Bungee Cords
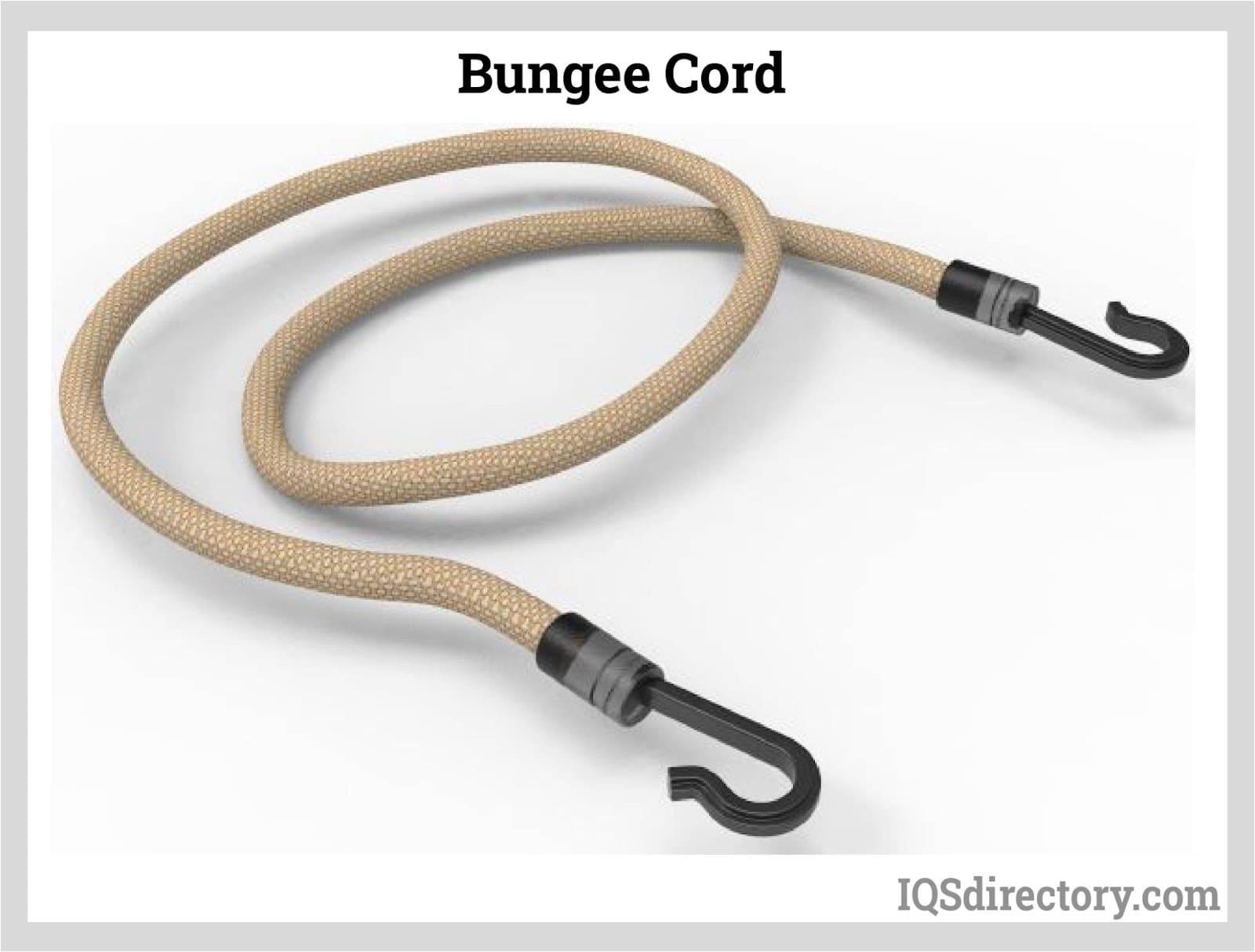
A bungee cord is a rope that is composed of two or more elastic strands coated with a woven fabric. It has hooks that are placed on both ends. A bungee cord is also known as shock cord and elastic cord...
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
This article takes an in depth look at high strength ropes.
This will cover topics such as:
High strength ropes are engineered assemblies of strands, fibers, plies, and yarns that are combined to create a robust, load-bearing structure capable of handling demanding mechanical forces. These individual elements are twisted, braided, or interlocked in specific patterns to produce rope with high tensile strength, enhanced durability, and resistance to stretching or failure under load. High strength ropes are widely used for lifting, pulling, hoisting, towing, and securing loads in industrial, marine, construction, and transportation applications. Historically, ropes have been essential tools for humanity since prehistoric times, serving purposes such as hunting, climbing, hauling, fastening, and securing goods. Early ropes were made exclusively from natural fibers, while the introduction of synthetic fibers in the mid-20th century revolutionized rope manufacturing by significantly increasing strength, consistency, and longevity. Today, high strength ropes are broadly classified into natural fiber ropes and synthetic fiber ropes, each offering distinct performance characteristics.
Natural ropes are produced from biodegradable, environmentally friendly materials that generate minimal harmful byproducts during manufacturing. Common natural fibers used in rope construction include cotton, hemp, sisal, and manila, all of which offer reliable grip and flexibility. In some designs, natural fibers are blended with synthetic materials to improve tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and overall durability. While natural fiber ropes perform well in many general-purpose and traditional applications, they are more vulnerable to environmental factors such as moisture, mildew, mold, and prolonged UV exposure. These ropes can absorb water, leading to shrinkage and potential loss of dimensional stability, and they may not fully recover their original size once dried. Natural ropes are resistant to high temperatures but will burn when exposed to open flames. Despite these limitations, their non-slip texture, ease of handling, and eco-friendly composition make natural fiber ropes effective for securing loads, decorative uses, and applications where grip is prioritized over extreme strength.

Synthetic fiber ropes are manufactured from manmade materials such as nylon, polyester, polypropylene, and other advanced polymers engineered for strength and durability. Compared to natural fiber ropes, synthetic ropes offer superior tensile strength, longer service life, and improved resistance to wear and environmental exposure, often lasting up to 30 percent longer. These ropes are highly resistant to water absorption, making them ideal for wet or marine environments, and they are not susceptible to damage from mildew, mold, or prolonged UV exposure. However, synthetic ropes have lower heat resistance and can melt or deform when exposed to high temperatures or friction-generated heat. Although their production involves processes that may release harmful byproducts, their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, flexibility, and reliability make synthetic ropes the preferred choice for heavy lifting, towing, rigging, and industrial operations.

High strength ropes are produced in a variety of construction styles, each defined by how the fibers or strands are twisted, braided, or layered. The construction method directly influences the rope’s strength, flexibility, abrasion resistance, and suitability for specific applications. Ropes are categorized and named according to these construction techniques, with each style offering unique performance advantages.
Single braid 12 strand ropes are commonly manufactured from HMPE fibers and are known for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and superior breaking strength compared to wire rope. These ropes are created by interlocking twelve individual strands using a precise over-and-under braiding pattern that evenly distributes load across the rope. This construction results in a lightweight yet extremely strong rope suitable for lifting, pulling, and heavy-load applications. To further enhance durability and prevent premature wear or failure, single braid 12 strand ropes are often jacketed with elastomer coatings that protect against abrasion, moisture, and environmental damage.

Plaited rope, also referred to as square braid rope, is constructed from multiple sets of twisted strands that are interwoven to form a square or braided profile. Typically composed of four groups of strands, this construction produces a rope that is flexible, strong, and easy to handle. Plaited ropes are well suited for applications requiring frequent knotting, as they hold knots securely. However, because the strands are exposed around a central core, plaited ropes can be more susceptible to environmental wear, abrasion, and damage over time.
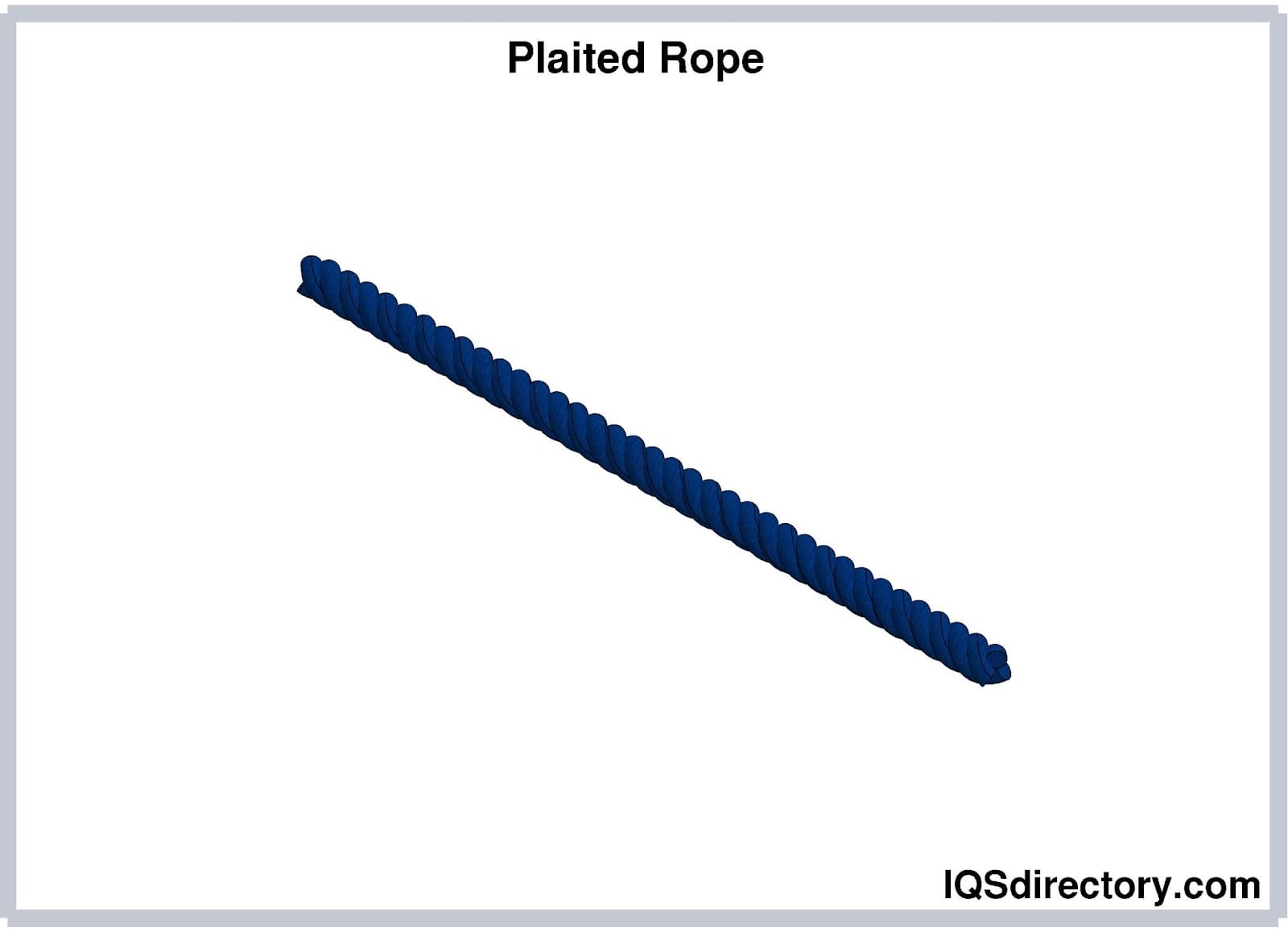
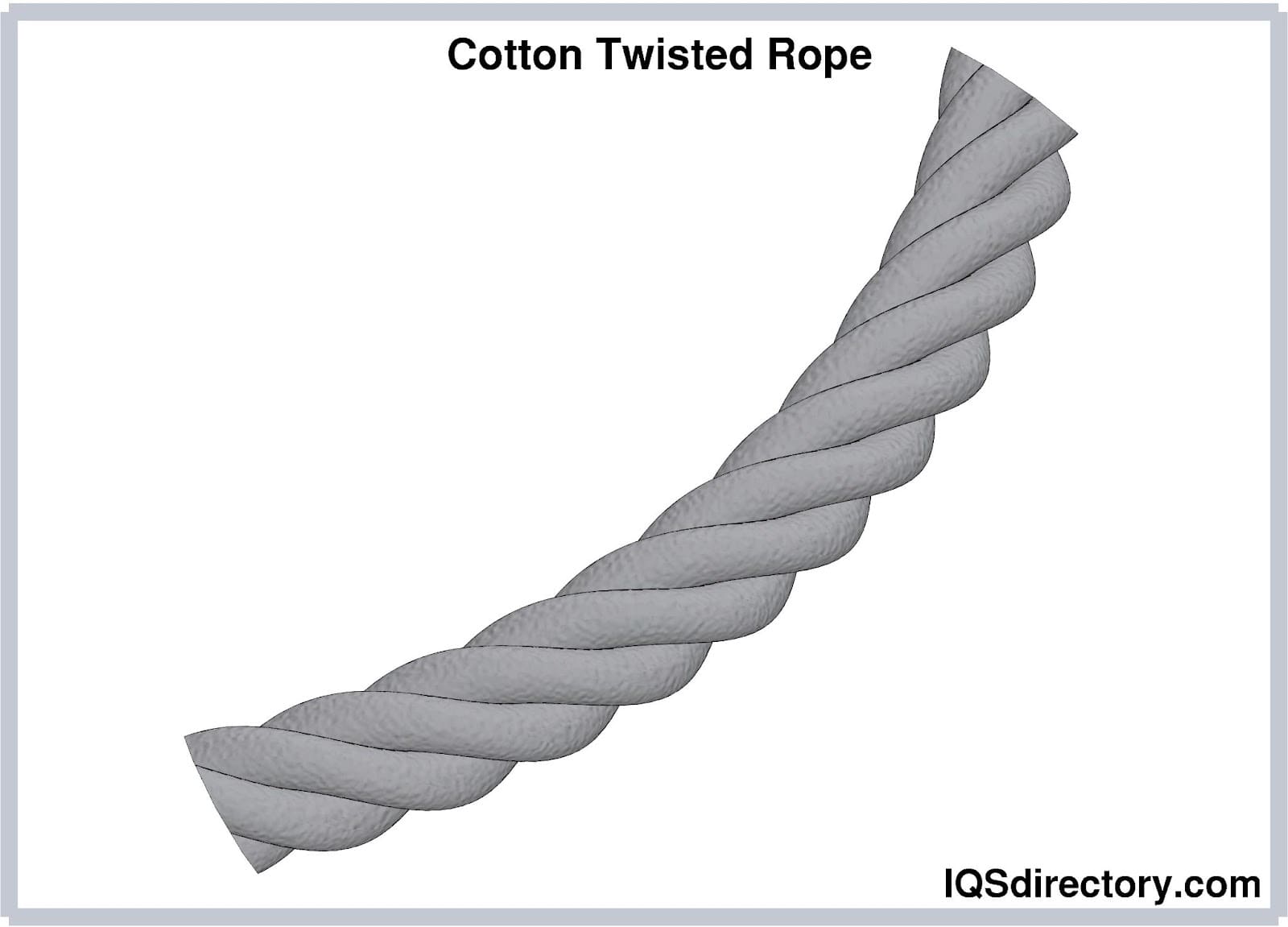
Twisted rope, commonly known as laid rope, is constructed by twisting individual strands together in the same direction to form a cohesive structure. In most cases, three primary strands are twisted in opposite directions to improve balance and grip strength. This construction makes twisted ropes ideal for splicing and traditional applications such as dock lines, general utility lines, and towing. While twisted ropes provide good grip and load control, they are less flexible than braided ropes and can kink or untwist if not properly handled or stored.

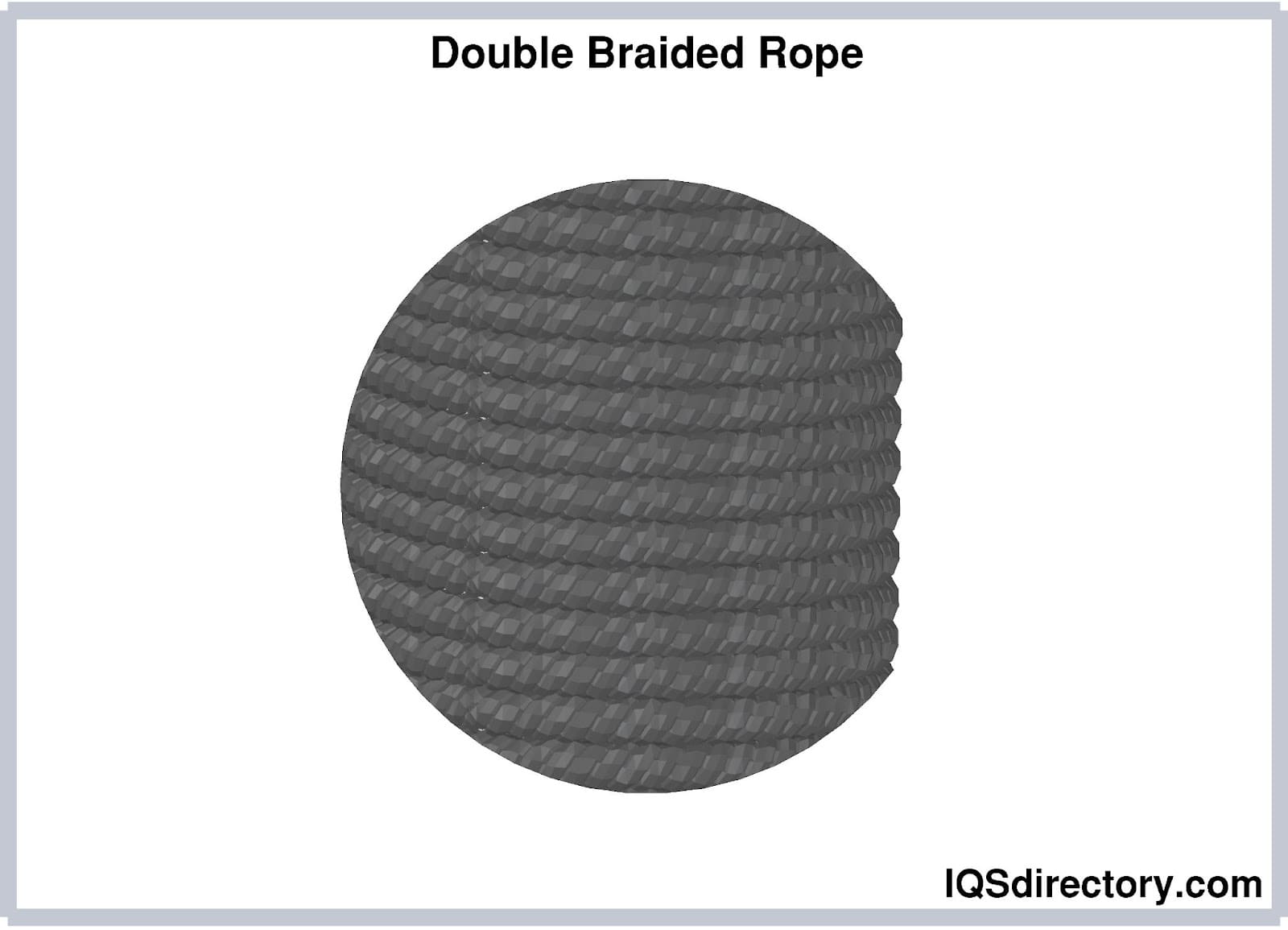
Double braided rope is designed for applications where both high strength and flexibility are essential. It consists of a braided core surrounded by a second braided outer sheath, creating a balanced and durable structure. This dual-layer construction provides excellent resistance to abrasion, reduces kinking, and enhances overall stability under load. Double braided ropes are commonly used in marine environments due to their durability and smooth handling characteristics, although they may be less suitable for certain manufacturing settings where extreme abrasion or heat is present.
Hollow ropes are lightweight synthetic ropes with an empty internal core, allowing for easy splicing and modification. Their low weight and flexibility make them ideal for applications such as ski towing and anchor lines. Hollow ropes are water resistant and float, which further enhances their performance in marine and recreational environments.

Diamond braid ropes are manufactured by tightly braiding fibers around an inner core to produce a firm, round, and rigid structure. This precise braiding process results in a rope with excellent dimensional stability, smooth appearance, and high durability. While diamond braid ropes are generally more expensive than other rope types, they offer superior performance in demanding conditions and maintain their shape under load. Their construction also allows for easy splicing, making them compatible with other braided rope systems.

Jacketed rope incorporates a protective outer layer designed to shield the rope’s core from abrasion, UV exposure, moisture, and chemical damage. This outer jacket is typically made from durable synthetic materials such as urethane elastomers or thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), which act as a barrier against friction and harsh environmental conditions. The jacket is applied as a resin coating with a controlled thickness and can be color-coded to assist with identification and safety compliance.
Jacketed ropes are especially valuable in outdoor, industrial, and heavy-duty applications where prolonged exposure to the elements would otherwise degrade rope performance. By extending service life and maintaining structural integrity, jacketed ropes provide a reliable solution for demanding operational environments.
High strength ropes are made from strands, fibers, piles, and yarn that are either twisted or braided. Materials include natural fibers like cotton, hemp, and sisal, as well as synthetic materials such as nylon, polyester, and polypropylene.
Natural ropes are eco-friendly and heat resistant but vulnerable to moisture and UV damage. Synthetic ropes, like nylon and polyester, are stronger, more durable in wet conditions, and resistant to mildew but can melt in heat and are less environmentally safe.
Single braid 12 strand ropes made from HMPE and double braided ropes provide exceptional strength and durability. Double braided types are especially resistant to abrasion and kinking, making them suitable for demanding applications.
High strength ropes are used for lifting, dragging, towing, climbing, securing, and marine applications like ski towing and anchor lines. Their properties make them suitable for both indoor and outdoor environments.
Double braided ropes are highly abrasion-resistant and ideal for marine environments due to their stability, flexibility, and resilience in wet conditions.
Jacketed ropes have a protective synthetic coating that shields them from abrasion, UV exposure, and harsh weather, extending their lifespan and performance outdoors.
High strength ropes are engineered from specialized fibers and polymers selected for tensile performance, fatigue resistance, abrasion resistance, chemical compatibility, and predictable behavior under load. The materials below represent some of the most common high-performance options used to manufacture modern high strength rope, rigging line, and specialty cordage.
These materials form the foundation of most high strength rope designs. Each one can be produced in multiple grades and constructions, and performance can vary widely based on fiber treatment, braid style, coatings, and protective jackets. The sections below explain what makes each material distinct and where it tends to perform best.
Aramid, also known as poly(para-phenylene terephthalamide), is a high-strength, low-stretch fiber valued for its thermal stability, high tensile performance, and resistance to creep under sustained loads. It is among the earliest high-performance fibers adopted for rope manufacturing and is widely recognized through commercial variants such as Technora, Twaron, and Kevlar. While aramid fibers deliver excellent strength, they typically require additional protection because abrasion and UV exposure can reduce service life. For this reason, aramid ropes are often jacketed or blended with materials such as polyester to improve surface durability and weathering resistance. Meta-aramids (such as Nomex and Teijinconex) are known for outstanding heat resistance and protective applications, while para-aramids generally provide higher tensile strength for load-bearing rope and cable replacements.
High modulus polyethylene (HMPE) is one of the strongest rope fibers available and is produced in several grades to match different performance requirements. HMPE’s long molecular chains provide exceptional durability, high impact resistance, and a strength-to-weight advantage that makes it a leading choice for high strength rope, lifting lines, and marine rigging. In many applications, HMPE is compared to steel in terms of strength, while remaining far lighter and easier to handle. This combination of low weight, very high tensile strength, and excellent moisture resistance explains why HMPE has become one of the most widely used fibers for high-performance ropes worldwide.
VECTRAN, often described as an aromatic liquid crystal polyester, is a high-strength fiber with very low stretch and strong dimensional stability under load. It performs similarly to aramids in terms of controlled elongation and heat resistance, but it is also valued for its creep resistance in applications where long-term load holding and precise length control are important. These traits make VECTRAN useful in specialty rope applications where predictable performance is critical.
Zylon, commercially known as PBO (poly(p-phenylene-2,6-benzobisoxazole)), is a newer entry in the high-performance rope market and is recognized for exceptionally high tensile strength, minimal stretch, and excellent temperature resistance. Like many advanced fibers, PBO benefits from protective design features because UV exposure and abrasion can degrade performance over time. When properly shielded with jackets or coatings, Zylon-based ropes can deliver extremely high strength for specialty, high-demand applications.
Polyester is one of the most widely used synthetic rope materials due to its strong resistance to water, UV light, and abrasion, making it a dependable choice for outdoor and marine environments. Polyester is often used as a protective jacket material over higher-strength cores, extending rope life while maintaining good handling characteristics. It offers consistent performance in wet conditions, controlled stretch, and excellent stability under sustained loads. Polyester has a density of 1.38, a melting point of 260°C, and a breaking extension of approximately 12%.
Nylon, also known as polyamide, is valued for high strength and outstanding elasticity, particularly in applications that benefit from shock absorption. Nylon can lose up to 10% of its strength when wet, but it remains a popular choice for dynamic loading conditions because it can stretch significantly and recover, reducing peak forces on hardware and anchors. Its combination of toughness, abrasion resistance, and stretch makes it useful for lines that must handle sudden loads. Nylon has a relative density of 1.14 and a melting point of 220°C, with elongation that can reach 30% or more depending on construction.
Polypropylene is a lightweight, economical fiber with a density of 0.91, allowing it to float on water and making it useful for marine and utility applications where buoyancy matters. It offers moderate UV and abrasion resistance and performs well in many chemical environments due to strong chemical resistance. While polypropylene can have a breaking extension similar to polyester, it is generally lower in strength and may require larger diameters for comparable load ratings. Its melting point is approximately 170°C.
Polyethylene shares several characteristics with polypropylene, including low density and good chemical resistance, but it typically provides slightly improved UV resistance. With a relative density of 0.97 and a melting point of 165°C, polyethylene can be a practical choice when a lightweight rope material with balanced environmental performance is needed.
PEEK, or polyetheretherketone, is a high-performance polymer known for exceptional dimensional stability, thermal endurance, and resistance to aggressive chemicals and abrasive conditions. In fiber form, such as Zyex PEEK fiber, it is engineered to maintain strength and stability in extreme service environments where many conventional rope fibers would degrade. PEEK is often selected for niche industrial applications that demand long-term reliability under heat, chemical exposure, and mechanical wear.
High strength ropes made from these fibers are used across marine, industrial, construction, safety, and specialized engineering fields. Many materials are also known by well-established product names, including Kevlar, Twaron, and Technora for aramids, and Dyneema and Spectra for HMPE. Polyester and nylon remain widely used due to their balance of durability, handling, and cost. The sections below explore how these fibers behave and where they are most commonly applied.
Due to their high tensile strength, stiffness, and thermal stability, aramid fibers are a strong choice for applications requiring low stretch and reliable load holding. Kevlar rope is often selected for high-strength applications but has limited shock-load tolerance compared to more elastic fibers. When Kevlar ropes experience sudden impact loading, they can be damaged more easily, which is why aramid ropes are frequently jacketed and designed with protective outer layers. Proper rope selection, hardware matching, and installation practices are essential to maximize aramid rope life in real-world conditions.
Kevlar’s chemical structure is characterized by a highly ordered, crystalline arrangement that contributes to its exceptional strength. As a polar molecule, Kevlar can bond with substances such as epoxy resins, which can be beneficial in composite reinforcement. However, that same polarity can allow moisture to wet the fiber, which may influence handling and long-term performance depending on service conditions and protective coverings.
Kevlar fibers form strong, tightly bonded chains that give aramid ropes a distinctive combination of strength, stiffness, and thermal performance. The physical characteristics of Kevlar include:
Kevlar ropes provide a lightweight alternative to steel cables in many use cases, especially where strength, low stretch, and heat resistance are required. Because UV exposure can degrade aramid fibers, most rope designs rely on a protective cover, often using a UV-resistant polyester jacket over an aramid core. Kevlar ropes are used in boating, specialized winching systems, and applications where controlled elongation matters. They are not typically recommended for climbing or situations involving repeated shock loading, because sudden impacts can cause rapid fiber damage without obvious warning signs. Aramid’s high heat resistance also supports use as a substitute for asbestos in certain high-temperature applications, and aramid-based ropes can be found in structural and utility uses such as guy wires and other tensioned support systems.

High modulus polyethylene, often referred to as high-performance polyethylene (HPPE), is widely recognized in sailing, boating, and industrial rigging under the trade names Spectra and Dyneema. These HMPE ropes are popular because they combine very high strength with low weight, strong abrasion resistance, and excellent performance in wet environments.
HMPE’s chemical structure is dominated by very long molecular chains with no reactive side groups, which limits chemical interaction with water, many chemicals, and microorganisms. This contributes to a fiber that stays dry, resists rot, and maintains consistent handling over time. Commercial HMPE fibers such as Dyneema and Spectra are commonly manufactured using a gel-spinning process to align molecules and maximize strength.
High modulus polyethylene is defined by a combination of hydrophobic behavior, high strength, and low friction, all of which affect how HMPE ropes are selected, handled, and terminated. These include:
HMPE is a strong, lightweight fiber that can float on water while maintaining excellent resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and UV exposure. It is widely used in high-performance sailing lines and rigging, and it is also common in industrial winching, towing, and lifting systems where weight reduction and handling efficiency are priorities. Beyond rope, HMPE fibers appear in body armor, vehicles, cut-resistant gloves, climbing gear, fishing lines, paragliding equipment, spear lines, bow strings, parachute suspension lines, and other demanding applications. Spectra and Dyneema rope are especially valued in marine environments due to buoyancy, corrosion resistance, and ease of deployment.
Terylene, Dacron, and Trevira are commercial names for polyester fiber. Polyester fibers are widely used for boat lines and general-purpose marine cordage because they balance durability, flexibility, UV stability, and cost. These fibers are typically white and produced in very fine diameters, and it can be difficult to visually distinguish polyester from nylon without labeling or testing. In rope applications, polyester is frequently selected where low creep and dependable outdoor performance matter most.
Polyester is a dependable synthetic fiber for applications where UV exposure, abrasion, and dimensional stability are major concerns. It is commonly used in sailing lines, mooring lines, and winch lines, and it is also widely applied as a protective jacket over more sensitive high-strength fibers such as aramids. Compared to many commodity plastics, polyester’s higher melting point improves performance where frictional heating is possible, and its low creep supports consistent tension over long periods. In many rope designs, polyester serves as a durable outer layer that helps extend service life in harsh outdoor environments.

Nylon, also known as polyamide, is a versatile synthetic fiber that can be molded, spun, and machined, making it common across industrial products and rope applications. In cordage, nylon is best known for high strength combined with high elasticity, allowing it to absorb shock loads and reduce peak forces on anchors, cleats, and hardware. Because nylon can behave differently in wet conditions, application environment and duty cycle should be considered when selecting nylon rope.
Nylon is commonly used for dock lines and anchor lines because its elasticity helps absorb waves, wind, and sudden loading events. It is also widely used in utility cordage such as paracord and in fishing lines where flexibility and toughness are beneficial. Nylon can be dyed in many colors for identification and organization, which can be useful in marinas and work sites. In aerospace and outdoor equipment, nylon cordage also appears in parachute suspension lines and general-purpose tie-down applications.
Zylon is considered one of the highest-performing synthetic fibers available, delivering extremely high tensile strength, rigidity, and excellent thermal resistance. Its tensile strength is often cited as significantly higher than Kevlar, making it attractive for specialized applications that demand maximum strength with minimal stretch. Zylon is used in products ranging from high-performance sporting goods to industrial reinforcement where weight savings and strength are critical.
Zylon is widely used in protective clothing and heat-resistant gear, and it can also be found in reinforcement applications such as coatings, specialty cables, and construction materials. In sports and recreation, Zylon appears in bike tires, tennis racquets, snowboards, and high-performance yacht ropes. It is also used in cable cover materials for welding machines, where heat and abrasion resistance are important.
Like Kevlar, Nomex is an aromatic polyamide, but as a Meta-Aramid it features a different molecular linkage that gives it a distinct performance profile. Nomex’s zigzag chemical bonding results in lower tensile strength and rigidity than Para-Aramids, but it delivers excellent flame resistance and protective performance. Nomex is often produced as an elongated fiber optimized for yarn formation, which supports its widespread use in protective textiles and filtration media.
Nomex fiber is best known for protective gear used by firefighters, pilot crews, and workers in environments where flame resistance and electrical protection are essential. It is also used as filter media in cement and asphalt plants, where heat and particulate exposure demand durable materials. In many industries, Nomex-based garments and materials help protect against flames, electrical hazards, and exposure conditions that would overwhelm conventional textiles.

Selecting high strength rope is comparable to choosing an essential piece of equipment and requires careful thought. These ropes are often used in safety-critical and high-load tasks, including lifting slings, hoisting systems, winching, rigging, and pulley-driven material handling. A rope that is correctly matched to the application helps reduce risk, improves efficiency, and supports long service life under real operating conditions. When chosen with precision, high strength ropes contribute to safer lifts, smoother movement, and better overall control during pulling, towing, or load securement.
Key Considerations for Purchasing High Strength Rope
High strength applications typically utilize synthetic materials, sometimes with protective jackets, that offer the necessary breaking strength, resilience, and durability to manage substantial loads while ensuring longevity. The best choice depends on whether the load is static or dynamic, whether the rope will be exposed to moisture, UV light, heat, or chemicals, and whether low stretch or shock absorption is more important. For example, certain grades of nylon start with a breaking strength of around 1000 lbs, whereas other synthetic materials can support loads in the thousands of pounds, especially when manufactured in larger diameters or higher-performance fibers.
HMPE is one of the most commonly used materials for ropes due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, which is comparable to steel. In configurations like double braid and 12-stranded braid, HMPE stands out as the strongest option available for many rope categories. A 12-stranded braided HMPE rope with a 48 mm diameter has a breaking strength of 165 tons and an impressive operational lifespan of 4000 hours, illustrating how high-performance fibers can deliver both capacity and durability when properly specified and maintained.
While the breaking strength is a valuable measure of a rope's durability, it is not always straightforward to predict due to construction variables, abrasion, temperature, UV exposure, bend radius effects, and termination method. Splices generally preserve more rope strength than knots, and using properly rated hardware and sheaves can prevent premature damage. Often, employing double-braided or 12-stranded braided ropes can help achieve a reliable safety margin for the breaking point while maintaining manageable handling and dependable long-term performance.
In most high-strength rope uses, larger diameters are favored, particularly in lifting and towing scenarios where load capacity is crucial and hand comfort matters. When selecting rope for pulleys, flexibility and pliability become important, as the rope must navigate smoothly through the pulley system without excessive friction or flattening. Double-braided or 12-stranded braided HMPE ropes are excellent options for these applications, as they can deliver high strength at smaller diameters while still maintaining good handling characteristics when paired with suitable hardware.

A bungee cord is a rope that is composed of two or more elastic strands coated with a woven fabric. It has hooks that are placed on both ends. A bungee cord is also known as shock cord and elastic cord...
Cordage is a series of intertwined fibers, strands, strings, or fabric that are joined by twisting or braiding to form a larger more formidable whole. The combination of the materials makes the final, larger strand stronger than its individual pieces...

An aircraft cable is a style of highly durable cable that is used for aircraft flight controls and other applications and is differentiated from normal cables by its diameter, stranding, and wires, which provide...

Electric hoists are material handling equipment used for lifting, lowering, and transporting materials and products. They are powered by an electric motor and have a controller to adjust the lifting parameters...

A gantry crane is an overhead crane that has an overhead beam supported by freestanding legs and moves on wheels, a track, or rail system carrying a bridge, trolley, and hoist. Workshops, warehouses, freight yards, railroads, and shipyards use gantry cranes as their lifting solution as a variation of overhead or bridge cranes...
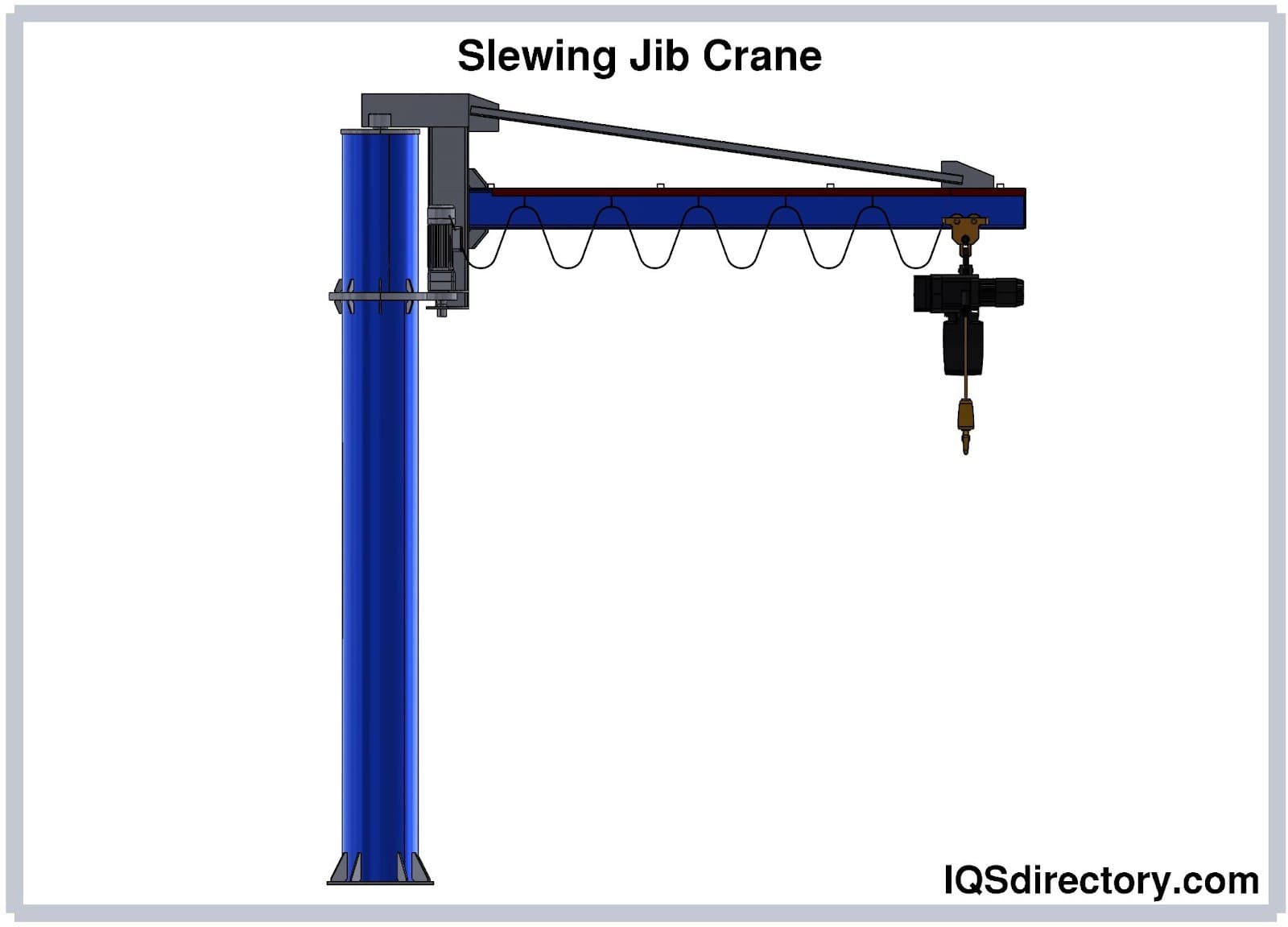
A jib crane is a lifting device with an arm or boom that extends off the main body of the crane to provide extra reach and has a lattice design to lower the weight added to a load. The design of jib cranes allows them to work...

An overhead crane is a type of heavy duty machinery that is capable of moving extremely heavy loads and equipment from one location to another in a safe and precise manner using the overhead space of a manufacturing facility. Due to the nature of the work they perform...

A push pull cable control is used for the transmission of multi directional precision control of mechanical motion. The many varieties of push pull cables or controls are adaptable to a wide range of applications and...

Stranded wire refers to thin bundled up wires that are compressed and covered up in insulating material. Stranded wires are more flexible thus making them very ideal for joining electronic circuit components in confined spaces where their bending...

Wire rope is a collection of metal strands that have been twisted and wound to form the shape of a helix with the purpose of supporting and lifting heavy loads and performing tasks that are too rigorous for standard wire...

A wire rope assembly is composed of wire rope and end fittings, terminals, or lanyards that are attached to various parts of the wire rope such that the assembly can be used to lift, hoist, and move loads. The various types of...

Wire rope is constructed of multiple strands of wire that are twisted and braided together to form a spiral design or helix. Once the separate wires are shaped into a solid form, they become a single wire with greater strength because...