Stranded and Braided Wire: Types and Applications
Introduction
This article will take an in-depth look at stranded wires, braided wires, and wire strands.
The article will bring more understanding on topics such as:
- Principle of Stranded Wire, Braided Wire, and Wire Strands
- Types of Stranded Wire, Braided Wire, and Wire Strands
- Applications and Benefits of Stranded Wire, Braided Wire, and Wire Strands
- And Much More…
Chapter 1: What are the principles behind stranded wire, braided wire, and wire strands?
This chapter will explore stranded wires, braided wires, and wire strands, including their construction, characteristics, and functional applications.
What is a Stranded Wire?
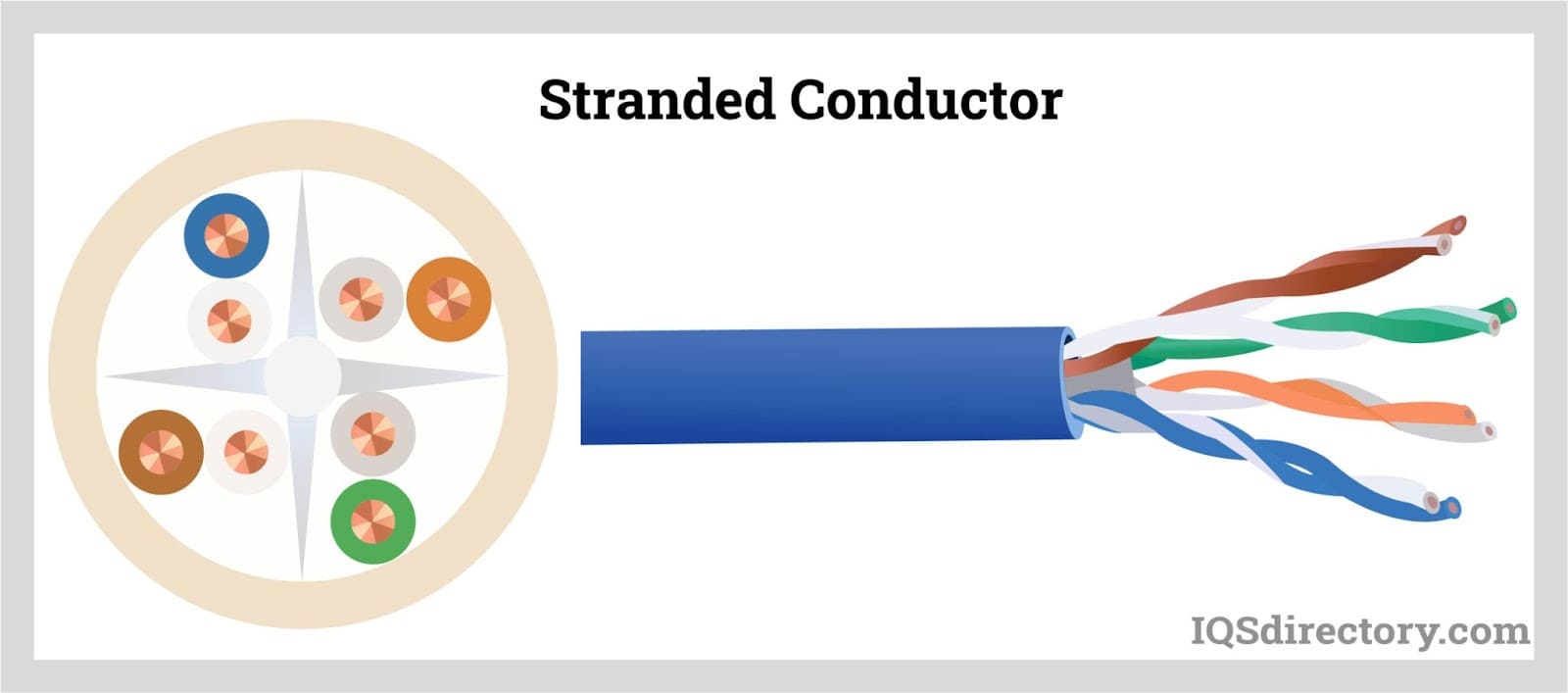
Stranded wire consists of multiple thin wires bundled together and covered with insulating material. This construction enhances flexibility, making stranded wires ideal for connecting electronic circuit components in tight spaces where their ability to bend and twist is advantageous.

Unlike solid wires, stranded wires are highly flexible and malleable, making them less prone to breaking under stress.
What is a Braided Wire?
Braided wire consists of a mesh-like shielding woven around a cable to protect the wiring from electromagnetic interference and enhance its mechanical strength.
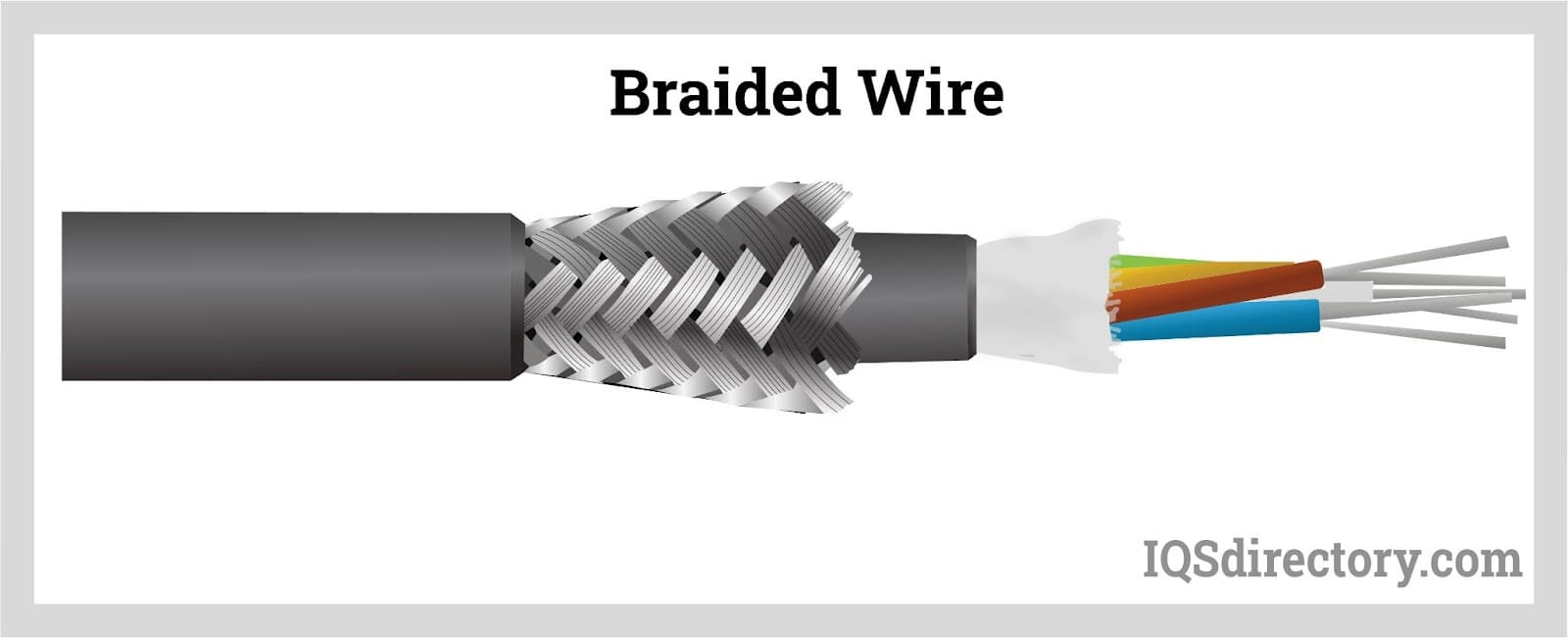
The shielding is composed of numerous thin wires woven tightly in a standard mesh formation around the conductor. In some designs, the braid can be flattened to achieve the desired width. A thin insulating layer covers the braid and other internal components of the cable.
What are Wire Strands?
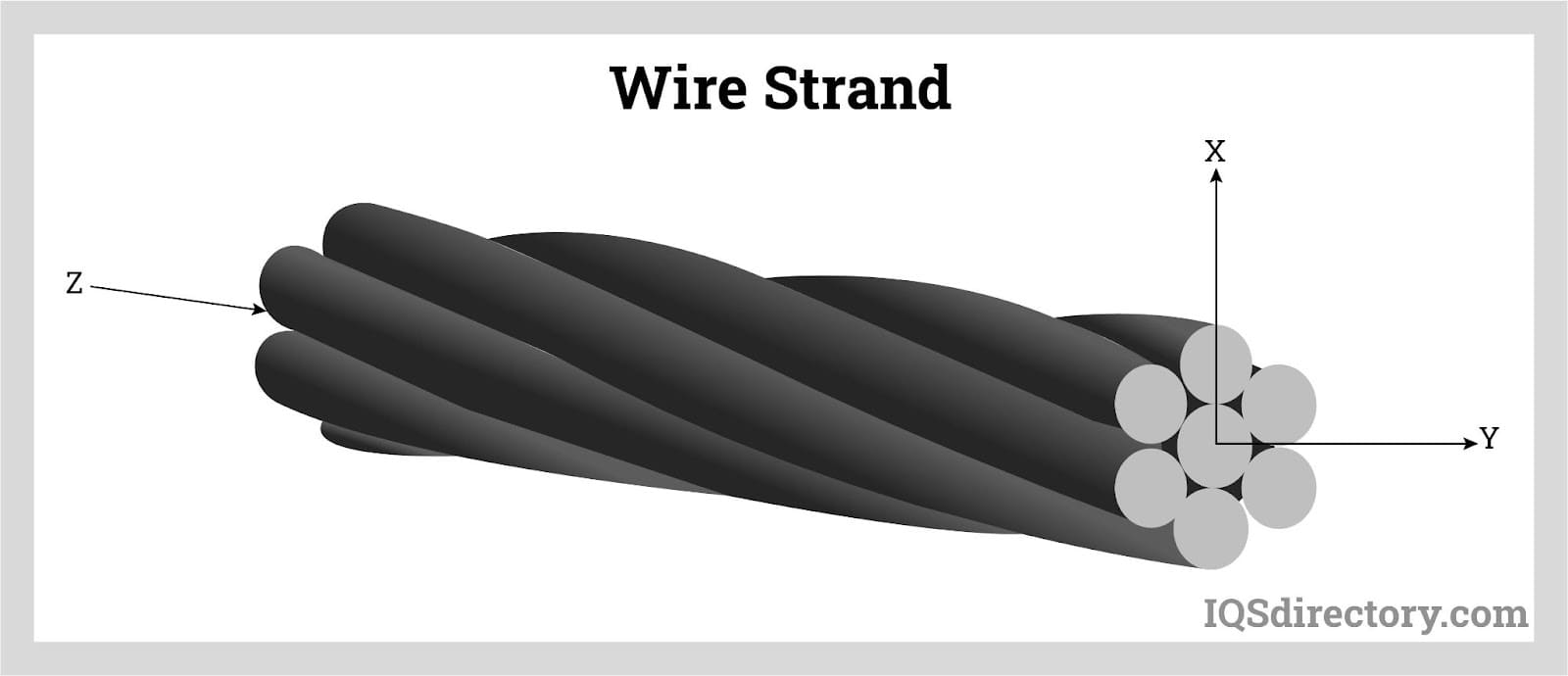
A wire strand consists of wires wound concentrically in a helix. The strands are wound around a central wire and then around a core.
Wire strands can be configured in various ways. Generally, a higher strand count increases the wire's flexibility. These strands can be made from materials such as stainless steel or precious metals like tungsten, gold, and silver.
Functioning of Stranded Wire, Braided Wire, and Wire Strands
Understanding how these wires operate involves:
Stranded Wire
Stranded wires are frequently utilized as conductors in electrical transmission and distribution networks.
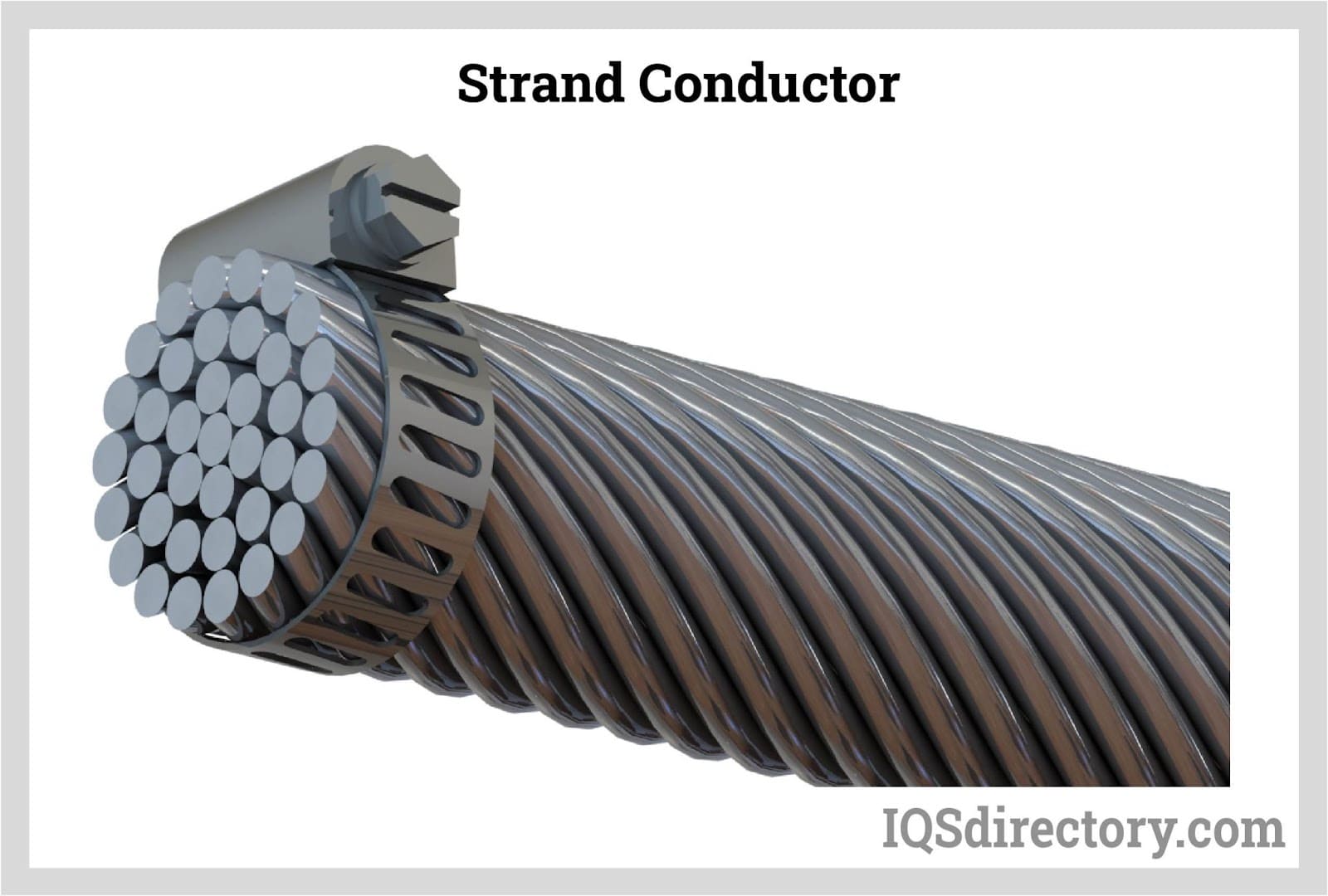

In the diagram provided, the core of the strand is composed of steel, which imparts significant tensile strength to the stranded conductor. The outer wires are made of aluminum, which enhances the conductor's overall conductivity. This design ensures that the conductor remains flexible.
Compared to a single solid conductor, which lacks flexibility and poses challenges in transportation, a stranded conductor offers superior ease of handling. For instance, a 100-meter length of solid conductor would be cumbersome to transport, while a stranded conductor can be conveniently coiled and packed for shipping.
Facts on Stranded Conductors
Here are some key points to consider about stranded conducting wires:
- A stranded conductor is very flexible such that it can be coiled easily packed and be transported over a long distance.
- The flexibility of any conductor will increase with the number of strands.
- Stranded conductors are formed by winding the strands together in several layers.
- The several strands are laid one on top of the other in a helical format and this process is commonly known as stranding.
- For the stranding to hold, the successive layers are laid opposite the direction of the preceding layer. This means if the first strand is twisted in a clockwise fashion the strands of the following layer are twisted in an anticlockwise fashion and so on.
- The formula gives the total number of strands of any given conductor. N = 3 x2 - 3 x + 1, Where N refers to the total number of strands in the conductor
- The diameter of the conductor is calculated by using the following formula D = (2 x – 1)d, Where D refers to the diameter of the given conductor and d refers to the diameter of each strand.
Stranded wires are also frequently utilized in AC power cords, connections for computer peripherals, musical instruments, cables for moving machinery, and various types of equipment.
Braided Wire
Braided wires are often employed for electromagnetic shielding and in cables designed for noise reduction.
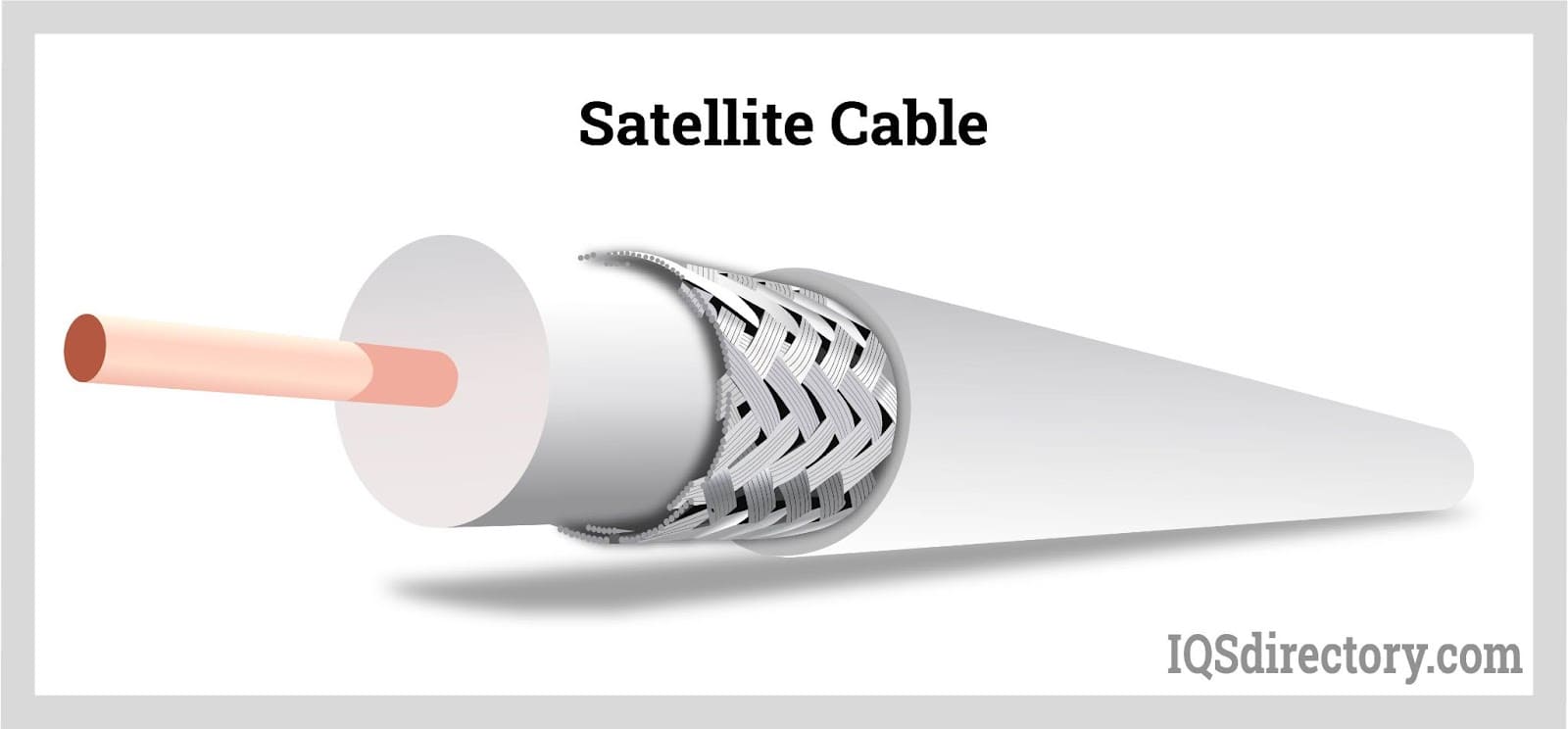
Braided cables are frequently utilized in satellite cable connections, leveraging their primary attribute of shielding against interference and mitigating electromagnetic disturbances.
Wire Braid Manufacture
Wire braids are typically made from copper, which can be either bare or coated depending on the specific application. While silver- or nickel-plated copper are also viable choices, tinned copper is often preferred for its superior conductivity and corrosion resistance. The process starts with numerous fine and pliable wire strands, which are then wound around a central core using fast-rotating spools. This winding creates a woven structure, resulting in a flexible and robust braided wire.

The dimensions of the wire braid are determined by the number of carriers used in the braiding machine. Typically, machines have sixteen, twenty-four, or forty-eight carriers. Each carrier is equipped with a bobbin that can hold up to sixteen strands of wire. The braid's configuration is usually described by a set of three numbers (e.g., 24-4-36), where:
- 24 is the number of carriers
- 4 is the number of wires per carrier
- 36 is the AWG of each wire.
A flat braided wire originates from a round braid, which is then flattened using a force roller positioned on the capstan. The capstan, a large rotating drum, pulls the wire through the braiding mechanism. Although flat braids maintain the same stretch and strength as round braids, they offer a larger surface area, which reduces the resistance encountered by electric current flowing through them.
Wire Strands
The wire strands are wound up concentrically in a helix.
Manufacture of Wire Strands
Wire rope consists of multiple components: individual wires, wire strands wound around a core, and the core itself. There are two primary types of cores used. The most common is the Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC), which is made from a wire cord of suitable size. This core type provides significant strength and flexibility.
The alternative core type is the Wire Strand Core (WSC), which comprises several wire strands that may have a similar structure to the main strands of the rope. In a wire rope, each strand is made up of multiple wires, contributing to the overall strength and durability of the rope.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between stranded wire and braided wire?
Stranded wire consists of multiple thin wires bundled together for flexibility, while braided wire is a mesh-like shield woven around a cable, offering protection against electromagnetic interference and increased mechanical strength.
How does increasing strand count affect wire flexibility?
Increasing the number of strands in a conductor directly improves its flexibility, making it easier to bend, coil, and install in confined or complex areas.
What are the key applications of braided copper wire?
Braided copper wire is used primarily for electromagnetic shielding, electronic connections in vehicles, exhaust systems, and constructing swing gates in high-rise buildings due to its flexibility and resistance to corrosion.
When should solid cables be used instead of stranded or braided types?
Solid cables are ideal for applications requiring durability under harsh conditions, such as outdoor overhead lines, heavy-duty installations, and stationary wiring, where flexibility is less important.
What construction details define concentric stranded wire?
Concentric stranded wire features a central conductor surrounded by one or more layers of helically wound wires, with each new layer containing six more wires than the previous, ensuring tight packing and maintained shape.
What factors should be considered when selecting wire for electronics or circuit boards?
For electronics or circuit boards, stranded or braided wires are preferred for their flexibility, resilience against vibration, and reliability when bent, making them suitable for intricate wiring in tight spaces.
Chapter 2: What are the different types of stranded wire, braided wire, and wire strands?
This section will explore the various types of stranded wires, braided wires, and wire strands.
Types of Stranded Wires
The multitude of thin wire strands grouped together forms a flexible conductor, adaptable for numerous applications. These strands can be configured in various symmetrical patterns to satisfy specific design requirements for different devices or applications. Here are some common types of stranded wire:
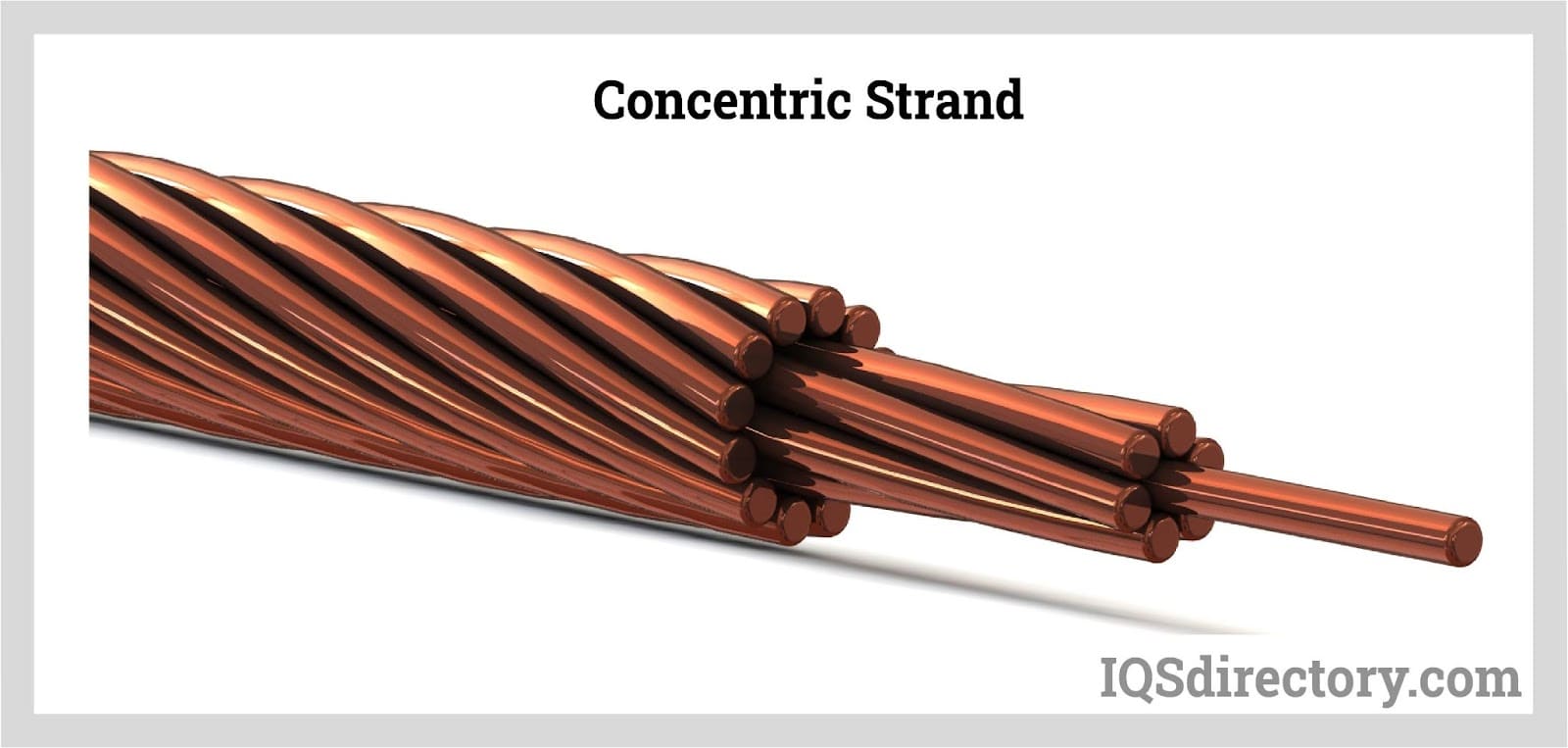
Concentric Strand
Concentric stranded wire is a widely used arrangement where a central conductor is surrounded by one or more layers of helically wound wires. Each subsequent layer consists of six more wires than the layer beneath it, arranged in concentric circles. This configuration reduces the need for filler material and ensures that the wires are tightly packed, which helps maintain the wire’s shape and enhance conductivity.
Bunch Strand
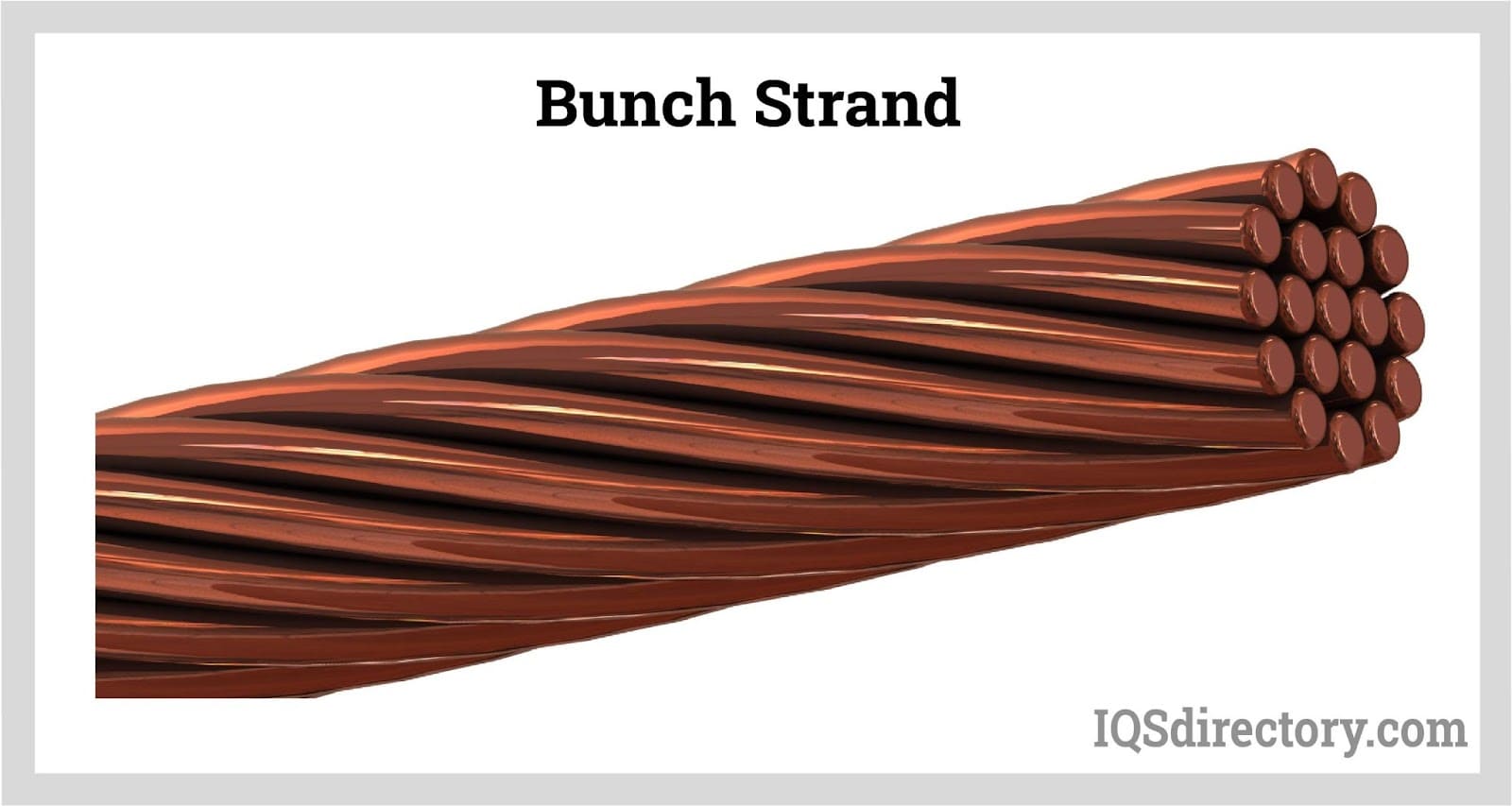
Bunched stranded wires lack a specific geometric pattern, with strands loosely gathered and aligned in similar directions. The wires are tightly twisted to maintain a consistent packing density. This arrangement provides the wires with significant strength and flexibility, making them particularly suitable for bending around tight corners due to their high malleability.
Rope Strand
Rope stranding involves grouping wires into several small bundles. Each strand is first twisted into smaller groups before being arranged into concentric rings to form a rope-like cable. This configuration enhances flexibility, allowing the wire to move more freely in various directions. Using larger gauge wires in rope stranding increases the wire's durability and functionality, making it suitable for applications that require frequent movement.
Compact Conductor
A compact stranded conductor is typically used for applications requiring a smaller diameter. The individual strands of a larger, round conductor are arranged in layers, similar to other stranded wires. After arranging the strands, they are compressed to eliminate any air gaps between them. This process results in a more compact conductor with no airspaces, while maintaining the same cross-sectional area as the original conductor.
Braided Wires
Common materials for braided wires include tinned copper and silver-plated copper. Additionally, other options such as nickel-plated copper, gold-plated copper, pure silver, pure nickel, and gold alloys are also used.
Electromagnetic waves, including those from phones, radio signals, and natural sunlight, can interfere with data transmission. To minimize data interruptions and losses, metallic wires are intricately woven to shield against these interferences, ensuring smooth data transfers.
Braided Wire and Foil Shielding Differences
Foil shielding, made from metal tape, serves as an alternative to braided wire. It provides excellent protection against high-frequency interference and is more cost-effective than braided shielding. However, foil shielding can be prone to folding and breaking due to its lack of structural reinforcement.
Wire Strands
The different wire strands include:
Wire and Cable Strand
Strands are created through the stranding process, where individual wires or cables are twisted together to form a conductor with a larger cross section. This technique enhances the conductor's mechanical properties, such as flexibility and vibration resistance, and prepares it for subsequent stranding or sheathing stages.
The characteristics of strands are defined by the length of the layers and the direction of the twist. The two primary twisting directions are left-hand lay (often denoted as S) and right-hand lay (denoted as Z).

Strands can be classified into three distinct categories based on their structural arrangement:
Bunched Strand
Bunched strands are created by grouping together single or multiple wires in one step. These strands have an irregular structure with an undetermined layout for each wire, and they can be twisted in either S or Z directions. The surface of bunched strands is uneven, and the diameter and roundness of the wires are not consistently uniform. Due to their irregularity, bunched strands are not ideal for applications requiring thin-wall linings. However, they are well-suited for flexible or stretchable cords, construction cables, and control cables.
Concentric Strand
Concentric strands feature a consistent and symmetrical construction, with a specific arrangement of wires in patterns such as 1 + 6 + 12 + 18 + 24 + 30. These strands can have wire counts of 7, 19, 37, 61, or 91. Concentric strands are categorized into two types: True concentric and unilay. True concentric strands have varying lay directions for each layer from the core to the outer layers, while unilay strands have uniform lay directions throughout. All concentric conductors are known for their precise outer layer surface and consistent conductor diameter. They are especially suitable for applications involving thin-wall insulation that requires high-quality insulating materials.
Semi-Concentric Strand
This type of strand features a regular arrangement, but it lacks the symmetric wire counts found in concentric strands (such as 2 + 8 + 4 or 3 + 9 + 16). The outer layers are evenly distributed around a central wire, resulting in a smooth outer surface. These strands are suitable for applications involving thin-wall insulation.
Semi-concentric and concentric stranded conductors can be processed with rollers or dies to achieve a very smooth surface and minimize the conductor's outer diameter, which reduces the amount of insulation material needed during the insulation process.
The term "strand" refers to assemblies of 7, 19, or 37 clusters or concentric strands arranged in a consistent pattern. These are typically categorized as rope lay bunch stranded or rope lay concentric stranded configurations.

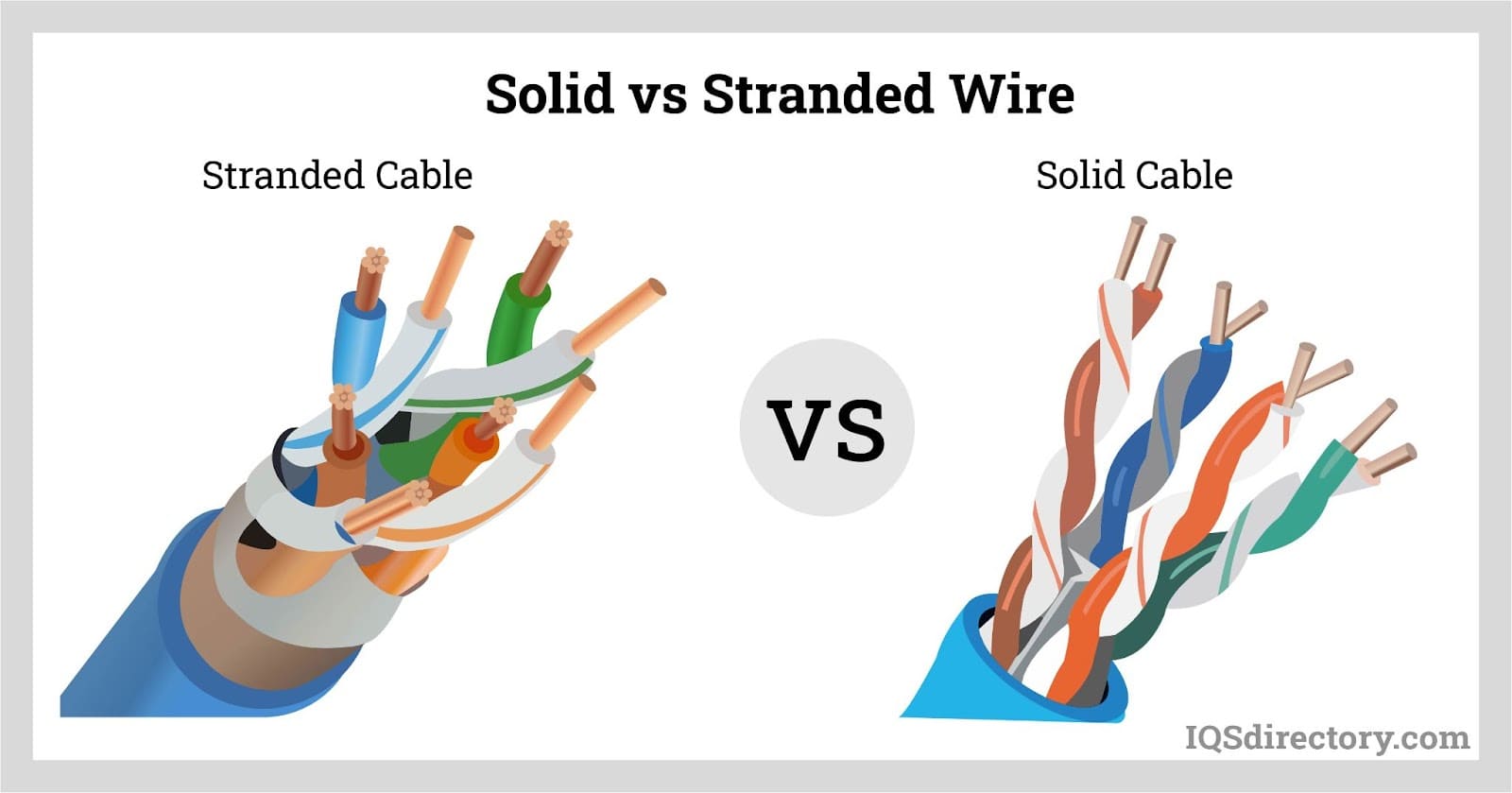
Stranded vs. Solid Wires-Key Differences
To distinguish between stranded and solid wires, it's essential to evaluate their respective advantages and disadvantages. This assessment helps determine the most suitable wire type based on its attributes and the specific requirements of the project. Factors such as climate resistance, flexibility, and durability against splitting, cutting, or breaking should be considered. By understanding these needs, you can select the wire that best aligns with your application requirements.
Here are some common differences between stranded wire and solid wire:
Current Carrying Capacity
Solid wire is typically denser and thicker, offering a smaller surface area for current dissipation. In contrast, stranded wire consists of multiple thinner wires, which creates air gaps and a larger surface area, resulting in better current transmission and heat dissipation. For residential wiring setups, solid wire usually provides a higher current capacity due to its denser construction.
Routing Stranded Wires
Stranded wires offer superior elasticity, bendability, and flexibility compared to solid wires, making them more adept at navigating around obstacles and tight spaces.
Stranded Wire Flexibility
Stranded wires exhibit remarkable flexibility and durability, allowing them to endure extensive vibrations and bending without breaking. In contrast, solid wires are more prone to damage and may need to be replaced more often in environments with substantial movement or vibrations.
Wire Cost
Solid wires are generally less expensive to produce than stranded wires, making them a more cost-effective choice for various applications.
Relative Ease of Manufacturing
Solid wires have a straightforward single-core design that simplifies their manufacturing process. In contrast, stranded wires require a more complex production method, involving the twisting of multiple thinner wires together.
Solid and Stranded Wire Distance
For extended distances, solid wires are preferable due to their lower electrical current dissipation. On the other hand, stranded wires are more effective for shorter runs.
Superiority of Wire
Comparing stranded and solid wires in terms of overall superiority is challenging, as each type excels in different scenarios based on specific advantages.
Differences Between Braided Wiring and Foil Shielding
Foil shielding utilizes metallic tape as an alternative to braided wire. This type of shielding provides excellent protection against high-frequency interference and other signal disruptions, while also being more cost-effective compared to braided shielding.
However, foil shielding's primary limitation is its lack of lattice reinforcement, which means it cannot withstand twisting, bending, or confined spaces as effectively as braided shielding. This makes it less suitable for applications requiring high durability.
On the other hand, braided wire is more versatile and resilient, offering significant protection against mechanical stress and electromagnetic interference (EMI), making it a valuable option for robust cable shielding.
Braided wire typically provides only 70 – 90% shielding effectiveness and can add extra thickness to the cable, which might not be ideal for environments with limited space or where complete coverage is required. If you need a shielded cable and are uncertain about which option to select, it’s important to conduct thorough research on your specific needs, as choosing the wrong cable can lead to significant issues.
Leading Manufacturers and Suppliers
Chapter 3: What are the applications and benefits of stranded wire, braided wire, and wire strands?
This section will explore the uses and advantages of stranded wire, braided wire, and wire strands.
Applications of Stranded Cables
For intricate wiring needs, such as those required for circuit boards and electronic devices, stranded wires are preferred. They stay secure and reliable even when twisted or bent while connecting to other components.
Advantages of Using Braided Copper Wire
Copper wires come in various forms, including stranded and braided types, each with its own set of benefits and limitations. It's crucial to carefully consider these factors before making a purchase. Research the specific applications for which these different types are suitable. For tasks requiring high flexibility, braided copper wire is advantageous. It is commonly used for electronic connections in motor vehicles, such as in exhaust systems, and also in the construction of swinging doors and gates in high-rise buildings.
Braided Copper Wire vs. Solid Wire
- The solid copper wire is thicker compared to the braided one and the latter has a bunch of strands of copper which would have been twisted and braided together so as to create a whole wire. This is the reason why the braided sorts are more flexible and bendy as compared to the single solid wires. The solid wire is not easily moldable since it is rigid.
- Braided copper wire also has more resistance to corrosion and its malleability improves its resilience to wearing and tearing that is continuous. This is the reason why these bundles of copper wire strands are usually used for making electric cords and computer peripherals cables.
- The braided kinds are ideal for appliances which are used where there are a lot of vibrations. This makes such appliances tougher due to the braided wires that are flexible and strong.
- Unlike the usual copper cables, the braided types are easier to set up as they are made of many thin strands which would have been twisted.
In addition to their numerous benefits, braided wires are often more cost-effective compared to alternatives like coaxial cables. While both can transmit electrical power efficiently, each has distinct characteristics that make them suitable for specific home or business applications.
Solid wires are generally more suited for heavy-duty appliances and outdoor applications, whereas braided wires excel in electronic devices and circuit boards due to their flexibility and durability. They are especially useful in robotics and automotive applications. When selecting braided copper cables, it's important to ensure that the suppliers are reputable and reliable.
Always purchase these cables from manufacturers who use high-quality raw materials and have been rigorously tested for safety in both home and industrial applications. Verify the legitimacy of suppliers by reading online reviews and customer feedback. This research will help you identify trustworthy manufacturers who provide safe and competitively priced braided wires. Copper remains a top choice for electrical conductors due to its flexibility and durability in various devices and appliances.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Wire Strands
In reinforced and prestressed concrete bridges, the prestressing system includes components such as wire, strands, anchorage systems, force stressing jacks, corrosion-resistant materials, and ducting. Typically, wire diameters range from 5 to 7 mm, with a minimum tensile strength of about 1570 N/mm², capable of handling forces up to 45 kN. Strands consist of multiple high-strength steel wires twisted together. Anchorages are used at both ends of the tendons to transfer the resultant forces into the base concrete, which is achieved through the anchorage mechanism after the forces are applied by the stressing jacks.
Solid vs. Stranded Cable
A solid cable consists of a single strand, often with a core that includes non-conductive insulation. This type of cable is commonly used for residential electrical wiring, laboratory breadboards, and other applications where the wires are stationary and not subject to frequent movement.
Stranded cables, on the other hand, are composed of multiple small gauge wires bundled together and insulated with non-conductive materials. These cables are ideal for applications where flexibility is important, allowing them to maneuver through tight spaces and endure movement, flexing, or vibrations. Common uses include speaker wiring, headphone cables, and appliance wiring.
In environments where cables are exposed to harsh conditions such as corrosive substances, heavy movement, or extreme weather, solid cables are preferred. They are chosen for applications like outdoor overhead electrical lines and other heavy-duty scenarios due to their durability and resistance to such conditions.
Benefits of Solid Cables
Solid cables are often preferred for their cost-effectiveness compared to stranded cables, largely due to their simpler manufacturing process. They are highly resistant to corrosion and mechanical wear, thanks to their single, thick strands. The compact diameter of solid cables does not compromise their current-carrying capacity. Additionally, solid cables are generally less prone to failure from deterioration and corrosion, which further contributes to their high regard and widespread use.
Disadvantages of Solid Cables
While solid cables have many advantages, they also come with some notable drawbacks. One major issue is that they are often available in limited quantities. Additionally, continuous flexing or vibrations can lead to wear and eventual failure of the cable, necessitating replacement. As a result, solid cables are generally unsuitable for applications involving significant movement, such as robotics or vehicles. If bent into rigid shapes, solid cables lack the flexibility and resilience needed to maintain their integrity.
Benefits of Stranded Cables
Stranded cables are more adaptable in tight spaces compared to solid cables. Their flexibility and bendability allow them to withstand significant vibrations and repeated flexing without degrading or failing. Consequently, stranded cables typically require less frequent replacement than solid cables.
Disadvantages of Stranded Cables
While stranded cables offer several benefits, they are not without their drawbacks. Their larger diameter often matches the current-carrying capacity of solid wires, but they come at a higher cost due to the more complex manufacturing process. This increased cost stems from the intricate production required to assemble the multiple wires. Stranded cables are also more susceptible to corrosion through capillary action and may not be the best choice for minimizing electronic interference. The air gaps between the wires can exacerbate the “skin effect” caused by magnetic fields along the cable. Consider these factors carefully when deciding between solid and stranded cables for your home or business needs.
Conclusion
In summary, there are various types of wiring used in the industries and home level appliances and some common types of wiring are stranded wires, braided wire, and wire strands.
Stranded wire refers to thin bundled up wires that are compressed and covered up in insulating material. Stranded wires are more flexible thus making them very ideal for joining electronic circuit components in confined spaces where their bending and twisting capabilities can be put to use.
Braided wire is a jersey-like shielding built around a cable to shield the wiring from electromagnetic interference and to improve its mechanical strength. The shielding is made up of numerous tiny wires tightly woven in a standard mesh tabular formation around the conductor. In some designs, it can be flattened to achieve the desired width.
A wire strand is when wires are wound up concentrically in a helix. The strands are wound around a central wire then around the core. Wire strands can be wound in varying numbers of configurations. The strands there are the more flexible the wire will be.
It is therefore imperative that a careful selection should be done depending on the job requirement and area of application.