Heat Treating Metal
Heat is applied to a material and then it is cooled through a procedure known as "heat treatment” to enhance a material's performance, durability, and other characteristics. To increase formability, metal can be softened by heat treatment.
Heat Treatment Process
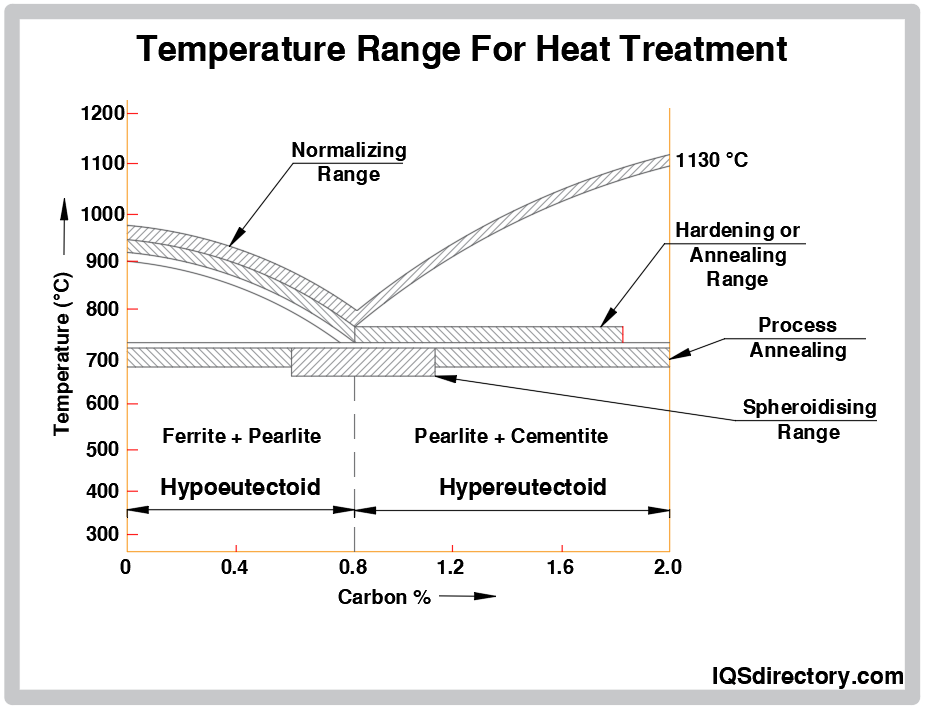
The primary goal of the heat treatment process is to ensure that the metal heats uniformly. One section of the metal may expand more quickly than another if it is heated unevenly, leading to distortion or cracking in that area. Therefore, selecting the heating rate is based on the following considerations:
- The metal's capacity to conduct heat: High-heat conductivity metals heat up more quickly than low-heat conductivity metals.
- The metal's dimensions and cross-section: To allow the inside temperature to be near the surface temperature, larger portions or components with uneven cross-sections must be heated more slowly than small parts. Otherwise, there is a chance of significant warping or cracking.
Soaking Stage
The soaking stage aims to maintain the metal at the right temperature while the correct internal structure develops. The length of time a metal is kept at the proper temperature is known as the "soaking period. The metal's mass and chemical analysis are needed to calculate the proper time. For example, one may calculate the soaking time for uneven cross-sections using the largest cross-section.
The metal's temperature should only be raised slowly, from room to soaking temperature. Therefore, one must gradually heat the metal to a point just below which the structure will change and then maintain that temperature until the metal is uniformly heated. Layers of preheating may be necessary for parts with more intricate designs to stop warping.
Cooling Stage
The metal needs to be cooled to room temperature at this stage. Depending on the type of metal, there are numerous methods for cooling it. A liquid, gas, or a combination of liquid and gas may be required to cool the metal. The metal itself and the cooling medium determine the rate of cooling. As a result, the intended metal qualities depend greatly on the cooling decisions selected.
When a metal is quenched, it is rapidly cooled in a medium such as air, water, oil, brine, or another one. The rapid cooling that occurs during quenching causes quenching to be associated with hardening, but hardening is not always brought on by quenching or other forms of rapid cooling. For example, copper is annealed by water quenching, whereas other metals are hardened by slow cooling.
Heat Treatment Objectives
There are several uses for heat treatment, including:
- To enhance a material's hardness, tensile strength, shock resistance, ductility, and corrosion resistance.
- To decrease brittleness and increase machinability.
- To relieve the metal's internal tensions by hot or cold working.
- To refine it or alter the grain's size.
- To enhance the electric and magnetic characteristics.
- To boost both wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
- To increase the material's surface's hardness.
- To increase the tolerance for wear on small and medium-sized parts, such as shafts, wrist pins, and gears.
- To make the hardened surface appear clean, bright, and appealing.
Types of Heat Treatment
Carburizing Treatment Process
During this procedure, carbon atoms are added to the steel's surface and subsurface to increase the steel's surface hardness. Allowing carbon to permeate the metal portion strengthens its surface and improves its microstructure and mechanical properties.
The depth at which carbon can diffuse depends on the amount of carbon in the atmosphere, the material used, the temperature, and the length of time the metal was exposed to that temperature. Hardening takes place right after the part has been quenched. Carburizing also improves wear resistance and fatigue strength in addition to surface hardness.
Nitriding Treatment Process
Like carburizing, the thermochemical case-hardening process of nitriding is used to increase the hardness, fatigue life, and wear resistance of metal parts. Nitrogen is diffused into the metal's surface during nitriding to provide the hardening effect. Ferrous material is heat treated before being exposed to active nitrogen at precisely controlled subcritical temperatures as part of the nitriding process.
To prevent the metal's mechanical qualities from being impacted, temperatures applied during the exposure to active nitrogen range between 752 °F and 1094 °F (400 °C to 590 °C), which is lower than the temperature of the final tempering. In addition, alloy steel materials that contain nitride-forming elements are best for nitriding. As a result, alloy nitride precipitates can occur.
Heat-Treating Applications
Metallurgical heat treatment is used most frequently. Many materials, including glass, are manufactured by heat treatment. The following are more fields in which heat treatment is used.
Benefits of Heat Treating
Heat treatment can:
- Use the annealing process to soften a metal or plastic.
- Make metals harder through case hardening, hardening, nitriding, and carburizing.
- Utilize induction hardening to harden or soften just a single region of a metal component.
- Homogenize injection-molded plastic components through annealing.
- Remove stress from material that has been extruded, shaped, bent, or sliced through stress relief.
Choosing the Proper Heat Treating Metal Manufacturer
To ensure you have the most productive outcome when selecting a heat treating metal manufacturer, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of heat treating metal manufacturers. Each heat treating metal manufacturer has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each heat treating metal business website using our proprietary website previewer to quickly learn what each company does.