Plastic Tubing: Types, Materials, Manufacturing Processes, and Applications
Introduction
Here is everything you need to know about plastic tubing on the internet.
You will learn:
- What is Plastic Tubing?
- Applications for Plastic Tubing
- How Plastic Tubing is Made
- Plastic Tubing Design
- And much more …

Chapter One – What is Plastic Tubing?
Plastic tubing refers to tubes created from polymers blended with various chemicals to produce materials that can range from solid to flexible. Since its introduction in the 1950s, plastic tubing has transformed industrial processes, playing a crucial role across an extensive range of applications.

The rising preference for plastic tubing stems from its versatility and adaptability. Produced in numerous wall thicknesses, diameters, tolerances, and strengths, plastic tubing can be tailored with different material combinations to meet the unique requirements of diverse applications.
Chapter Two – Applications for Plastic Tubing
The flexibility, durability, and adaptability of plastic tubing make it an ideal choice for a vast range of industrial applications where long wear and endurance are essential, as well as for commercial use in consumer products and residential plumbing systems. One of the key benefits of engineered plastic tubing compared to traditional materials like steel, aluminum, or copper is its high tensile strength-to-weight ratio and cost efficiency. Because plastic tubing is far less expensive to produce, install, and maintain, it continues to replace metal tubing in industries seeking long-term value, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation.
Applications for Plastic Tubing
Pneumatic
Pneumatic tubing made from flexible plastics such as polyurethane, polyethylene, and nylon is widely used in air-powered systems for automation, robotics, and control equipment. This type of industrial plastic tubing efficiently transports compressed air between components, ensuring consistent pressure and system performance. Plastic pneumatic tube is ideal for outdoor and factory applications, as it can endure temperatures ranging from -4° F to 140° F, and resist moisture, UV exposure, and chemical corrosion. Under normal use, plastic pneumatic tubing withstands up to 115 PSI at 68° F, making it essential in pneumatic conveying and air tool lines.

Mailing
Clear plastic mailing tubes, typically made from polycarbonate or PETG, offer secure and lightweight packaging solutions for delivering literature, product samples, posters, blueprints, and promotional materials. Their heavy thick walls are engineered for durability to withstand the rigors of postal and parcel shipping, preventing damage during transport. Available in a wide variety of lengths and diameters, plastic mailing tubes protect contents from moisture, bending, and impact, offering a clear presentation and reusable container for further storage and mailing needs. Custom labeling and closure options further enhance their value for shipping and branding.
Banking
Financial institutions rely on pneumatic tube systems, utilizing plastic tubing, for secure and efficient transfer of documents, cash, and transaction carriers within drive-thru banking facilities. The long interconnecting tubes from teller to customer are manufactured from thick-walled polycarbonate or acrylic for enhanced security, visibility, and impact resistance. Transaction carriers that travel through these vacuum-powered tubes are also made from durable, impact-resistant plastic to handle frequent transfers and ensure reliable operation over time. The transparency of plastic tubing enables fast problem identification and system maintenance, contributing to higher operational efficiency.


Farming
In agriculture and irrigation, plastic tubing made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is preferred for water distribution systems, drip irrigation, and fertilizer transport. These flexible, lightweight tubes are easy to install, require little maintenance, and exhibit excellent resistance to weathering, UV rays, chemicals, rust, and corrosion. The smooth interior of plastic tubing reduces friction, enhancing water flow efficiency for extensively long runs—sometimes spanning hundreds of feet—without the need for additional joints or connectors. As a result, plastic tubing supports sustainable farming practices and consistent crop yield by delivering water directly to plant roots.

Liquid
Plastic tubing is extensively used to transfer liquids in food and beverage processing, chemical handling, and water purification systems. For applications involving drinking water and beverages, FDA-compliant food grade tubing—often manufactured from polyurethane, polyethylene, nylon, or PVC—ensures safety, hygiene, and resistance to leaching or taste transfer. These liquid transfer tubes must meet rigorous standards for pressure, temperature resistance, clarity, and cleanliness. In chemical processing plants, corrosion-resistant PVC or fluoropolymer tubing is used for aggressive fluid delivery. Specialized sanitary tubing may also be required for pharmaceutical and biotech manufacturing where contamination prevention is critical.

Automotive
Modern vehicles rely on various types of plastic tubing and automotive hose for vital systems. These include flexible fuel lines, vapor recovery tubes, brake line covers, coolant transport, windshield washer lines, and air conditioning connections. Plastic materials such as nylon, polypropylene, and reinforced PVC are chosen for automotive applications due to their flexibility, chemical compatibility, and high temperature performance. Compared to metal counterparts, plastic tubing resists corrosion and abrasion, reduces overall vehicle weight for improved fuel economy, and facilitates easier routing in compact engine compartments.

Marine
Marine-grade plastic tubing is critical for boats and watercraft, especially in harsh aquatic environments. PVC and reinforced flexible tubing are routinely used for bilge pump discharge, live well circulation, potable water transfer, and fuel line systems due to their resistance to saltwater, oil, chemicals, and abrasion. Flexible plastic tubing maintains its structural integrity when exposed to variations in temperature, pressure, and humidity, which are common in marine conditions. The addition of UV stabilizers to marine tubing extends product life and ensures continued performance, supporting boating safety and reliability.

Medicine
Medical plastic tubing is an essential component in the healthcare industry, utilized for IV infusion sets, catheters, oxygen delivery, peristaltic pump transfer, and drainage systems. These specialized tubes—often made from PVC, medical-grade silicone, polyurethane, or TPE—must satisfy stringent quality and regulatory requirements, including FDA and USP Class VI standards. Manufactured in clean room environments to prevent contamination, medical tubing is available in a variety of configurations, such as single, dual, or multi-lumen channels, kink-resistant designs, and custom cut lengths or reels. Advanced extrusion processes ensure biocompatibility, flexibility, and transparency, crucial for patient safety and accurate fluid delivery.

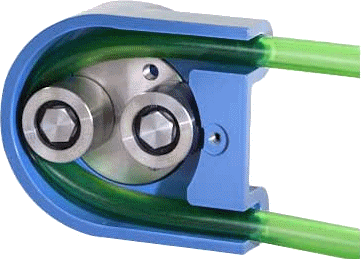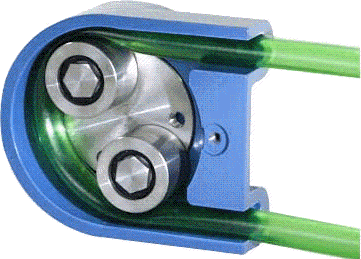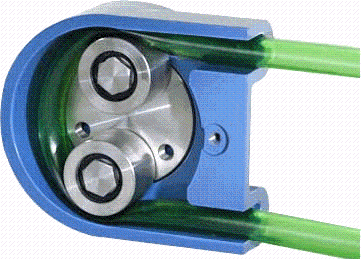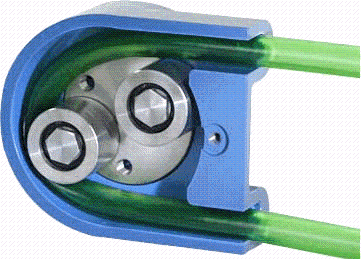
Peristaltic Pump
Peristaltic pumps rely on highly flexible, resilient plastic tubing to move liquids accurately and hygienically in applications ranging from chemical dosing and laboratory sample transfer to pharmaceutical manufacturing and food processing. These systems work by sequentially compressing and relaxing the tubing with rotating rollers, propelling the fluid forward without direct contact with pump components—thus minimizing contamination risk. Tubing material compatibility is crucial for maintaining integrity under repeated flexing and cyclic pressure, with options like silicone, thermoplastic elastomer (TPE), and specialized PVC preferred for optimal pump lifespan and performance. Choosing the right tubing for peristaltic pumps enhances metering precision and system reliability.
Leading Plastic Tubing Manufacturers:
| Manufacturer | Description | Website |
|---|---|---|
NewAge® Industries, Inc.  |
A leading manufacturer and fabricator of flexible plastic tubing and hose, we produce and stock large quantities of a wide variety of materials, including PVC, polyurethane, silicone, nylon and many more. Tubing and hose styles are available in unreinforced tubing and reinforced hose for extra strength and pressure capabilities. Many of these meet 3A, NSF, USP Class VI, etc. We have over 60 years of experience that we want to share with our customers. | View Website: |
Absolute Custom Extrusions, Inc. |
At Absolute Custom Extrusions, we specialize in plastic tubing, while providing custom plastic extrusions and profiles. Products include distributor tubes, hot or cold water tubes, automotive tubing, medical tubing, shipping tubes and golf club tubes. Experienced since 1986, ISO 9001:2008 certified. Other capabilities along with our plastic tubing include labeling, printing, custom cutting, etc. | View Website: |
GSH Industries, Inc. |
GSH is a manufacturer of plastic, extruded, nylon, polycarbonate and polyethylene tubing. We serve a variety of industries with our products, including automotive, consumer, electrical and marine. Superior customer service, product knowledge, on-time delivery and competitive pricing since 1986! With over 40,000 square feet of manufacturing, we offer extruded plastic tubing, in house tooling, etc. | View Website: |
Petro Extrusion Technologies, Inc. |
Petro specializes in plastic tubing, offering custom extruded tubing, coiling & angle cutting. Our clear & color plastic tubing is available in Polycarbonate, Acrylic & PE-PP-Nylon. We have a full staff of engineers who can assist you, & we ship out stock products within 24 hours of your order. We strive for service. Our services, along with plastic tubing also include coiling & angle cutting. | View Website: |
Polytec Plastics, Inc. |
If you are in search of quality plastic tubing then you have found the company that can meet your needs. We have a wide variety of stock plastic tubing items and our solutions are very reliable. Whether you need custom rods, strips, or some form of plastic tube, we can help. Our speedy delivery teams will get your requests to your facility right away. Please give us a call for more information! | View Website: |
| View More Manufacturers | ||
Leading Manufacturers and Suppliers
Chapter Three – How Plastic Tubing is Made
The two primary methods for the manufacture of plastic tubing are extrusion and pultrusion. Both processes are used extensively in the plastic tube and pipe industry, but the difference between the two lies in how the molten plastic or reinforced composites move through the die. With plastic extrusion, the heated, molten plastic polymer is pushed (or "extruded") through a specifically engineered die. In contrast, in the pultrusion process, reinforced fibers saturated with thermosetting resin are pulled through a heated die to form continuous lengths of tubing with consistent cross-sections.
Plastic Tubing Manufacturing
Extrusion
The extrusion process for manufacturing plastic tubes is central to producing a vast range of tubing products for many industries, including medical, food processing, chemical, and industrial fluid transfer. The main ingredient in extrusion is a polymer resin—known in the industry as nurdles, pellets, granules, flakes, or powder. These raw materials are fed into a hopper mounted on the extruder’s barrel. Inside the extruder, a rotating screw precisely moves the resin through heated zones of the barrel, raising its temperature until it becomes molten and plasticized. Sophisticated temperature controls, tension regulation, and synchronized speed mechanisms ensure the molten polymer is consistently pushed through a die, creating tubing with precise internal and external dimensions and tolerances. This process allows for the production of both flexible plastic tubing and rigid plastic pipes tailored for plumbing, medical devices, pneumatic systems, and more.
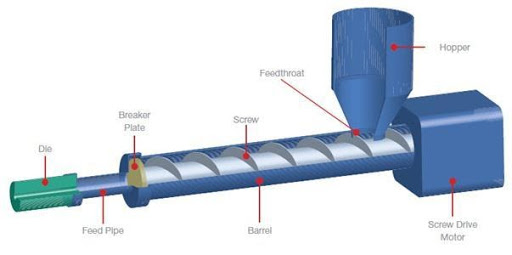
Flexible, semi-rigid, and rigid tubing—such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) tubes and polyethylene pipes—are all commonly formed using the extrusion process. State-of-the-art extrusion lines can also utilize coextrusion, allowing two or more different plastic materials to be extruded simultaneously into multilayer tubing, offering features like a rigid core for strength and a flexible or chemical-resistant sheath for functionality.
Throughout modern plastic extrusion, quality assurance is paramount; computer-controlled monitoring systems measure circumference, wall thickness, and concentricity in real-time to confirm the final tube perfectly matches specified engineered standards. This technology-driven process decreases scrap, improves consistency, and meets strict regulatory compliance for food-grade or medical-grade plastic tubing.
Pultrusion
Pultrusion is a continuous manufacturing process used for producing fiber-reinforced plastic tubing and structural profiles with exceptional strength-to-weight ratios. Unlike extrusion, which pushes material, pultrusion pulls strands of reinforced fibers—such as fiberglass or carbon fiber—that have been impregnated (wetted) with a thermosetting resin, usually polyester or epoxy, through a heated die. As the material passes through the die, it is shaped and cured by heat, causing polymerization that bonds the resin and reinforcement. This process creates composite tubing that is lightweight, corrosion resistant, non-conductive, and ideal for demanding environments in construction, infrastructure, telecommunications, and electrical insulation.
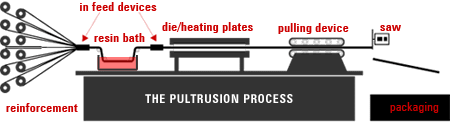
Pultrusion is valued in the manufacture of plastic tubes for its low maintenance, durability, and efficiency, consistently generating tubing profiles with complex shapes. Pultruded tubing is notable for its excellent corrosion resistance, low thermal conductivity, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for structural components exposed to harsh chemicals or extreme weather conditions.
Plastic Tubing Materials
Different types of plastic tubing are manufactured depending on the required application, chemical compatibility, mechanical performance, and environmental resistance. The selection of the right plastic material is critical, affecting the tube's flexibility, temperature range, pressure resistance, and overall durability. Below are some of the most common plastic tubing materials and their industry use cases:
Acrylic Tubing:
Acrylic tubing is a clear, rigid plastic tube with high impact strength and UV resistance. Its lightweight properties—half the weight of glass—make it ideal for display fabrication, lighting covers, sight glasses, and various industrial processes requiring transparency and visual monitoring of fluids.

PVC Tubing (Polyvinyl Chloride):
PVC tubing is a leading choice in the plastic tubing market due to its broad chemical compatibility, superior flexibility, and high resistance to corrosion, abrasion, and wear. Food-grade and medical-grade PVC tubing are available, making it suitable for everything from beverage dispensing to chemical transfer, air and water lines, and pharmaceutical applications.

CPVC Tubing (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride):
The main difference between CPVC and standard PVC tubing is CPVC’s higher temperature rating and superior corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures. CPVC tube is commonly chosen for transporting hot water or aggressive chemicals in plumbing, water treatment, and industrial fluid handling systems.
Fiberglass Tubing:
Fiberglass-reinforced plastic tubing is pultruded and consists of glass fibers bound in a thermoset polyester or vinyl ester matrix. Available in countless diameters and configurations, fiberglass tubing is corrosion and UV resistant, widely used as an electrical insulator, and employed in outdoor structures and infrastructure for its dimensional and mechanical stability.

Nylon Tubing:
Nylon tubing is a lightweight, abrasion-resistant plastic tube with excellent corrosion and chemical resistance. Its exceptional elastic memory allows for repeated flexing—making nylon tubing ideally suited for pneumatic hoses, fuel lines, air brake systems, robotics, and industrial automation. Nylon's resilience at subzero temperatures and its low moisture absorption enhance its versatility for demanding applications.
Polycarbonate Tubing:
Polycarbonate tubing is a tough, flame, and impact-resistant plastic tube known for its clarity and high strength-to-weight ratio. It withstands harsh or outdoor environments and can be machined or drilled without cracking, making it popular for protective covers, safety shields, and sight flow indicators.
Polyethylene Tubing:
Polyethylene tubing is a tough, flexible plastic tubing recognized for its chemical resistance and non-toxic qualities. It is often selected for potable water lines, beverage transfer, laboratory tubing, irrigation, and cable protection due to its low cost, durability, and high resistance to stress cracking under adverse environmental conditions.

Polystyrene Tubing:
Polystyrene tubes are lightweight, durable, and flexible, making them suitable for transporting fluids and gases in laboratory, medical, and scientific equipment. Their excellent moisture and vapor barriers and customizable heat resistance contribute to safe containment of volatile substances.

Silicone Tubing:
Silicone tubing is highly valued for applications requiring flexibility, purity, and biocompatibility. Common in medical, pharmaceutical, food and beverage processing, and laboratory environments, silicone tubing is naturally non-toxic, features a wide operating temperature range (-100° F to 500° F), and is suitable for both fluid and air transfer where regulatory and hygienic standards are strict.
Vinyl Tubing:
The majority of vinyl tubing is made from flexible PVC. Vinyl tubes are favored for their chemical resistance, light weight, mechanical strength, non-toxicity, and high transparency. Their wide use includes food and beverage dispensing, laboratory delivery systems, aquarium tubing, and household water lines. Their high melting point and clarity further enhance their appeal in diverse applications.

Polypropylene Tubing:
Polypropylene tubing is similar to polyethylene but offers greater rigidity, a higher melting point, and resistance to punctures and chemicals. Its optical clarity and ability to handle a broad temperature range (freezing to 275° F) make it a preferred solution for chemical processing, laboratory applications, and fluid transfer systems that demand cleanliness, sterilization, and structural strength.

HDPE Tubing (High-Density Polyethylene):
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) tubing features a remarkable strength-to-density ratio and demonstrates exceptional resistance to shattering, corrosion, and chemical degradation. Used extensively for potable water distribution, chemical transport, and pneumatic lines, HDPE tubing can be sterilized by boiling, withstands high pressure, and delivers excellent abrasion resistance for tough environmental conditions.

PTFE Tubing (Polytetrafluoroethylene):
PTFE tubing—often referred to by the brand name Teflon®—is a versatile, chemically inert, and lubricious plastic tube. It withstands extreme temperatures (-390°F to 500°F) and provides outstanding resistance to corrosive liquids and gases, making it the tubing of choice for laboratories, medical research, and chemical processing plants. PTFE tubing will not crack under heat stress and is commonly integrated into fluid transfer systems where contamination must be avoided.

EVA Tubing (Ethyl Vinyl Acetate):
EVA tubing is a flexible, impact-resistant plastic tube capable of withstanding very low temperatures and resisting grease, oil, and UV rays. It is used extensively in hospitals, surgical environments, medical devices, and the pharmaceutical industry due to its clarity, flexibility, and FDA approval for food and medical contact. Its temperature range (-76°F to 140°F) and chemical resistance make it ideal for sensitive fluid transfer.

Polyurethane Tubing (PU):
Polyurethane tubing is a flexible, kink-resistant plastic tube with high abrasion resistance and superior memory. It stretches easily yet quickly returns to its original shape, making it excellent for pneumatic control lines, medical devices, robotics, and applications where flexibility and repeated flexing are critical. Polyurethane's resistance to gasoline, oils, and petrochemicals sets it apart for use in automotive and fuel line applications.

Choosing the Right Plastic Tubing for Your Application
When selecting plastic tubing, important factors include application requirements, regulatory compliance (such as FDA, NSF, or USP standards), chemical and temperature compatibility, flexibility, and strength. Whether you need custom extruded tubing for medical devices, heavy-duty pipes for industrial chemical processing, or clear plastic tubes for food and beverage dispensing, understanding these variables will help you choose the ideal material and manufacturing process. For further details about custom plastic tubing solutions, medical-grade tubing, industrial plastic pipes, or to receive expert guidance, reach out to a reputable plastic tubing manufacturer or supplier. Comparing technical specifications and consulting datasheets can also support optimal selection for your unique needs.
Ultimately, knowledge of the manufacturing process and material options ensures your plastic tubing performs safely and cost-effectively, delivering reliable results in even the most demanding applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main advantages of using plastic tubing over metal tubing?
Plastic tubing offers superior corrosion resistance, lower production and installation costs, high tensile strength-to-weight ratio, and easier maintenance. Its versatility allows for customization in wall thickness, diameter, and material composition for diverse applications.
Which industries benefit from specialized plastic tubing materials?
Industries such as medical, automotive, agriculture, marine, food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, and banking utilize specialized plastic tubing. Material selection depends on properties like chemical resistance, clarity, flexibility, and regulatory compliance.
How is plastic tubing manufactured?
Plastic tubing is produced primarily by extrusion or pultrusion. Extrusion pushes molten plastic through a die, while pultrusion pulls reinforced fibers through a heated die, creating continuous, consistent tubing profiles for various applications.
What factors should be considered when choosing plastic tubing?
Key factors include application requirements, temperature and chemical compatibility, regulatory compliance (e.g., FDA, USP), flexibility, strength, and pressure ratings. Understanding these ensures safe, efficient, and regulatory-compliant performance.
Which plastic tubing materials are best for outdoor or harsh environments?
Materials like PVC, polyethylene, HDPE, fiberglass, CPVC, and marine-grade tubing are chosen for outdoor use due to their UV resistance, durability, and corrosion resistance—suitable for agriculture, marine, and infrastructure applications.
How does plastic tubing improve local agricultural irrigation systems?
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or PVC tubing in agriculture enables efficient water distribution, drip irrigation, and fertilizer delivery. Its flexibility, resistance to weathering, and ease of installation support sustainable and cost-effective local farming.
Chapter Four – Plastic Tubing Design
With the wide variety of materials and applications for plastic tubing, producing a tubing to fit a specific application requires a close examination of the qualities required. Since plastic is such a resilient material, it is easy to decide to use it as a component. The difficulty arises when deciding what will be the necessary features.
Plastic Tubing Design
Strength
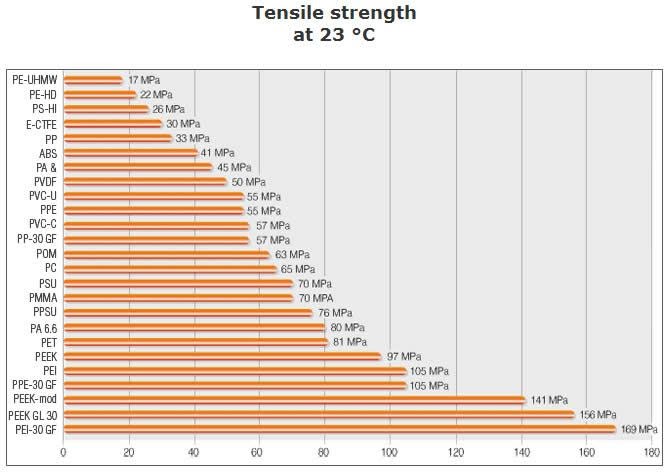
Measuring the mechanical properties of a material, and its tensile strength, is the first determination for choosing a material. Tensile strength is the amount of stress plastic can endure before breaking. The tensile strength of plastic varies between 12,400 psi up to over 20,000 psi. The chart below has a list of a wide variety of plastics and their megapascal tensile strength at 23° C or 73° F.
Diameters
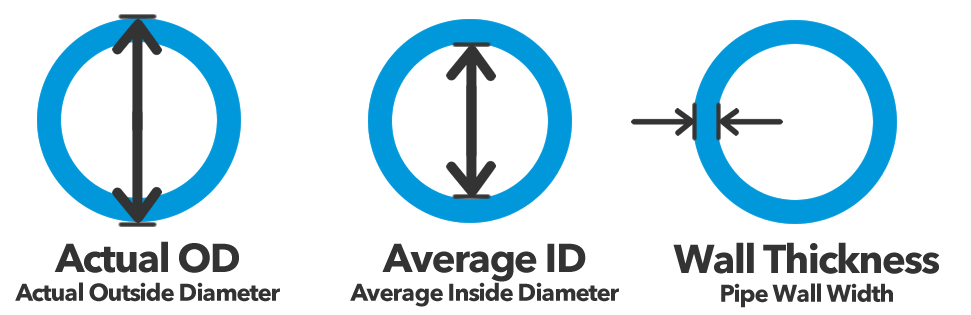
Tubing is measured by the inside diameter (ID) and outside diameter (OD), which can vary between 0.125" to 4". The measurement between the ID and OD is the wall, a means for determining the strength of the tubing.
Wall Thickness
The wall thickness is determined by subtracting the ID from the OD (OD) and dividing the answer by two.
Flexibility
The flexibility of plastic tubing is determined by the material used to manufacture it. PVC and polyurethane are the most flexible.

Fittings
There are a variety of fittings for plastic tubing that include compression, push to connect, quick turn, threaded, barbed, socket, and flanged. The determination of the type of fitting is in accordance with how the tubing will be used.

Color
There is a limitless number of colors used to make plastic tubing, which also include translucent and clear.
Length
Plastic tubing can be made to any length, depending on the needs of the application. It can be a few inches up to hundreds of feet.

Cost
When examining the cost of plastic tubing and comparing it to steel or stainless steel for tensile strength, steel and stainless steel are far stronger. The biggest difference between plastic and steel is cost. For the cost of producing a half dozen stainless steel tubes, hundreds of flexible plastic tubes can be made.
Durability
The durability and strength of plastic depends on wall thickness and resin blend. The strength of plastic tubing is proportional to the amount of stress it will endure. Plastic can take a great deal of abuse before it gives out.
Corrosion
All plastic is corrosion resistant. The type of polymer used determines the amount of corrosion resistance. The types of corrosion resistant plastics are polyolefins and PVC. Polyolefins are polyethylene and polypropylene, which come in various densities and molecular structures for ease of design.

Microbial Properties
The resin for plastic tubing can be manufactured with antimicrobial properties included in the pellets. The microbial properties of plastic tubing are required for food storage, coolers, water tubes, and medical tubing. The antimicrobial additives prevents contamination and keeps the tubing sanitized.

Toxicity
Plastic products have the potential for being toxic. The amount of toxicity depends on the type of plastic resin used in the manufacturing process. When making the decision to produce plastic tubing, consideration is given to the toxic nature of the materials and is part of the design process.
Chapter Five – Characteristics of Plastic Tubing
The characteristics of plastic tubing vary depending on the materials, configuration, and production methods used in its manufacturing. Surgical and industrial tubing widely vary in their application. Though there may be radical differences between functions, all plastic tubing has certain common features.
Characteristics of Plastic Tubing
Hollow Shafts
Plastic tubing is a hollow shaft of plastic designed to transport gas, fluids, or some form of solid, flaky material. Though circular is the most common form of a plastic tubing profile, it comes in a variety of other shapes, as pictured below.
Polymer
As the name implies, all plastic tubing is made of one of the many forms of plastic, which begins with a polymer. It is chosen as the base material for its strength, endurance, corrosion and rust resistance, and cost.

Versatility
The strength, endurance, and transparency of plastic tubing varies according to the materials used to produce it. Regardless of those distinctions, it is one of the most used components in manufacturing due to its low cost and versatility.


Clear
Plastic tubing can be produced with the same clarity as glass but not as fragile or breakable with greater strength and endurance.

Functionality
Plastic tubing can be manufactured to withstand any conditions or materials. Unlike other tubing types, plastic tubing does not have to be specially treated to move chemicals or corrosive substances.
Durability
Though plastic does not have the tensile strength of steel or stainless steel, it is more capable of withstanding the strain of daily wear. It is able to take significant harm and damage and still maintain its strength.

Recyclable
All plastics can be reprocessed and reused for the manufacturing of other products. Once plastic tubing has reached the end of its usefulness, it can be sent back to the manufacturer to be processed into pellets or resin and sent through extrusion a second time.

Chapter Six – Types of Plastic Tubing
The number of materials used to manufacture plastic tubing is matched by the number of types of plastic tubing, which ranges from highly sanitary tubes used in cleanrooms and surgery to drainage tubes for sewage and waste removal. Plastic tubing is engineered and designed to fit specific applications and can be formed, shaped, and configured for any number of conditions.
Types of Plastic Tubing
Corrugated Plastic Tubing
Corrugated tubing is used for chemical processing, in corrosive environments, laboratories, and high purity fluid and solvent transfer. It is very flexible and can be extended or compressed without affecting the ID. Corrugated plastic tubing can be produced in any length in a variety of ID‘s.

Heat Shrinkable Plastic Tubing
Heat shrinkable tubing is used as insulation for wiring. It is placed around the wire and then shrunk to fit snuggly. It is resistant to fuels, lubricants, acids, and solvents at high temperatures.

Medical Plastic Tubing
Medical plastic tubing is manufactured to the exacting standards of the United States Pharmacopeia organization (USP) and the National Sanitation Foundation (NSF). USP Class VI defines the requirements for biological reactivity, while NSF 51 outlines the use of plastics with food products. Medical tubing has to be translucent, able to be sterilized and reusable, and nonreactive with bodily fluids or tissues.

Square Plastic Tubing
Square plastic tubing has limited use and is sometimes used for its appearance. It has the same functions as cylindrical tubing and is able to transport liquids and gases. Due to its strength, it is included in the production of lawn furniture.

Hard Plastic Tubing
Hard or rigid plastic tubing is made from all of the different types of fabricating materials. It is used as a conduit or construction material and has multiple industrial applications.

Small Diameter Plastic Tubing
Small diameter tubing, also known as miniature tubing, is used in applications that need regular tubing but of a smaller size. It is made from polycarbonate, polypropylene, polyethylene, polystyrene, and PVC to name a few. It is used in electrical components, swab sticks, medical products, and dispensing tubes in various lengths.
Centrifuge Plastic Tubing
Centrifuge plastic tubing is cylindrically shaped tubes that are placed in centrifuge slots to analyze and separate tested materials. They are high strength, precision containers that can safely hold a wide variety of materials. Plastic centrifugal tubes are more commonly used due to their cost effectiveness.

Chapter Seven – Plastic Tubing Regulations and Specifications
The regulations for the production of plastic tubing mainly pertains to its use in the food industry and the transport of water. Aside from governmental regulations, several other organizations monitor and develop specific guidelines for materials that come in contact with the public.
Plastic Tubing Regulations and Specifications
FDA (Food & Drug Administration)
The FDA oversees any products that come in contact with food or beverages. Since plastic tubing is a major part of the food industry, the FDA has established regulations specifying the cleanliness and sanitary standards for food processing plastic tubing. Materials used in plastic tube production are tested for composition, additives, and properties. If it meets the requirements, it is classified as FDA compliant. FDA CFR 21 is an all-encompassing regulation that includes requirements for materials used for medical purposes.
USDA (U.S. Department of Agriculture)
The USDA regulates equipment used in the production of meat and poultry products. The Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS), a department of the USDA, provides guidelines regarding several aspects of food production following FDA requirements listed in CFR 9.
3A-Dairy
The 3A-Dairy group is a voluntary organization that has the goal of improving the quality, standards, and equipment used in the production of dairy products. Its main focus is enhancing the sanitary conditions involved in production. The organization works with food handling manufacturers that are interested in improving their methods and gives a 3-A Sanitary Standards, Inc. compliance seal to those who meet their requirements.
NSF (National Sanitation Foundation)
The NSF was founded to standardize sanitation and food safety requirements. It has over 80 requirements for public health and safety. It covers all sectors of food production. One of its critical areas for examination and testing is all equipment that comes in contact with drinking water such as plumbing, water treatment chemicals, and water filters.
NSF Standards that relate to Plastic Tubing are:
- 51 Plastics in Food Equipment
- 61 Drinking Water System
- 14 Manufacture of Fittings
USP (United States Pharmacopoeia)
The USP is a public standards authority for medicines and health care items. It sets standards for quality, purity, strength, and consistency. USP Class VI standards determine the toxicity of materials and their dangers to people. Any tubes that come in contact with body tissue or muscles are tested and graded. The USP uses a variety of tests to determine if a material meets their standards.
Conclusion
- Plastic tubing is a form of tubing that is manufactured from a mixture of a polymer with a variety of chemicals to form a material that can be solid or flexible.
- Plastic tubing is produced in any wall thickness, diameter, tolerance, and strength using a combination of materials to specifically fit various applications.
- The main benefit of plastic tubing over steel, aluminum, or other materials is its consistent strength and cost effectiveness since it is far less expensive to produce.
- The two methods for the manufacture of plastic tubing are extrusion and pultrusion.
- The number of materials used to manufacture plastic tubing is matched by the number of types of plastic tubing, which ranges from highly sanitary tubes used in cleanrooms and surgery to drainage tubes for sewage and waste removal.