Canopies

A canopy is a structure with a connected fabric or metal covering that can give shade or shelter from weather elements such as the sun, hail, snow, and rain. For example, a tent with no floor can be...
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
This article contains information and an explanation of the cut and sew process.
You will learn more about topics such as:
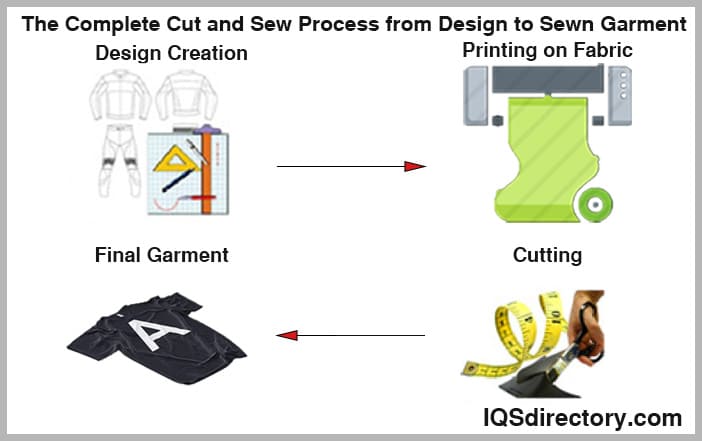
The cut and sew method is a specialized manufacturing process used to produce a wide range of fabric-based products, including dust covers, tents, apparel, guitar cases, upholstery components, and foam cushions. This broad range of applications highlights the critical role the cut and sew industry plays in textile manufacturing, product development, and custom fabric fabrication.
The process begins with a precise pattern that is printed or laid out on raw fabric, serving as the blueprint for the finished product. Accurate cutting is essential to ensure proper fit, consistency, and adherence to design specifications such as dimensions, seam placement, and color alignment. Cut and sew manufacturing is highly detail-oriented, emphasizing craftsmanship, repeatability, and quality control at every stage of production. Each fabric component is carefully assembled and inspected to meet the performance, aesthetic, and durability standards required by designers, brands, and manufacturers.

One of the key advantages of cut and sew production is its design flexibility. Because graphics, patterns, and branding can be printed directly onto fabric before assembly, manufacturers are not restricted by seam placement or pre-sized material limitations. This approach enables greater creative freedom, precise pattern placement, and access to virtually unlimited color options without the need to stock pre-dyed fabrics.
The adaptability of cut and sew manufacturing makes it valuable across nearly every industry, from consumer goods and apparel to industrial equipment, medical products, and protective coverings. Any product that incorporates fabric components can benefit from this method, allowing for customization, scalability, and consistent quality.
By efficiently producing high-quality fabric products at competitive costs, the cut and sew industry supports innovation, brand differentiation, and commercial success for its clients. Whether used for prototyping, small-batch production, or large-scale manufacturing, cut and sew remains a foundational process in modern textile and fabric-based product manufacturing.
Cut and sew manufacturing is a specialized textile and apparel production process that transforms original design concepts into finished garments and fabric-based products. This method is widely used by apparel brands, designers, and private-label companies that require flexibility, precision, and high-quality construction. By working with experienced cut and sew manufacturers, businesses gain access to professional guidance in fabric sourcing, technical pattern development, garment construction, sampling, and scalable production. From emerging fashion labels to established clothing brands, cut and sew manufacturing provides a reliable pathway from design to market-ready products.
While custom cut and sew production is accessible to designers and companies of all sizes, most professional sewing manufacturers implement a vetting process to confirm project viability before production begins. This ensures efficient use of materials, labor, and production capacity. Although apparel items such as streetwear, activewear, hoodies, outerwear, and dresses are the most common requests, cut and sew manufacturing extends far beyond clothing. The same process is used to create a broad range of soft goods and textile products, including accessories, home furnishings, and promotional items.
Common cut and sew products include hoodies, sweatshirts, custom t-shirts, tailored jackets, leggings, uniforms, sportswear, and fashion dresses. The process also supports non-apparel applications such as textile wall art, curtains, decorative rugs, plush toys, tote bags, and custom upholstery. In practice, any product constructed from individually cut fabric panels can be produced using professional cut and sew manufacturing techniques.
The first stage of cut and sew manufacturing is pattern design, which serves as the technical foundation for garment construction. Patterns are typically developed using industry-standard software such as Adobe Illustrator, Photoshop, and computer-aided design (CAD) programs. Many designers begin with hand-drawn sketches or physical patterns that are scanned at high resolution—usually 300 dpi or higher—to ensure accuracy during digital conversion. Bold, well-defined lines improve clarity and ease of editing during the digitization process.
Once imported into design software, the image is rasterized and refined to allow precise vector tracing, sizing, and color adjustments. This step ensures that every measurement, seam allowance, and construction detail aligns with the intended garment fit and design specifications. Accurate digital pattern development improves material efficiency and reduces errors during sampling and production.

During pattern preparation, design elements are separated into layers and adjusted for placement, scale, and color consistency. For repeating patterns or all-over prints, elements are aligned at the edges to ensure seamless continuity across fabric panels. Designers carefully review pattern dimensions and placements to balance aesthetic appeal with manufacturability.
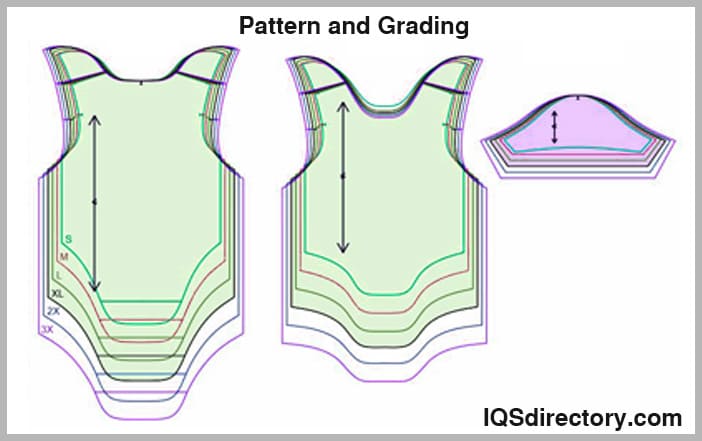
The completed pattern is then evaluated for repeat accuracy, sizing, and compatibility with garment construction requirements. Before sampling begins, pattern files are cross-checked against technical specifications to ensure consistency with fit, grading, and production standards. This review process minimizes revisions and supports a smooth transition into the manufacturing phase.
Once approved, the finalized pattern files are ready for fabric printing and cutting. Well-executed pattern development is critical to producing high-quality cut and sew apparel, whether for small-batch collections or large-scale garment production.
After pattern approval, selecting a qualified cut and sew manufacturer is the next critical step. The right sewing contractor ensures product quality, cost control, and reliable turnaround times. Established cut and sew facilities—ranging from boutique sewing shops to full-scale apparel production houses—have the skilled labor and equipment needed to meet varying production volumes.
Cut and sew manufacturers specialize in placing patterns onto fabric, cutting materials accurately, and assembling garments according to detailed specifications. While many focus on apparel production, some also manufacture accessories, branded merchandise, and soft goods. Most cut and sew facilities do not produce seamless knitwear, footwear, or rigid bags, as these products require specialized machinery and alternative manufacturing processes.
A key advantage of cut and sew manufacturing is its flexibility with minimum order quantities (MOQs). Many sewing contractors support low-volume production, making this model ideal for startups, limited-edition collections, and product testing. This approach allows designers to refine products and scale production without the high financial commitment required by traditional mass manufacturing.
Key production stages managed by professional cut and sew manufacturers include:
When sourcing a sewing contractor, designers often use industry directories, manufacturer databases, and verified references. Domestic cut and sew manufacturers are frequently preferred for their communication transparency, faster lead times, and easier collaboration. While offshore production may offer lower labor costs, it can introduce challenges related to quality control, logistics, and oversight.
Experienced cut and sew partners may also provide value-added services such as technical consulting, pattern grading, and prototyping. Building a collaborative relationship with your manufacturer—through sampling, factory visits, and clear communication—helps ensure consistent quality across production runs.
Offshore cut and sew manufacturing has historically been used to reduce costs for high-volume apparel production. Factories in regions such as Asia, Central America, and Eastern Europe often offer lower labor costs, making them attractive for large wholesale orders. However, offshore production can present challenges including longer lead times, communication delays, and reduced quality oversight.
As a result, many apparel brands now favor domestic manufacturing for improved reliability, ethical transparency, and faster turnaround. Onshore cut and sew production supports closer collaboration, better quality assurance, and responsiveness—factors that are especially important for limited releases and direct-to-consumer brands.
The choice between offshore and domestic manufacturing ultimately depends on production volume, budget, brand values, and timeline requirements. Careful evaluation ensures that finished products meet quality expectations and align with long-term business goals.
Fabric printing plays a major role in cut and sew manufacturing, influencing color vibrancy, durability, and overall garment appearance. Modern digital textile printing enables high-resolution graphics, complex patterns, and precise color reproduction. Common fabric printing methods include:
Digital Fabric Printing – Transfers computer-generated designs directly onto uncut fabric panels, making it the preferred method for cut and sew applications.
Digital textile printing includes both sublimation and direct-to-fabric processes, each selected based on fabric type and desired finish.
After printing, fabrics undergo finishing treatments such as steaming, washing, drying, and pressing to set colors and improve texture. Proper printing and finishing ensure durability, comfort, and visual consistency in the final product.
The cutting stage is critical to garment fit and construction accuracy. During cut and sew production, fabric panels are cut according to approved patterns and graded size specifications. Manufacturers typically perform rough cutting to separate fabric sections, followed by precision cutting to achieve exact pattern shapes.
Cut and sew facilities use manual cutting, powered cutting tools, or computer-controlled cutting systems to ensure consistency and minimize waste. Automated cutting technology improves efficiency, repeatability, and material utilization, particularly in larger production runs.

Accurate pattern placement and precision cutting form the foundation of high-quality apparel manufacturing. By combining skilled labor with advanced cutting systems, professional cut and sew manufacturers deliver consistent results that meet the demands of premium apparel brands and custom textile projects.
In the cut and sew industry, a wide variety of sewing machines are utilized, each engineered to perform specific garment construction functions and boost manufacturing efficiency. These machines are robust, power-driven, and capable of operating at high speeds to meet the demands of commercial garment production. Industrial sewing machines are classified based on the types of seams they create, their stitch classes, and their use in different fabric and apparel applications. Understanding the different types of industrial sewing machines and their features is essential for apparel manufacturers, fashion designers, and sewing contractors who are evaluating equipment for mass production, custom clothing, or specialty sewn products.
Lock Stitch Machines – Lock stitch machines are among the most commonly used industrial sewing machines. Featuring a single needle and bobbin, lock stitch sewing machines efficiently join two or more layers of fabric with precision. They are versatile and can handle multiple fabric weights, making them ideal for high-volume sewing and apparel manufacturing. The resulting seam is strong and durable, suitable for garment assembly, dressmaking, and even upholstery applications.

Overlock Machines – Overlock sewing machines, also known as sergers, use three, four, or five threads to create clean, finished edges on fabric panels. These machines excel at serging garment edges, attaching elastic, and performing overedge stitching, making them indispensable in both cut and sew production and knitwear manufacturing. While overlock sewing machines are essential for creating durable, stretchable seams in T-shirts, sportswear, and underwear, they are also used in finishing raw edges to prevent fraying and unraveling in various textile products.

Flatlock Sewing Machines – Flatlock sewing machines utilize two or three needles, threading through materials and interlooping with a looper thread to set secure, flat seams. These machines are pivotal in hemming sleeves, producing seamless decorative accents, and reducing seam bulk in sportswear, activewear, and underwear manufacturing. Flatlock technology creates comfortable, flat-finished seams that enhance garment appearance and wearer comfort—a key advantage in performance clothing production.

Feed Off the Arm Machine – Feed off the arm sewing machines are designed for fast and accurate assembly of tubular and flat-felled seams using two needle threads to produce chain stitches. These specialized machines are ideally suited for constructing shirt side seams, underarm seams, jean inseams, and other continuous seams found in jeans, workwear, and outerwear. Their unique configuration allows garment factories to sew long, straight seams more efficiently, increasing productivity in bulk apparel manufacturing.

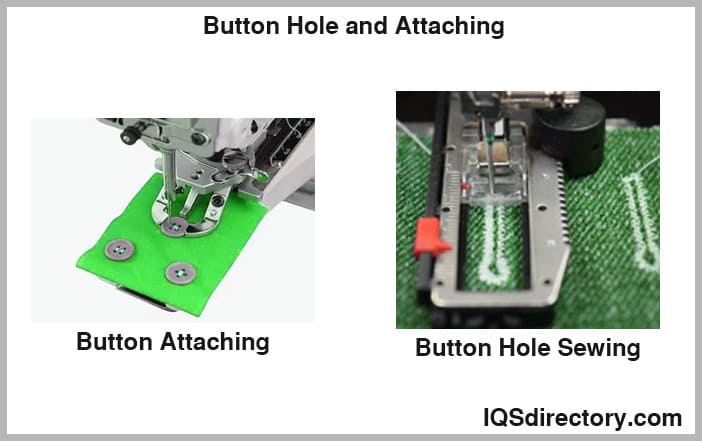
Button Hole and Attaching – Button hole and button attaching sewing machines are highly specialized, automating the process of creating buttonholes and securely attaching buttons of various sizes and styles to garments. These machines offer multiple buttonhole configurations—such as keyhole and straight buttonholes—and are indispensable for dress shirt, blouse, and jacket manufacturing. By automating repetitive tasks, they increase production speed, ensure consistency, and reduce labor costs in mass garment production.
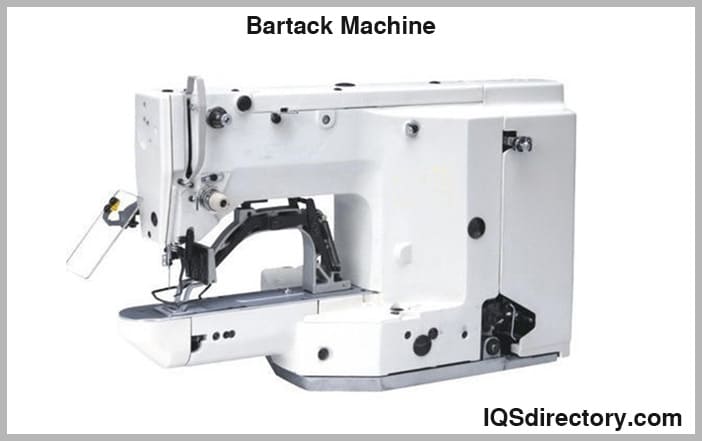
Bartack Machine – A bartack sewing machine is utilized to reinforce high-stress areas and secure attached components on a garment, such as belt loops, pocket openings, and zipper ends. By creating a tight, densely stitched bar, bartack machines enhance garment durability and prolong the lifespan of apparel items. They are essential in denim manufacturing, work uniforms, and any application where garments encounter frequent tension or pulling.

Zigzag Stitching – Zigzag sewing machines produce a wide spectrum of zigzag stitch patterns, which provide stretchability and flexibility in seam construction. Commonly used for sewing garment edges, attaching lace, elastics, or for decorative topstitching, zigzag stitching is essential in swimwear, lingerie, and jacket manufacturing. These machines enable designers to incorporate both structural integrity and decorative detail in a single operation.

The cut and sew manufacturing process is highly efficient and flexible, enabling the rapid creation and scalable production of intricate fashion designs and custom sewn products—from small-batch clothing lines to large-scale uniform manufacturing. Leveraging advanced industrial sewing machines, apparel manufacturers can quickly transform digital patterns and computer-rendered visuals into finished products, offering endless opportunities for creativity, precision, and innovation in the textile and fashion industry. Whether you are a start-up clothing brand, an established garment producer, or a specialty textile contractor, understanding the capabilities and advantages of each type of industrial sewing machine ensures you can select the right equipment for your project needs, streamline your workflow, and achieve the highest standards in quality apparel manufacturing.
When choosing the best sewing machine for your production requirements, consider factors such as fabric type (woven, knit, synthetic), volume of production, desired stitch quality, ease of maintenance, machine automation levels, and available technical support. Investing in the appropriate sewing machinery not only increases operational efficiency, but also empowers your business to adapt to trending designs and rapidly evolving fashion industry demands, enhancing your ability to bring unique, high-quality garments to market.
Cut and sew manufacturing is a method of creating fabric products by cutting raw, patterned fabric panels and sewing them together. This tailored process ensures custom design, superior fit, and quality control for a wide array of apparel and textile goods.
Common cut and sew items include hoodies, custom t-shirts, jackets, dresses, leggings, uniforms, sportswear, textile wall art, curtains, tote bags, soft toys, and custom upholstery. The process is adaptable to nearly any product constructed from fabric panels.
Key steps include digital pattern design, fabric inspection, precise cutting, skilled sewing, multiple quality checks, and sample development. Advanced digital tools and strict quality control ensure product accuracy, consistency, and superior finished garments.
Digital textile printing allows complex, high-resolution graphics and vibrant colorways to be applied directly onto raw fabric panels. This achieves exceptional creative control, unlimited color options, and detailed patterns without seam or size limitations.
Industrial lock stitch, overlock (serger), flatlock, feed off the arm, buttonhole, bartack, and zigzag sewing machines are essential in the cut and sew industry. Each type specializes in particular seams, finishes, or garment features.
US-based cut and sew manufacturers offer consistent quality, transparent processes, faster turnaround, and better collaboration. These advantages are ideal for limited-edition collections, direct designer oversight, and responsible production initiatives.
Cut and sew manufacturing has transformed modern garment production by allowing designers to move beyond standard, pre-made patterns when creating new brands or original apparel concepts. This production method supports greater design freedom, customization, and precision, making it ideal for high-quality, fashion-forward clothing.
One of the greatest advantages of cut and sew manufacturing is the level of control it offers throughout the entire production cycle. Designers can oversee each stage—from initial concept and fabric printing to cutting, sewing, and finishing—ensuring the final garment accurately reflects their vision. Unlike modifying blank garments, cut and sew production enables truly original apparel creation with consistent quality and fit.
The fashion industry continues to adopt cut and sew manufacturing because it creates opportunities for independent designers and emerging brands to bring unique ideas to market. This approach removes many of the barriers associated with traditional apparel production.
Working with an experienced cut and sew manufacturer provides valuable insight during the planning phase of garment development. These professionals help refine concepts, adjust designs for manufacturability, and ensure the final product meets industry standards. Their guidance helps transform creative ideas into production-ready apparel.
A tech pack, also known as a technical package, is an essential document in cut and sew manufacturing. It acts as a detailed roadmap for production, outlining every specification needed to develop and manufacture a garment accurately and efficiently.
Tech packs contain precise measurements, construction details, and material requirements that guide production teams from sampling through final assembly. They help eliminate miscommunication and reduce costly errors during manufacturing.
As a garment progresses from design to completion, it passes through multiple departments and hands. A well-prepared tech pack serves as a standardized reference, ensuring consistency, quality, and adherence to the original design throughout the entire production process.
Common elements found in a cut and sew tech pack include:
The complexity and depth of a tech pack often depend on the capabilities and experience of the cut and sew manufacturer, which should be assessed during the selection process.

Cut and sew professionals play a critical role in helping designers—especially newcomers—turn concepts into finished garments. Their technical expertise and production knowledge directly influence the quality, consistency, and success of a clothing line.
A manufacturer’s professionalism is often reflected in their history of supporting designers and delivering successful products. Strong communication, clear processes, and demonstrated results are indicators of a reliable cut and sew partner.
Many new designers struggle to find manufacturers willing to produce small quantities, as large factories often require high minimums. Cut and sew manufacturers are typically more flexible, making them well-suited for startups, limited runs, and product testing.
Lower MOQs allow designers to refine fit, construction, and design details before scaling production. This flexibility reduces financial risk and supports a smoother product launch.
Cut and sew manufacturers often provide hands-on service and guidance throughout the production process. These relationships frequently evolve into long-term partnerships built on collaboration, trust, and shared goals, helping designers navigate challenges and optimize results.
There is an important distinction between traditional sewing factories and full-service cut and sew operations. In standard sewing factories, designers are typically responsible for delivering a fully completed tech pack and managing much of the production preparation.
Cut and sew manufacturers, on the other hand, offer end-to-end support, including design refinement, sampling, and coordination of outsourced production for larger runs. This comprehensive approach sets cut and sew manufacturing apart from other apparel production models.
Choosing the right cut and sew manufacturer is a critical step in bringing a clothing design to market. Evaluating a manufacturer’s experience, capabilities, and track record requires time and diligence, but it is essential for ensuring a successful production outcome.
Full-service cut and sew manufacturers typically provide everything from design support to finished garments within a single operation. Designers often pay a flat or bundled rate, simplifying budgeting and reducing the need to manage multiple vendors.
This integrated approach helps control costs while maintaining quality. While lower-priced options may appear attractive, limited services can result in production issues or compromised garment quality, making value and expertise just as important as price.
Unlike many traditional apparel factories, cut and sew manufacturers are structured to accommodate a wide range of production volumes. Their flexibility allows them to support small batches, prototypes, and scaled production runs as a brand grows.
Experience is one of the most valuable assets a cut and sew manufacturer can offer. A company’s portfolio, client history, and case studies provide insight into their ability to deliver consistent, high-quality results.
Many established apparel brands began with cut and sew services, and these same manufacturers often continue to support new designers. This openness highlights the collaborative and growth-oriented nature of the cut and sew industry, making it an ideal entry point for emerging fashion brands.

A canopy is a structure with a connected fabric or metal covering that can give shade or shelter from weather elements such as the sun, hail, snow, and rain. For example, a tent with no floor can be...

Contract sewing is a specialized industry that provides services to manufacturers for production of a wide range of products using highly skilled workers and technologically advanced sewing machines. The strength of the contract sewing industry is its ability to perform any type of sewing services...

A protective cover is a sewn fabric that is specifically designed and used for protecting equipment, people, surfaces, and enclosures. Protective covers provide protection from the elements, UV rays, dirt, dust, moisture, and...

A carrying case is a way of conveniently organizing and transporting a collection of similar or dissimilar items for future use. There is a type and kind of carrying case to fit every possible application from protecting and storing cell phones to cases for speaking systems and technical equipment...
Contract manufacturing is a business model in which a company hires a contract manufacturer to produce its products or components of its products. It is a strategic action widely adopted by companies to save extensive resources and...

A hard case is a type of carrying case that is made from molded plastic, aluminum, veneered or laminated wood, or different types of metals. They are the most secure and durable forms of carrying cases and...

A road case is a ruggedly built, highly functional protective container with varying wall thicknesses that is capable of withstanding the riggers and handling of shipping. They are designed to meet...

A tool case is a portable case designed to organize and protect tools and allow easy access and convenient availability. Standard tool cases can be used when working on a project. In addition, specialty and custom-designed tool cases are...
Cases designed to carry special valuables have been part of society throughout history back to the time of the Egyptians and before. Carrying cases are commonly found in any house stored in a garage, tucked away in a basement, or setting on a shelf...