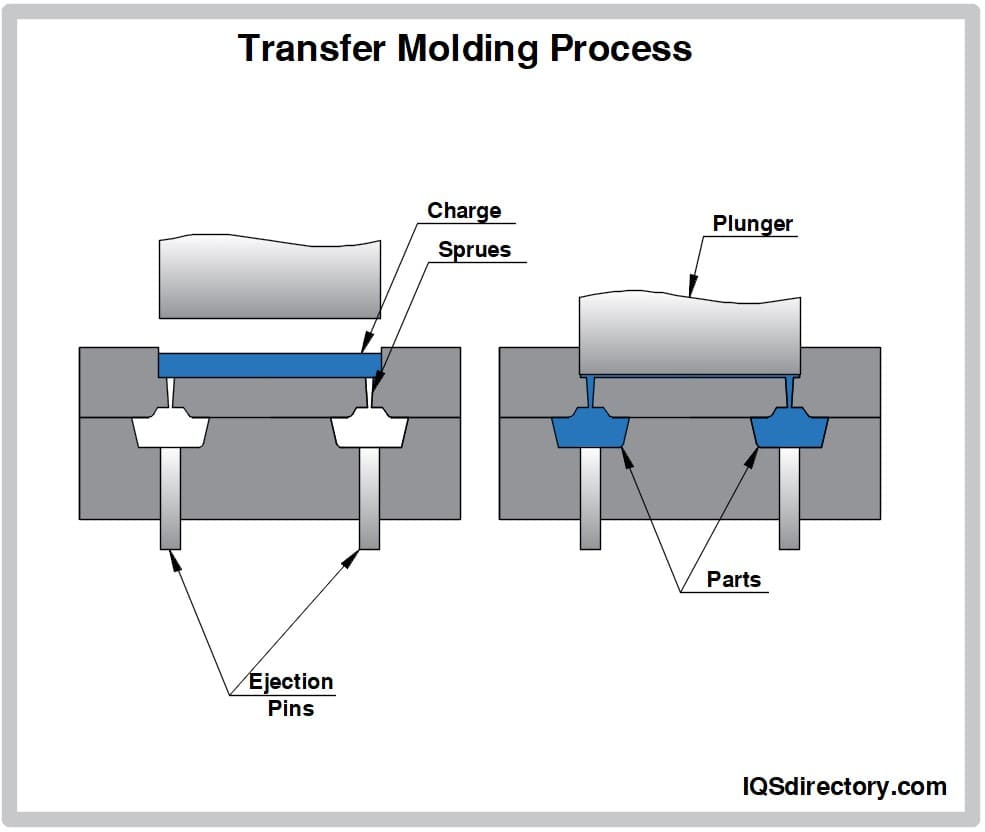 In transfer molding, metal inserts are positioned in a heated mold and solid rubber is pressed in, surrounding the metal for a tight bond.
In transfer molding, metal inserts are positioned in a heated mold and solid rubber is pressed in, surrounding the metal for a tight bond.
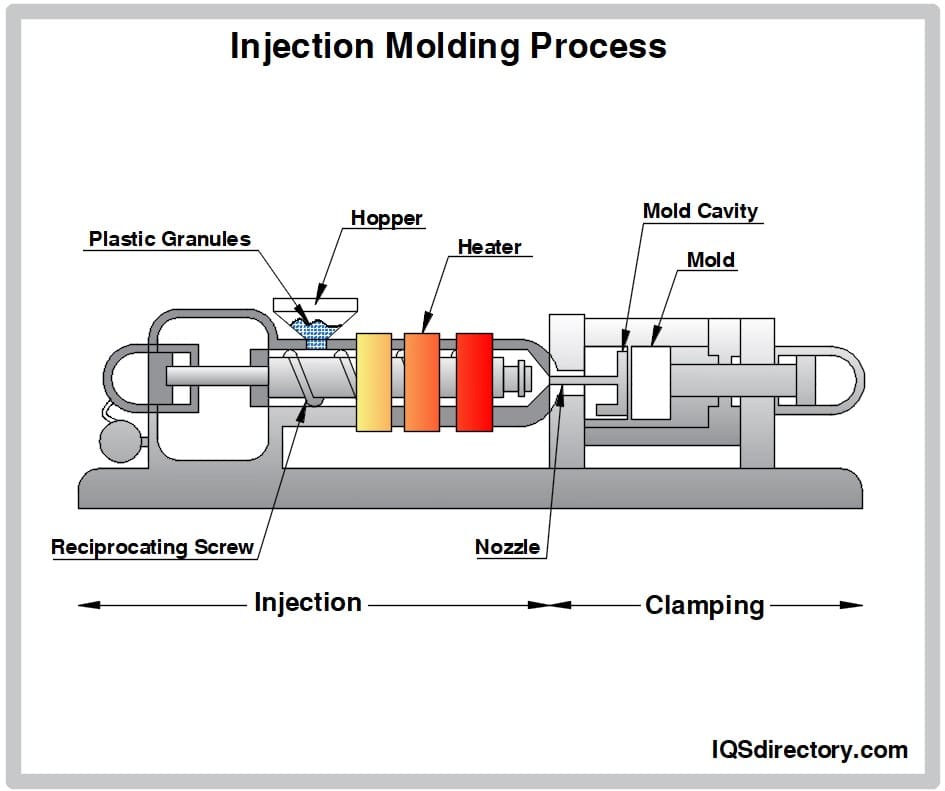 Injection molding is similar to transfer molding but injects liquid elastomer, which fills the mold and cures to form a bonded part.
Injection molding is similar to transfer molding but injects liquid elastomer, which fills the mold and cures to form a bonded part.
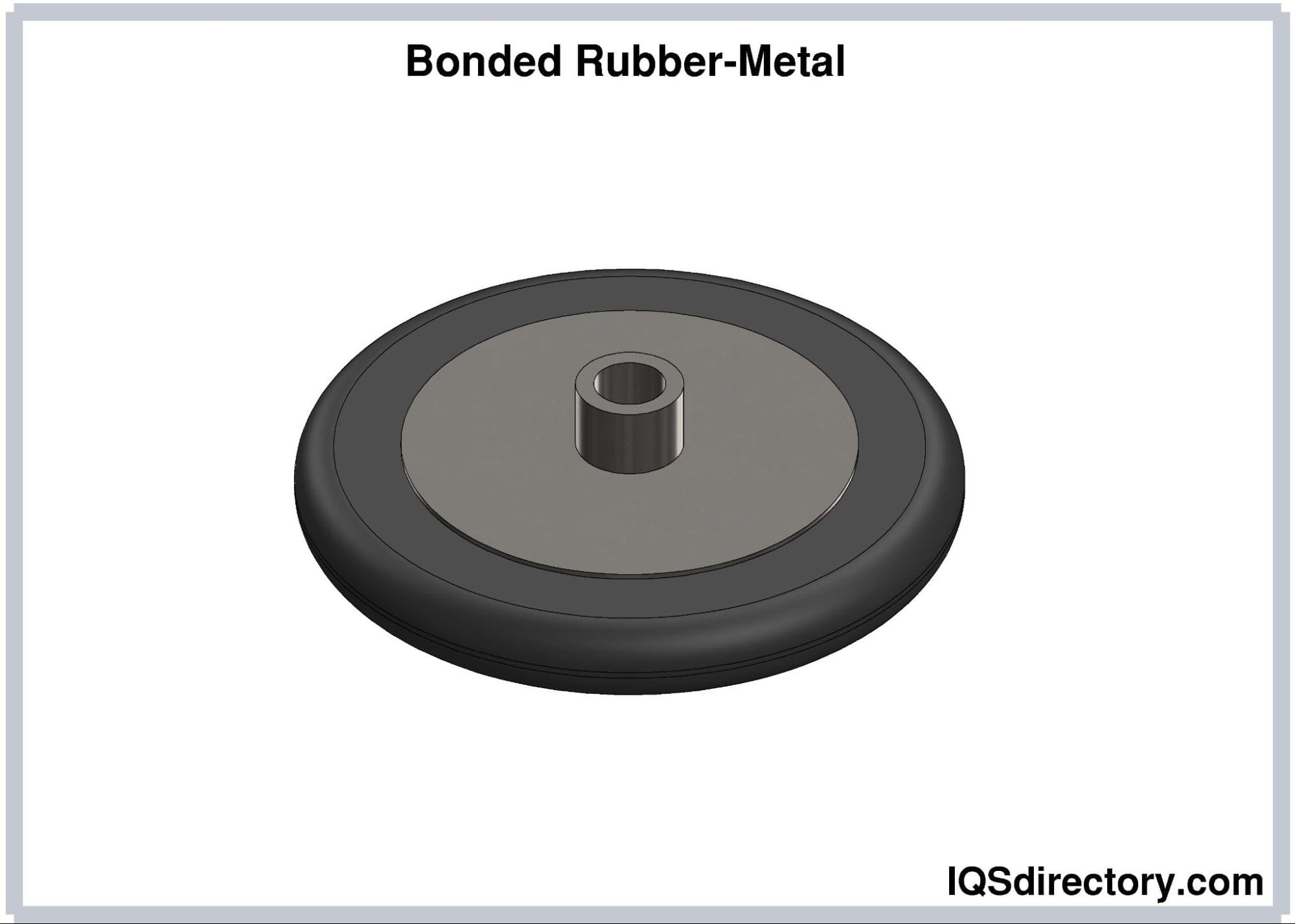 Bonded rubber forms a continuous, seamless surface and can be used for larger parts compared to poured rubber.
Bonded rubber forms a continuous, seamless surface and can be used for larger parts compared to poured rubber.
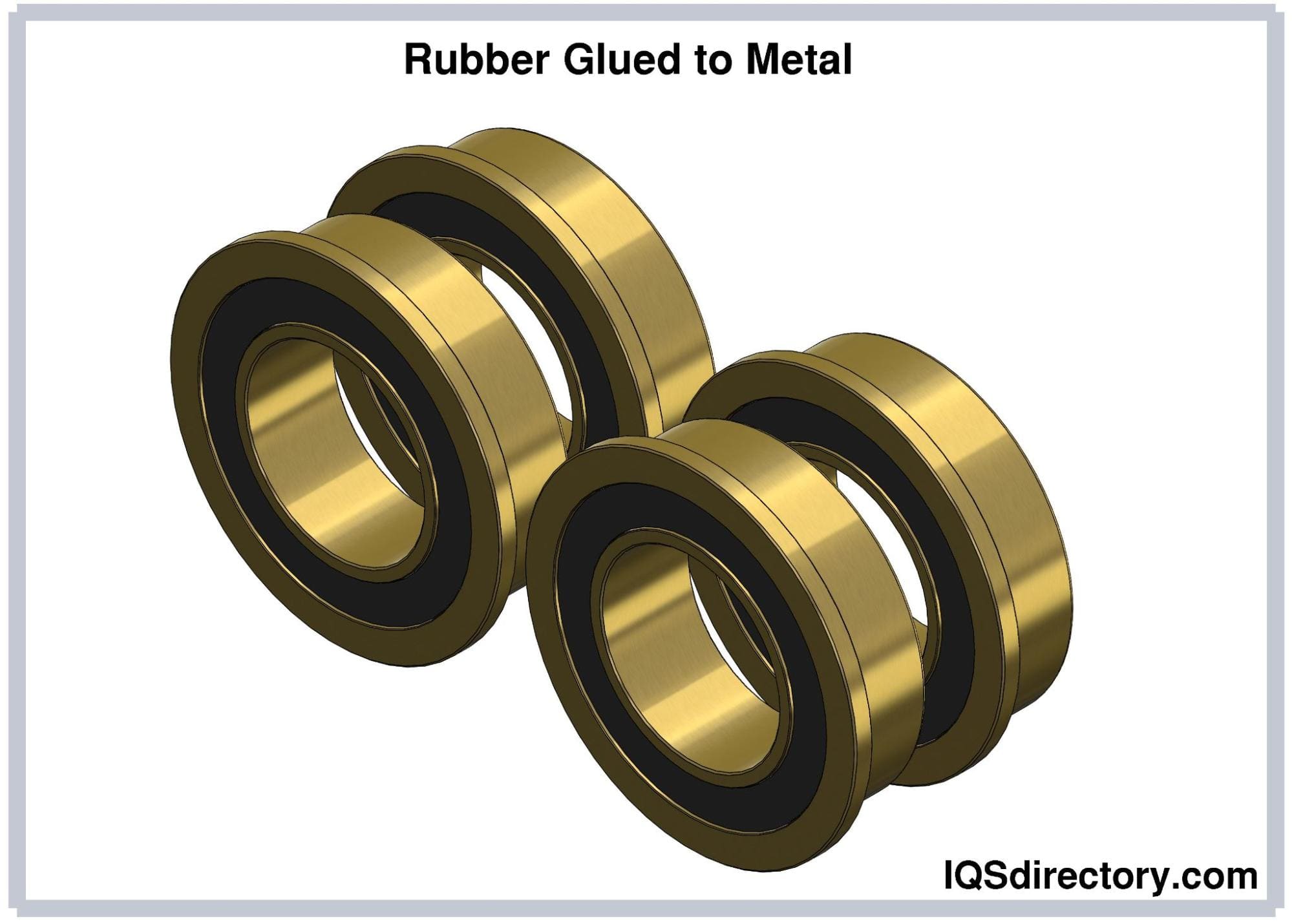 Adhesives containing polychloroprene rubber are commonly used for bonding rubber to metal surfaces.
Adhesives containing polychloroprene rubber are commonly used for bonding rubber to metal surfaces.
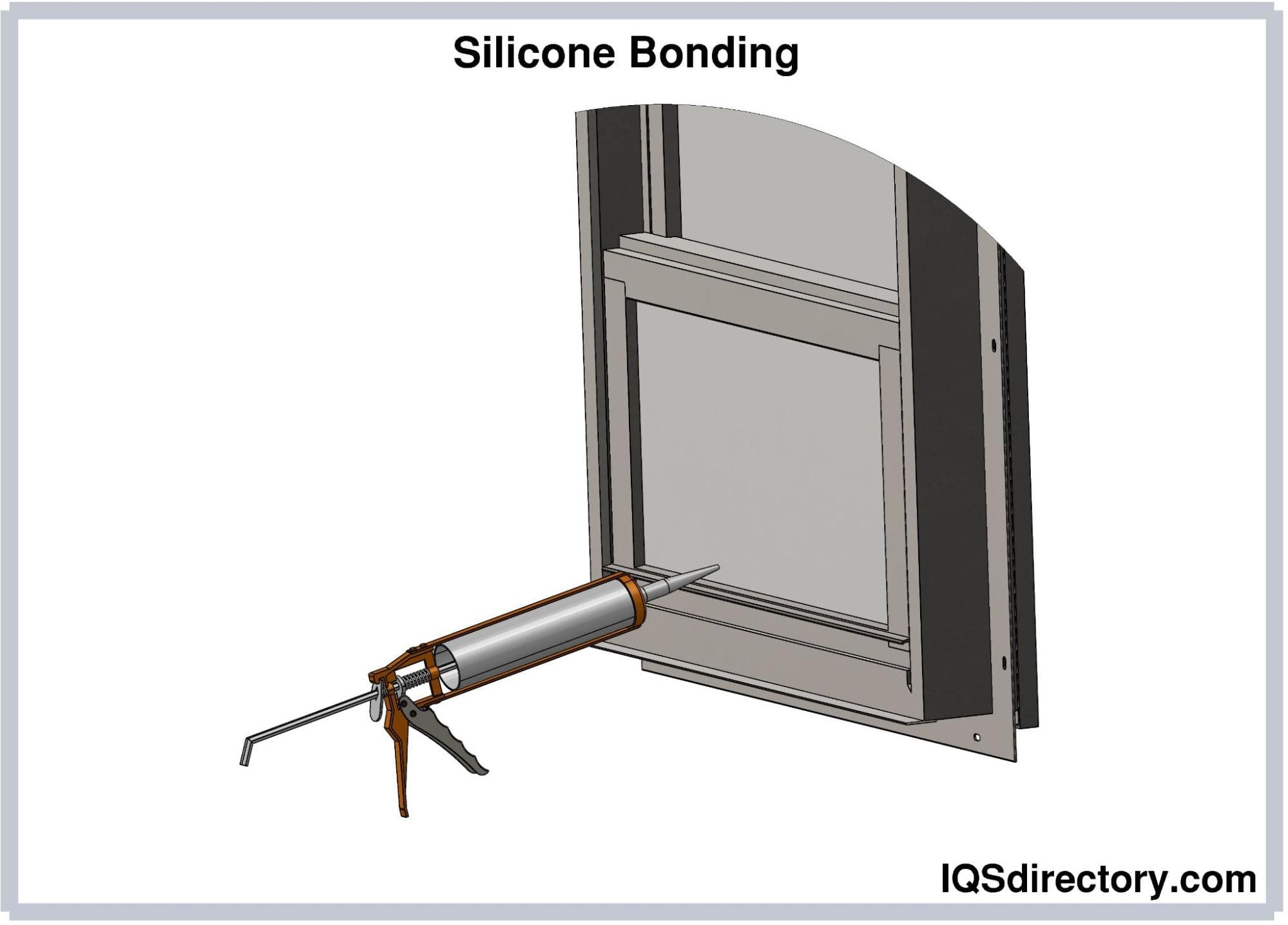 Silicone delivers superior flexibility and performance, and sometimes a primer is applied to achieve optimal bonding.
Silicone delivers superior flexibility and performance, and sometimes a primer is applied to achieve optimal bonding.
- Aluminum Bonding
- Aluminum is frequently used in rubber-to-metal bonding due to its strong mechanical properties, resistance to corrosion, low cost, and lightweight nature.
- Bonded Metal
- Encompasses a range of metals or alloys bonded with rubber, resulting in products such as vehicle tires, industrial gaskets, or medical-grade items.
- Bonded Rubber
- Refers to synthetic or natural rubber heat-bonded to materials like metal, glass, or fabric to create products with enhanced strength and flexibility.
- Bonding Rubber to Metal
- The process of adhering or molding rubber onto sandblasted metal surfaces, resulting in a secure and durable bond.
- Glue Rubber to Metal
- Utilizes specialized adhesives for rubber-to-metal bonding, widely used in automotive, medical, and other industries.
- O-Rings
- Sealing rings made from rubber or silicone that cover metal, commonly used in rotating or sliding applications such as shock absorbers and differentials.
- Piping
- Sometimes coated with rubber to enhance insulation and absorb vibrations.
- Press Bonding
- A method that bonds rubber to metal using a mild adhesive, without the use of heat or chemicals, by pressing preformed rubber onto the metal.
- Rubber Bonding
- This process joins rubber to various substrates, producing materials like rubber bonded to metal that offer elasticity and vibration damping.
- Rubber Grommets
- Components manufactured by rubber bonding, designed to act as protective eyelets for wires or lines.
- Rubber Products
- Goods produced from natural or synthetic rubber materials.
- Rubber Rollers
- Employed in paper production to remove water from pulp, featuring a metal core surrounded by a rubber coating for effective operation.
- Seals for Shut Off
- Sealing products made using rubber bonding, commonly used as shut-off elements in hydraulic equipment.
- Silicon Bonding
- A bonding method using silicone, often applied in the manufacturing of medical surgical instrument handles.
Rubber-to-metal bonding is vital for manufacturing products used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, plumbing, electrical systems, industrial equipment, vibration absorbers, medical devices, and custom rubber roller production.
The automotive sector especially utilizes many rubber-metal bonded components, such as those connecting the steering wheel to the column, and rubber-metal elements in pedals and bumpers.
Following consistent procedures from design through final testing ensures the bond meets all functional and environmental requirements for the application.
- Evaluate the part’s design and configuration for manufacturing suitability.
- Select the appropriate rubber and bonding agent based on the intended use.
- Assess the compatibility of the metal surface with the selected rubber.
- Procuring the Insert
- The insert material is chosen collaboratively, and responsibility for procurement is assigned to either the manufacturer or molder according to specifications. Allowing the molder to procure the insert can shorten lead times and benefit from established supplier networks for better quality control.
- Preparing the Part
- Optimal bonding relies on thorough preparation, which addresses the chemical interaction between rubber and metal, as well as the specific molding technique. Key steps may include:
- Completely cleaning the substrate to remove contaminants.
- Using a degreasing system to eliminate impurities from inserts prior to bonding.
- Applying primers and bonding agents through suitable methods.
- Masking areas of the insert that should not be bonded.
- Curing the primed insert to get it ready for the molding phase.
- Bonding Agents Used
- Bonding agents are applied in layers, typically starting with a gray primer followed by a black topcoat using a low-pressure spray.
- For parts exposed to less severe conditions, a single adhesive coat may be sufficient. The adhesive type is selected based on operating conditions and material compatibility.
- Adhesives are often diluted for easier application. Achieving the correct mixture ratio is critical, as improper viscosity can prevent the adhesive from curing and setting properly.
- Drying and Curing Phase
- After assembly, the substrate is thoroughly cleaned of any debris or oil. Plated inserts may be added for reinforcement. The rubber is allowed to cure and harden before the part is finalized.
- The molding process involves placing metal into the mold and injecting heated rubber. Additional steps may include deflashing, post-curing, cleaning, and custom packaging.
- Proper storage and handling of inserts and finished parts after molding are vital to avoid contamination. Store completed components at room temperature, away from sunlight and welders that emit ozone, which can degrade rubber.
With the broad use of rubber-to-metal bonded components, manufacturers frequently provide tailored solutions from the initial design phase through production.
When choosing a provider for rubber-to-metal bonding, look for companies that deliver cost-effective options while meeting production objectives for fast turnaround and premium rubber parts.
IQS Directory offers a comprehensive list of rubber-to-metal bonding companies. Use our directory to compare and select top providers that fit your rubber-to-metal bonding requirements.